Summary of the Day:
Russia and Iran formalized a new strategic partnership with Presidents Vladimir Putin and Masoud Pezeshkian signing the Russia-Iran Comprehensive Strategic Partnership Agreement. Notably, the agreement lacks a mutual defense clause, suggesting Russia’s limited military bandwidth beyond Ukraine and its prioritization of the mutual defense treaty with North Korea for additional manpower.
Russian forces achieved territorial gains on multiple fronts, with the capture of Vremivka marking a significant advance in their efforts to envelop Velyka Novosilka. Additionally, Russian forces progressed across several axes including Kursk Oblast, Kharkiv, Kupyansk, Borova, Toretsk, Pokrovsk, and Kurakhove directions. Looking ahead to force generation, Putin signed a decree authorizing the call-up of Russian reservists (“personnel mobilization resource” or zapas) for training in 2025.
On the diplomatic front, Putin’s phone call with Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan revealed mounting Kremlin concerns over Armenia’s strengthening ties with the West. Meanwhile, newly declassified US documents highlighted the significant impact of American monetary and technical assistance in expanding Ukraine’s domestic drone production capabilities. The documents also emphasized how lessons learned from Ukraine’s drone operations are being integrated into the US defense industry, directly benefiting American national security.
Picture of the Day:
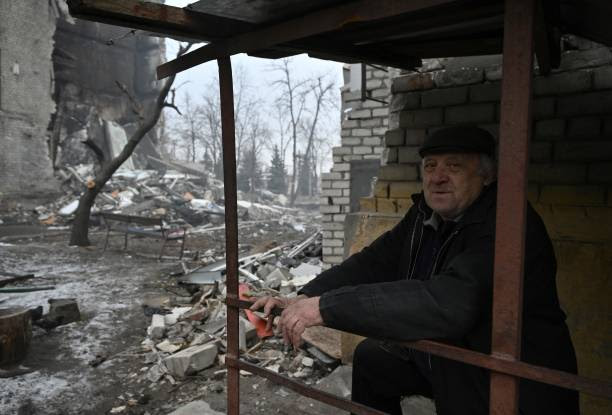 A local resident stands at the entrance to the basement of the damaged residential building where he lives in the town of Lyman, near the frontline in Donetsk Oblast. (Photo by Genya Savilov/AFP via Getty Images)
A local resident stands at the entrance to the basement of the damaged residential building where he lives in the town of Lyman, near the frontline in Donetsk Oblast. (Photo by Genya Savilov/AFP via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Russia and Iran signed a 20-year strategic partnership agreement in Moscow, covering military cooperation, intelligence sharing, nuclear energy, and transportation, with provisions to prevent either country’s territory from being used to threaten the other. The agreement could enable Russia to establish military bases in Iran, including aircraft refueling stations and naval facilities, though Iran may be hesitant due to potential additional Western sanctions. The partnership appears designed to help both nations evade existing Western sanctions through improved economic and transportation connections, a strategy Russia has already implemented with other international partners.
The agreement notably comes at a time when Russia faces significant military constraints and base access challenges due to the Ukraine war and setbacks in Syria, including Assad’s fall and difficulties maintaining bases at Hmeimim Air Base and Port of Tartus. Iran has been supplying Russia with Shahed drones and ballistic missiles used against Ukrainian cities, with Russia subsequently developing its own version called Geran-2. However, Russia appears to be prioritizing its military alliance with North Korea over deeper cooperation with Iran, having deployed North Korean troops to Kursk Oblast to free up Russian soldiers for the Ukraine war.
This consolidation of partnerships between Russia, Iran, and North Korea represents a significant shift in global power dynamics, particularly in the Middle East and Mediterranean regions. While the agreement strengthens military and economic ties between Russia and Iran, it excludes mutual defense commitments, reflecting Russia’s current military limitations and its strategic choice to value North Korea’s direct military manpower over Iran’s technical support, which it has been receiving since 2022. This evolving military dynamic could further destabilize regional security and challenge Western-aligned countries’ interests in both Ukraine and the Middle East.
Putin and Pashinyan discussed Armenia’s role in the Russian-led Eurasian Economic Union by phone, with Armenia reporting they focused on EAEU matters while the Kremlin claimed they also addressed Armenia’s recent moves toward the European Union, including a January 9 EU accession bill and Armenia’s January 14 Strategic Partnership launch with the United States, which prompted Russian concerns about Armenia’s loyalties. Although Armenian officials deny plans to leave the Russian-led EAEU, Putin’s emphasis on economic cooperation during the call suggests Moscow is worried about losing influence over Armenia to the West, highlighting growing tensions as Armenia potentially shifts away from Russia’s influence toward the West – a diplomatic tension that reflects Russia’s struggle to maintain control over its traditional sphere of influence in the wake of its Ukraine war and could alter the balance of power in the Caucasus region.
A French military aircraft faced aggressive Russian behavior when targeted by a ground-to-air defense system’s radar while patrolling international airspace over the Baltic Sea. French Defense Minister Sebastien Lecornu condemned the action as unacceptable.
An Australian volunteer soldier, Oscar Jenkins, is confirmed to be a prisoner of war in Russian custody, contradicting earlier reports of his execution. Jenkins, a 32-year-old Melbourne teacher serving in Ukraine’s 402nd Separate Rifle Battalion, went missing on December 16, 2024, during a combat mission near Mykolaivka in Luhansk Oblast. The incident has escalated diplomatic tensions, with Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese warning of “strongest action possible” if harm comes to Jenkins. Russia’s treatment of foreign volunteers as “mercenaries” rather than POWs protected by the Geneva Conventions raises serious concerns for international humanitarian law and could further strain global diplomatic relations.
The Path to Peace
Secretary of State Antony Blinken stated that the incoming Trump administration could broker a “good” and “strong” peace deal in Ukraine, contingent on Ukrainian agreement. He emphasized that any ceasefire must include deterrence against future Russian attacks and not merely allow Russia time to regroup. While Trump has pledged to seek a peace settlement, Ukraine maintains it will not recognize Russian control over occupied territories, which comprise about 20% of Ukraine.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukraine’s innovative drone capabilities, particularly first-person view (FPV) and long-range drones, have proven highly effective at limiting Russian military movements and disrupting their war efforts. These developments in drone warfare are likely to influence military strategies worldwide, suggesting a significant shift in how future conflicts will be fought. This evolution in military technology, driven by Ukraine’s innovations under wartime conditions, could reshape global military doctrine and defense strategies.
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative Russia
Russian forces have made recent advances in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast region. The Russians have pushed southwest of Viktorivka, with ongoing battles near several settlements including Pogrebki, Cherkasskoye Porechnoye, and Makhnovka. While the Russian Ministry of Defense claims to have retaken 63.2% of the Ukrainian salient, independent assessments suggest the figure is closer to 50%. Reports indicate Russian forces are using “scorched earth” tactics, notably destroying the settlement of Darino, and are conducting infantry assaults using ATVs and motorcycles to preserve armored vehicles. The fighting involves multiple Russian military units concentrated around the settlements of Nikolayevo-Darino, Leonidovo, Alexandriya, and Berdin.
Independent Russian media outlet Mediazona reported that at least four Russian officers were killed in Ukraine’s attack on Lgov in Russia’s Kursk Oblast on December 30. While Russian officials initially claimed only civilian injuries, obituaries revealed that Lieutenant Colonel Valeriy Tereshchenko, Lieutenant Colonels Pavel Maletsky and Alexei Seliverstov, and Major Ali Tsurov were killed. The attack reportedly killed eight senior staff members and injured 22 others. A previous attack on December 26 allegedly killed 18 Russian soldiers when a command post was struck.
Ukrainian forces conducted precision strikes on January 16 against Russian military targets in Belgorod Oblast, hitting the Russian 568th Anti-Aircraft Missile Regiment’s S-400 missile system radar station and positions of the 336th Radio-Technical Regiment’s radio engineering battalion. Additionally, Ukrainian forces carried out drone strikes on an oil depot in Voronezh Oblast, a gunpowder factory in Tambov Oblast, and an oil depot in Lyudinovo, Kaluga Oblast, which caused a significant fire – these attacks on Russian fossil fuel infrastructure are part of Ukraine’s strategy to reduce funding for Russia’s war effort and demonstrate Ukraine’s continued ability to strike strategic Russian military assets within Russian territory.
Russia’s seaborne petroleum exports fell 9.1% to 113.7 million metric tons in 2024, with Ukrainian drone strikes significantly impacting operations at refineries in Tuapse, Ilyich, and Novoshakhtinsk, leading to major export declines through Baltic, Black Sea, and Azov Sea ports, with the Tuapse facility alone seeing exports drop by one-third to 9.1 million tons – this disruption comes amid new U.S. and U.K. sanctions targeting Russia’s oil sector, including its shadow fleet, with G7 nations considering tightening the existing $60-per-barrel price cap.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces have made recent advances northeast of Kharkiv City, with documented progress in northern Vovchansk along Zernova Street and in southern Tykhe. Ukrainian sources report that Russian forces have shifted their drone tactics along the northern border, now favoring reusable drones over single-use FPV drones for explosive drops. Ukrainian forces reportedly launched three counterattacks in the Vovchansk area.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Kupyansk
Russian forces made small advances in the Kupyansk direction along the P-07 Svatove-Kupyansk highway near Stepova Novoselivka. Fighting continues north of Kupyansk near Holubivka, east near Petropavlivka, and southeast near Stepova Novoselivka and Pishchane. Russian forces are reportedly pushing toward the P-79 Kupyansk-Dvorichna highway south of Dvorichna, where Ukrainian forces are launching counterattacks.
Borova
Russian forces advanced east of Zeleny Hai in the Borova direction, with claims of pushing 1.8 kilometers northeast of the settlement. Russian attacks occurred across multiple locations: north of Borova near Novoplatonivka; northeast near Kruhlyakivka, Zeleny Hai, and Zahryzove; east near Kopanky; and southeast near Tverdokhlibove, Hrekivka, Makiivka, and Novoserhiivka. Russian sources claim advances near Makiivka, though these claims remain unconfirmed.
Lyman
Russian forces continued offensive operations in the Lyman direction without confirmed advances, despite claims of progress near Makiivka, Ivanivka, and west of Novosadove. Fighting occurred north of Lyman near Zelena Dolyna, northeast near Terny and Torske, and east near Zarichne. Ukrainian sources report that Russian forces are using a two-soldier attack strategy, with unarmed soldiers (often convicts) advancing first to expose Ukrainian positions, followed by armed soldiers. One Ukrainian brigade noted a recent decrease in Russian attacks, contrasting with the previous constant infantry assaults in 2024.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Ukraine’s Special Operations Forces reported that they targeted Russian soldiers who had executed two Ukrainian prisoners of war, resulting in several Russian casualties and three captures. The operation, which took place in Donetsk Oblast, led to the capture of Russian marines, including one identified as “Yaryy.” The captured Russians reportedly admitted during interrogation that they had executed the Ukrainian Territorial Defense Forces fighters under orders from their company commander. Ukraine’s Prosecutor General’s Office has documented at least 124 POW executions by Russian forces since the start of the war, highlighting ongoing violations of the Geneva Conventions.
Siversk
Russian forces conducted offensive operations in the Siversk direction without making advances. Fighting continued near Bilohorivka (northeast of Siversk), Verkhnokamyanske (east), and Ivano-Darivka (southeast). Ukrainian forces report that Russians are using cars and motorcycles to transport troops to the frontline for infantry assaults in this area.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces launched multiple attacks around Chasiv Yar, though no confirmed advances were made. Russian military bloggers claimed advances in several areas including northern, central, and western parts of Chasiv Yar, as well as near Hryhorivka, but these claims remain unverified. Fighting continued within Chasiv Yar itself and in nearby settlements including Pryvillya, Stupochky, and Bila Hora.
Toretsk
Russian forces made a confirmed advance west of Toretsk, specifically along Lesi Ukrainky Street in eastern Petrivka. Fighting continued in Toretsk itself and in nearby settlements including Krymske, Dyliivka, Leonidivka, and Shcherbynivka.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces made confirmed advances in the Pokrovsk direction ocapturing Yasenove and advancing along the Solona River north of Uspenivka. Fighting continued across multiple settlements near Pokrovsk, including Vodyane Druhe, Zelene Pole, Yelyzavetivka, Promin, Myrolyubivka, Lysivka, Shevchenko, Novyi Trud, Udachne, Sribne, Zvirove, and Kotlyne. A Ukrainian brigade officer reported inflicting approximately 300 Russian casualties per day in this area.
Kurakhove Region
Russian forces advanced southwest of Kurakhove with confirmed progress near Sukhi Yaly along the northern bank of the Sukhi Yaly River. Fighting continued around Kurakhove and nearby settlements including Slovyanka, Petropavlivka, Andriivka, Dachne, Ulakly, Yantarne, and Zelenivka.
Velyka Novosilka
Russian forces captured the settlement of Vremivka marking a strategic advance in their efforts to encircle Velyka Novosilka, with forces advancing northeast and southeast of Novosilka and appearing to aim at cutting off the Velyka Novosilka-Hulyaipole highway, though Ukrainian defenses may complicate further Russian advances in the area – Ukrainian military officials reported that Russian forces near Velyka Novosilka have three times as many troops as Ukrainian defenders, operating in small teams of four to five soldiers, and with this significant manpower advantage, Russian forces may try to close the three-kilometer gap in their positions north and west of Velyka Novosilka.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched limited ground assaults near Novodanylivka, north of Robotyne, but failed to make any territorial gains.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces conducted offensive operations along the Dnipro axis but failed to make any advances.
Ukraine News
Russia launched a major aerial assault on Ukraine, using 2 Iskander-M ballistic missiles and 50 drones launched from multiple Russian regions. Ukrainian forces intercepted 33 drones across eleven oblasts, though some attacks got through. Russian strikes damaged civilian infrastructure in Kryvyi Rih and port facilities in Izmail Raion. The attacks also caused damage from falling debris in Kharkiv, Cherkasy, and Kyiv oblasts. One drone strayed into Romanian airspace during the assault.
President Zelensky met with Progressive Slovakia party leader Michal Simecka in Kyiv, expressing Ukraine’s willingness to engage in energy security dialogue with Slovakia and readiness to help ensure Slovakia’s energy stability, while seeking Slovak support for Ukraine’s EU and NATO aspirations – this visit follows Zelensky’s original invitation to Prime Minister Fico and comes after Ukraine’s January 1 decision to end Russian gas transit through its territory, which prompted Fico to threaten limiting aid to Ukraine and cutting electricity supplies. Meanwhile, Slovak opposition parties have initiated a no-confidence vote against Fico’s government, which, along with Hungarian Prime Minister Orban, has maintained friendly ties with Putin and opposed Ukraine’s decision to stop Russian gas transit.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 3 INJURIES: 3
A Russian ballistic missile attack on Kryvyi Rih killed four people and wounded 14 others, including four children (with three injured and one hospitalized), while damaging multiple buildings including residential structures and an educational facility – of the total victims, five remain hospitalized with three in serious condition.
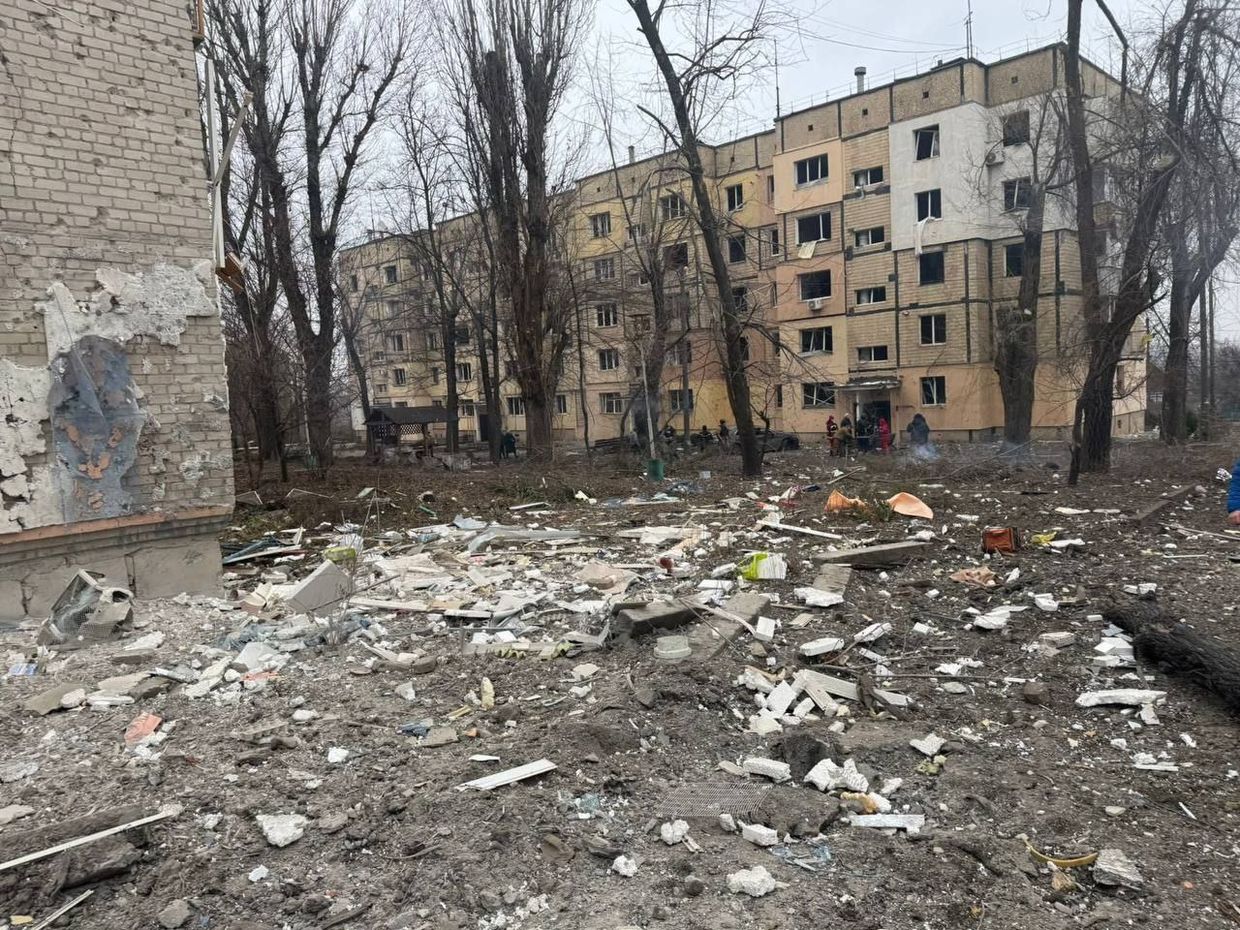 Aftermath of the Russian missile attack on Kryvyi Rih, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. (Governor Serhii Lysak / Telegram)
Aftermath of the Russian missile attack on Kryvyi Rih, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. (Governor Serhii Lysak / Telegram)
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine’s Defense Ministry announced that mandatory military training will begin for university students in September 2025. The program includes 90 hours of theory (mandatory for all students aged 18-25) and 210 hours of practical training (mandatory for men only, optional for women). Students will learn basic military skills, including tactical training, weapons handling, and first aid. Upon completion, graduates will receive military specialization but won’t be drafted until age 25 unless they volunteer. This initiative is part of Ukraine’s broader effort to prepare civilians for wartime challenges, which includes updating military education programs in schools.
Ukraine significantly expanded its drone warfare capabilities in 2024, producing over 30,000 bomber drones capable of night operations, mine dispersal, and logistics support. These drones, nicknamed “Baba Yaga” by Russian forces due to their nighttime capabilities, are part of Ukraine’s broader domestic drone program that delivered more than 200,000 drones to front-line units by the end of 2024. During UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s visit to Kyiv, Strategic Industries Minister Herman Smetanin highlighted this achievement and announced a joint UK-Ukraine development of a new FPV drone carrier platform. This rapid expansion of Ukraine’s drone capabilities represents a significant enhancement of its military capabilities, particularly in nighttime operations and logistics support for front-line forces.
Ukraine’s Allies
U.S. National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan revealed through declassified documents that since Russia’s invasion, American investments have helped Ukraine dramatically expand its drone production capabilities, with support beginning in Fall 2022 and increasing in Summer 2023, including a $1.5 billion program from September 2024 that helped develop new drone technology and facilitated partnerships between American tech companies and Ukrainian manufacturers. By late 2024, Ukraine had delivered over 200,000 domestically produced drones to its forces, which have proven highly effective, notably destroying 25% of Russia’s Black Sea Fleet and helping to slow Russian advances in eastern Ukraine – this assistance has also provided valuable insights for America’s own defense industry, demonstrating how supporting Ukraine’s defense innovations directly benefits U.S. national security interests.
The U.S. has imposed sanctions on six Russian oil tankers still under construction at Russia’s Zvezda shipyard, marking the first time sanctions have targeted vessels before their deployment. The vessels include the Nursultan Nazarbayev, Alexander Beggrov, Alexey Bogolyubov, and three unnamed vessels (Zvezda 131080, 131060, and 131040). This is part of broader sanctions targeting over 180 vessels in Russia’s “shadow fleet” used for evading sanctions. The move aims to undermine Russian oil exports, which help fund its war in Ukraine, and has already driven up prices for non-sanctioned tankers.
NATO has assumed coordination of some Ukrainian aid responsibilities from the U.S., according to NATO Military Committee Chief Admiral Rob Bauer. Speaking in Brussels, he confirmed that NATO will take over the Security Assistance Group – Ukraine (SAG-U) and International Donor Coordination Center (IDCC), based on decisions from the July 2024 NATO Washington Summit.
Italy has approved a new military aid package for Ukraine, announced during Italian Defense Minister Guido Crosetto’s visit to Kyiv. Meeting with Ukrainian Defense Minister Rustem Umerov, Crosetto confirmed the package is already en route and includes modern weaponry. The two nations plan to strengthen defense cooperation and support Ukraine’s defense industry. During his visit, Crosetto also met with President Volodymyr Zelensky to discuss security guarantees.
German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock criticized her government’s hesitancy in supporting Ukraine, stating Germany is not a “driving force for peace policy in Europe.” The criticism comes amid upcoming snap parliamentary elections on February 23, triggered by coalition instability. Chancellor Olaf Scholz is reluctant to approve an additional 3 billion euros in military aid to Ukraine, despite Berlin being Ukraine’s second-largest military donor. The proposed package would include IRIS-T air defense systems, Skyranger systems, howitzers, and other military equipment.
Life in Ukrainian Occupied Russia
Ukrainian and Russian human rights officials met Thursday to discuss locating missing residents from Russia’s Kursk region, where Ukraine gained control of territory last August. Ukraine reports about 2,000 civilians remain in the area, while Russia lists fewer than 1,000 missing. The meeting, which included Red Cross representatives, focused on prisoner of war conditions and returns.
Russian drones struck a school housing displaced civilians in Sudzha, a Ukrainian-held town in Russia’s Kursk region. The attack occurred at a facility sheltering about 100 civilians, mostly women and children, with two people suffering concussion injuries. Sudzha, with a pre-war population of 5,000, is the largest Ukrainian-controlled town in Kursk and houses important gas facilities. Ukrainian officials report approximately 2,000 civilians remain in the area, with dozens killed in Russian strikes. Ukraine has held parts of Kursk since their offensive last year, viewing these territories as potential leverage in future peace talks. Reports indicate Russia has deployed North Korean troops to help reclaim the region.
Russia News
Russia is spending 540 billion rubles ($5.29 billion) in 2025 to teach schoolchildren how to design, build, and operate military drones. The program, called Unmanned Aerial Systems, includes training students to use FPV strike drones and munitions-dropping drones to hit targets. Schools are creating drone clubs for children as young as 10 years old, where they learn drone design, operation, and participate in competitions.
President Biden revealed in an MSNBC interview that he assured Putin that the U.S. would not deploy nuclear weapons in Ukraine. During their discussions, Putin expressed concerns about nuclear weapons in Ukraine and NATO membership. Biden criticized Putin’s apparent goal to “re-establish the Warsaw Pact.” This comes amid increased nuclear tensions, as Russia recently updated its nuclear doctrine to allow nuclear arms use against non-nuclear states and launched the nuclear-capable “Oreshnik” missile. A Levada Center survey showed 39% of Russians support potential nuclear weapons use in Ukraine. The situation contrasts with the 1994 Budapest Memorandum, where Ukraine gave up the world’s third-largest nuclear arsenal for security assurances from the U.S., U.K., and Russia.
Three former lawyers of deceased Russian opposition leader Alexei Navalny were sentenced to prison terms ranging from 3.5 to 5.5 years in Russia’s Vladimir Oblast. Vadim Kobzev, Alexei Liptser, and Igor Sergunin were convicted on “extremism” charges related to their work with Navalny’s Anti-Corruption Foundation. The sentences included a three-year ban from practicing law after their release. Two other Navalny lawyers, Olga Mikhailova and Alexander Fedolov, have fled Russia. The case highlights Russia’s intensifying crackdown on opposition voices since the start of its war against Ukraine in 2022.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1340 817160 |
Tanks 9803 |
Artillery +21 22040 |
Arm. Veh. +13 20394 |
Aircraft 369 |
Heli 331 |
Ships 28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a decree that requires Russian military reservists to undergo combat training in 2025. The order applies to personnel in multiple agencies including the Armed Forces, Rosgvardia, Emergency Situations Ministry, and FSB security service.
Russia’s state defense corporation Rostec announced that it has tested a new drone defense system called “Sfera.” The electronic warfare system, produced by the Polet Chelyabinsk Radio Plant, is designed to detect and block drones over several square kilometers. Rostec claims it has successfully tested Sfera both in civilian areas and on the battlefield.
Russia’s Allies
Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban called for the EU to end sanctions against Russia, describing the EU as being in a “drunken stage” and advocating for a sanctions-free relationship with Russia. Orban reportedly plans to wait for Trump’s inauguration before deciding on extending EU sanctions against Russia. He claimed there would be no Russia-Ukraine war if Trump had won in 2020. Amid strained EU relations and corruption allegations, Hungarian opposition leader Peter Magyar has called for early elections, criticizing Orban’s leadership and claiming Hungary has become “the EU’s poorest, most corrupt nation.”
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
