Summary of the Day:
Ukrainian forces have dealt a significant blow to Russian military capabilities with a recent strike on an ammunition facility near Toropets. The attack reportedly destroyed enough munitions to impact Russian operations for months, potentially hampering their ability to sustain offensive actions in the near future.
In Moscow, the Kremlin appears to be reassessing its nuclear threat strategy. As Western officials have become increasingly desensitized to such rhetoric, Russian leadership is exploring new ways to exert pressure on the international stage. This shift in approach comes as Russia faces mounting challenges in its conventional military capabilities.
Adding to Russia’s strategic concerns, a failed test of the Sarmat intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) at Plesetsk Cosmodrome has highlighted ongoing difficulties in the country’s missile development program. This setback raises questions about the readiness and reliability of Russia’s nuclear deterrent.
Meanwhile, Ukraine is ramping up its drone production capabilities in response to Russia’s own unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) manufacturing plans. Kyiv aims to significantly increase its drone output by 2025, recognizing the crucial role these systems play in modern warfare.
On the battlefield, Ukrainian forces have made advances near Svatove, pushing back Russian positions in the area. Conversely, Russian troops have achieved marginal gains near Toretsk, Pokrovsk, and along the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border area, though these advances have come at a high cost in personnel and equipment.
Reports from the front lines suggest that Russian soldiers in some sectors are being forced to dig trenches without proper equipment, raising concerns about troop morale and the overall state of Russian logistics. This development may indicate broader supply issues facing the Russian military as the conflict continues.
Picture of the Day:
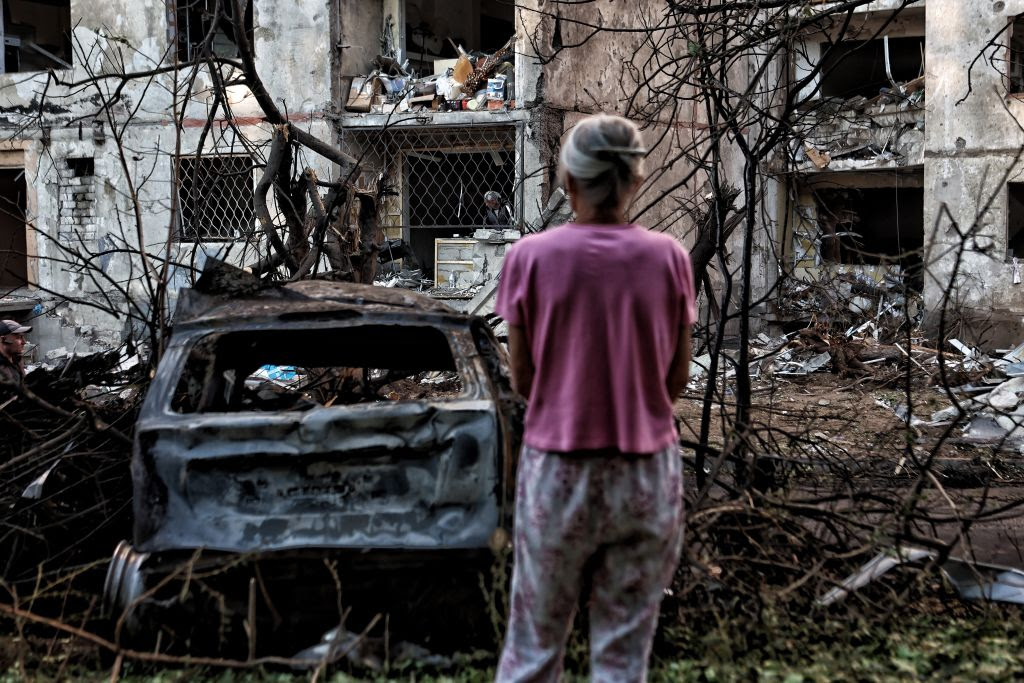 A local woman looks at a residential high-rise building in the Shevchenkivskyi district damaged by a Russian aerial bombing in Kharkiv, Ukraine. At least 21 people were injured, including two persons in acute condition. (Yan Dobronosov/Global Images Ukraine via Getty Images)
A local woman looks at a residential high-rise building in the Shevchenkivskyi district damaged by a Russian aerial bombing in Kharkiv, Ukraine. At least 21 people were injured, including two persons in acute condition. (Yan Dobronosov/Global Images Ukraine via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
The Kremlin appears to be reassessing its strategy of nuclear saber-rattling to influence Western support for Ukraine. This shift comes as Russian officials reportedly acknowledge the diminishing effectiveness of such threats on Western decision-makers. The potential recalibration of Russia’s nuclear rhetoric signals a recognition of changing global dynamics and could lead to new, potentially destabilizing approaches in its foreign policy. Reports of dissatisfaction among Russia’s “Global South” partners regarding nuclear threats highlight the delicate balance Moscow must maintain in its international relationships. This development may force Russia to adapt its diplomatic strategies, potentially altering the geopolitical landscape in regions where it seeks to maintain or expand influence.
Russia’s reported increase in intelligence operations in Mexico marks a significant escalation in its global espionage efforts. This move, attributed to the expulsion of Russian operatives from Europe, demonstrates Moscow’s adaptability in maintaining its intelligence capabilities. The expansion raises concerns about increased tensions between Russia and the United States, potential destabilization of US-Mexico relations, and broader implications for security in the Western Hemisphere. The shift in Russian intelligence focus to Mexico represents a return to Cold War-era tactics, suggesting a long-term strategic approach to challenging US interests and global influence.
These evolving strategies in both nuclear posturing and intelligence operations indicate Russia’s ongoing efforts to reshape its global influence amidst changing international dynamics. As these shifts unfold, they are likely to contribute to increased global tensions and necessitate careful diplomatic navigation by all involved parties. The development may prompt reassessments of counterintelligence strategies among Western allies and heighten vigilance in diplomatic and security circles, further complicating the already complex web of international relations.
The Path to Peace
In a recent statement, Russian Foreign Ministry Spokesperson Maria Zakharova announced that Russia will not participate in Ukraine’s upcoming peace summit or any similar events. The Russian government has dismissed Ukraine’s Peace Formula as an “ultimatum” rather than a fair proposal for negotiations.
Instead, Russia is insisting on discussing what it terms “serious” peace proposals that align with President Vladimir Putin’s demands from June 14. These demands include Ukraine surrendering control of Luhansk, Donetsk, Zaporizhia, and Kherson oblasts, including areas that Russia does not currently occupy. This stance has raised concerns that Russia may not be genuinely interested in fair peace negotiations but could be using the concept of peace talks to pressure Ukraine into making concessions through Western influence.
Meanwhile, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has criticized ideas for ending the war proposed by J.D. Vance, who is Donald Trump’s running mate in the upcoming U.S. presidential election. In a recent interview with The New Yorker, Zelensky described Vance’s suggestions as “too radical.” Vance had proposed creating a demilitarized zone between Ukraine and Russia, with Ukraine retaining sovereignty but agreeing not to join NATO. Zelensky rejected this concept, warning that it could potentially lead to global conflicts.
Vance has consistently opposed U.S. aid to Ukraine throughout the conflict. According to leaked text messages, he has even refused to take calls from Ukrainian officials.
As these developments unfold, President Zelensky has begun a visit to the United States. During this trip, he plans to share his “victory plan” with foreign leaders, seeking continued support for Ukraine’s efforts in the ongoing conflict.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
In recent developments from the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, reports have emerged of dire conditions for Russian soldiers engaged in trench-digging operations. According to Ukrainian forces, Russian commanders are ordering their troops to construct trenches without proper equipment or protection. Many of these soldiers are said to be lacking essential gear such as weapons, armor, and even uniforms. Despite the well-constructed nature of the trenches, the hazardous conditions have reportedly led to a staggering casualty rate, with only half of the soldiers surviving the task.
In a separate incident, Ukrainian forces reportedly launched a missile strike against a Russian military target in occupied Crimea on the evening of September 21. A Russian military blogger claimed that Russian air defenses, specifically the 31st Air Defense Division, intercepted the missile near Dzhankoi. However, no details were provided about the specific target or any potential damage caused by the strike.
Earlier, on September 18, Ukraine conducted a strike on a Russian munitions facility near Toropets in the Tver Oblast. The attack has reportedly had significant consequences for Russian military supplies. Estonian Defense Forces Intelligence Center Head Colonel Ants Kiviselg stated that the explosion destroyed 30,000 tons of munitions, equivalent to 750,000 artillery shells. This loss could potentially impact Russian operations for months, as it may represent two to three months of Russia’s ammunition supply. The facility was said to have stored various missiles and artillery ammunition.
The strike on the Toropets facility is expected to put pressure on Russian military logistics, potentially forcing changes in how Russia organizes and disperses its support systems. The loss of such a substantial amount of ammunition could have far-reaching effects on Russian military capabilities in the ongoing conflict.
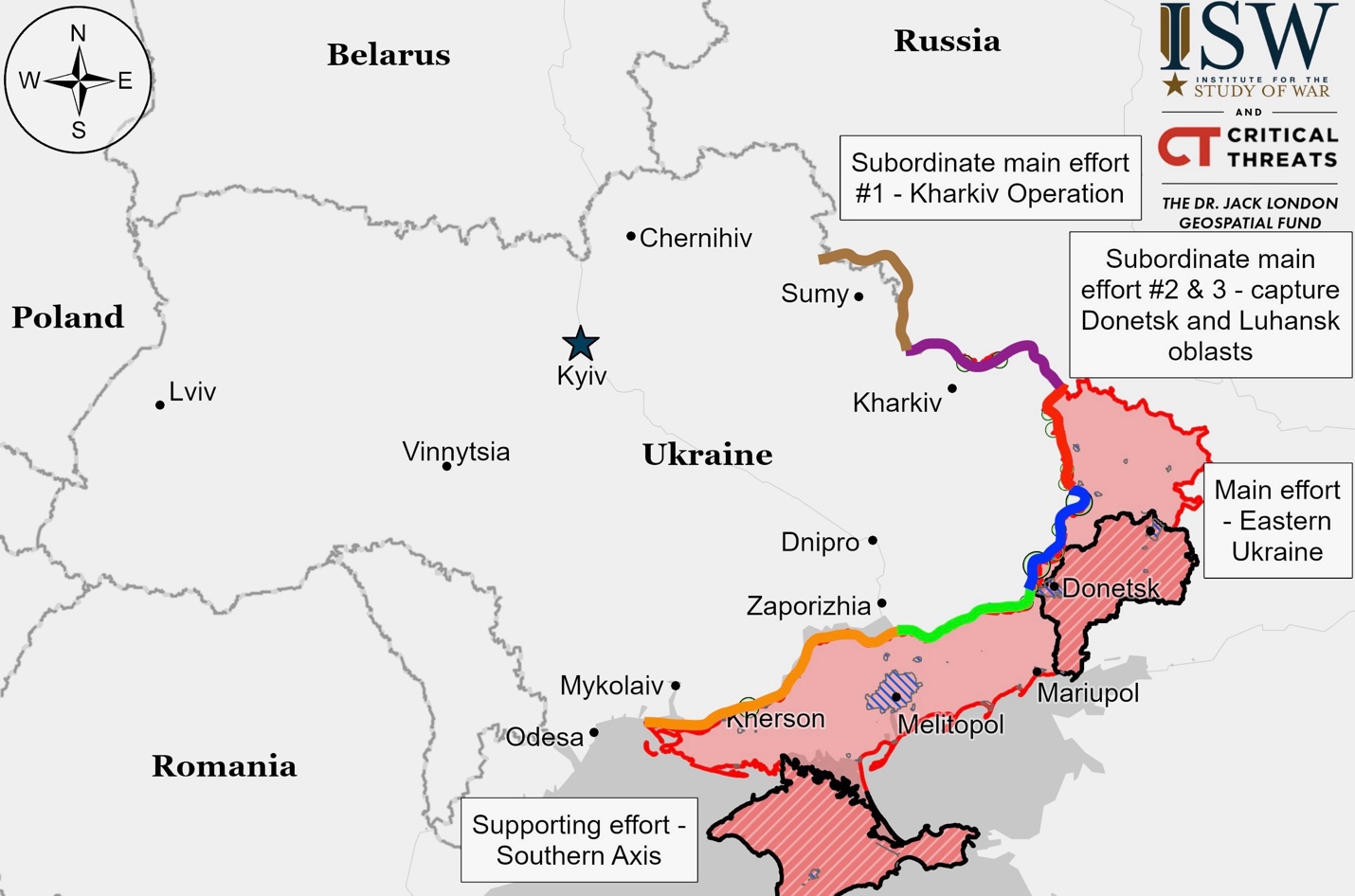
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
In recent developments along the Russia-Ukraine border, Ukrainian forces launched attacks in the Glushkovsky Raion, west of their salient in Russia’s Kursk Oblast, on September 22. The offensive targeted areas near Novy Put, Obukhovka, and Medvezhye. Simultaneously, Ukrainian troops continued their offensive operations elsewhere in the Kursk Oblast salient, including near Korenevo, Sudzha, and Plekhovo.
Russian forces responded with their own offensive operations in the area. Elements of the 83rd Airborne Brigade reportedly assaulted Ukrainian positions in the Kalinnik tract. Despite the intense military activity, neither side has made confirmed advances in these engagements.
President Volodymyr Zelensky of Ukraine provided an update on the ongoing incursion into Russia’s Kursk Oblast, stating that the operation has achieved some success. According to Zelensky, the Ukrainian offensive has managed to divert approximately 40,000 Russian troops from other fronts. The operation has resulted in the seizure of around 100 settlements and over 1,300 square kilometers of territory.
While Zelensky cautioned that it is too early to judge the full success of the operation, he emphasized that it demonstrates Ukraine’s military capabilities to its international partners. The Ukrainian president also noted that Russian counterattacks in the region have reportedly been halted.
As the situation continues to evolve, both Ukrainian and Russian forces remain engaged in active combat operations in the Kursk Oblast region, with each side attempting to gain strategic advantages along the border area.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Fighting continued north of Kharkiv City near Hlyboke and northeast near Vovchansk on September 21-22, with no confirmed frontline changes. A Ukrainian officer reported that Russian forces are adopting defensive positions in the area, deploying “Storm-Z” convict recruits and former Wagner Group personnel with minimal training. These troops are conducting small-scale infantry assaults. Ukrainian forces report occasional advances in unspecified areas, noting that Russian forces haven’t launched large-scale assaults in the Kharkiv direction for several weeks.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Ukrainian forces regained limited positions near Kyslivka, northwest of Svatove, amid ongoing Russian offensives along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line on September 21-22. Russian forces reportedly advanced east of Kruhlyakivka and claimed to have seized most of Makiivka and entered Nevske. Fighting continued in various settlements including Synkivka, Petropavlivka, Stepova Novosilka, Hlushkivka, Kotlyarivka, Stelmakhivka, Druzhelyubivka, Cherneshchyna, Hrekivka, Novosadove, Torske, Terny, and Dibrova.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces launched attacks near Vyimka, southeast of Siversk, on September 21 and 22. However, these assaults did not result in any confirmed changes to the frontline in the area.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued offensive operations near Chasiv Yar on September 22, with no confirmed frontline changes. They attacked areas including Hryhorivka, Mayske, Kalynivka, Ivanivske, Klishchiivka, Andriivka, Stupochky, and Bila Hora on September 21-22. Russian sources claimed advances west of Klishchiivka, but this remains unconfirmed.
Toretsk
Russian forces made small advances south of Toretsk on September 22. They progressed in central Niu York along Hobrusyeva and Niu-Yorkska streets. Unconfirmed claims suggest Russian forces captured Nelipivka, advanced in southern Toretsk, and seized buildings in Pivnichne. Attacks continued near Dachne, in Toretsk, and towards Shcherbynivka on September 21-22.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces made small advances east and southeast of Pokrovsk on September 22. They progressed north of Novooleksandrivka, into southern Krutyi Yar, and west of Mykhailivka. Fighting continued near Vozdvyzhenka, Novotoretske, Hrodivka, Krasnyi Yar, Novohrodivka, Selydove, Marynivka, and Hirnyk. An unconfirmed claim suggests Russian forces captured Novohrodivska Mine No. 2 south of Novohrodivka.
West of Donetsk City
Russian sources claimed advances west of Donetsk City on September 22, including in Hostre, Maksymilyanivka, and areas near Krasnohorivka and Oleksandropil. However, these claims are unconfirmed, and no frontline changes were verified. Russian forces attacked near Heorhiivka on September 21.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces advanced southwest of Donetsk City on September 22, progressing northwest of Pavlivka and reportedly crossing the Kashlahach River west of Vuhledar. Attacks occurred near Kostyantynivka, Katerynivka, Vuhledar, Vodyane, and Pavlivka.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces have made recent advances near the border of Donetsk and Zaporizhia Oblasts in Ukraine. Video evidence from September 21 shows Russian troops moving north of Staromayorske, a settlement south of Velyka Novosilka. No further attacks in this area were reported on September 22 by either side.
Zaporizhia Line
Russian forces continued their offensive in Zaporizhia Oblast on September 21-22. They launched attacks near Hulyaipole in the east, and around Robotyne in the west, including areas near Novodanylivka and towards Novoandriivka. Despite these efforts, no confirmed territorial gains were reported in any of these locations.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian forces launched an attack in an unspecified area of the Kherson direction on September 22. No further details were provided about the exact location or outcome of this attack.
Ukraine News
In a significant escalation of hostilities, Russian forces conducted a large-scale attack on Ukraine overnight from September 21 to 22. The assault involved the deployment of 2 cruise missiles and 80 Shahed drones launched from various locations. Ukrainian defense forces successfully intercepted 71 drones across multiple regions and electronically disrupted an additional 6.
The attacks resulted in damage to a residential building in Khmelnytskyi City and energy infrastructure in Poltava and Sumy oblasts. In Kharkiv City, glide bomb strikes injured at least 21 people. President Volodymyr Zelensky reported that over the past week, Russia has intensified its offensive, using more than 900 glide bombs, 400 drones, and nearly 30 missiles against Ukraine.
The recent escalation has taken a heavy toll on civilian life. In Kryvyi Rih, a 12-year-old boy and two elderly women lost their lives in the attacks. President Zelensky stated that at least 31 civilians have been killed and over 200 injured across Ukraine during this period. In response to the mounting civilian casualties, Zelensky has called for long-range strike capabilities to better protect Ukrainian lives, arguing that targeting Russian military assets could prevent attacks on Ukrainian cities. However, Western allies have so far limited Ukraine’s ability to strike deep inside Russia due to concerns about potential escalation.
On a more positive note, Ukraine’s mental health landscape has shown signs of improvement one year after First Lady Olena Zelenska’s summit on the issue. Three key developments have been observed: destigmatization of mental health issues, growth in community-based services, and increased government recognition and allocation of resources. Experts attribute this progress to Zelenska’s leadership in bringing attention to mental health concerns.
Despite these advancements, significant challenges persist due to the ongoing war. Mental health professionals have identified a condition they term “Continuous Trauma Stress Disorder” among the population. Ukraine also faces a severe shortage of qualified mental health professionals, with only 0.7 qualified psychologists per 100,000 people, compared to approximately 7.5 in Germany and the United States.
In response to these challenges and the growing demand for mental health services, Ukraine is working to establish a comprehensive ecosystem of mental health care. This initiative aims to address the immediate and long-term psychological impacts of the conflict on the Ukrainian population.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 2 INJURIES: 44
A series of Russian strikes on Ukrainian cities has resulted in numerous civilian casualties over the weekend. In Kharkiv, Ukraine’s second-largest city, a Russian attack on a residential area late Saturday injured 21 people, including three minors. Eight of the victims required hospitalization, with two in critical condition.
Another Russian assault targeted Zaporizhzhia overnight on September 23, causing injuries to 22 people, two of whom were children. The strike partially destroyed an apartment building, damaged nearby structures, and sparked a fire. Among the casualties were seven men and 13 women, with two women hospitalized in moderate condition. Governor Ivan Fedorov reported that the city endured six separate strikes. Some monitoring groups suggested this might have been the first instance of a guided aerial bomb reaching Zaporizhzhia, though this claim has not been independently verified. Emergency services promptly responded to the scene, and the injured are currently receiving medical care.
In a separate incident, Russian forces shelled a mine in Donetsk Oblast on September 22, resulting in the deaths of two female employees and injuring one person. The attack ignited a fire above the mine, necessitating the evacuation of 371 miners who were underground at the time. Ukraine’s Energy Ministry confirmed that the two women were discovered dead during an inspection of the mine area, while the injured individual was transported to a hospital for treatment.
These attacks underscore the ongoing conflict’s impact on civilian areas and infrastructure across Ukraine, with residential zones and workplaces continuing to be targets of military strikes.
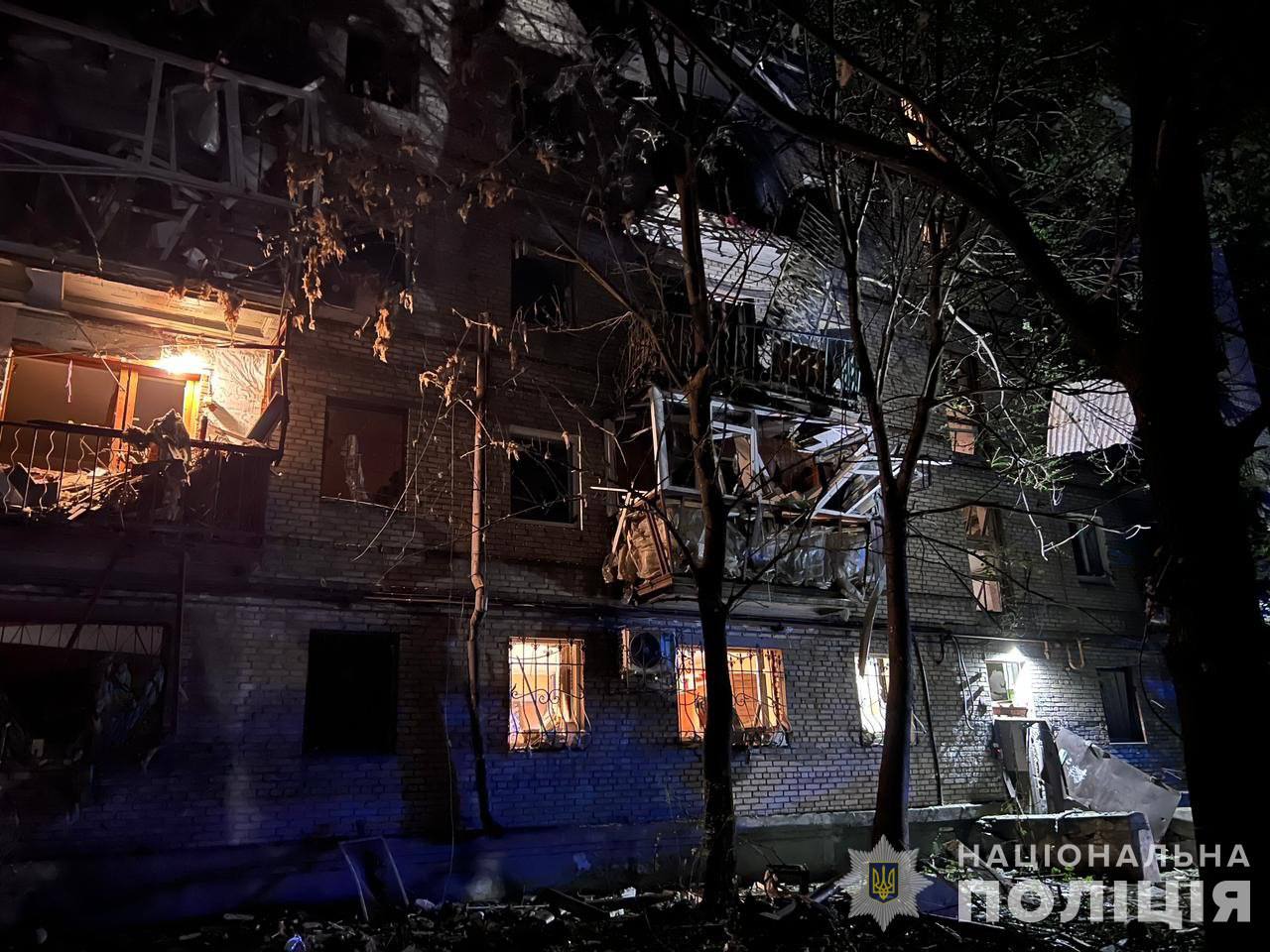 Nine civilians were injured in Russian attack on Zaporizhzhia overnight. (Ukrainian National Police/Telegram)
Nine civilians were injured in Russian attack on Zaporizhzhia overnight. (Ukrainian National Police/Telegram)
Ukrainian Mobilization and Industrial Defense Base
Ukraine’s Defense Minister Rustem Umerov has unveiled ambitious plans to significantly ramp up the country’s drone production by 2025. The initiative aims to maintain Ukraine’s superiority over Russian production in this crucial area of military technology. According to Umerov, Ukraine has the capacity to produce “several million” drones, with funding coming from both the state budget and international partners.
In addition to expanding drone capabilities, Umerov announced that Ukraine is actively developing its domestic missile program. The country has shared details of this program with Western allies and has received verbal consent for funding, though it is still awaiting final written approval. This development in missile technology is intended to complement Ukraine’s growing drone capabilities.
President Volodymyr Zelensky has previously reported successful tests of new military technologies, including a drone missile called “Palianytsia” and a Ukrainian ballistic missile. While specific details about Ukraine’s missile program remain limited due to security considerations, the country is making strides towards utilizing its own missiles in combat situations.
One notable example of Ukraine’s progress in domestic missile manufacturing is the R-360 Neptune cruise missile. This success story demonstrates the country’s growing capacity to produce advanced military hardware domestically.
The focus on developing both drone and missile technologies reflects Ukraine’s strategy to enhance its defensive and offensive capabilities in the ongoing conflict. By aiming to produce several million drones by 2025 and advancing its missile program, Ukraine is working to strengthen its position in modern warfare technology.
Ukraine’s Allies
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky is set to visit Washington next week as part of a crucial diplomatic mission to secure stronger military support for Ukraine in its ongoing conflict with Russia. The visit comes at a critical juncture in the war, with both sides grappling for resources and strategic advantages.
Zelensky’s itinerary includes meetings with President Joe Biden, Vice President Kamala Harris, and potentially former President Donald Trump. The Ukrainian leader plans to present a comprehensive “victory plan” that seeks to boost Ukraine’s chances of success and gain an advantage in future peace negotiations. A key element of this strategy involves lobbying for permission to use Western-supplied long-range missiles for strikes deep into Russian territory, a move currently restricted by the United States and the United Kingdom.
The Ukrainian president’s U.S. tour will begin with a visit to the White House on September 26, followed by discussions with other political figures and members of Congress. Zelensky is also scheduled to address the United Nations General Assembly and meet with German and Brazilian leaders. He has emphasized that the coming fall is crucial for determining the war’s outcome and hopes to strengthen Ukraine’s position with international support.
As part of his visit, Zelensky toured a Pennsylvania ammunition factory producing vital 155 mm artillery shells for Ukraine. The Scranton Army Ammunition Plant has increased its monthly production from 24,000 to 36,000 rounds. Zelensky expressed gratitude to the workers, underscoring the urgent need for more ammunition to support Ukraine’s defense efforts against Russian forces.
In response to Ukraine’s appeals, the U.S. is planning to launch initiatives to bolster Ukraine’s position in the coming weeks. Michael Carpenter, Senior Director for Europe at the U.S. National Security Council, stated that the Biden administration will focus on delivering critical military capabilities to Ukraine using remaining funds from the April supplemental. A new $375 million military aid package for Ukraine may be announced next week.
Ukraine’s Defense Minister Rustem Umerov has announced an agreement to receive French Mirage 2000 jets and ongoing talks for Swedish Gripen and Eurofighter Typhoon fighters. France has previously pledged to transfer Mirage 2000-5 jets and train Ukrainian pilots, with the first group already completing Alpha Jet training. Sweden has expressed openness to providing Gripen jets after the F-16 program is completed. Ukraine has already received its first 10 F-16s out of 79 promised by the Netherlands, Denmark, Norway, and Belgium.
President Zelensky’s diplomatic efforts come amid frustration from some European officials over Washington’s perceived hesitancy to take the lead in strengthening Ukraine’s military capabilities. While President Biden has expressed his commitment to supporting Ukraine, critics argue that more decisive action is needed to ensure a Ukrainian victory. As Zelensky continues his high-stakes mission, the international community watches closely to see how these discussions will shape the future course of the conflict.
Life in Ukrainian-Occupied Russia
Ukrainian officials have stated that they are providing aid to Russian civilians in the affected areas. However, there are conflicting accounts regarding the ability of these civilians to leave the region.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Recent satellite imagery suggests a failed test of Russia’s RS-28 “Sarmat” nuclear-capable intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome in Arkhangelsk Oblast. The images show a large crater and fire trucks at the Yubileynaya launch silo, specifically converted for Sarmat launches. This apparent failure would be the fourth for the Sarmat, which Russia intends to replace its Soviet-era Voevoda ICBM. While Russia reportedly put the Sarmat on combat duty in September 2023, it has only had one successful test in April 2022. This latest setback indicates ongoing challenges in Russia’s missile development, potentially due to international sanctions and war-related demands on its defense industry.
A recent test launch of Russia’s RS-28 Sarmat ICBM, also known as Satan II, reportedly failed at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome in Russia. Open-source intelligence project MeNMyRC claims the missile detonated in its silo, destroying the test site. This marks the fourth failure for Sarmat since its combat deployment in 2023. The missile, announced by President Putin in 2018, has faced numerous setbacks in its development, which began in 2013. Notably, Russia’s ICBM maintenance was previously handled by Ukraine until relations soured in 2014 following the annexation of Crimea.
Russia’s Allies
Iran has delivered Fath-360 ballistic missiles to Russia but not the mobile launchers, according to anonymous sources cited by Reuters. This raises questions about when Russia might use these weapons in Ukraine. U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken confirmed the missile delivery, which Iran denies. The move has led to new sanctions against Iran from Ukraine, the EU, and the U.S. Iran and Russia have strengthened their military cooperation since the full-scale invasion of Ukraine began, with Iran previously supplying Shahed kamikaze drones to Russia.
Controlling the Narrative and Russian Propaganda
Ukrainian officials warn that Russian actors are spreading false claims on social media about Ukrainian soldiers using US-supplied drugs. These rumors, aimed at discrediting Ukraine’s military, are reportedly based on fake confessions from Ukrainian prisoners of war. This comes as Russian sources recently alleged drug trafficking issues within their own ranks.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
