Summary of the Day:
As diplomacy and internal politics intertwined with battlefield developments, Russia pursued a multi-faceted strategy in its ongoing conflict with Ukraine. In Saudi Arabia, Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov engaged in strategic dialogue, seeking to advance Russia’s geopolitical vision and influence international peace efforts.
On the home front, the Kremlin capitalized on recent regional elections, integrating war veterans into government roles to shore up domestic support for the conflict. This move aimed to appease servicemembers while cultivating a cadre of loyal local officials.
The situation on the ground remained fluid. Russian forces made advances along several fronts, including the Kupyansk-Svatove line and near Donetsk City, while also regaining lost positions in Kursk Oblast. Ukrainian forces, for their part, managed to reclaim some ground near Siversk. Amid these territorial shifts, Ukrainian officials raised alarming concerns about Russia’s alleged increased use of chemical weapons, adding a grave dimension to the ongoing hostilities.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Picture of the Day:
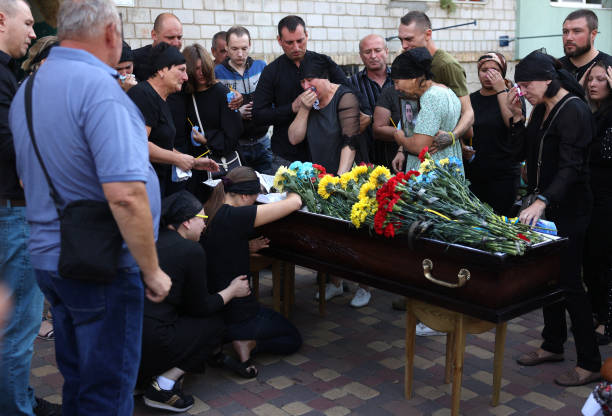

 Relatives and friend attend the funeral ceremony of Oleksandr Bezsmertny in Bucha, on Sept. 9, 2024. Oleksandr Bezsmertny was seriously wounded during a strike on the Ukrainian military academy in Poltava on September 3, 2024 and died of his wounds. (Anatolii Stepanov / AFP / via Getty Images)
Relatives and friend attend the funeral ceremony of Oleksandr Bezsmertny in Bucha, on Sept. 9, 2024. Oleksandr Bezsmertny was seriously wounded during a strike on the Ukrainian military academy in Poltava on September 3, 2024 and died of his wounds. (Anatolii Stepanov / AFP / via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov attended a Russia-Gulf Cooperation Council meeting in Saudi Arabia, discussing strengthened cooperation, trade, and investments with GCC and Saudi officials. Lavrov invited Saudi Crown Prince Mohammad bin Salman to the upcoming BRICS summit in Russia, likely aiming to promote Russia’s proposed “Eurasian security architecture” and reshape the global order.
Meanwhile, a series of drone-related incidents unfolded across Eastern Europe. Latvia experienced its first confirmed Russian drone crash when an explosive-laden Shahed drone veered off course and crashed in Gaigalava parish. Latvian military chief Lieutenant General Leonids Kalnins reported that Latvia was not the intended target. In response, Latvia summoned the Russian Embassy’s charge d’affaires to protest the airspace violation.
Similar events occurred in Romania, where the Defense Ministry confirmed finding Russian drone fragments near Periprava village and is investigating a possible second impact site near Caraorman. This followed a Russian drone briefly entering Romanian airspace during an attack on Ukraine, prompting alerts and the deployment of F-16 jets.
These incidents have raised concerns among NATO members about airspace violations, with experts suggesting Russia may be testing NATO countries’ air defense systems. While NATO has condemned these violations, no direct action has been taken to intercept Russian projectiles to avoid being seen as directly involved in the Ukraine conflict.
In a related development, Poland announced that its security forces dismantled a group of saboteurs working for Russian and Belarusian intelligence services. Digital Affairs Minister Krzysztof Gawkowski revealed the group’s objectives included information extortion, blackmail, and cyberwarfare. This coincided with NATO countries accusing a Russian military intelligence unit of conducting cyberattacks against Ukraine and European nations. Poland has seen a significant increase in cyberattacks, with over 400,000 reported in the first half of 2024, compared to 370,000 in all of 2023.
Path to Peace
Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov engaged in diplomatic discussions with his Brazilian and Indian counterparts during a Gulf Cooperation Council meeting in Saudi Arabia. The talks centered on the ongoing war in Ukraine, revealing a complex web of international perspectives and mediation efforts.
Brazil and China have been promoting a peace plan that appears to favor Russian interests, indicating their stance in the conflict. India, while supporting peace, emphasized the importance of basing any resolution on international law, showcasing a more neutral position.
Lavrov’s dismissal of Ukraine’s Peace Formula as an “ultimatum” highlights Russia’s reluctance to engage in what it perceives as unfavorable negotiation terms. This stance suggests that Russia is attempting to shape international mediation efforts to its advantage, potentially complicating the path to genuine negotiations.
Despite Russia’s apparent unwillingness to participate in Ukraine-led peace initiatives, Ukraine continues to extend invitations for Russian involvement in an upcoming peace summit. This move by Ukraine demonstrates its ongoing efforts to seek a diplomatic resolution to the conflict, even in the face of Russian resistance.
The divergent approaches and viewpoints expressed during these diplomatic exchanges underscore the challenges in finding a universally acceptable solution to the Ukraine conflict. As various nations propose and support different peace plans, the international community remains divided on the best path forward, with Russia seemingly intent on influencing the narrative and terms of any potential negotiations.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Russian forces are reportedly escalating their use of chemical weapons in Ukraine, with 447 instances recorded in August 2024 alone and a total of 4,035 cases between February 2023 and August 2024. These attacks, utilizing K-51 and RG-VO gas grenades to deliver banned chemical agents, violate the Chemical Weapons Convention that Russia has signed. Both Ukrainian officials and a Russian military unit have acknowledged this growing trend in combat.
In response to the ongoing conflict, Ukraine’s Defense Intelligence chief Kyrylo Budanov announced a significant advancement in their military capabilities. Ukrainian-made drones can now reach targets up to 1,800 kilometers away, potentially allowing strikes deep into Russian territory, including cities like Yekaterinburg and Chelyabinsk, as well as Russian airbases in Syria. Despite this progress, Ukraine continues to seek Western long-range weapons such as ATACMS and Storm Shadow missiles for their superior speed and accuracy in targeting enemy airfields.
The artillery situation on the battlefield has shown some improvement for Ukraine.
Commander-in-Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi reports that Russia is currently firing shells at a 2:1 to 2.5:1 ratio compared to Ukraine, a significant reduction from earlier in the year when the ratio was 10:1 in Russia’s favor. To counter Russia’s numerical advantage in weapons and personnel, Ukraine is focusing on high-tech weapons like drones.
While U.S. weapons aid has helped narrow the gap, delays in deliveries continue to pose challenges, impacting the combat capabilities of some Ukrainian units. The West’s reluctance to provide certain long-range weapons stems from concerns about potentially escalating the conflict, leaving Ukraine to balance between developing its own capabilities and seeking continued international support.
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Russian forces have launched a series of counteroffensives in Kursk Oblast, reclaiming several positions in response to ongoing Ukrainian operations. The Russians successfully regained ground west of Ulanok, near Sudzha, marking a significant shift in the local balance of power.
Ukrainian attacks have been reported across various locations in the region, including areas near Korenevo and Sudzha. However, Russian sources claim to have made substantial progress, reportedly retaking the settlements of Komarovka and Vishnevka. These advances, if confirmed, would represent a notable setback for Ukrainian forces in the area.
The Russian military appears to be deploying a diverse array of units to bolster their position in Kursk Oblast. Reports indicate the presence of naval infantry, airborne troops, and special forces operating in the region. This mix of specialized units suggests a concerted effort by Russian command to solidify their hold on contested areas and potentially prepare for further offensive actions.
As the situation continues to evolve, the recapture of these positions by Russian forces could have strategic implications for the broader conflict, potentially altering the dynamics of Ukrainian operations in the region. The coming days will likely see continued intense military activity as both sides vie for control in this critical sector of the front.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Fighting continues to rage north and northeast of Kharkiv City, with both Russian and Ukrainian forces engaged in a series of attacks and counterattacks. While no confirmed changes to the frontline have been reported, the area remains a hotspot of military activity.
Russian sources claim to have successfully repelled Ukrainian counterattacks near Hlyboke and Vovchansk, while simultaneously launching their own offensives against Hlyboke, Vovchansk, Starytsya, and Tykhe. Ukrainian intelligence suggests that Russian units are actively operating in the region, with efforts underway to reinforce their positions, particularly near Hlyboke, possibly in preparation for future offensives.
In a strategic move, Russian air forces reportedly destroyed a bridge over the Vovcha River near Okhrimivka and Mala Vovcha in Kharkiv Oblast, northeast of Vovchansk. This action could potentially impact supply lines and troop movements in the area.
A significant development in aerial warfare occurred when Ukrainian forces from the 3rd Tank Brigade successfully shot down a Russian Orlan reconnaissance drone at a record altitude of 3,620 meters in Kharkiv Oblast. The Orlan, known for its long-range capabilities and often used to guide artillery attacks, was neutralized through a coordinated effort between the brigade and border guard units. While the specific method of downing the drone wasn’t disclosed, evidence suggests another drone may have been used in a ramming maneuver.
This incident underscores Ukraine’s growing proficiency in countering Russian aerial reconnaissance and highlights their increasing use of innovative drone tactics. As the conflict continues to evolve, both sides are adapting their strategies, with drone warfare playing an increasingly crucial role in reconnaissance and offensive operations.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces have made notable advances along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line. They’ve gained ground near Makiivka and Pishchane, while also claiming progress in the vicinity of Synkivka and Nevske.
The conflict continues to unfold across multiple locations, with active engagements reported in Synkivka, Petropavlivka, Hlushkivka, Stelmakhivka, Lozova, Myasozharivka, Cherneshchyna, Torske, Dibrova, and the Serebryanske forest. These widespread clashes indicate the intensity and scope of the ongoing military operations in the region.
In the Kupyansk area, Russian tank and motorized rifle units are actively participating in the offensive, suggesting a concerted effort to strengthen their position and potentially push for further territorial gains. The deployment of these units underscores the significance of this sector in the current phase of the conflict.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Ukrainian and Russian forces have been engaged in a dynamic exchange of territory in the vicinity of Siversk. Ukrainian troops successfully reclaimed positions in the eastern part of Ivano-Darivka. Simultaneously, Russian forces made a slight advance to the northwest of Bilohorivka.
The Russian military continues to launch attacks on multiple settlements surrounding Siversk. These offensives have targeted Hryhorivka, Verkhnokamyanske, Spirne, Zvanivka, and Pereizne. Among these operations, a notable mechanized assault was reportedly carried out near Zvanivka.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces made progress near Chasiv Yar, pushing forward in western Kalynivka. The offensive didn’t stop there, as attacks persisted in multiple locations surrounding Chasiv Yar. These included Mayske, Novyi, Zhovtnevyi, Predtechyne, Bila Hora, Klishchiivka, and Andriivka. Reports also indicated the presence of Russian snipers in the vicinity of Chasiv Yar, adding another layer of complexity to the ongoing military operations in the area.
Toretsk
Russian forces maintained their offensive operations in the vicinity of Toretsk. Their attacks focused on several key areas: Druzhba, Pivnichne, Zalizne, Niu York, and Nelipivka. Some Russian sources reported making progress in Toretsk itself and to the west of Niu York. However, these claims of advancement remain unverified at this time.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces made a significant advance near Pokrovsk, successfully capturing Mykhailivka. Their offensive continued with attacks on multiple settlements, including Zelene Pole, Vozdvyzhenka, Hrodivka, Novohrodivka, Marynivka, Dolynivka, and Halytsynivka. Russian drone operators were reported to be active in the area, adding to the complexity of the military operations.
Claims of Russian advances near Hirnyk, Ukrainsk, Memryk, and Selydove were made but remained unconfirmed. More notably, Russian forces claimed to have captured Novohrodivka in Donetsk Oblast, a town approximately 20 kilometers from Pokrovsk, which serves as a crucial Ukrainian logistics hub. This claim was met with conflicting information from the Ukrainian side, which reported ongoing battles in the area.
A Ukrainian officer mentioned a withdrawal from Novohrodivka, citing its “unfavorable geographical location.” However, this withdrawal has not been officially confirmed by the Ukrainian General Staff. Russian sources also claimed to have taken four other nearby settlements.
In contrast to these reported Russian advances, Ukraine’s Commander-in-Chief Syrskyi stated that Russia’s progress in the Pokrovsk direction had been halted in recent days. He attributed this to Ukraine’s incursion into Russia’s Kursk Oblast, which he said was intended to divert Russian forces.
The region around Pokrovsk has been a hotspot of intense fighting for months, with both sides vying for control of this strategically important area.
West of Donetsk City
Russian forces reportedly made advances to the west of Donetsk City. Claims emerged of their capture of Krasnohorivka, with suggestions that they had pushed even further beyond this point. However, these reports of territorial gains have not been independently verified. Meanwhile, Russian military operations persisted in the area, with ongoing attacks reported near both Krasnohorivka and Heorhiivka.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces made significant progress southwest of Donetsk City. They successfully captured the Pivdennodonbaska Mine No. 1, located northeast of Vuhledar, and continued their advance southwest of Prechystivka. Reports also circulated about Russian forces seizing Vodyane, but these claims remain unverified. The offensive in this region didn’t stop there, as attacks persisted near several key locations including Vodyane, Vuhledar, Shakhtarske, and Zolota Nyva.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
In the area along the border between Donetsk and Zaporizhia Oblasts, a notable lull in ground combat was observed. Both Russian and Ukrainian sources reported no significant ground attacks in this region.
Zaporizhia Line
In western Zaporizhia Oblast, Russian and Ukrainian forces remained locked in ongoing battles. The frontlines held steady, with no confirmed changes in territorial control. The fighting was particularly intense near two key locations: Robotyne and Mala Tokmachka, where both sides continued to engage in military operations.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
In the Dnipro River Delta, Russian forces reportedly made progress on the islands scattered throughout the area. Claims emerged of their advance to the southern part of Kruhlyk Island. Meanwhile, along the east bank of Kherson Oblast, the conflict persisted as both sides continued to engage in ongoing military operations.
Ukraine News
Russia launched a series of attacks against Ukraine using cruise missiles and drones. Ukraine’s Air Force reported intercepting two missiles and six drones, while electronic warfare measures thwarted three other projectiles. The attacks originated from Kursk Oblast and occupied Donetsk Oblast.
UN Human Rights Commissioner Volker Turk expressed concern about Russian attacks on Ukrainian energy facilities, highlighting ongoing strikes on civilian targets and energy infrastructure causing nationwide blackouts.
Ukraine’s new Foreign Minister, Andrii Sybiha, recalled the Ukrainian charge d’affaires, Mykhailo Kharyshyn, from Georgia amid worsening relations between Kyiv and Tbilisi. This decision is part of broader personnel changes in Ukraine’s diplomatic corps, including a motion to dismiss Deputy Foreign Minister Iryna Borovets.
Yaroslav Oliinyk, an advisor to Ukraine’s strategic industries minister and soldier, died in a car accident along with his wife Nina. Known as “Loki,” Oliinyk had served as a drone operator in the Ukrainian military and later joined the ministry overseeing drone manufacturer cooperation.
A recent poll revealed that 54% of Ukrainians oppose a full ban on Telegram but support certain restrictions. While many view Russian disinformation on social media as a serious threat, Telegram remains popular for news consumption. Ukraine’s military intelligence chief has called Telegram a threat to national security, and lawmakers are working on legislation to regulate information-disseminating platforms.
David Knowles, founder and co-host of the Telegraph’s “Ukraine: The Latest” podcast, died in Gibraltar. Knowles was known for his dedication to reporting on Ukraine and his podcast had become a popular weekday program.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 7 INJURIES: 32
Russian forces launched an artillery attack on Nikopol in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, resulting in the death of a 16-year-old girl and injuries to three others. The assault, involving about a dozen shells, caused damage to houses in the area. Among the injured were two elderly men and a woman. Nikopol, situated near the Russian-occupied Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant, has been a frequent target of such attacks.
This incident was part of a larger wave of Russian aggression across Ukraine, which claimed seven lives and left at least 32 people injured in the past day.
August 2024 saw a significant spike in civilian casualties in Ukraine, with the U.N. human rights monitoring mission reporting 184 deaths and 856 injuries. This toll represents the second-highest monthly casualty count for the year, with 91% of these casualties occurring in Ukraine-controlled territories.
Notable attacks during August included a devastating missile strike on a supermarket in Kostiantynivka, resulting in 14 deaths and 44 injuries. A large-scale assault on August 26 impacted 15 oblasts and damaged 25 energy facilities, including the Kyiv Hydroelectric Power Plant. Kharkiv also suffered heavy bombardment, leading to 7 fatalities and over 90 injuries.
Since the onset of Russia’s full-scale invasion in February 2022, the U.N. has documented at least 11,743 civilian deaths and 24,614 injuries. However, these figures are believed to be conservative estimates, as ongoing occupation and limited access to conflict zones hinder accurate reporting.
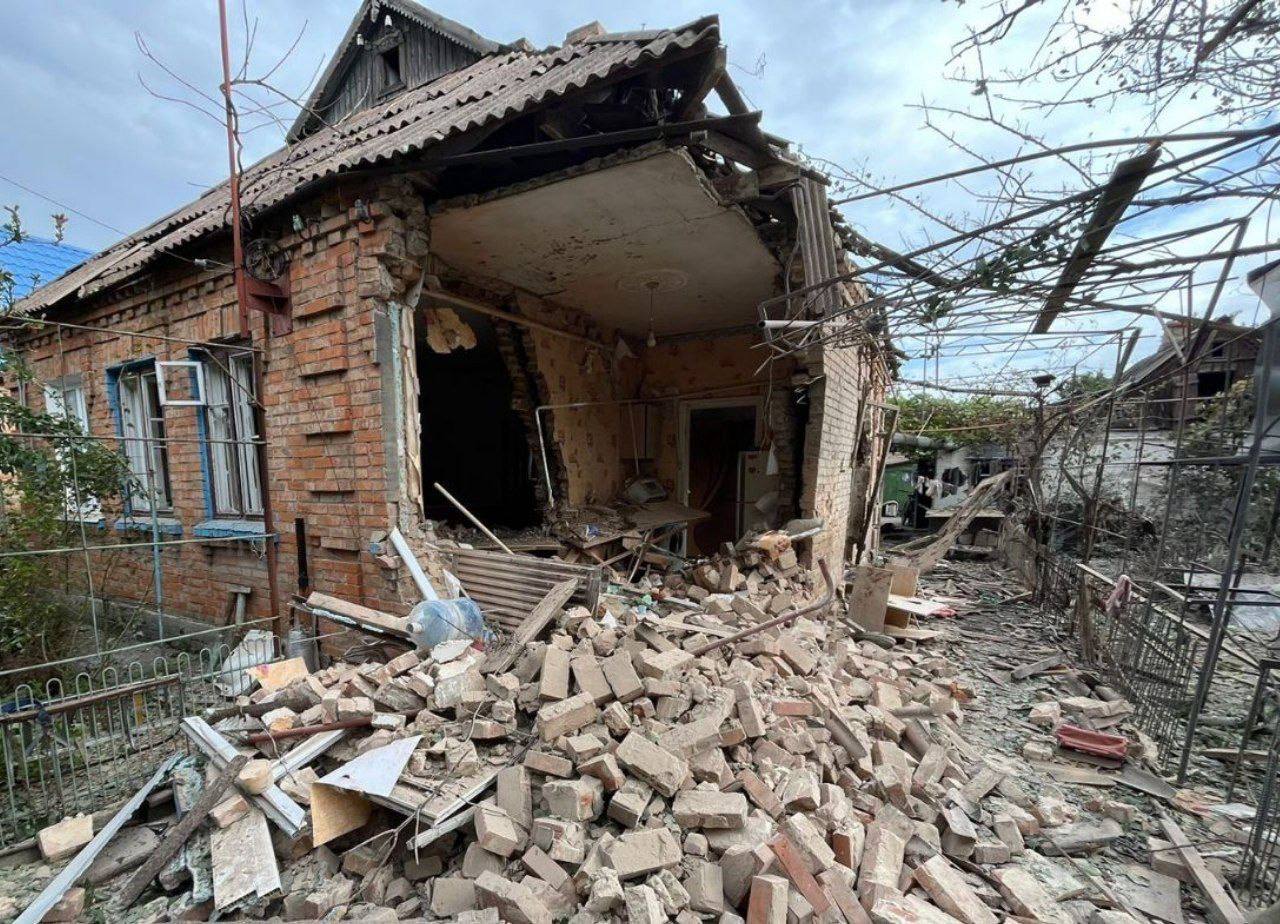 The aftermath of a Russian attack on the town of Nikopol in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. (Serhii Lysak/Telegram)
The aftermath of a Russian attack on the town of Nikopol in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. (Serhii Lysak/Telegram)
Ukraine’s Allies
In a significant show of support, Sweden announced its 17th military aid package for Ukraine, valued at $443 million. The comprehensive package includes combat boats, anti-tank weapons, ammunition, and spare parts for Gripen jets. While Sweden isn’t currently transferring Gripen jets to Ukraine, it’s investing $222 million in parts, potentially preserving some jets for future donation. The aid also encompasses ammunition for Combat Vehicle 90s, camouflage equipment, air defense systems, and marine equipment to counter Russian threats in the Black Sea.
This latest contribution follows Sweden’s largest package announced in May, worth $1.3 billion, and aligns with their plans to allocate $7 billion in military support from 2024 to 2026.
Meanwhile, the European Union is preparing to make adjustments to its sanctions list. Former Russian F1 driver Nikita Mazepin and Violetta Prigozhina, mother of the late Wagner Group founder, are set to be removed from the EU’s sanctions list this week. This decision comes as part of the EU’s broader extension of sanctions against 2,300 entities and individuals linked to Russia’s war in Ukraine.
Hungary, known for its opposition to sanctions on Russia, reportedly advocated for these removals. The EU’s legal service considers both cases “weak,” with Mazepin having previously won a case to lift sanctions. Prigozhina had remained sanctioned even after her son’s death in August 2023. This development follows the EU’s March decision to lift sanctions against Arkady Volozh, co-founder of Yandex.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
In a brazen display of disregard for international law, Russia conducted sham elections in occupied Crimea, drawing swift condemnation from the European Union. The EU unequivocally declared the results “null and void,” emphasizing that these elections violate Ukraine’s sovereignty and will not be recognized by the international community.
The illegitimate polls, held over a three-day period, were marred by widespread irregularities. Independent watchdog Golos reported a staggering 651 potential violations across Russia during the electoral process, casting further doubt on the legitimacy of the proceedings.
This latest affront to democratic principles follows a pattern of illegal electoral activities in occupied Ukrainian territories. Just months earlier, Russia organized a presidential election that secured Vladimir Putin another six years in power, similarly conducted in violation of international norms in areas under Russian occupation.
The roots of this crisis trace back to 2014 when Russia illegally annexed the Crimean peninsula following a sham referendum. Today’s events serve as a stark reminder of Russia’s ongoing defiance of international law and its continued attempts to legitimize its unlawful occupation of Ukrainian territory.
Russia News
In a series of significant political developments, regional elections across Russia have revealed the Kremlin’s strategic maneuvering and its efforts to maintain control amid ongoing challenges.
In the Altai Republic, Andrei Turchak, former United Russia Secretary, secured a five-year term as leader. Despite a previous demotion, possibly due to perceived disloyalty and failure to integrate veterans into government, Turchak’s victory was celebrated by Kremlin-affiliated bloggers. This election, part of the “Time of Heroes” program, suggests a broader effort to rebrand United Russia as a pro-veteran party and further militarize Russian society and government.
Meanwhile, in Kursk Oblast, Acting Governor Alexei Smirnov won with over 65% of the vote. The Kremlin’s decision to proceed with elections here, despite recent Ukrainian incursions, appears to be an attempt to portray the situation as a “new normal” and avoid creating panic. Officials claimed high voter turnout, supporting President Putin’s narrative that the incursion has unified rather than divided Russian society.
On the national level, President Putin expanded Defense Minister Belousov’s authority, allowing him to grant access to state secrets within the Defense Ministry, with FSB approval. This follows a May 2024 decree requiring those with access to state secrets to notify the FSB and Foreign Intelligence Service before traveling abroad, indicating a tightening of control over sensitive information.
In international affairs, an unexpected twist occurred when Russian President Putin endorsed Kamala Harris for the U.S. presidency, prompting a strong reaction from Donald Trump. Trump expressed offense at the endorsement, claiming he was tougher on Russia than any other president and that Russia wouldn’t have invaded Ukraine under his leadership. This development has raised concerns in Ukraine about potential pressure for concessions in the event of Trump’s reelection.
These events collectively paint a picture of a Russian government working to maintain control domestically while navigating complex international relations, all against the backdrop of ongoing conflict with Ukraine and tensions with the West.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russia’s ruling United Russia party has successfully integrated 308 war veterans into government positions during recent regional elections. This initiative, part of President Putin’s “Time of Heroes” program, aims to reward veterans, boost war support, and create a network of Kremlin-aligned local officials. The program also serves to incentivize military service by presenting it as a pathway to a government career.
The country’s military recruitment efforts have seen a significant uptick, with 166,200 people enlisted for service in Ukraine during the first half of 2024. This surge, averaging 27,700 recruits per month, is likely driven by new federal-level incentives. Russia is also actively recruiting Ukrainians and FSB personnel for service in occupied Crimea, offering land plots to volunteers and bolstering internal security in the region.
In a parallel move to militarize its youth, Russia has introduced new school programs. A “Fundamentals of Security and Defense of Motherland” class has been added to the curriculum, with teachers set to undergo military training with the 76th Airborne Division in Pskov. War veterans are expected to participate in teaching these classes, despite the division’s controversial involvement in alleged war crimes in Bucha, Ukraine, in March 2022.
On the home front, Russian fitness clubs are seeking government funding to offer free rehabilitation services for active and mobilized servicemen and their families. The Russian National Fitness Community, representing over 3,000 clubs, has proposed this idea to the Ministry of Defense, with Deputy Defense Minister Dmitry Chernyshenko instructing the Ministry of Sports to consider the program.
In technological developments, the Synergy Design Bureau has announced that its new plastic reconnaissance drone, “Asya,” will soon be tested in Ukraine. The drone is reportedly radar-invisible, 3D-printable, and cost-effective, capable of flying for an hour, covering up to 30 kilometers, and carrying a one-kilogram payload.
These multifaceted efforts reflect Russia’s comprehensive strategy to militarize its society, from youth education to veteran integration, while simultaneously advancing its technological capabilities in the ongoing conflict with Ukraine.
Russia’s Allies
In a series of significant military developments, China and Russia are strengthening their strategic partnership through joint naval and air exercises. The Chinese Navy announced its participation in the “Northern United-2024” drills, set to take place in the Sea of Japan and Sea of Okhotsk. This collaboration extends to China joining Russia’s Ocean-2024 drills and the two nations conducting their fifth joint maritime cruise in the Pacific Ocean. These exercises aim to enhance strategic cooperation and joint responses to security threats, signaling a deepening military alliance between the two powers.
Simultaneously, Russia is fortifying its ties with Belarus. The two countries plan to adopt a new Union State security concept and treaty in 2025, focusing on joint resistance against perceived threats from the US, NATO, and EU. Belarus has also positioned 4,500 troops near its border with Ukraine, though officials assert these forces do not pose a threat.
On the international stage, Iran has denied reports of delivering ballistic missiles to Russia, dismissing them as “psychological warfare.” However, conflicting reports suggest that 200 Iranian Fath-360 missiles may have arrived at a Caspian Sea port, potentially for use in frontline targets in Ukraine. The U.S. has not officially confirmed this transfer, adding to the complexity of the situation.
These events unfold against a backdrop of rising tensions with the West, particularly due to Russia’s ongoing invasion of Ukraine. NATO has identified China as a “decisive enabler” of Russia’s actions and a threat to alliance security. China’s role as a crucial economic partner for Russia, helping it navigate Western sanctions, further complicates the geopolitical landscape.
The convergence of these military collaborations, strategic alliances, and alleged weapons transfers paints a picture of shifting global power dynamics, with Russia and its allies seemingly consolidating their positions in opposition to Western interests.
Controlling the Narrative and Russian Propaganda
In a concerted effort to shape public perception, Russian occupation authorities in Donetsk are ramping up their propaganda machine, targeting the youth in particular. Through organized events in Donetsk City, they are propagating false narratives about Ukraine’s actions in 2014, aiming to justify Russia’s current war and indoctrinate Ukrainian children. This campaign extends to the digital realm, with Russian authorities promoting Rutube, a Russian video platform, in occupied Crimea to further disseminate their messaging online.
Meanwhile, the international cultural scene has become an unexpected battleground for competing narratives about the war. A controversial war documentary titled “Russians at War,” by Russian-Canadian filmmaker Anastasia Trofimova, has ignited fierce debate after its screening at the Venice International Film Festival. The film, which follows Russian forces in eastern Ukraine, claims to present an anti-war perspective by showcasing ordinary Russian soldiers. However, it has drawn sharp criticism from the Ukrainian government, which condemns it as Russian propaganda.
Ukraine’s authorities have called for the removal of the documentary from both the Venice and Toronto film festivals, arguing that it whitewashes Russian aggression. This situation has sparked a broader discussion about the responsibility of international cultural events in platforming content related to ongoing conflicts, and the fine line between documentary filmmaking and propaganda.
These events highlight the multifaceted nature of the information war surrounding the Russia-Ukraine conflict, playing out not only in occupied territories but also on the global stage of cultural events. The controversy underscores the ongoing struggle to control the narrative of the war, with both sides keenly aware of the power of media and cultural productions in shaping international opinion.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
