Summary of the Day:
Ukrainian forces struck Russian drone storage facilities in Oryol Oblast destroying over 200 Shahed drones and warehouses containing thermobaric warheads. The strike caused multiple explosions at the site. While Russian officials claimed they intercepted some Ukrainian drones, Ukrainian officials noted this was their second strike on this same facility since December 2024.
Ukrainian forces recently recaptured lost positions near Toretsk, while Russian forces advanced near Toretsk, Chasiv Yar, and Kurakhove. In a key military leadership change, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky appointed Ground Forces Commander Major General Mykhailo Drapatyi to also lead the Khortytsia Group of Forces, while moving former commander Brigadier General Andrii Hnatov to serve as Deputy Chief of the Ukrainian General Staff.
The European Union proposed an emergency aid package to help Moldova and its breakaway region Transnistria deal with their gas crisis. The package includes an immediate loan of three million cubic meters of gas to Transnistria and a 30 million euro grant to Moldova for gas purchases. With Transnistrian gas reserves expected to run out by early February 2025, discussions are underway between Moldova’s gas company Moldovagaz and Hungarian companies MOL and MVM for additional gas supplies.
Meanwhile, the Russian government continues expanding its “Time of Heroes” program, which aims to install Kremlin-selected veterans into government positions at both federal and regional levels.
Picture of the Day:
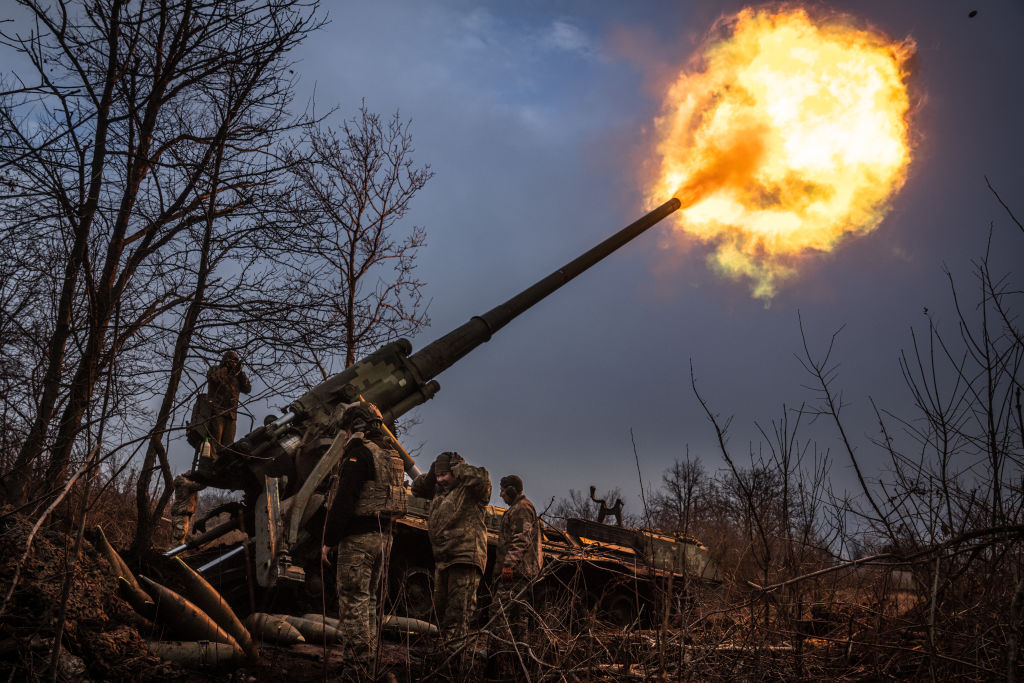 Ukrainian soldiers of the 43rd Brigade work with a Soviet-era Pion self-propelled howitzer in the direction of Chasiv Yar. (Wolfgang Schwan/Anadolu via Getty Images)
Ukrainian soldiers of the 43rd Brigade work with a Soviet-era Pion self-propelled howitzer in the direction of Chasiv Yar. (Wolfgang Schwan/Anadolu via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
The European Union proposed an emergency aid package to help Moldova and its breakaway region Transnistria deal with their gas crisis. The package includes an immediate loan of three million cubic meters of gas to Transnistria and a 30 million euro grant to Moldova for gas purchases. With Transnistrian gas reserves expected to run out by early February 2025, discussions are underway between Moldova’s gas company Moldovagaz and Hungarian companies MOL and MVM for additional gas supplies. The EU aid aims to reduce Russia’s ability to use energy supplies as leverage over Moldova and Transnistria, despite Transnistria’s previous rejection of aid from Moldova and Ukraine.
Alexander Lukashenko, who has ruled Belarus since 1994 and is a key ally of Russian President Vladimir Putin, has secured his seventh term as president with 86.82% of the vote in an election featuring only regime-approved candidates. The result was immediately endorsed by Moscow but condemned by the international community, including the EU, with diplomat Kaja Kallas calling it “a blatant affront to democracy” and Ukraine’s Foreign Ministry describing it as “a farce.” Exiled opposition leader Sviatlana Tsikhanouskaya denounced the vote as a “special operation” by the Russia-backed regime to maintain power, while this continuation of authoritarian rule poses ongoing concerns for regional stability, particularly given Belarus’s role in supporting Russia’s war against Ukraine and its deepening divide with Western democracies.
The European Union has resolved an internal dispute over Russian energy sanctions after providing Hungary with guarantees about its energy security, with Foreign Minister Peter Szijjarto confirming that the EU Commission committed to protecting gas and oil pipelines to member states following Ukraine’s stoppage of Russian gas transit through its territory. The diplomatic solution prevents Hungary, under Prime Minister Viktor Orban – one of the most Russia-friendly EU members – from vetoing the extension of EU sanctions against Russia, which require unanimous approval and are set to expire January 31. President Trump may have influenced Hungary’s decision to support the EU’s six-month extension, according to Polish Foreign Minister Radoslaw Sikorski, as the breakthrough came after Trump threatened Moscow with additional sanctions and tariffs if Putin doesn’t negotiate to end the war in Ukraine, with Orban, a Trump ally who had previously blocked the sanctions extension, dropping his opposition after receiving the EU guarantees. This development highlights the complex interplay between maintaining pressure on Russia while ensuring European energy security, U.S. influence, and Western unity in supporting Ukraine, representing a significant diplomatic achievement in maintaining a unified response to Russian aggression.
The European Union has partially suspended its visa facilitation agreement with Georgia, targeting government officials and judges but not ordinary citizens, in response to democratic concerns. The decision comes amid mass protests in Tbilisi over disputed parliamentary elections and Prime Minister Kobakhidze’s suggestion of delaying EU integration until 2028. The ruling Georgian Dream party, led by oligarch Bidzina Ivanishvili, has faced criticism for aligning Georgia more closely with Russia while undermining EU accession efforts through controversial legislation, including a foreign agents law. This development signals growing tensions between Georgia’s proclaimed European aspirations and its current political trajectory, potentially affecting regional stability and the balance of influence between the EU and Russia in the Caucasus region.
A Malta-flagged vessel named Vezhen, which departed from Russia’s Ust-Luga port, is under investigation by Swedish prosecutors for potentially damaging undersea cables in the Baltic Sea. The latest incident damaged a fiber-optic cable connecting Latvia’s Ventspils to Sweden’s Gotland island on January 26. While this adds to a series of recent cable damages in the Baltic Sea that prompted NATO to increase patrols, U.S. and European intelligence services increasingly believe these incidents are accidental rather than deliberate Russian sabotage. The damaged cable’s operator, LVRTC, reports minimal service disruption as data transmission continues through alternate routes. This situation highlights ongoing concerns about the security of critical undersea infrastructure in the Baltic region, though the emerging consensus about accidental causes may help reduce international tensions.
Lithuania and Estonia have become the first NATO members to commit to raising defense spending to more than 5% of GDP, following U.S. President Trump’s recent demands for increased NATO defense contributions. Lithuania plans to spend between 5-6% of GDP on defense until 2030, while Estonia will increase its spending from 3.7% to 5%. Poland is set to join them in 2025 with 5% GDP allocation. This dramatic increase puts these Baltic nations ahead of most NATO members, including the U.S. at 3.38%. Trump’s pressure for higher defense spending, coupled with his controversial statement about letting Russia “do whatever the hell they want” to NATO members who don’t meet spending criteria, has raised international concerns about U.S. commitment to NATO’s collective defense. These developments reflect growing security concerns in Eastern Europe amid Russia’s ongoing war in Ukraine and could significantly impact NATO’s unified defense strategy and regional stability.
The EU foreign ministers have agreed to ease sanctions on Syria following the December 8 collapse of Bashar al-Assad’s regime when opposition forces captured Damascus. EU chief diplomat Kaja Kallas announced plans to increase humanitarian aid and reconstruction efforts, while noting that sanction relief could be reversed if necessary. The agreement may include lifting energy and transportation restrictions, though financial transaction sanctions remain under discussion. Germany and France have expressed willingness to work with Syria’s new leadership, which has begun distancing itself from Russia, including terminating a 49-year Russian investment deal at the port of Tartus. Ukraine’s Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha visited Damascus on December 30 to discuss Russia’s military presence, with both countries reportedly sharing similar views on the issue.
The Path to Peace
Despite President Trump’s stated willingness to meet “immediately” with Vladimir Putin regarding the Ukraine conflict, Russian officials confirm no contact has been made between the new US administration and the Kremlin. Deputy Foreign Minister Sergei Ryabkov stated that communication remains limited to embassy channels. While Trump has indicated he’s “not looking to hurt Russia,” he threatened additional sanctions if Putin doesn’t make a deal. Putin praised Trump as “smart” and “pragmatic,” suggesting the Ukraine conflict might have been prevented under his leadership. Meanwhile, Kyiv has expressed concern about being excluded from potential peace talks, warning that Putin may try to “manipulate” Trump.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Russian forces are now threatening Ukraine’s Dnipropetrovsk region for the first time in the three-year war, advancing to within 4 kilometers of its border. In the village of Novopavlivka, resident Svitlana Rudokvas describes recent bombardments, including one that destroyed a local restaurant. In nearby Mezhova, a town of 5,000, cafe manager Polina Yakovenko reports growing anxiety among residents as the fighting draws closer. While Ukrainian serviceman Vadym remains optimistic at the border crossing, local residents are preparing for possible evacuation. Military analyst Mykhailo Samus suggests that while a Russian breakthrough could take months, even a small advance would serve as a psychological victory for Russian forces.
Reports suggest China may be secretly sending troops to assist Russia in Ukraine, though this remains unverified.
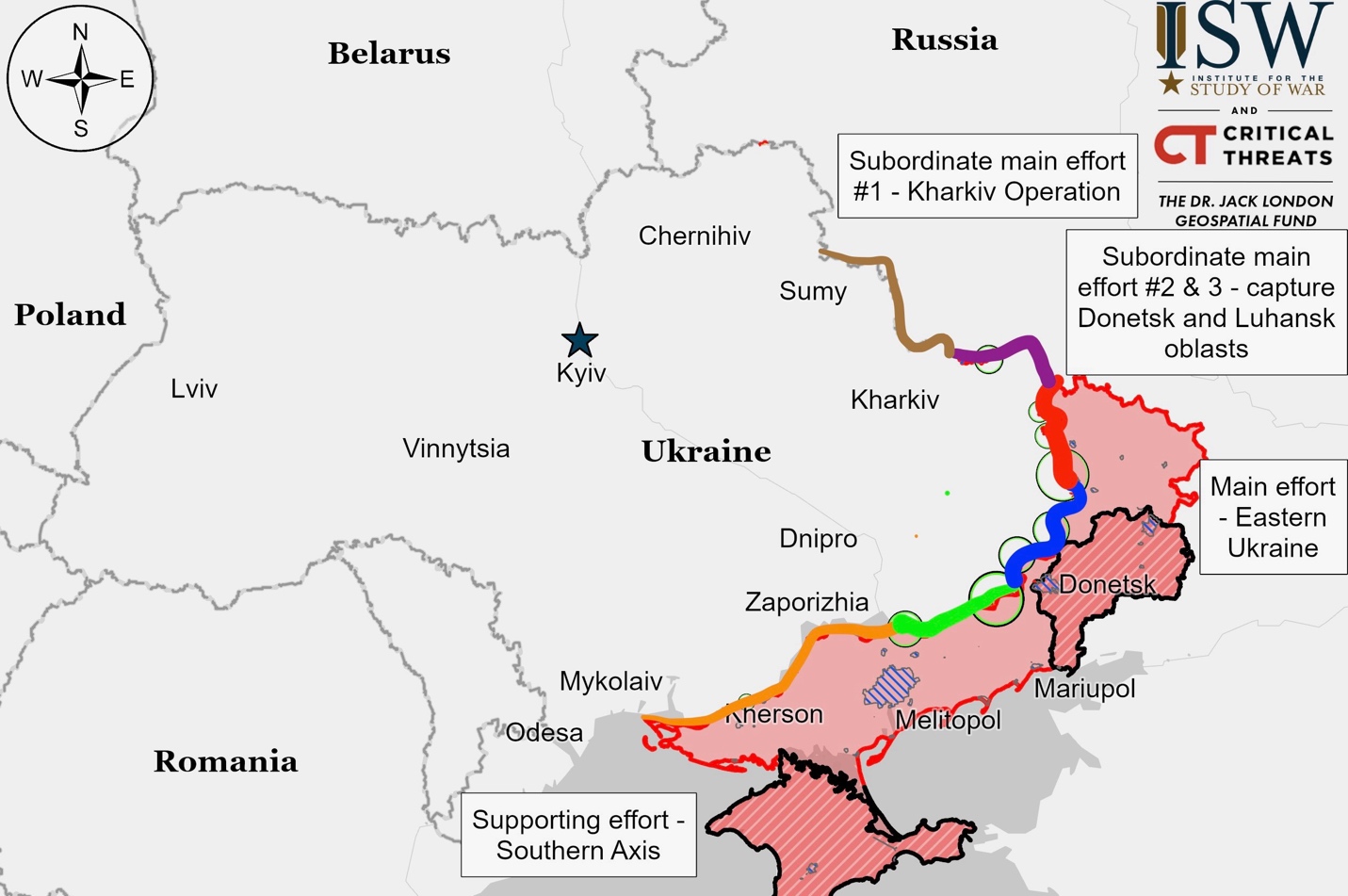
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative Russia
Russian and Ukrainian forces continue to clash in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast. While Russia claims to have captured the settlement of Nikolayevo-Darino near Sudzha, this likely occurred earlier on January 21. Fighting persists around Kositsa, with Ukrainian forces launching counterattacks near Nikolayevo-Darino.
Ukrainian special forces commander “Puls” reports that North Korean troops have temporarily withdrawn from Russia’s Kursk region frontline after suffering heavy losses, with British intelligence indicating they lost approximately 4,000 of their 11,000 deployed troops by mid-January, while Ukrainian President Zelensky confirmed 3,800 North Korean casualties this month. The North Korean forces, while showing exceptional discipline and morale but being unfamiliar with modern warfare tactics, attacked in large groups on foot, making them vulnerable to drones and artillery, with Ukrainian forces recently collecting DNA samples and documents from 25 North Korean soldiers killed in a drone strike who carried Russian identification in an apparent attempt to conceal their origins. According to Ukrainian Special Operations Forces spokesperson Colonel Oleksandr Kindratenko, poor coordination and language barriers between Russian and North Korean forces have led to friendly fire incidents, while the Institute for the Study of War estimates that at the current casualty rate of 92 per day, North Korea’s deployed forces could be completely depleted by mid-April. Though neither Kim Jong Un nor Vladimir Putin has officially acknowledged North Korean troop deployment, South Korean intelligence and Ukrainian military sources indicate that Pyongyang is preparing to send reinforcements, particularly artillery units, within the next two months.
Ukrainian forces successfully attacked Russian drone storage facilities in Oryol Oblast destroying over 200 Shahed drones and warehouses containing thermobaric warheads. The strike caused multiple explosions at the site. Russian officials claimed they intercepted some Ukrainian drones.
A Ukrainian drone strike on January 24 has forced Russia’s Ryazan Oil Refinery to suspend operations. The attack damaged oil storage facilities, a railway loading track, and processing equipment. The refinery, which processes nearly 5% of Russia’s oil and can handle 17 million metric tons annually, was targeted in a joint operation by Ukraine’s Security Service (SBU) and Special Operations Forces. Local residents reported additional explosions at the facility two nights later. Ukraine considers oil refineries legitimate military targets due to their role in funding Russia’s war effort.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces attacked near Kharkiv City targeting areas around Lyptsi to the north and Vovchansk to the northeast but failed to gain ground. Ukrainian Border Guards reported stopping a Russian assault near Vovchansk that involved 10 military vehicles and infantry. Russian sources also claimed their forces attacked in the Derhachi area north of Kharkiv City, possibly near Kozacha Lopan.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Kupyansk
Russian forces launched attacks near Kupyansk targeting Petropavlivka to the east, Pishchane and Stepova Novoselivka to the southeast, and Hlushkivka to the south, but failed to gain any territory.
Borova
Russian forces attacked in the Borova area with reports of attempted advances near multiple settlements. While Russian sources claimed gains near Novoyehorivka and west of Nadiya, these remain unconfirmed. Russian forces targeted several locations around Borova including Lozova, Kolisnykivka, Zahryzove, Zelenyi Hai, Kopanky, Nadiya, Makiivka, Novoyehorivka, and Hrekivka.
Russian military bloggers have openly challenged the Russian Defense Ministry’s claims of battlefield success near Borova. They dispute the Ministry’s January 20 announcement of capturing Novoyehorivka, stating Russian forces remain 1.5 kilometers away, and claiming that recent footage of Russian troops in the settlement is fake. The bloggers warn that such false reports harm Russian operations, as commanders withhold fire support from areas they wrongly believe are under Russian control. This follows similar complaints about false claims regarding Bilohorivka, which led to the removal of several Russian commanders in November 2024.
Lyman
Russian forces continued attacks in the Lyman area. While Russian sources claimed advances near Novosadove and Ivanivka northeast of Lyman, these remain unverified. Russian forces attacked several locations including Terny, Kolodyazi, Yampolivka, Zelene Dolyna, Zarichne, and Torske.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
No Russian attacks were reported in the Siversk area by either Russian or Ukrainian sources.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces have made advances in central Chasiv Yar, with confirmed movement along Myru and Horkoho streets. While claims of Russian advances near Hryhorivka and Orikhovo-Vasylivka remain unconfirmed, Russian forces attacked multiple locations including Stupochky, Bila Hora, and Predtechnye. Ukrainian officials report increased Russian armored vehicle activity near Chasiv Yar, with Russian forces destroying parts of the Siverskyi Donets Donbas Canal to create passage routes.
Toretsk
Both Ukrainian and Russian forces made gains near Toretsk. Ukrainian forces advanced in northwestern Toretsk, while Russian forces gained ground near the Toretska Mine in the northern part of the city. Russian attacks continued around Toretsk and nearby settlements including Dyliivka, Krymske, and Shcherbynivka.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces have launched attacks in the Pokrovsk direction with unconfirmed claims of capturing Nadiivka and Novoandriivka, conducting operations at multiple locations including Vodyane Druhe, Myrolyubivka, Lysivka, Zelene, and numerous other settlements, while using small, armored columns to deploy infantry and taking advantage of the open terrain. Ukrainian military spokesperson Major Viktor Trehubov reported numerous small-scale engagements near Pokrovsk, noting that Russian forces have changed tactics to use small groups to try to encircle Ukrainian positions instead of direct attacks, possibly due to personnel shortages, as they attempt to surround Pokrovsk and Kurakhove while avoiding direct urban combat. While the fighting is less intense than at Toretsk, the Pokrovsk area remains the most active section of the front, with the offensive continuing across multiple areas including Lyman, Siversk, Kramatorsk, and Toretsk, though Moscow has not yet succeeded in cutting off Pokrovsk’s supply lines.
Kurakhove Region
Russian forces advanced near Kurakhove, with confirmed progress in northern Andriivka. While Russian sources claim advances near Slovyansk toward the T-0515 Pokrovsk-Andriivka highway, these remain unverified. Russian forces attacked several locations including Shevchenko, Dachne, Kostiantynopil, Ulakly, Yantarne, Rozlyv, and Zelenivka.
Velyka Novosilka
Russian forces attacked near Velyka Novosilka targeting the town itself and nearby settlements including Rozdolne, Novyi Komar, and Novosilka, with Ukrainian forces withdrawing from the southern part of the town to avoid encirclement while maintaining positions on its outskirts. Viktor Trehubov, spokesperson for the “Khortytsia” operational group, confirmed that while Russian forces now occupy about 89% of the settlement, denying claims of complete capture, with Ukraine’s 110th Motorized Rifle Brigade reporting that fighting continues within the town despite their strategic withdrawal from some areas.
The village, previously home to 5,000 people and located just 15 kilometers from Zaporizhzhia Oblast, would represent Russia’s most significant gain in Donetsk Oblast since taking Kurakhove in early January if its capture is verified, though the Institute for the Study of War notes that despite this Russian advance, their overall progress in western Donetsk has been notably slow for modern mechanized warfare. While both sides have similar equipment levels, Russia holds a significant advantage in troop numbers, and the area’s Mokri Yaly River, previously a challenge for Ukrainian supply lines, now serves as a natural barrier against further Russian advances.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
There were no reports of combat activity in the Polohy direction from either Russian or Ukrainian military sources.
Russian forces launched limited ground attacks in the Zaporizhia region without gaining territory. The attacks focused on areas around Robotyne, specifically near Novodanylivka and towards Novoandriivka.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks but made no advances. A Russian military blogger reported that weather conditions are hampering both Russian and Ukrainian drone operations in the Kherson area.
Ukraine News
Russia launched a major drone assault against Ukraine, deploying 104 Shahed drones and decoys from multiple locations including Oryol, Kursk, Millerovo, Primorsko-Akhtarsk, and occupied Crimea. Ukrainian forces intercepted 57 drones across ten regions including Kyiv, Mykolaiv, and Kharkiv. Thirty-nine decoy drones were neutralized by electronic warfare. The attacks damaged infrastructure and residential areas in Dnipropetrovsk, Sumy, Ivano-Frankivsk, and Kyiv regions.
The US has temporarily suspended most foreign aid, significantly impacting humanitarian projects in Ukraine. The freeze affects organizations supporting veterans, local media, and healthcare services. USAID’s mission in Ukraine confirmed that most projects have been ordered to stop. This comes after President Trump signed a 90-day suspension of foreign assistance programs, with exceptions only for Israel and Egypt. One immediate impact was seen at Veteran Hub in Vinnytsia, which had to pause operations. The organization provides legal and psychological support to veterans and their families. Since Russia’s 2022 invasion, USAID has given Ukraine $2.6 billion in humanitarian aid, $5 billion in development assistance, and over $30 billion in direct budget support.
Presidents Zelensky and Macron met in Oświęcim, Poland, during the 80th anniversary commemoration of Auschwitz’s liberation, where they discussed Ukraine’s security guarantees and EU accession prospects, with Zelensky seeking French support for Ukraine’s EU membership bid. Before traveling to Poland, Zelensky visited Babyn Yar in Kyiv, where Nazis massacred Jews in 1941, while the date, which marks the Red Army’s liberation of one of the largest Nazi death camps, serves as International Holocaust Remembrance Day, honoring the 6 million Jews and other victims of Nazi Germany. The commemoration is being attended by numerous world leaders, including German Chancellor Olaf Scholz, Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, British King Charles III, and European Council President Antonio Costa.
Ukraine’s military intelligence (HUR) has officially denied media reports that its chief Kyrylo Budanov warned of threats to Ukraine’s existence without negotiations by summer. While news outlet Ukrainska Pravda cited an unnamed source claiming Budanov made these statements at a closed parliamentary meeting, both HUR and opposition lawmaker Oleksii Honcharenko disputed this characterization. The discussion occurs as Ukraine enters its fourth year of war, with Russia maintaining pressure on multiple fronts, and amid U.S. presidential candidate Donald Trump’s stated intentions to broker peace talks between the nations.
The European Commission announced that Ukraine’s screening process for EU membership compliance will continue until fall 2025. Having applied for membership in 2022 during Russia’s invasion, Ukraine achieved candidate status and began formal negotiations in June 2024. The Commission submitted its first Cluster I screening report on January 16, marking the initial step in assessing Ukraine’s alignment with EU standards. President Zelensky has set an ambitious goal of opening five or all six EU accession negotiation clusters in 2025, with plans to open several clusters during both Polish and Danish EU presidencies. The process requires unanimous approval from all EU member states, highlighting the significant diplomatic and legislative work ahead for Ukraine’s potential EU membership.
David Arakhamia, who leads President Zelensky’s Servant of the People party in parliament, attended Donald Trump’s recent presidential inauguration alongside other international figures like former UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson and Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni. Arakhamia also participated in pre-inauguration events and indicated that a formal Ukrainian delegation plans to meet with Trump’s team next month.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 4 INJURIES: 12
Russian forces attacked Kupiansk in Kharkiv Oblast, injuring an 86-year-old woman and killing two other women.
Russian attacks in Donetsk Oblast resulted in one death and four injuries.
Russian forces attacked Kherson city and 28 other settlements in Kherson Oblast, killing one person and wounding two others.
Russian artillery struck Nikopol in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, injuring five men between ages 30-39 and damaging an industrial facility where a fire broke out.
Russian drones struck a critical infrastructure facility in Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast in western Ukraine, causing a fire but no casualties.
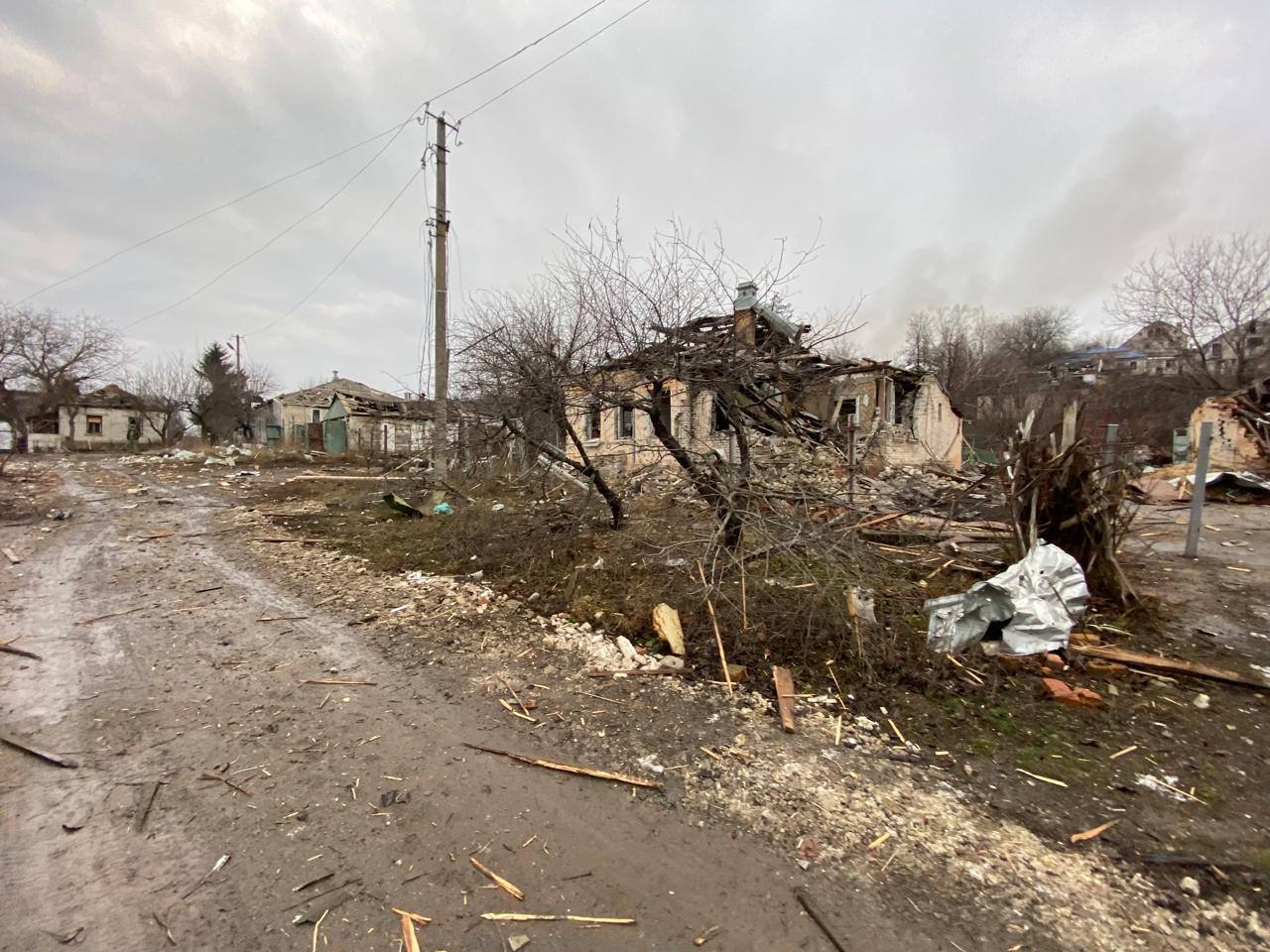 The aftermath of Russian attacks against Kharkiv Oblast, Ukraine. (Governor Oleh Syniehubov/Telegram)
The aftermath of Russian attacks against Kharkiv Oblast, Ukraine. (Governor Oleh Syniehubov/Telegram)
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
President Volodymyr Zelensky addressed Ukraine’s military mobilization challenges in a recent interview, emphasizing that increasing troop numbers is crucial to forcing Russia to end the war. Despite passing new mobilization laws in April 2024, Ukraine continues to face manpower shortages while Russian forces advance in the east. Currently, Ukrainian men aged 25-60 are eligible for the draft, though the government is working on reforms to encourage voluntary enlistment from those 18-25. Zelensky acknowledged the need for better troop rotation policies but stressed that maintaining adequate forces is essential for Ukraine’s survival. The situation highlights the critical balance between military necessity and sustainable mobilization practices in Ukraine’s defensive war.
A controversy has emerged in Ukraine’s defense sector after Defense Minister Rustem Umerov decided not to extend Maryna Bezrukova’s contract as head of the Defense Procurement Agency (DPA) despite the supervisory board’s vote to extend it, instead appointing Arsen Zhumadilov as her replacement, though Bezrukova contests the legality of this appointment. G-7 delegates have urged for a quick resolution as Bezrukova warns this legal conflict could block contracting and supply processes and disrupt Ukraine’s weapons supply chain, potentially affecting relationships with foreign partners, while the Anti-Corruption Action Center has filed a complaint with Ukraine’s National Anti-Corruption Bureau to investigate Umerov for possible abuse of power over this decision.
Ukraine’s Allies
The European Union has extended sanctions against Russia for another six months, following approval by EU foreign ministers. The decision came after Hungary received assurances from Brussels about energy security, resolving earlier threats by Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban to veto the extension. The key issue centered around Ukraine’s recent termination of Russian gas transit through its territory, which had concerned Hungary and Slovakia regarding their energy supplies. While Ukraine has stopped Russian gas transit, it continues to allow oil transit, though legislation to ban this is pending. The EU has already implemented 15 sanctions packages against Russia, with a 16th package under consideration that would target additional sectors including aluminum, agricultural products, and LNG.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1380 833000 |
Tanks +5 9876 |
Artillery +27 22366 |
Arm. Veh. +12 20573 |
Aircraft 369 |
Heli 331 |
Ships 28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian officials are expanding their “Time of Heroes” program from the federal to regional level, with Kursk Oblast being the latest to adopt the initiative. Governor Alexander Khinshtein announced “Kursk. Heroes!” which aims to place military veterans in government positions.
Russia has approved new legislation to simplify military conscription, with Defense Committee Chair Andrei Kartapolov introducing a draft bill that would extend the military’s authority to conscript individuals up to one year after their original conscription cycle and allow draft boards to more easily recruit young men aged 18-27, including those who previously avoided service. Under the changes, which received cabinet support and may begin discussions before Spring 2025’s conscription period, medical fitness decisions will remain valid for one year, enabling direct drafting in subsequent recruitment cycles without additional examinations. These reforms come after Russia’s recent conscription campaigns reached record numbers, with 133,000 drafted in fall 2024 and 150,000 in spring, though while conscripts rarely see combat, Russia continues seeking alternative methods to boost military numbers following widespread resistance to its 2022 mobilization, which led to over 261,000 Russians fleeing the country.
Controlling the Narrative and Russian Propaganda
A new military history textbook released in Moscow portrays Russia’s invasion of Ukraine as a continuation of the Soviet Union’s fight against Nazi Germany. The three-volume work, edited by presidential advisor Vladimir Medinsky, claims Russia was forced to invade Ukraine in 2022 due to NATO expansion and Ukraine’s 2014 political changes. The textbook describes Ukraine as an “anti-Russian bridgehead” and is part of broader educational changes that include teaching children as young as six about the war, which Russia calls a “special military operation.” The initiative includes video lessons featuring Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov and Patriarch Kirill, focusing on patriotism and traditional values.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
