Summary of the Day:
Ukrainian forces launched strategic strikes against key Russian infrastructure, targeting the Lisinskaya Oil Refinery in Voronezh Oblast and the Tambov Gunpowder Plant with drone attacks. Ukrainian forces also reported advances in Kursk Oblast, while Russian forces gained ground near Chasiv Yar, Toretsk, Pokrovsk, Kurakhove, and Velyka Novosilka.
North Korean forces in Kursk Oblast continue to suffer significant casualties, with 3,800 personnel killed or wounded since early December 2024. At the current loss rate of 92 casualties per day, military analysts project the entire 12,000-person North Korean contingent could be depleted by mid-April 2025.
Ukraine and the UK strengthened their alliance by signing the “Centennial Partnership Agreement”, establishing a 100-year framework for cooperation. The agreement includes British support for Ukraine’s NATO membership bid, annual military aid commitments, and immediate military support including 150 artillery barrels and a Danish-funded mobile air defense system.
Russia is negotiating alternative gas supply routes to Transnistria through European markets, attempting to bypass pipeline restrictions by purchasing gas through Moldovan company Natural Gaz DC. This arrangement, estimated to cost Russia $164 million through April 2025, comes as Ukraine has halted Russian gas transit through its territory, potentially impacting Moldova’s upcoming parliamentary elections.
Picture of the Day:
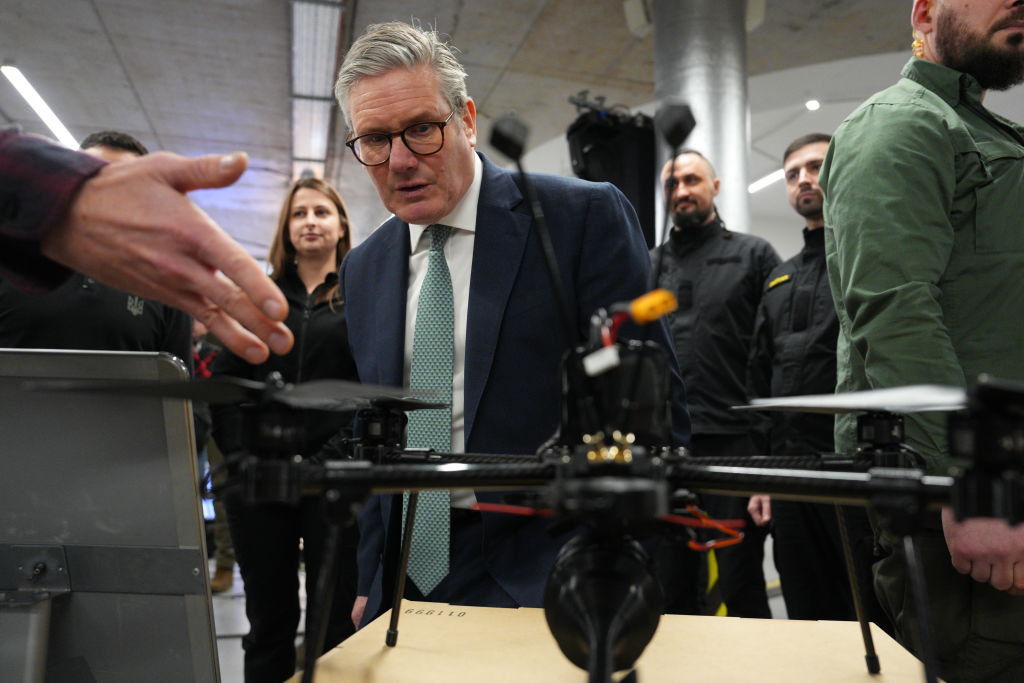 U.K. Prime Minister Keir Starmer and President Volodymyr Zelensky (not pictured) attend a presentation of Ukrainian military drones at an undisclosed location in Kyiv. (Carl Court/Getty Images)
U.K. Prime Minister Keir Starmer and President Volodymyr Zelensky (not pictured) attend a presentation of Ukrainian military drones at an undisclosed location in Kyiv. (Carl Court/Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Russia is negotiating a complex gas supply arrangement through European markets to provide gas to Transnistria, Moldova’s breakaway region, after Ukraine stopped Russian gas transit through its territory and Gazprom halted direct supplies on January 1, 2025. According to Russian business outlet Kommersant, Russia plans to purchase European gas through Moldovan company Natural Gaz DC to supply up to 3 million cubic meters of gas daily to Transnistria from January to April 2025, with the arrangement potentially costing Russia $164 million, likely covered as “humanitarian aid.” The Russian-controlled region has experienced widespread power outages threatening industrial collapse since the halt in gas transit, and this situation has broader implications for regional stability, as Russian manipulation of gas supplies could influence Moldova’s upcoming Summer 2025 parliamentary elections, demonstrating how energy resources continue to be used as a political tool in Eastern Europe, affecting international relations.
Belarus Security Chief Alexander Volfovich made threats against Western nations claiming they planned to occupy Belarus’ border regions with peacekeeping forces. In response, he threatened the use of nuclear weapons and advanced missile systems. This escalation of rhetoric raises tensions between Belarus and Western nations, potentially destabilizing regional peace in Eastern Europe.
North Korea will make history by participating in Russia’s Victory Day parade in Moscow on May 9, deepening the military alliance between the two nations. This unprecedented move follows North Korea’s recent deployment of troops to Russia’s Kursk Oblast to support Moscow’s war against Ukraine. Russia has invited military forces from 19 “friendly” countries to the parade, and Slovak Prime Minister Robert Fico has accepted Putin’s invitation to attend. The collaboration between Russia and North Korea, both under international sanctions, raises concerns about global security and the potential escalation of military tensions. Russia continues to use Victory Day celebrations to promote its military strength and justify its invasion of Ukraine through false claims of “de-Nazification,” while strengthening ties with isolated regimes.
Slovakia’s Prime Minister Robert Fico’s growing alignment with Russia, including criticism of Ukraine’s military aid and a recent Moscow visit, has drawn sharp criticism from President Zelensky. In a Polish media interview, Zelensky warned that Slovakia is “playing a very dangerous game” that could threaten their own security. The tension escalated after Fico threatened Ukraine over its decision to stop Russian gas transit to the EU. Zelensky drew a pointed parallel between Russia’s aggression and a May 2024 assassination attempt on Fico, questioning why the Slovak leader would prosecute his own attacker but advocate forgiveness for Russian aggression. This diplomatic rift between neighboring states highlights growing divisions within European unity regarding support for Ukraine and relations with Russia, potentially weakening regional security cooperation.
The Path to Peace
US President-elect Trump’s Secretary of State nominee Marco Rubio called for ending the war in Ukraine through concessions from all parties during his Senate confirmation hearing, expressing doubt about Ukraine’s ability to reclaim all its territory from Russia due to population constraints. Rubio stated that while Putin’s actions were “unacceptable,” the conflict needs to end through compromises from Russia, Ukraine, and the United States. This position may signal a shift from the current US policy of “Nothing about Ukraine without Ukraine,” potentially leading to direct US-Russia talks without Ukrainian participation.
In response, President Volodymyr Zelensky stated in a Polish media interview that Trump could help end Russia’s war against Ukraine when he takes office on January 20, emphasizing that Trump should secure real security guarantees for Ukraine and pressure Putin toward diplomacy, while acknowledging Trump’s claimed relationship with Putin. The statement comes amid concerns that Trump’s push for a quick peace deal could pressure Ukraine into territorial concessions, with Trump’s advisors suggesting negotiations could take several months. Bloomberg reports that incoming Trump administration advisers are developing a dual-track sanctions strategy on Russia, considering either easing sanctions to facilitate peace talks or expanding them to increase pressure on Moscow.
France and the UK are exploring potential peacekeeping deployment options in Ukraine, contingent on a ceasefire agreement between Kyiv and Moscow. Three scenarios are under consideration: manning a 1,300-kilometer buffer zone along the frontline, protecting Kyiv from Russian advances, or conducting training missions in western Ukraine. French President Macron has discussed this with Ukrainian President Zelensky and Polish PM Tusk. While UK Prime Minister Starmer has shown interest, no firm commitments have been made.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
On January 15, 2025, Ukraine’s 67th Separate Mechanized Brigade reported repelling a Russian assault near Zhuravka in Sumy Oblast, which borders Russia’s Kursk Oblast. While Russia has amassed troops near Zhuravka and may attempt further attacks, monitoring website Deep State notes decreased fighting intensity in the Kursk region compared to previous weeks. The main combat activities are focused around Lebedevka-Sverdlikove and Nikolayevo-Darino. Sumy Regional Military Administration denied recent reports of Russian forces breaking through near Zhuravka and Prokhody.
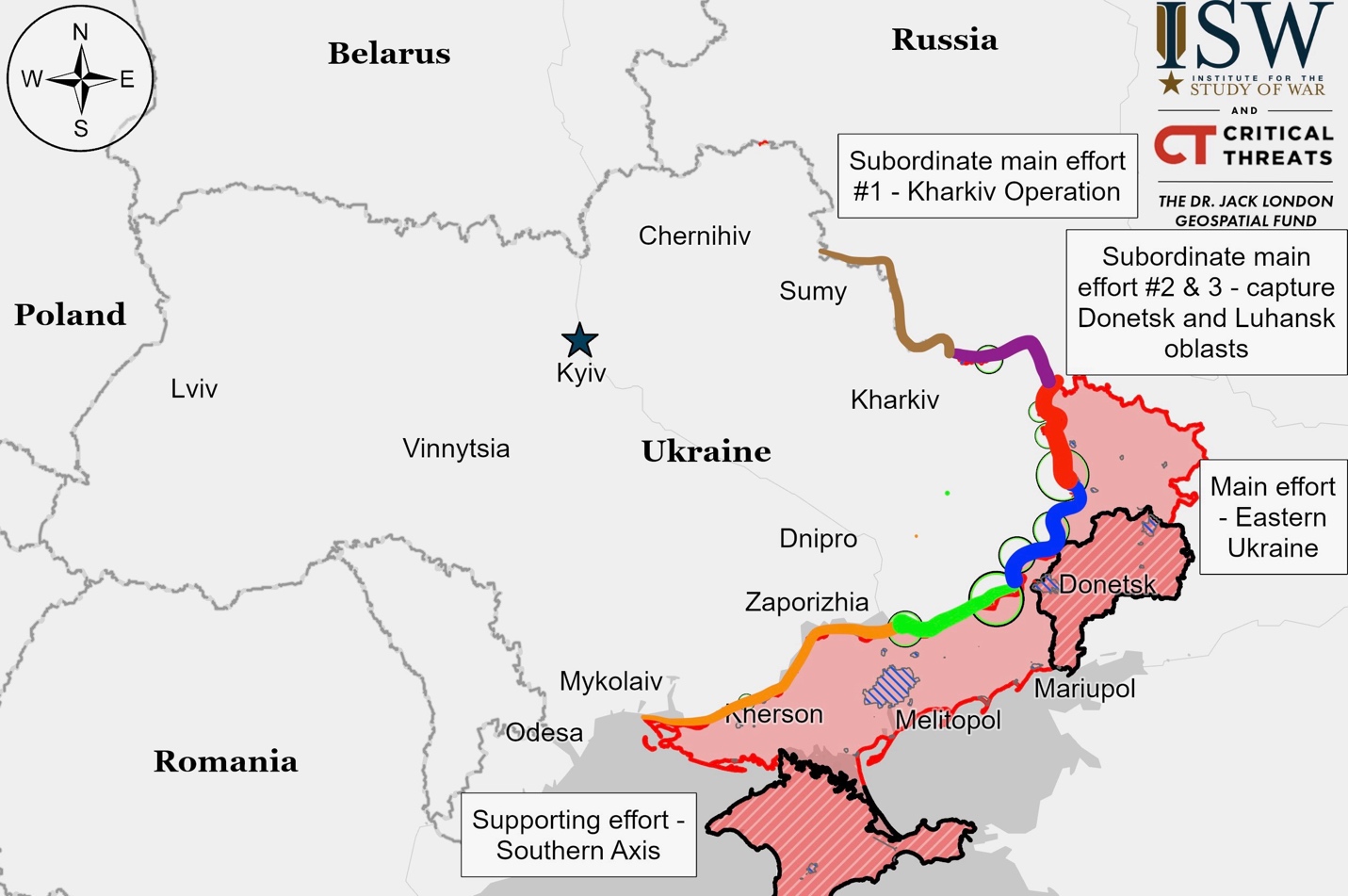
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative Russia
Ukrainian forces made a recent advance in Kursk Oblast near the Russian-Ukrainian border, moving into central Uspenovka, south of Korenevo, while a Russian military blogger claimed unconfirmed advances near Makhnovka. Several Russian military units are active in the area, including naval infantry, airborne forces, and specialized drone operators positioned across various settlements near Sudzha, and Ukrainian paratroopers reported capturing 27 Russian service members in Kursk Oblast, including officers and enlisted personnel from various military units.
North Korean forces in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast are experiencing significant casualties, with President Zelensky reporting 3,800 personnel killed or wounded by early January 2025. From an initial contingent of 12,000 troops deployed to the region, South Korea’s National Intelligence Service confirms 300 North Korean soldiers killed and 2,700 wounded. Based on the current rate of losses (approximately 92 casualties per day since December 2024), analysts project the entire North Korean force could be depleted by mid-April 2025 if these casualty rates continue.
Ukrainian forces conducted successful drone strikes against two strategic Russian facilities: the Lisinskaya Oil Refinery in Voronezh Oblast, located 150 kilometers from the Ukrainian border, which stored military fuel supplies, and the Tambov Gunpowder Plant in Kuzmino-Gat, located 450 kilometers from the Ukraine-Russia border, which produces explosives and materials for Russian weapons systems and was previously targeted in July 2024. At the oil refinery, at least three drones hit the facility causing a large fire, with Russian officials reporting multiple drone strikes in the Liski Raion area. Local residents near Kotovsk reported drone activity at the gunpowder plant, with Russian forces claiming to have intercepted three drones in Tambov Oblast as part of a larger interception of 27 Ukrainian drones overnight. These attacks were part of Ukraine’s broader campaign targeting Russian energy and military infrastructure.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched attacks near Kharkiv City targeting the areas around Vovchansk and Tykhe but failed to gain any confirmed territory.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Kupyansk
Russian forces continued attacks in multiple areas around Kupyansk targeting Kindrashivka to the north, Topoli to the northeast, Petropavlivka to the east, and Pishchane to the southeast. While Russian sources claimed to have advanced into Petropavlivka, these claims remain unconfirmed.
Borova
Russian forces launched attacks near Borova striking numerous settlements including Novoplatonivka, Nova Kruhlyakivka, Zeleny Hai, Zahryzove, Kopanky, Makiivka, Novoyehorivka, Hrekivka, Novoserhiivka, and Tverdokhlibove. A notable mechanized assault on January 8-9 involved 20 Russian vehicles, of which Ukrainian forces reportedly destroyed 16, despite Russian attempts to protect them from drone strikes. While Russian sources claimed advances northwest of Makiivka, these remain unconfirmed.
Lyman
Russian forces attacked several areas near Lyman targeting Terny and Kolodyazi to the northeast, Zarichne to the east, and the Serebryanske forest area to the southeast. Russian forces are reportedly preparing for an assault on Yampolivka with artillery strikes. No Russian advances were confirmed.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces attacked several areas around Siversk, including Hryhorivka to the northeast, Verkhnokamyanske to the east, and Ivano-Darivka to the southeast. While no advances were confirmed, Ukrainian forces reported destroying significant Russian equipment during five mechanized assaults on January 14, including two infantry fighting vehicles, 39 motorcycles, and two ATVs.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces advanced in Chasiv Yar gaining ground within the Chasiv Yar Refractory Plant in the central part of the city. Russian forces are reportedly using the Siverskyi Donets Donbas Canal pipes to move troops during foggy conditions. They also continued attacks near Predtechyne, Stupochky, and Bila Hora. While Russian sources claimed to have captured all of northern Chasiv Yar (Pivnichnyi Microraion), these claims remain unverified.
Toretsk
Russian forces made a small advance in northern Toretsk and conducted attacks in multiple surrounding areas, including Krymske, Dyliivka, Shcherbynivka, and Leonidivka. Russian forces are reportedly using small group tactics supported by mortars and FPV drones. While Russian sources claimed advances northwest of Toretsk and suggested they were exploiting Ukrainian manpower shortages, these claims remain unconfirmed.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces advanced in southwestern Zvirove and conducted a platoon-sized mechanized assault near Yelyzavetivka. They continued attacks across multiple areas around Pokrovsk, including Myrolyubivka, Baranivka, Lysivka, Novyi Trud, Shevchenko, Zelene, Udachne, Kotlyne, and Uspenivka. Ukrainian counterattacks reportedly prevented Russian forces from fully capturing Uspenivka. Russian forces are reportedly using drones with fiber optic cables to counter Ukrainian electronic warfare. While Russian sources claimed additional advances near Kotlyne and Novoserhiivka, these remain unconfirmed.
On December 20, 2024, Ukrainian forces destroyed mine shaft No. 3 near Pishchane, Donetsk Oblast, to prevent Russian troops from using it to outflank Ukrainian positions near Pokrovsk. The mine, which produced essential coking coal for Ukraine’s steel industry, was abandoned after Russian forces advanced to within a mile of the facility. Metinvest, Ukraine’s largest steel producer, has suspended operations at the Pokrovsk coking coal mine due to security risks. The loss of this facility could significantly impact Ukraine’s steel production, potentially reducing annual output from a projected 7.5 million tons to 2-3 million tons in 2025.
Kurakhove Region
Russian forces made small advances southwest of Kurakhove, particularly near Rozlyv. They are attacking several settlements including Ulakly, Dachne, Andriivka, Kostiantynopil, Zelenivka, Yantarne, Petropavlivka, and Stari Terny. The Russian Ministry of Defense reports striking a bridge near Kostiantynopil.
Velyka Novosilka
Russian forces made small advances in the Velyka Novosilka area, entering the town of Vremivka and advancing along Shyroka and Heroia streets. Russian forces are also attacking several nearby settlements including Novyi Komar and Neskuchne, as well as Velyka Novosilka itself. While some Russian sources claim additional advances in central Vremivka and near Velyka Novosilka, these claims remain unconfirmed.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces attacked several settlements in western Zaporizhia Oblast targeting Shcherbaky, Novoandriivka, Novodanylivka, and Mala Tokmachka. Despite these offensive operations, they failed to make any confirmed advances.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces attacked in the Dnipro direction but failed to make any confirmed advances.
Ukraine News
Russia launched 55 drones and over 40 missiles in attacks against Ukraine from multiple locations, with the missile strikes specifically targeting energy infrastructure including gas facilities such as the Oparske underground storage facility in Drohobych and another in Stryi, both in the Lviv region, which Moscow claimed was retaliation for Ukraine’s alleged attempt to attack the TurkStream pipeline’s compressor station in Russia’s Krasnodar region on January 13. Ukrainian forces intercepted 34 drones across eleven regions and disrupted 18 decoy drones through electronic warfare, though some drones struck a farm in Chernihiv Oblast, and debris from downed drones damaged homes in Kharkiv, Poltava, and five districts of Kyiv, with one drone reported near the Mariinskyi Palace in Kyiv during British Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s visit to meet President Zelensky. While the missile attacks damaged facilities in Drohobych and Stryi districts, Naftogaz reported their gas facilities remain operational, and this attack followed Ukraine’s largest aerial strike on Russian military and energy facilities behind front lines the previous day.
Russia’s Ministry of Defense claimed their large-scale drone and missile strikes against Ukraine on January 14-15 were retaliation for Ukrainian ATACMS and Storm Shadow strikes on Russian targets, including an alleged attack on the Russkaya compressor station. However, analysts assess these Russian strikes are likely part of an ongoing strategy to damage Ukraine’s energy infrastructure, reduce its military production capacity, and weaken civilian morale.
Slovak Prime Minister Robert Fico announced that he may meet with Ukrainian President Zelensky in the coming days, following Ukraine’s decision to end Russian gas transit through its territory. While Zelensky invited Fico to Kyiv, the Slovak leader, who along with Hungary’s Viktor Orban maintains friendly ties with Russia, has declined to visit the capital. The meeting discussion comes amid tensions over Ukraine’s January 1 termination of Russian gas transit agreements, a decision that affects European countries still dependent on Russian energy, including Slovakia and Hungary.
The International Register of Damage for Ukraine has begun accepting compensation claims from families who lost relatives during Russia’s invasion. The program, based in The Hague and established under the Council of Europe, was briefly delayed by a December 2024 cyberattack on Ukrainian state registers. Claims can be filed for over 40 types of damages, including deaths, property loss, and environmental destruction. The World Bank estimates Ukraine’s reconstruction costs at $486 billion, while $300 billion in Russian Central Bank assets remain frozen by Western nations until Moscow pays reparations.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 4 INJURIES: 28
Russian forces attacked 36 settlements across Kherson Oblast, including the city of Kherson, killing three people and wounding 10 others.
Russian forces attacked Nikopol in Ukraine’s Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, killing a 54-year-old woman and injuring a 45-year-old man. The strike damaged approximately 30 homes, five apartment buildings, several businesses, and vehicles.
Russian attacks in Donetsk Oblast injured 15 people across multiple settlements including Kramatorsk, Kostiantynopil, Oleksiyevo-Druzhkivka, Stinky, and Chernihivka.
A Russian drone strike on Kupiansk in Kharkiv Oblast wounded a 73-year-old man.
Russian drone strikes on Kyiv Oblast resulted in falling debris that injured a 12-year-old boy and sparked a 200-square-meter fire at a local café. While air defenses intercepted the drones, debris damaged nearby buildings. The injured child is receiving hospital treatment, and no other casualties were reported.
Ukraine’s Allies
UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer and Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky signed a historic “Centennial Partnership Agreement” in Kyiv, establishing a 100-year partnership between the two nations. The comprehensive agreement includes British support for Ukraine’s potential NATO membership, annual military aid, enhanced maritime security cooperation in the Baltic, Black, and Azov Seas, and broad collaboration in defense, economic trade, energy, climate, and justice. During the signing ceremony at Kyiv’s Mariinsky Palace, a Russian drone was detected flying overhead, with air defense systems engaging the drone and debris falling in five districts of Kyiv, though no casualties were reported.
As part of the agreement, the UK announced new military aid including 150 artillery barrels, a Danish-funded mobile air defense system, expanded training initiatives for Ukrainian forces, and will release £1.5 billion ($1.8 billion) of a G7 loan program to be repaid using frozen Russian assets, all part of the UK’s £3 billion ($3.6 billion) commitment for lethal aid. During their meeting, Starmer and Zelensky discussed potential peacekeeping operations, with Starmer confirming talks with French President Macron about deploying British and French troops to monitor a potential ceasefire, emphasizing that Russian aggression would have long-term implications beyond Ukraine’s borders. The leaders also honored fallen defenders at Kyiv’s Mykhailivska Square, with Starmer emphasizing that the partnership demonstrates Putin’s failure to isolate Ukraine from its allies.
Italian Defense Minister Guido Crosetto met with President Volodymyr Zelensky in Kyiv to discuss military aid and security cooperation. During the meeting, they addressed air defense systems, military training, and joint defense production, particularly drones. Crosetto announced plans for Italy’s 11th military aid package, emphasizing increased support at this critical moment.
The Netherlands is providing Ukraine with new aid worth 27 million euros, announced Dutch Foreign Minister Kaspar Veldkamp during his Kyiv visit. The package splits into 7 million euros for NATO-coordinated non-lethal support and 20 million euros for energy infrastructure.
The U.S. State Department prefers broad sanctions over designating Russia as a state sponsor of terrorism, spokesman Matthew Miller stated. The latest U.S. sanctions, announced January 15, target over 150 entities and individuals linked to Russia’s defense industry and those helping Russia evade sanctions. Miller noted that current sanctions have successfully disrupted Russian oil shipments, while arguing that a terrorism designation could hamper humanitarian aid efforts in the region.
In his farewell speech, President Biden highlighted his administration’s support for Ukraine, noting that under his leadership the U.S. provided $65.9 billion in military assistance since Russia’s 2022 invasion. While Biden’s administration was Ukraine’s largest donor, it faced criticism for hesitancy in approving certain military capabilities. The text discusses concerns about future U.S. support under new leadership, noting ongoing challenges for both Ukraine and Russia, including Ukraine’s manpower shortages and Russia’s economic struggles.
Russia News
Russian air defense officer Igor Pashkov was sentenced to 2 years and 10 months in prison for accidentally shooting down a Russian Mi-8 helicopter in occupied Crimea. The incident occurred on December 18, 2023, when Pashkov mistook the helicopter for a drone and fired from a TOR-M2DT anti-aircraft system, causing the aircraft to crash into the Black Sea with its crew. After admitting guilt in May 2024, his original three-year sentence was reduced, and he is now barred from holding administrative positions for one year.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1670 815820 |
Tanks +12 9803 |
Artillery +4 22019 |
Arm. Veh. +13 20381 |
Aircraft 369 |
Heli 331 |
Ships 28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
A former Russian military instructor reported that Russian forces are facing severe infantry shortages and high casualties. The shortage stems from heavy losses in 2022 and delayed mobilization efforts. Despite regaining initiative in late 2023, Russian forces lack sufficient reinforcements in 2024. The source blamed poor combat planning, inadequate communication, limited reconnaissance, and command incompetence for the high casualty rates. Units are not being rotated out for rest and reinforcement, weakening experienced combat groups.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
