Summary of the Day:
Russian President Vladimir Putin claimed that Ukraine’s war could end within two months if Western military aid stops, dismissing Ukraine’s sovereignty. Putin continues positioning himself as an equal to US President Trump while reinforcing Russia’s claimed status as heir to Soviet power, making clear he has no intention of compromising on his demands for regime change and military control of Ukraine. His statements suggest he would likely breach any new peace agreement while still believing he can achieve his expansionist goals militarily.
Ukrainian forces conducted a significant drone strike on the Lukoil-Nizhegorodnefteorgsintez oil refinery in Kstovo, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, causing a fire. Additionally, Ukrainian drones reportedly struck the Russian 23rd Arsenal near Oktyabrsky in Tver Oblast, damaging multiple buildings including a weapons storage facility.
On the battlefield, Russian forces advanced near multiple locations including Lyman, Chasiv Yar, Toretsk, Pokrovsk, Kurakhove, Velyka Novosilka, Robotyne, and in the Dnipro direction, while Ukrainian forces made progress in Kursk Oblast and near Toretsk. The Russian Ministry of Defense confirmed Lieutenant General Alexander Sanchik as commander of the Russian Southern Grouping of Forces, even as Moscow experiences a sharp decline in military volunteer recruitment with Russian citizens showing increasing reluctance to serve in Ukraine.
Picture of the Day:
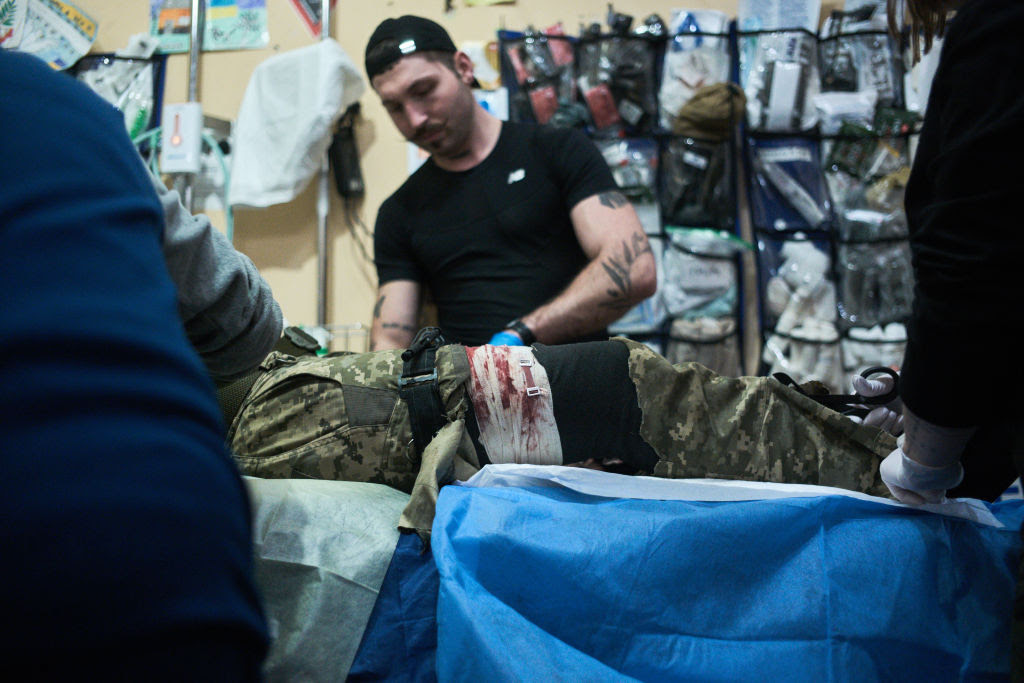 A wounded Ukrainian soldier is being treated at a stabilization point as Russia’s advance continues in the direction of Chasiv Yar, Donetsk Oblast. (Piotr Sobik/Anadolu via Getty Images)
A wounded Ukrainian soldier is being treated at a stabilization point as Russia’s advance continues in the direction of Chasiv Yar, Donetsk Oblast. (Piotr Sobik/Anadolu via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Syria’s new government held its first talks with Russian officials, demanding compensation, acknowledgment of “past mistakes”, and the extradition of former President Bashar al-Assad and his associates following his December overthrow and flight to Moscow. The discussions, led by Russian Deputy Foreign Minister Mikhail Bogdanov and Syria’s de facto leader Ahmad al-Sharaa, centered on Russia’s responsibility in Syria’s reconstruction after their 2015 military intervention, which enabled Assad’s regime to commit widespread human rights violations. Russia has begun withdrawing military equipment from its bases in Tartus and Khmeimim, while Ukraine has initiated diplomatic relations with Syria’s new leadership to address Russian military presence in the region. This shift in Syrian leadership and Russia’s diminishing influence in the country could significantly impact regional stability and power dynamics in the Middle East.
Georgia withdrew from the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) after the Assembly demanded new parliamentary elections following widespread fraud allegations in the fall 2024 elections won by the pro-Russian Georgian Dream party. PACE’s resolution called for new democratic elections, the release of political prisoners, and steps to resume Georgia’s EU integration process. Georgia’s ruling party, led by oligarch Bidzina Ivanishvili, has moved the country closer to Russia while delaying EU accession until 2028, resulting in sanctions from the U.S., EU, and Ukraine. This development signals growing tensions between Georgia’s pro-Russian government and Western institutions, potentially destabilizing regional security and democratic development in the Caucasus region.
Australian volunteer Oscar Jenkins, previously feared executed by Russian forces in Ukraine, has been confirmed alive and in Russian custody. Jenkins, who serves in Ukraine’s 402nd Separate Rifle Battalion, went missing on December 16, 2024, during a combat mission near Mykolaivka in Luhansk Oblast. A disturbing video emerged showing Jenkins being interrogated and beaten by Russian captors. Australia has demanded Russia treat Jenkins in accordance with international humanitarian law and the Geneva Conventions, which require humane treatment of prisoners of war. The incident highlights ongoing concerns about Russia’s treatment of POWs, as executing prisoners of war constitutes a war crime under international law.
Slovak-Ukrainian relations have deteriorated significantly, with Slovakia’s Foreign Ministry summoning Ukrainian Ambassador Myroslav Kastran following escalating tensions between Slovak Prime Minister Robert Fico and President Volodymyr Zelensky. The diplomatic crisis deepened after Fico labeled Zelensky “the enemy” of Slovakia and threatened to limit aid to Ukraine and cut electricity supplies. The conflict centers on Russian gas supplies and Fico’s pro-Moscow stance, which has sparked domestic protests and international concern. This diplomatic rift between NATO allies could potentially impact regional stability and weaken European unity in supporting Ukraine against Russian aggression. The situation highlights growing divisions within NATO and the EU over support for Ukraine, particularly concerning energy policy and military aid.
The Path to Peace
Russian President Vladimir Putin claimed that Ukraine’s war could end within two months if Western military aid stops, dismissing Ukraine’s sovereignty while attempting to portray the country as weak and dependent. However, Ukraine has demonstrated remarkable combat effectiveness when properly equipped, successfully defending itself against Russian aggression for nearly three years and forcing Russian withdrawals from Kyiv Oblast in April 2022 and slowing Russian offensives in Summer 2022. Putin’s strategy hinges on the West eventually abandoning Ukraine, though sustained Western support, particularly from the United States, remains crucial to potentially force diplomatic solutions.
Putin has signaled he won’t honor any peace agreement with Ukraine, falsely claiming President Zelensky is no longer a legitimate president and that Ukraine’s parliament could rescind his 2022 decree banning negotiations. This appears to be part of his broader strategy to delegitimize Ukraine’s government and potentially justify demands for complete regime change in Kyiv. Despite previously negotiating with Ukrainian officials and signing the Minsk agreements (2014-2015), Putin has consistently violated these agreements using similar claims about Ukraine’s illegitimacy.
His current rhetoric suggests he would likely breach any new peace agreement while believing he can achieve his expansionist goals militarily. Putin’s statements appear aimed at manipulating potential negotiations to exclude Ukraine entirely, positioning himself as an equal to US leadership while reinforcing Russia’s claimed status as heir to Soviet power. European officials have proposed helping fund US military assistance to Ukraine to maintain crucial support, but Putin continues to reject Ukraine’s right to exist as an independent state.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian forces successfully struck a Russian Buk-M3 air defense system in occupied Kharkiv Oblast, according to footage released by a Ukrainian drone battalion operating in the region.
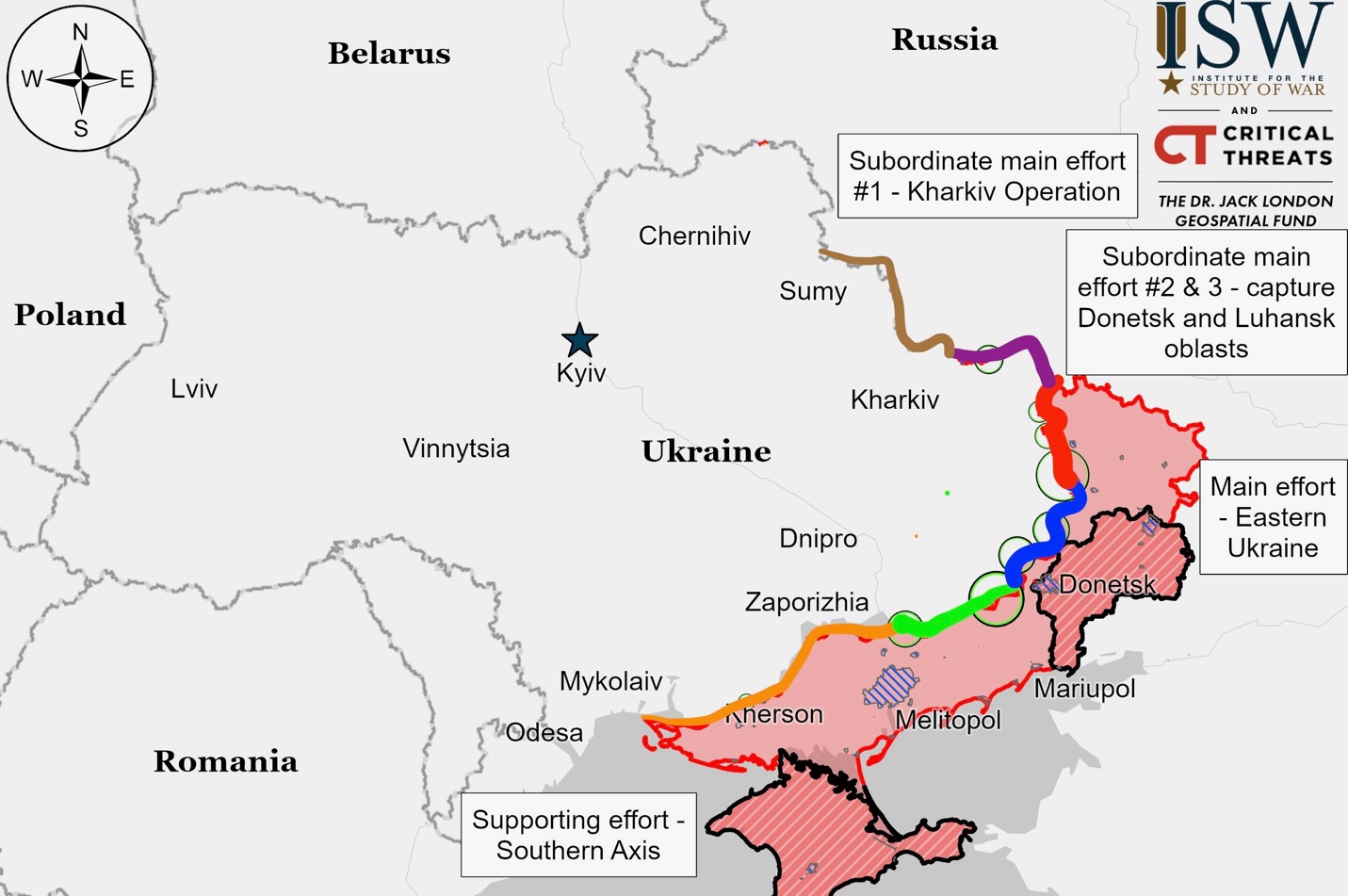
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative Russia
Ukrainian forces made small advances in Kursk Oblast, specifically along Novoselovka Street in northwestern Pogrebki. While Russian sources claimed advances near Plekhovo and Guyevo, these reports remain unconfirmed. Fighting continues around several settlements including Russkoye Porechnoye, Sverdlikovo, and Nikolskiy, where Ukrainian forces successfully repelled a Russian mechanized assault on January 19.
Ukrainian forces conducted a significant drone strike on the Lukoil-Nizhegorodnefteorgsintez oil refinery in Kstovo, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, causing substantial damage to its tank farm. The facility, which produces various petroleum products and processes up to 17 million tons of oil annually, supports Russian military operations. This attack was part of a larger operation involving over 100 drones across nine Russian regions, with Russian officials claiming they intercepted 104 drones, with the Kursk Oblast reporting the highest number (47), followed by Bryansk (27) and Smolensk (11). Ukrainian drones also struck the Russian 23rd Arsenal near Oktyabrsky in Tver Oblast, damaging multiple buildings including a weapons storage facility, and targeted the Andreapol oil pumping station, causing oil spills and fires that forced the shutdown of the Baltic Pipeline System-2’s main pipeline.
One drone reportedly targeted a nuclear facility in the Smolensk region, with debris falling near the Smolensk Nuclear Power Plant, though no damage was reported. This marks the third major drone strike on Russia in 2024, with Ukraine maintaining that oil refineries are legitimate military targets as they help fund Russia’s war effort. The attacks, occurring approximately 750-800 kilometers from the Ukrainian border, follow a recent successful strike on the Ryazan Oil Refinery, which subsequently suspended operations, and demonstrate Ukraine’s ability to conduct long-range precision strikes deep within Russian territory.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched ground attacks near Vovchansk and Starytsya, northeast of Kharkiv City, but failed to make any advances.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Kupyansk
Russian forces continued attacking near Kupyansk targeting several settlements including Kutkivka, Dvorichna, Kindrashivka, Novomlynsk, and Petropavlivka. While Russian sources claimed to have captured Dvorichna and advanced 3 kilometers, these claims remain unverified. Russian forces are using armored vehicles to support infantry assaults near Pishchane and have reportedly reinforced their positions along both banks of the Oskil River.
Borova
Russian forces launched attacks in multiple areas around Borova but failed to advance. The attacks targeted Kolisnykivka, Nova Kruhlyakivka, Lozova, Bohuslavka, Kopanky, and Makiivka. There are conflicting Russian claims about the capture of Novoyehorivka, with some sources criticizing the Russian Ministry of Defense’s premature announcement of its capture on January 20. Russian special forces drone operators are reportedly active near Hrekivka.
Lyman
Russian forces made advances in the Lyman direction with confirmed Ukrainian reports showing Russian progress northwest of Novosadove and Novolyubivka. While Russian sources claimed additional advances near Terny, these remain unconfirmed. Russian forces conducted attacks at multiple points including Zelena Dolyna, Torske, Yampolivka, and the Serebryanske forest area.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces attacked near Siversk but failed to advance. Ukrainian forces reported destroying significant Russian equipment during attacks near Bilohorivka, Verkhnokamyanske, and Ivano-Darivka, including two tanks, ten armored vehicles, and six motorcycles. Additional Russian attacks occurred near Novoselivka.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces advanced near Chasiv Yar with fighting reported in several key areas. Video evidence shows Chechen “Akhmat” forces attacking Ukrainian positions south of the city. Russian forces made gains along the Bakhmut-Kostyantynivka highway and near Orikhovo-Vasylivka. Russian military sources claim their forces captured parts of northern Chasiv Yar, including the Pivnichnyi and Novopivnichnyi areas. Additional fighting occurred near the settlements of Novomarkove, Stupochky, Bila Hora, and Predtechyne.
Toretsk
Fighting continues in the Toretsk area, with both sides making small advances. Ukrainian forces advanced in northwestern Leonidivka and northern Toretsk, while Russian forces made minor gains in northwestern Pivnichne. While Russian sources claim control of 90-95% of Toretsk, independent assessments indicate Russian forces hold about 88% of the city. Combat was also reported in Krymske, Dachne, Dyliivka, and Shcherbynivka.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces made small advances southwest of Pokrovsk, particularly west of Kotlyne. While Russian sources claim advances near Zvirove, along the railway towards Pokrovsk, and in Sribne and Udachne, these claims remain unconfirmed. Ukrainian forces reportedly launched counterattacks near Uspenivka and Novooleksandrivka. Fighting continues across multiple settlements including Baranivka, Vodyane Druhe, Vozdvyzhenka, Yelyzavetivka, Promin, Myrolyubivka, Sukhyi Yar, Lysivka, Zelene, Vidrodzhennya, Shevchenko, and several others in the Pokrovsk area.
Kurakhove Region
Russian forces advanced west of Kurakhove with confirmed progress in southern Dachne. Russian sources claim advances west of Petropavlivka and in western Andriivka, with attempts to encircle Dachne. Combat continues near multiple settlements including Andriivka, Zelenivka, Ulakly, Kostiantynopil, Rozlyv, and towards Oleksiivka.
Velyka Novosilka
Russian forces advanced near Velyka Novosilka with Ukrainian military maps showing Russian gains north of Rozdolne, southeast of Novodarivka, and east of Olhivske. While Russian sources claim additional advances northeast of Rozdolne and northwest of Velyka Novosilka, these remain unconfirmed. Fighting continues around Velyka Novosilka itself and in nearby settlements including Rozdolne, Novyi Komar, Novoocheretuvate, and Novosilka.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces conducted ground attacks in the Polohy direction but made no advances.
Russian forces advanced north of Robotyne with Ukrainian military maps showing Russian gains southwest of Novodanylivka. Russian airborne units are operating near Kamyanske, while other Russian forces are conducting drone strikes near Orikhiv and maintaining operations in the broader Zaporizhia area.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces advanced in the Dnipro River area capturing Nestryha Island southwest of Kherson City, while also making progress northward in the Dnipro River Delta.
Ukraine News
Russia launched a large-scale attack against Ukraine, using an Iskander-M ballistic missile from Crimea and 57 drones launched from multiple locations including Rostov Oblast, Krasnodar Krai, Kursk Oblast, and occupied Crimea. Ukrainian forces intercepted 29 drones and disrupted 14 others through electronic warfare. The strikes impacted Kharkiv, Kyiv, Mykolaiv, Odesa, and Sumy regions, with Russian sources claiming additional hits in Chernihiv, Cherkasy, and Dnipropetrovsk areas.
President Volodymyr Zelensky announced plans to seek alternative funding from domestic and European sources following newly-elected U.S. President Donald Trump’s 90-day freeze on foreign aid, which could potentially extend to six months. The suspension affects critical Ukrainian programs including energy infrastructure repairs, veterans’ services, border checkpoint modernization, agricultural projects, and independent media funding, though U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio has granted exceptions for life-saving humanitarian aid. The situation is particularly concerning for Ukraine’s energy sector, which continues to face Russian attacks, including a major assault in December 2024 that targeted the electric grid with 90 missiles and 200 drones. Zelensky has ordered an assessment of impacted U.S.-funded projects while Ukraine’s parliament works with European partners to maintain stability during the funding pause, seeking to temporarily replace the suspended U.S. assistance through domestic and European support.
In Ukraine, 93 companies have recently removed Russian ownership ties despite a legal ban on such changes, according to Opendatabot monitoring service. This occurred despite a law allowing Ukraine to seize Russian-owned assets and prohibiting ownership reregistration. Some companies, including Texter Ltd., Welesgard LLC, and Era Mobile, won government contracts worth millions of hryvnias after changing ownership. Of the over 18,000 companies with Russian ties at the start of the invasion, 621 have allegedly altered their ownership records. The Justice Ministry’s investigation of these cases found violations in 14 companies, with earlier inspections confirming illegal registration changes in 8 out of 10 examined cases.
Russia has increased its military budget by 25% for 2025, prompting Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal to call for stronger international sanctions and increased military aid during his meeting with Croatian Prime Minister Andrej Plenkovic in Zagreb. President Vladimir Putin approved record military spending for the next three years. The U.S. response includes President Trump’s threat of new sanctions and tariffs on Russian exports, with his peace envoy Keith Kellogg suggesting that targeting Russia’s oil sector could force negotiations. NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte has urged continued U.S. weapons support for Ukraine, with Europe offering to cover financial costs.
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Finland’s Insta company and Ukraine have jointly developed the Steel Eagle drone, as reported by Finnish broadcaster Yle. The drone features VR goggles for pilots, radio control, and anti-interference capabilities. It functions as a combined explosive charge and drone system, designed to detonate steel and tungsten pellets above targets, capable of penetrating light armored vehicles. This collaboration is part of broader Finnish-Ukrainian defense partnerships, with over 10 Finnish defense companies working directly with Ukrainian firms. Ukraine’s Defense Minister Rustem Umerov reported that over 200,000 domestically-produced drones were delivered to front-line units by late 2024.
Ukraine’s Allies
The European Union is proposing a new sanctions package against Russia that would disconnect approximately 15 Russian banks from the SWIFT international banking system and impose a gradual ban on Russian aluminum imports, with a one-year quota of 275,000 metric tons before a complete ban takes effect. The sanctions package, which would mark the EU’s 16th round of restrictions, also includes limitations on over 70 ships suspected of transporting Russian oil above the $60-per-barrel price cap. EU foreign ministers approved a six-month extension of current sanctions on January 27, following negotiations with Hungary, which had initially threatened to veto the extension over Ukraine’s termination of Russian gas transit. Ukraine ended Russian gas transit on January 1, citing its refusal to finance Russia’s war effort, though it continues to transit Russian oil.
U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio has modified the recent freeze on U.S. foreign aid by issuing a waiver for critical humanitarian assistance. The waiver, announced January 29, allows continuation of essential services including medical care, food, shelter, and basic survival assistance. This comes after President Trump’s executive order on inauguration day that initially suspended all foreign aid for a 90-day review period.
NATO Deputy Secretary General Radmila Shekerinska announced that NATO is on track to deliver its promised $41.6 billion in security assistance to Ukraine by year’s end, fulfilling a commitment made at the July 2024 NATO summit in Washington, D.C. During meetings in Brussels with Ukraine’s Deputy Prime Minister Olha Stefanishyna, NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte affirmed continued support for Ukraine while emphasizing increased European spending amid U.S. leadership transition.
Russia News
The Russian Ministry of Defense has confirmed Lieutenant General Alexander Sanchik as commander of the Russian Southern Grouping of Forces. This confirms earlier reports from November 2024 when Sanchik, who previously commanded the Eastern Military District, was reportedly appointed to lead both the Southern Grouping of Forces and Southern Military District.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1270 835940 |
Tanks +4 9890 |
Artillery +17 22412 |
Arm. Veh. +17 20614 |
Aircraft 369 |
Heli 331 |
Ships 28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Moscow’s military recruitment has dramatically declined, with daily volunteer numbers plummeting from 200-250 in August 2024 to just 40 currently, according to the Russian opposition outlet Verstka. Half of the current volunteers are foreigners, primarily from China, Africa, and former Soviet states, attracted by signing bonuses of 1.9 million rubles ($19,140), while the other half consists of Russian citizens and individuals with pending criminal charges. Despite suffering 1,500-1,750 daily casualties, Russia managed to make advances in late 2024 near Toretsk, Chasiv Yar, and Kupiansk in Donetsk Oblast, though NATO’s Supreme Commander suggests a major breakthrough is unlikely due to stretched military resources.
Russian authorities continue militarizing society through the “Time of Heroes” program, which places Ukraine war veterans in government positions. Sergey Kuzminchuk was appointed federal inspector for Kamchatka Krai in the Far Eastern Federal District.
Russia’s defense industry has developed a specialized sector for adding protective armor cages to MT-LB vehicles to shield troops from Ukrainian drone attacks. This adaptation comes as Russia struggles to produce enough new armored vehicles for the war in Ukraine. Similar modifications have been made to the “Tiger-M” special purpose vehicle, including additional armor plating on the engine, doors, wheels, hood, and windshield to improve survivability after strikes.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
