Summary of the Day:
Russian forces captured the settlement of Vuhledar following a Ukrainian withdrawal. However, some Russian sources express doubt about the potential for rapid advances beyond Vuhledar. Russian troops also made advances near Vovchansk, Kreminna, Toretsk, and Pokrovsk.
Ukrainian officials report a reduction in Russia’s artillery ammunition advantage, partly due to recent strikes on Russian ammunition depots. This development could impact the balance of firepower on the battlefield.
The United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (UN OHCHR) released its June-August 2024 report, detailing Ukrainian civilian casualties and systemic Russian mistreatment of prisoners of war (POWs). The report also noted limited Ukrainian mistreatment of Russian POWs. Russian state media largely misrepresented the report, ignoring assessments of Russia’s systemic abuse of Ukrainian prisoners.
In other developments, the Russian federal budget for 2025-2027 has allocated funding to support online platforms run by a prominent Kremlin propagandist and a former opposition outlet, highlighting Russia’s efforts to adapt its propaganda to social media. Additionally, Russian authorities are reportedly planning to increase recruitment within pre-trial detention centers.
Picture of the Day:
 A mural depicting Ukrainian poet and writer Taras Shevchenko reads ‘Fight and win your battle, God will help you’ in Pokrovsk, Donetsk Oblast. Russian invading forces, approximately 7 kilometers from Pokrovsk, are advancing and pushing Ukrainian defenses toward the city. (Pierre Crom/Getty Images)
A mural depicting Ukrainian poet and writer Taras Shevchenko reads ‘Fight and win your battle, God will help you’ in Pokrovsk, Donetsk Oblast. Russian invading forces, approximately 7 kilometers from Pokrovsk, are advancing and pushing Ukrainian defenses toward the city. (Pierre Crom/Getty Images)
The Path to Peace
Former Trump national security advisor HR McMaster dismissed Trump’s claims of being able to quickly end the Ukraine-Russia war as a “myth.” McMaster emphasized that favorable political outcomes in wars typically require favorable military outcomes. Trump has promised to end the invasion within a day if elected but hasn’t detailed his plan. Some reports suggest it might involve ceding territory to Russia. Even the Kremlin has expressed skepticism about Trump’s claims. McMaster argued that Ukraine needs continued support to demonstrate resolve against Russia. President Zelensky has called on Trump to reveal his plan to understand potential risks. Despite recent critical rhetoric towards Zelensky, Trump claimed in a recent interview that he likes the Ukrainian president and had a good relationship with him while in office.
Ukraine’s Foreign Ministry spokesperson Heorhii Tykhyi refuted a Financial Times report claiming that new Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha discussed territorial compromises with Western counterparts during the U.N. General Assembly in New York. Tykhyi, who attended all of Sybiha’s meetings, stated that no territorial compromises were suggested, discussed, or hinted at. He emphasized that Ukraine’s position on sovereignty and territorial integrity remains firm. The FT article had cited European diplomats who reported a more pragmatic tone from Ukrainian officials regarding potential ceasefire negotiations. Tykhyi dismissed this information as false and questioned the motives behind spreading such narratives.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
President Zelensky reported a “very challenging” situation on Ukraine’s front lines after discussions with military leaders. Russian forces are advancing in Donetsk Oblast, particularly near Pokrovsk, Vuhledar, and Toretsk, with Ukrainian troops facing difficult conditions. In Vuhledar, the situation is described as “extremely difficult” by the local governor. Russian troops may also be preparing for operations in Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zelensky emphasized the importance of the upcoming Ukraine Defense Contact Group meeting in Germany, stating it will be crucial for discussing Ukraine’s strategy and securing support from partners. He also presented a five-point victory plan to U.S. officials, aiming to strengthen Ukraine’s position and push for a just peace.
Ukrainian officials report a significant reduction in Russia’s artillery ammunition advantage. The ratio of Russian to Ukrainian artillery usage has decreased from 8-to-1 in Winter 2024 to 3-to-1 in early October 2024. This change is attributed to recent Ukrainian strikes on Russian ammunition depots, including attacks near Toropets and at the Tikhoretsk Arsenal. Additionally, Western military aid and increased Ukrainian ammunition production may be contributing factors. Some Russian sources report ammunition shortages on various front sectors, despite Russian factories operating daily. Ukrainian President Zelensky noted a similar decrease in the Pokrovsk direction, from 12-to-1 to 2.5-to-1, following Ukrainian incursions into Kursk Oblast in August 2024.
Russian Defense Minister Andrei Belousov inspected the Central Grouping of Forces.
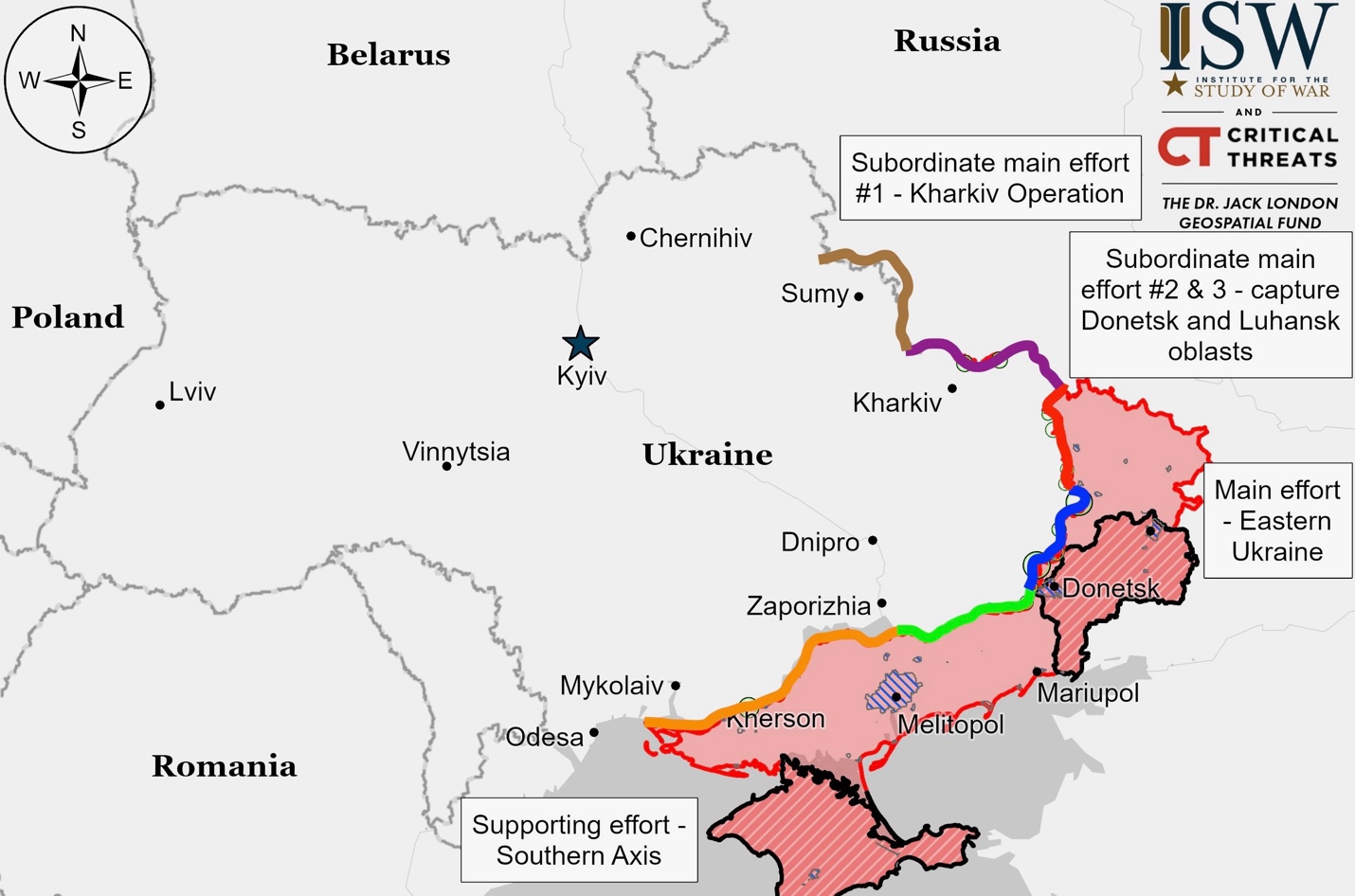
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Russian forces reportedly made advances southeast of Sudzha in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast. They claim to have repelled Ukrainian attacks near Plekhovo and advanced near Borki, though this lacks visual confirmation. Russians also report unverified progress between Kucherov and Brodina gully, while Ukrainians continue attacks near Kremyanoye. A Chechen commander claimed the capture of two unnamed settlements in Kursk Oblast. Russian naval infantry, airborne, and artillery units are said to be operating in the area.
Ukrainian forces continued offensive operations in Glushkovsky Raion, Kursk Oblast, but made no advances. Russian sources claim they repelled Ukrainian attacks near Novy Put and Veseloye. Ukrainian strikes on Krasnooktyabrskoye suggest it remains under Russian control. Russian airborne units are active in the area.
Ukrainian military spokesperson Vadym Mysnyk reported that Russia has significantly increased its forces in Kursk Oblast. However, he stated that these Russian troops lack the training and experience to effectively use their numerical advantage against Ukrainian forces in the region. Mysnyk also noted that Russia continues to deploy conscripts and border guards in Kursk Oblast.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched a mechanized assault on Vovchansk, northeast of Kharkiv City, using armored vehicles and tanks. They made small advances along Soborna Street near the Vovchansk Aggregate Plant before Ukrainian forces halted them using drones and artillery. Ukrainian officials reported repelling the attack, destroying most of the Russian vehicles. Russian attacks also occurred near Tykhe, Starytsya, and Buhruvatka.
Russian forces continued limited attacks north of Kharkiv City without confirmed advances. A Russian source claimed small gains near Zelene, but this is unverified. Ukrainian officials state Russian forces are mainly defensive along the Hlyboke-Lyptsi line, fortifying positions. Russian motorized rifle units are reportedly securing positions near Lukyantsi, east of this area.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces made confirmed advances northwest of Kreminna and claimed unconfirmed progress west of Svatove. They advanced slightly west of Makiivka. Russian sources claim advances near Kruhlyakivka and Vyshneve, but these are unconfirmed. Russian forces continued attacks in multiple areas including Synkivka, Novoosynove, Stelmakhivka, Andriivka, Hrekivka, and near the Serebryanske forest.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces launched offensive operations near Siversk. They attacked northeast of the city around Bilohorivka and to the east near Verkhnokamyanske. Despite these efforts, there were no confirmed changes to the frontline in this area.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces attacked near Chasiv Yar targeting the city itself and nearby areas like Hryhorivka and Stupochky. Despite these efforts, no frontline changes were confirmed. A Russian military blogger reported Ukrainian counterattacks and improved defenses in the area, calling for reinforcements.
Toretsk
Russian forces made a small advance in central Toretsk along Maiakovskhoho Street, as shown in recent footage. They continued attacks on Toretsk and nearby areas including Zalizne, Nelipivka, Niu York, and towards Shcherbynivka.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces advanced near Pokrovsk gaining ground in southeastern Tsukuryne and north of Mykolaivka. They also reportedly captured Krutyi Yar. Attacks continued in several areas east and southeast of Pokrovsk, including Novotoretske, Myrolyubivka, Vozdvyzhenka, Lysivka, Selydove, Novohrodivka, Hirnyk, and Mykhailivka. A Ukrainian officer noted increased Russian infantry assaults and armored vehicle use in recent days, with a shift in focus from Mykhailivka to the Tsukuryne-Ukrainsk area.
Military observer Kostyantyn Mashovets reported that Russian special forces had infiltrated Ukrainian rear areas near Pokrovsk. These groups were tasked with sabotage, disrupting Ukrainian command and logistics, and capturing important infrastructure like bridges.
West of Donetsk City
Russian forces attacked near Heorhiivka and Kurakhove west of Donetsk City but made no confirmed advances. A Ukrainian brigade reported repelling a large Russian mechanized assault near Kurakhove, destroying several tanks and armored vehicles. A Russian source claimed Ukrainian drones were hindering Russian advances near Maksymilyanivka.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces have reportedly captured Vuhledar, a key town in Ukraine’s Donetsk Oblast, after Ukrainian troops conducted a planned withdrawal to avoid encirclement. This capture marks a significant shift after more than two years of costly failed assaults, including major offensives in late 2022 and early 2023 that resulted in significant Russian losses. Governor Vadym Filashkin described the situation as extremely difficult, with fighting ongoing in the town center and humanitarian aid delivery nearly impossible. Most civilians have been evacuated, leaving only 107 residents.
Despite this achievement, some sources doubt that capturing Vuhledar will lead to rapid advances or significant breakthroughs for Russian forces. The town’s strategic importance lies in its location near major roads and its role in defending southern Donetsk Oblast. However, it is not a crucial logistics hub, and Russian forces already controlled nearby main roads. Located about 30 kilometers south of Russia’s main effort near Pokrovsk and 23 kilometers south of the H-15 highway, advancing from Vuhledar would require crossing open terrain during the muddy season, potentially hindering mechanized assaults. Consequently, while its potential loss could threaten Ukrainian control of the region’s southwestern portion, the town’s fall is unlikely to fundamentally change operations in western Donetsk Oblast in the near future.
Russian forces continued attacking near Kostyantynivka and Katerynivka southwest of Donetsk City. While a Russian blogger claimed a 400-meter advance south of Katerynivka, this remains unconfirmed. No changes to the frontline were verified. Russian motorized rifle units are reportedly operating in the Katerynivka area.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces are reportedly gathering troops near Pryyutne and Robotyne in the Zaporizhzhia sector, possibly preparing for attacks on Ukrainian positions. Ukrainian military spokesperson Vladyslav Voloshyn noted signs of troop concentration and accumulation of ammunition. Despite some Russian troops being moved to Kursk Oblast following a Ukrainian incursion, the number of forces in Zaporizhzhia remains stable. Russia is replenishing losses with 2,000-3,000 soldiers weekly but lacks sufficient troops for a large-scale offensive. Meanwhile, Russian attacks on Zaporizhzhia’s civilian infrastructure have intensified.
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces attacked near Zolota Nyva in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border area with no confirmed frontline changes. A Russian source claimed a 3km advance from Prechystivka towards Zolota Nyva, but this is unverified. Ukrainian officials report Russian forces gathering near Pryyutne for potential assaults.
Zaporizhia Line
Russian forces launched limited attacks near Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast targeting Mala Tokmachka, Mali Shcherbaky, and Novodanylivka. No confirmed advances were reported.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
No ground attacks occurred in Kherson Oblast. Russian BARS-33 forces are reportedly targeting Ukrainian boats on the Dnipro River.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched 32 Shahed drones against Ukraine overnight. Ukrainian forces destroyed 29 drones over several oblasts, while three failed due to electronic warfare. Ukrainian Ground Forces reported shooting down 143 Shahed drones in the previous week.
The United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights’ June-August 2024 report reveals a 45% increase in Ukrainian civilian casualties, with 589 deaths and 2,685 injuries. It highlights systematic Russian mistreatment of Ukrainian prisoners of war (POWs), including widespread torture and inhumane conditions likely coordinated by Russian state entities. While some Russian POWs reported ill-treatment by Ukrainian forces, conditions in official Ukrainian-run facilities generally complied with international law. Recent drone footage shows Russian forces executing 16 surrendering Ukrainian soldiers near Mykolaivka. Russian officials and media often use dehumanizing language about Ukrainian POWs, with some public figures openly calling for their unlawful treatment, and no known prosecutions exist against Russian perpetrators. In contrast, Ukraine has conducted five pre-trial investigations into possible ill-treatment of Russian POWs since mid-August 2024. Ukraine allows the UN regular access to Russian POWs, while Russia denies access to Ukrainian POWs. Russian state media selectively reported on Ukrainian mistreatment of POWs, omitting details of Russia’s systemic abuse.
Ukraine’s Defense Minister Rustem Umerov has initiated a significant reshuffle in his ministry, signing a submission to dismiss three deputy ministers and the state secretary. Umerov emphasized the need for clear and controlled processes within the Defense Ministry during martial law. The dismissals, pending approval by Ukraine’s Cabinet, include Deputy Ministers Oleksandr Serhii and Yurii Dzhygyr, and State Secretary Liudmyla Darahan. Deputy Minister Stanislav Haider is to be transferred to head the Minister’s Office. Umerov also announced plans to reform Ukraine’s defense acquisition system, including setting up supervisory boards for the Defense Procurement Agency and State Rear Operator. Additionally, Spetstechnoexport, a state foreign trade enterprise specializing in military equipment, is being transferred from military intelligence to the Defense Ministry.
Donald Trump is attempting to portray a friendly relationship with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky as U.S. elections approach. Trump claimed he “had a good relationship with Zelensky” and praised him as being “like a piece of steel” during Trump’s first impeachment. However, Trump mischaracterized their interactions, quoting a conversation that never occurred. The context for this is Trump’s 2019 impeachment for allegedly pressuring Ukraine to release compromising information on Joe Biden. At a recent joint press conference, Zelensky remained silent as Trump attempted to exonerate himself, likely aware that Trump could potentially be the next U.S. president signing aid bills for Ukraine.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 7+ INJURIES: 31
Russian forces attacked Zaporizhzhia City with at least six guided aerial bombs, which Ukrainian officials report have been modified to increase their range. The attack damaged buildings in Komunarskyi Raion and other residential areas, killing one person and injuring 24, including three children. Among the injured were nine men and 12 women. The State Emergency Service provided psychological assistance to 28 people at the site of the attack.
Russian forces attacked central Kherson, Ukraine, targeting a local market and public transport stop. The shelling resulted in six deaths and seven injuries, including three women (ages 68, 65, and 33) and a 65-year-old man, all suffering blast and shrapnel injuries. Five of the injured were hospitalized. The attack occurred during a nationwide moment of silence for fallen Ukrainian soldiers. President Zelensky condemned the attack, calling for an end to “daily Russian terror.”
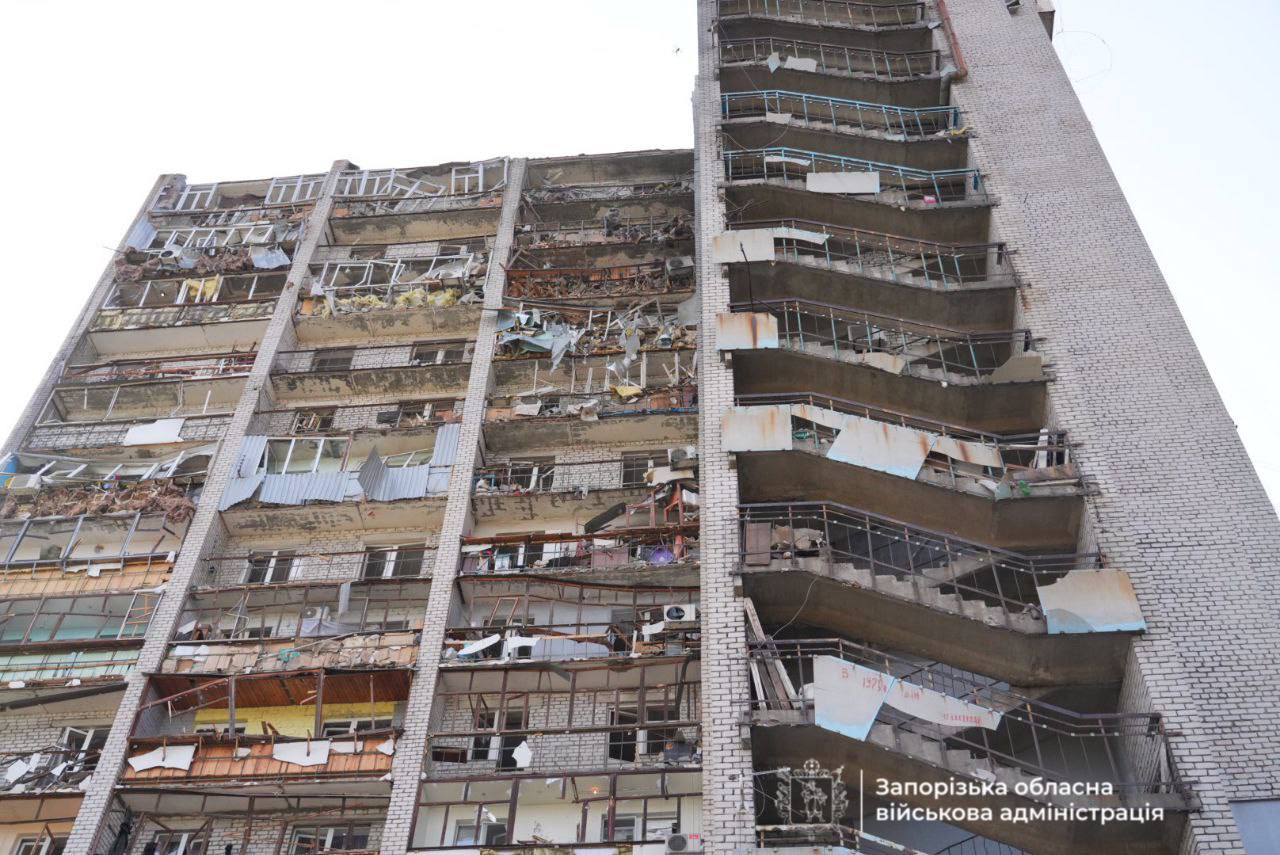 The aftermath of a Russian attack on the city of Zaporizhzhia. (Zaporizhzhia city military administration)
The aftermath of a Russian attack on the city of Zaporizhzhia. (Zaporizhzhia city military administration)
Ukrainian Mobilization and Industrial Defense Base
Ukraine’s defense industry has made significant progress, according to President Zelensky at the second international defense industry forum in Kyiv. Artillery and mortar ammunition production has increased 25-fold compared to 2022. Ukraine can now produce 4 million drones annually and 15-20 Bohdana howitzers monthly. The country has also successfully tested its own ballistic missile and developed the Palianytsia missile-drone. These domestic long-range weapons are crucial as Western partners restrict deep strikes in Russia with foreign-made missiles. The U.S. has stated that Ukraine can use its own weapons for such strikes without U.S. permission. Ukraine has already successfully targeted Russian military facilities using long-range drones.
French-German defense company KNDS has opened an office in Kyiv to support Ukraine’s domestic maintenance and repair of land systems and production of artillery ammunition. KNDS, formed from a 2015 merger of German and French companies, produces about 800 systems used by Ukrainian Armed Forces, including Caesar artillery guns, Gepard anti-aircraft tanks, and PzH 2000 howitzers. The company plans to jointly manufacture NATO-standard 155 mm artillery ammunition and spare parts with Ukrainian industry. This move aligns with Ukraine’s efforts to increase domestic ammunition production, with the Ukrainian Defense Industry already producing various calibers of ammunition, including 155 mm artillery rounds, as announced by former strategic industries minister Alexander Kamyshin in September.
Ukraine’s Allies
Mark Rutte, NATO’s new secretary general, emphasized Ukraine’s sovereignty and independence as he took office on October 1, stressing increased NATO member spending and deeper global partnerships. The Financial Times reports President Biden may advance Ukraine’s NATO membership bid before leaving office in January 2025, following President Zelensky’s U.S. visit and five-point victory plan. A U.S.-Ukraine security agreement was signed in June, and the July NATO summit launched the Ukraine Compact, affirming Kyiv’s path to membership without a definite timeline. Zelensky maintains Ukraine will join NATO post-war.
Latvian Foreign Minister Baiba Braze predicted Ukraine would have the second-strongest military in NATO on the European continent upon joining, citing battle experience and commitment. Ukrainian Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha emphasized Ukraine’s need to join NATO and the EU, calling for supportive policies and highlighting immediate military needs. He reaffirmed Ukraine’s stance on territorial integrity, including Crimea, and stressed the importance of international support for Ukraine’s peace formula.
Estonia is introducing an unprecedented security tax to boost defense spending and aid to Ukraine. Defense Minister Hanno Pevkur explained that the tax, effective from 2026 to 2028, will include a 2% levy on individual and business profits and an increase in VAT. Estonia has already committed significant support to Ukraine, allocating 520 million euros (1.4% of GDP) between 2022 and 2024. The country plans to increase its defense budget to 3.7% of GDP by 2026, with a focus on capabilities development and ammunition. Pevkur argues that NATO’s 2% GDP benchmark for defense spending is no longer sufficient, suggesting a need to increase to 2.5% or 3% to address the gap created by Russia’s significantly higher defense spending growth over the past decades.
German Chancellor Olaf Scholz is reportedly seeking to speak with Russian President Vladimir Putin by phone before the G20 meeting in Brazil this November, according to the German newspaper Zeit. This would be their first conversation since December 2022. Meanwhile, Germany has become Ukraine’s second-largest military donor after the U.S., recently ordering 17 additional IRIS-T air defense systems for Ukraine. However, Scholz maintains that Germany will not allow Ukraine to use German weapons, including Taurus missiles, to strike targets within Russia, despite ongoing discussions among Western allies about such tactics.
Polish-Ukrainian relations are facing renewed tensions over historical issues, particularly the 1943 Volyn Massacre. Polish Foreign Minister Radoslaw Sikorski recently demanded Ukraine allow exhumations of Volyn victims during a meeting with President Volodymyr Zelensky in Kyiv. Ukraine has blocked exhumations since 2017 due to vandalism of Ukrainian memorials in Poland. The conflict is complicated by differing interpretations of the massacre and ongoing political pressures in both countries. Polish sentiment towards Ukrainian refugees is also shifting, with many hoping they will return home after the war. Experts suggest these tensions may persist through Poland’s upcoming elections but could stabilize afterward. However, resolving historical disputes remains challenging while Ukraine is fighting Russia’s invasion. Both countries are advised to find common ground in strategic communication to prevent Russia from exploiting these disagreements.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Russian artillery strikes on the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant’s main substation disconnected a power line, specifically the “Ferrosplavnaya-1” line, risking a blackout. The ZNPP, Europe’s largest nuclear plant, has been under Russian occupation since March 2022 and has experienced eight complete blackouts. Ukraine’s Energy Minister Herman Halushchenko demanded the plant’s return to Ukrainian control for safe operation, while President Zelensky warned the U.N. Security Council that Russia may target three unspecified Ukrainian nuclear power plants. Russian authorities confirmed the line disconnection but didn’t specify the cause. The ongoing conflict continues to jeopardize the safety of Ukraine’s nuclear facilities, with the ZNPP being particularly vulnerable due to its occupied status and repeated power disruptions.
Russian officials in Chelyabinsk Oblast have issued guidelines for teachers on integrating deported Ukrainian children into local schools. These recommendations focus on promoting Russian patriotism and language skills among the Ukrainian students, highlighting Russia’s ongoing efforts to forcibly assimilate these children. The guidelines also acknowledge the psychological distress experienced by the deported children, contradicting Russia’s claims that these deportations are for the children’s benefit. This situation underscores the destructive impact of Russia’s campaign to deport and Russify Ukrainian children.
Ukraine’s Security Service and Prosecutor General’s Office have accused Denis Pushilin, head of the self-proclaimed Donetsk People’s Republic, and other Russian-installed officials of forcibly deporting 31 Ukrainian children from occupied Donetsk Oblast to Russia. The group included 19 orphans from Mariupol and 12 children from Shakhtarsk, Khartsyzk, and Mariupol. Pushilin allegedly signed a resolution authorizing the deportation under the guise of “rehabilitation” and “recreation.” The children were first taken to Rostov-on-Don, then flown to Moscow on a plane linked to Putin’s administration and sent to the “Polyany” camp. They were given Russian passports and placed with adoptive families. One 17-year-old was reportedly adopted by Maria Lvova-Belova, Putin’s Commissioner for Children’s Rights. The International Criminal Court has issued arrest warrants for Putin and Lvova-Belova for their roles in these deportations. While six children have returned to Ukraine, 25 remain in Russia. The Prosecutor General’s Office acknowledges the role of investigative journalists in uncovering this information, highlighting Russia’s ongoing efforts to forcibly assimilate Ukrainian children.
Russia News
The Crimean Bridge, a critical supply route for Russian forces in occupied Crimea, has faced recent challenges. Protective barriers installed to defend against Ukrainian attacks were washed ashore during a storm, with locals reportedly scavenging the metal components. Russia has been attempting to strengthen the bridge’s defenses, including the construction of an unidentified structure and underwater drone traps. However, harsh weather conditions are hampering these efforts. The 19-kilometer bridge, completed in 2018 after Russia’s illegal occupation of Crimea, has been targeted and damaged by Ukrainian forces. Ukraine argues at the Permanent Court of Arbitration that the bridge is unlawful and impedes international shipping in the Sea of Azov and Kerch Strait.
Russian authorities are investigating commanders of the 6th Motorized Rifle Division for crimes against their own soldiers in occupied Ukraine. The case, opened in March 2024, alleges that these commanders murdered seven servicemembers in Donetsk Oblast and tortured 19 others in Luhansk Oblast in 2023 for disobeying orders. Despite a Russian Ministry of Defense inspection, the abuses reportedly continued and were concealed.
Russian President Vladimir Putin has suspended the national population census. This move may be an attempt to hide the extent of Russian losses from the ongoing war in Ukraine.
Two years after explosions damaged Russia’s Nord Stream pipelines under the Baltic Sea, the investigation remains inconclusive. Initially, Russia was suspected, but later reports suggested Ukrainian involvement, which Kyiv denies. The incident has become politicized, with various parties using it to advance their agendas. Some opponents of Western aid to Ukraine cite the alleged Ukrainian involvement as a reason to cut support. Meanwhile, Eastern European countries have used the incident to criticize Germany’s past reliance on Russian energy. The mystery surrounding the explosions has exposed political divisions within Europe and sparked debates about energy security and relations with Russia. Despite multiple investigations, no definitive culprit has been identified, leaving the case open and subject to ongoing speculation and debate.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian authorities plan to increase military recruitment in pre-trial detention centers, aiming to enlist about 100 defendants from each of Russia’s 210 centers. This comes as the number of prisoners joining the war in Ukraine is reportedly decreasing. A recent bill allows prosecutors to drop charges against defendants who sign contracts to serve in Ukraine.
Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov announced that the BARS-Belgorod volunteer group has started operations. The group will carry out combat missions and protect important infrastructure in the region.
Russia’s defense industry is grappling with a severe labor shortage, exacerbated by the full-scale invasion of Ukraine. Over 90,000 job vacancies were posted between mid-August and mid-September 2024, with salaries three to four times higher than regional averages. This has led to intense competition between the military and businesses for recruits. Defense factories are offering triple the standard pay and other incentives to attract workers, particularly for high-demand roles like engineers, turners, and CNC machine operators. The shortage is compounded by Russia’s overall labor crisis, mobilization efforts, declining migrant numbers, and a looming population decline. Some factories have resorted to recruiting minors and offering temporary housing to workers from other regions. Working conditions can be harsh, with some positions advertising 11-hour shifts without days off.
Russia’s main tank maker, Uralvagonzavod, has obtained a German Leopard 2A6 tank for study. They plan to examine its components and systems, possibly aiming to reverse-engineer Western military equipment. However, Russia likely lacks the necessary parts to fully replicate such advanced Western technology.
Russia’s Allies
Russian Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin and Belarusian Prime Minister Roman Golovchenko met to discuss accelerating the integration of their countries into the Union State over the next three years. They focused on strengthening economic ties, developing joint industrial projects, and enhancing “technological sovereignty.” The leaders also noted progress in cultural and educational exchanges between the two nations.
Controlling the Narrative and Russian Propaganda
The Russian federal budget for 2025-2027 allocates significant funding to online platforms run by prominent Kremlin propagandist Vladimir Solovyov and former opposition outlet Readovka. Solovyov Live Telegram channel will receive 4.5 billion rubles ($47 million), while Readovka news aggregator gets 49 million rubles ($511,000). This marks the first time these platforms receive federal funding. Readovka, once posing as semi-opposition, now actively promotes pro-Kremlin views. This funding shift highlights the Kremlin’s efforts to adapt its propaganda to Russians’ increasing reliance on social media for information, moving beyond traditional TV and print media.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
