Summary of the Day:
Russian forces continued offensive operations along multiple axes while utilizing banned chemical agents against Ukrainian positions. The Ukrainian General Staff reported 323 instances of Russian forces using chemical weapons in October 2024, violating the Chemical Weapons Convention. These attacks involved riot control agents and unidentified chemical compounds delivered via grenades and other ammunition.
Russian forces advanced south of Chasiv Yar, southeast of Kurakhove, and north of Vuhledar. Ukrainian forces, meanwhile, achieved gains in northern Novoivanovka, Kursk Oblast. Russian regional authorities are actively expanding territorial defense formations, with a notable focus on recruiting women to strengthen their forces.
Russian President Vladimir Putin made several significant statements during this period. He acknowledged Russia’s serious labor shortage and reliance on migrant workers, while continuing to justify the invasion of Ukraine with claims about violated neutrality. Putin notably attempted to downplay Russia’s relationship with North Korea, likely to preserve ties with South Korea and discourage their support for Ukraine, while simultaneously strengthening connections with Venezuela to expand influence in the Western hemisphere.
Picture of the Day:
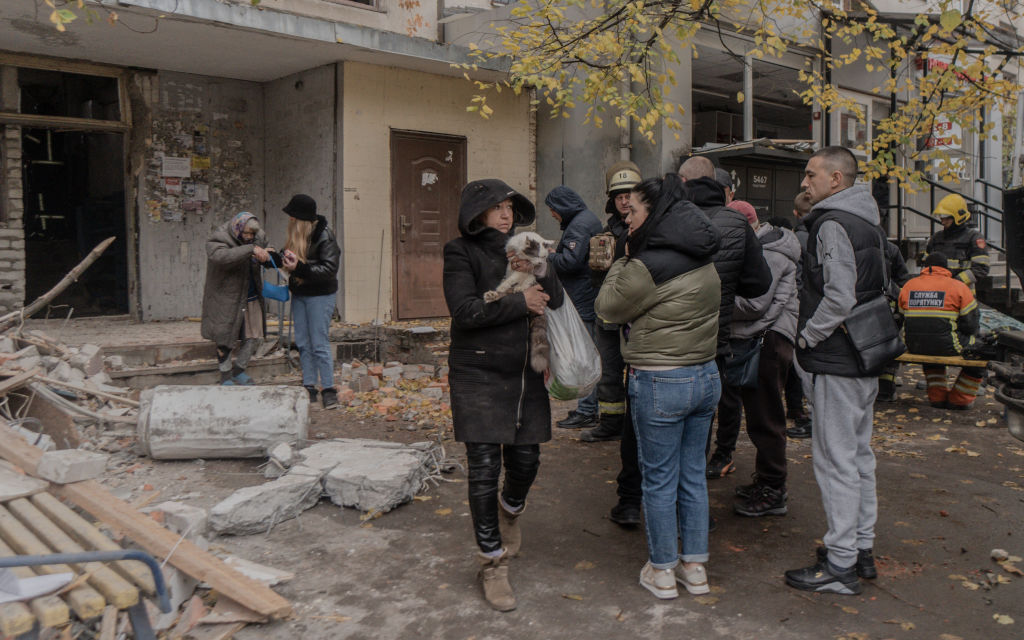 Evacuated residents of a 12-story residential building in Kharkiv’s Saltivskyi district stand near their building after it was heavily damaged by Russian bombs. (Ivan Samoilov/Gwara Media/Global Images Ukraine via Getty Images)
Evacuated residents of a 12-story residential building in Kharkiv’s Saltivskyi district stand near their building after it was heavily damaged by Russian bombs. (Ivan Samoilov/Gwara Media/Global Images Ukraine via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Russian President Vladimir Putin’s recent stance raises significant concerns for global peace efforts. During his November 7 Valdai Club address, Putin’s conditional offer to restore US-Russia relations comes with demands that could destabilize international security – namely, ending US sanctions and abandoning Ukraine’s defense. Despite appearing open to dialogue, the Kremlin’s unchanged military objectives in Ukraine, as confirmed by spokesperson Dmitry Peskov, signal a troubling reluctance to seek genuine peaceful resolution. This rigid position, combined with internal messaging portraying Putin as the architect of a “new world order,” suggests a concerning prioritization of power politics over meaningful diplomatic compromise, potentially prolonging global tensions and the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
Russian President Putin’s recently proposed “six-point plan” for a “new world order” appears to contradict his own actions on the world stage. While Putin advocates for international equality, rejection of security blocs, and respect for all countries’ perspectives, his regime actively undermines these principles through ongoing military aggression in Ukraine, destabilization efforts in Moldova and Georgia, and strategic alliances with anti-Western states like North Korea, China, and Iran. This disconnect between Putin’s peaceful rhetoric and aggressive actions poses a significant threat to global stability, particularly as Russia continues to challenge NATO and expand its influence through BRICS and new Eurasian security arrangements. His contradictory approach raises serious concerns about the prospects for genuine peace and international cooperation.
Russia’s deepening military alliance with North Korea marks an alarming escalation in global tensions. While President Putin attempts to downplay their new strategic partnership as routine diplomacy, the unprecedented deployment of up to 12,000 North Korean troops to fight in Ukraine, with forces already engaged in combat in Kursk Oblast, represents a dangerous shift in international relations. This collaboration between two nuclear-armed nations, one under heavy international sanctions, threatens global stability and peace efforts. Putin’s attempt to minimize this significant military partnership while acknowledging potential joint exercises suggests a concerning expansion of military cooperation that could destabilize not only Ukraine but also East Asian security. The involvement of North Korean forces in Ukraine transforms a regional conflict into a broader international crisis, potentially undermining decades of efforts to maintain peace and nuclear non-proliferation.
South Korea is reconsidering its level of support for Ukraine in direct response to North Korea’s growing military alliance with Russia. The catalyst for this potential shift is North Korea’s substantial military involvement in the Ukraine conflict, including the deployment of troops to fight alongside Russian forces. Putin’s attempt to publicly downplay Russia’s “unprecedented” relationship with North Korea at the Valdai Club appears specifically aimed at preventing South Korea from increasing its military aid to Ukraine. This emerging dynamic shows how Russia’s partnership with North Korea could backfire diplomatically, potentially pushing South Korea to become a more active supporter of Ukraine’s defense efforts. The situation highlights how regional Asian alliances are increasingly influencing support for Ukraine in its conflict with Russia.
Russia’s drone strike on the Kyiv residence of Estonian Ambassador Annely Kolk marks a significant escalation in international tensions, potentially violating diplomatic protocols protected under international law. While Ambassador Kolk escaped harm at Jack House in Kyiv’s Pechersk district, the attack on a NATO member state’s diplomatic residence raises serious concerns about Russia’s disregard for diplomatic immunity and international norms. Estonian Prime Minister Kristen Michal and Foreign Minister Margus Tsahkna emphasized this incident demonstrates the urgent need for enhanced Ukrainian air defense capabilities. The attack, part of Russia’s broader campaign of over 2,000 drone strikes last month, represents a dangerous precedent that threatens diplomatic security and global stability, particularly as it targets representatives of NATO-aligned nations.
Russia’s expanding alliance with Venezuela signals a concerning shift in global power dynamics that could destabilize international peace. The signing of 17 agreements in Caracas, including intelligence sharing and drone development, extends Russian influence into the Western hemisphere through 2030. This strategic partnership, marked by Venezuela’s extradition of Ukrainian-allied fighters and resistance to international “coercive measures,” creates a new axis of anti-Western cooperation. While Russia’s promise of sophisticated military equipment to Venezuela may be limited by its Ukraine war commitments, the alliance represents a troubling expansion of global military tensions. The partnership effectively creates a Russian foothold in South America, potentially transforming regional disputes into broader international conflicts and challenging the existing peaceful order in the Western hemisphere. This development risks escalating global tensions beyond the current Ukraine conflict into a wider geopolitical confrontation.
European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen’s discussion with President-elect Trump about replacing Russian LNG with U.S. exports signals a critical moment for global stability. This energy shift could significantly reduce Russia’s economic leverage over Europe, potentially affecting Moscow’s ability to fund military operations.
The termination of Ukraine’s air service agreement with Iran highlights an escalating global security concern, as Iran’s military alliance with Russia threatens international stability. Iran’s role in both the 2020 downing of Ukraine International Airlines flight PS752, killing 176 civilians, and its current supply of drones and missiles to Russia for the war against Ukraine, demonstrates a pattern of actions that undermines world peace. This strengthening military partnership between Iran and Russia represents a significant shift in global alliances that could have far-reaching implications for regional stability and international security, particularly as Iran continues to arm Russia’s aggressive military campaign in Ukraine.
The Path to Peace in Ukraine
Russian President Putin’s continued distortion of historical facts presents a major obstacle to peace negotiations with Ukraine. His false claim that Russia only invaded after Ukraine sought NATO membership – when in fact Ukraine didn’t abandon neutrality until after Russia’s 2014 Crimean invasion – reveals a troubling pattern of rewriting history to justify aggression. By violating the 1994 Budapest Memorandum, where Russia promised to respect Ukraine’s sovereignty in exchange for nuclear disarmament, and by attempting to legitimize territorial seizures through sham referendums in Crimea, Donetsk, Luhansk, Zaporizhia, and Kherson, Putin demonstrates an unwillingness to engage in honest diplomatic dialogue. This manipulation of facts and international agreements severely undermines the foundation of trust necessary for any meaningful peace negotiations, suggesting a concerning preference for military conquest over diplomatic resolution.
Ukrainian President Zelensky firmly rejected any European concessions to Russia during a summit in Hungary on Thursday, calling such compromises “unacceptable.” The situation has become more complex following Donald Trump’s election victory, as questions arise about future US support for Ukraine. Russia’s President Putin has demanded Ukraine surrender territory as a condition for peace talks, while Zelensky maintains Ukraine will not give up land for peace.
Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orbán warned on Friday that Europe cannot sustain Ukraine’s war effort alone if the US withdraws support following Donald Trump’s election victory. Speaking at an EU summit in Budapest, Orbán stated that Ukraine is losing the war and predicted American withdrawal from the conflict. According to The Wall Street Journal, Trump’s team has drafted a peace plan that would require Ukraine to postpone NATO membership for 20 years, freeze current front lines, and establish a demilitarized zone. The plan suggests European allies would monitor any ceasefire, while the US would continue providing military training and weapons support.
Turkish President Erdogan expressed optimism Friday that Donald Trump’s election victory could help end the conflict in Ukraine. Speaking after a summit in Budapest, Erdogan emphasized that peace would come through diplomatic efforts rather than more weapons and fighting, stating “More weapons, bombs, chaos and conflict will not end this war, but more dialogue, diplomacy and agreement will open the door to peace.”
A significant diplomatic breakthrough occurred as Ukrainian and Russian Ombudsmen met in Belarus, marking their first public meeting since March 2022. The humanitarian talks, facilitated by the International Committee of the Red Cross, demonstrated both sides’ willingness to engage in diplomatic dialogue despite ongoing hostilities. The meeting yielded concrete humanitarian results: the dignified return of 600 fallen soldiers to their homelands (563 to Ukraine, 37 to Russia), establishment of a letter exchange system between Ukrainian families and POWs, and the emotional reunion of a 91-year-old woman with her son. Following October’s successful exchange of 95 prisoners from each side, this meeting represents a potential channel for continued humanitarian cooperation and dialogue, even as military conflicts persist.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Russian forces used chemical weapons 323 times against Ukrainian positions in October 2024, bringing the total to 4,613 documented cases since February 2022. The attacks utilized K-51 and RG-VO munitions containing banned riot control agents and unidentified chemical compounds, including chloropicrin, delivered via grenades and other ammunition. Ukrainian soldiers report facing up to six gas attacks daily on the front line. While these agents are not necessarily lethal, their military use violates the Chemical Weapons Convention, which Russia has signed, making them prohibited under international law. Both the U.S. and UK have confirmed Russia’s use of chemical weapons and imposed sanctions on responsible Russian units. According to the CDC, chloropicrin exposure can cause severe irritation to skin, eyes, and internal organs when inhaled.
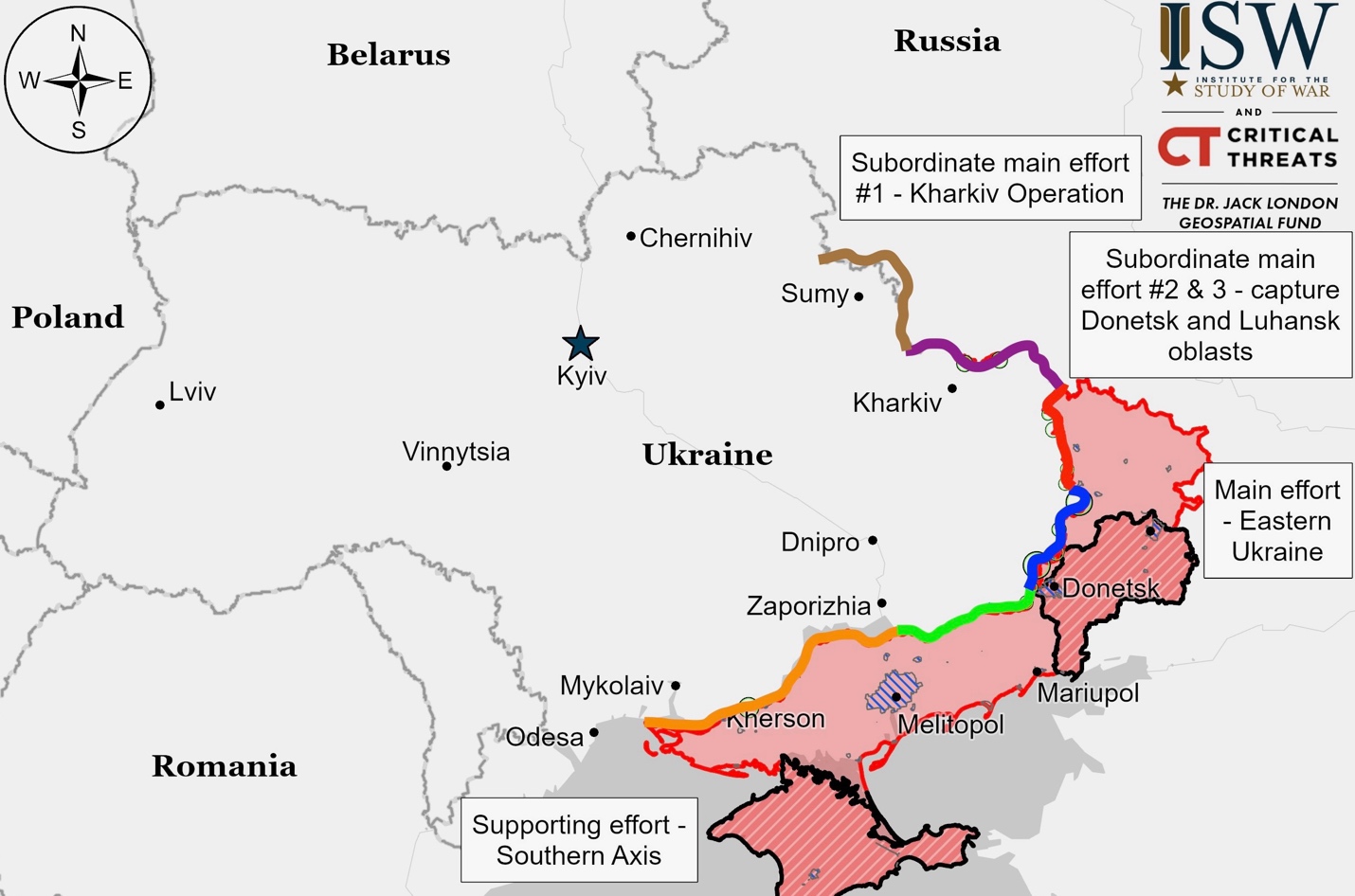
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Russian and Ukrainian forces are engaged in increased fighting along the northwestern edge of the Ukrainian salient in Kursk Oblast. Ukrainian forces made a small advance near Novoivanovka, while Russian forces claimed heavy combat around Darino and Plekhovo. The Russian Ministry of Defense reports ongoing battles near several settlements including Darino, Nikolaevo-Darino, Novoivanovka, Zeleny Shlyakh, Pogrebki, Malaya Loknya, and Staraya Sorochina.
According to Ukrainian President Zelensky, approximately 11,000 North Korean troops are currently stationed in Russia’s Kursk Oblast near the Ukrainian border, with some having already engaged in combat against Ukrainian forces and suffered casualties. Ukraine’s Defense Minister Umerov confirmed the first clashes between Ukrainian and North Korean soldiers. The deployment appears to be part of Russia’s strategy to reinforce its positions while maintaining offensive operations in eastern Ukraine.
Ukrainian military intelligence (HUR) conducted a drone strike on the Saratov Oil Refinery in Russia, located about 1,500 kilometers from the Ukrainian border, causing a fire and damaging the facility. The refinery, owned by Russian state oil company Rosneft, produces seven million tons of oil annually and was reportedly hit when drone debris struck a fuel tank and equipment at the site. While Russian officials claim air defenses intercepted the drone with debris falling in the industrial Zavodsky district and report intercepting 17 Ukrainian drones overnight with six shot down over Saratov Oblast, Ukrainian sources report successful hits on oil refineries and fuel tanks at the facility. This attack marks the resumption of Ukraine’s long-range drone campaign against Russian oil infrastructure after a month-long pause.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched attacks near Vovchansk, northeast of Kharkiv City, but failed to make any advances.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces attacked along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line but made no confirmed advances, despite claims of capturing positions near Kucherivka, Petropavlivka, and Kolisnykivka. A Ukrainian brigade spokesperson reported that Russians are relying more on infantry assaults than armored vehicles in the Kupyansk area, with poor weather reducing their air operations. Fighting continues across multiple settlements including Kindrashivka, Kruhlyakivka, Zahryzove, Berestove, Lozova, Vyshneve, Pershotravneve, Terny, Zarichne, Torske, Serebryanka, and Hryhorivka.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces launched attacks near the city of Siversk, focusing on three areas: Bilohorivka to the northeast, Vyimka to the southeast, and Pereizne to the south. While a Russian military blogger claimed advances north of Ivano-Darivka, these claims remain unconfirmed.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces made advances south of Chasiv Yar on November 8, with confirmed movement to a mine area east of Stupochky. Russian forces reportedly captured the mine and crossed the Siverskyi-Donets Donbas canal near Klishchiivka. While Russian sources claim their infantry advanced three kilometers along Chasiv Yar’s flanks and continued operations near Bondarne, Bila Hora, and Stupochky, some of these claims remain unverified.
Toretsk
Russian forces conducted offensive operations near Toretsk and toward Shcherbynivka with no confirmed frontline changes.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces continued operations near Pokrovsk. While Russian sources claim advances near several locations including Novooleksandrivka, Selydove, Hryhorivka, Petrivka, and Yurivka (reportedly up to 400 meters), these claims lack visual confirmation. Fighting continued around multiple settlements including Myrolyubivka, Novotoretske, Promin, Krutyi Yar, Sukyi Yar, Lysivka, Selydove, Hryhorivka, and Vyshneve.
Kurakhove
Russian forces made small advances southeast of Kurakhove along the H-15 highway, confirmed by video evidence. A Ukrainian brigade spokesperson reported Russian attacks from both north and south of Kurakhove, with increased intensity despite poor weather. While Russian sources claim advances near several locations including Zorya, Sontsivka, Novoselydivka, Voznesenka, Illinka, and Berestky, most remain unconfirmed. Fighting continues around multiple settlements near Kurakhove.
Russian General Pavel Klimenko, commander of the 5th Donetsk Motorized Rifle Brigade, was killed near Krasnohorivka, Ukraine on November 7, reportedly by a drone strike while riding his motorcycle. The 47-year-old general allegedly ran torture camps in occupied Donetsk, where he extorted soldiers’ salaries and forced injured troops into assault groups. His brigade was also accused of torturing pro-Kremlin U.S. blogger Russell Bentley to death in April 2024, after mistaking him for an American spy. Klimenko is the eighth confirmed Russian general killed in the Ukraine war, with his death verified through his sisters’ social media posts and Russian investigative media.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces advanced north of Vuhledar with video evidence showing Russian forces progressing near Bohoyavlenka. Russian sources claim their armored vehicles moved 1.6 kilometers north of Bohoyavlenka, with additional advances northeast of Vuhledar and near Yasna Polyana and Maksymivka. Fighting continues around several settlements including Antonivka, Katerynivka, Yelyzavetivka, Bohoyavlenka, Trudove, Maksymivka, Sukhyi Yaly, and Rozlyv.
Two Russian soldiers, Anton Sopov, 21, and Stanislav Rau, 28, received life sentences from a Russian military court for murdering the nine-member Kapkanets family, including two children aged five and nine, in occupied Volnovakha, Donetsk Oblast. The soldiers killed the family in their sleep on October 27 after they refused to vacate their home for the soldiers’ use. While Russia typically denies war crimes in Ukraine, this rare prosecution of its own troops comes amid Ukraine’s documentation of 137,000 Russian war crimes, including mass child abductions, torture, and civilian murders. Both soldiers pleaded not guilty in a secret trial, having been arrested in Russia the same day Ukraine reported the killings.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces are reportedly operating near Pryyutne, southwest of Velyka Novosilka, along the border area between Donetsk and Zaporizhia Oblasts.
Zaporizhia Line
Positional fighting continued near Novoandriivka, northwest of Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast with no confirmed frontline changes.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Fighting continues along the eastern bank of the Dnipro River in Kherson Oblast with no confirmed frontline changes. Russian military bloggers report that five Russian units are seeking funds to purchase boats, highlighting ongoing shortages of watercraft for their Dnipro River operations.
Ukraine News
Russia launched a major overnight attack against Ukraine using 97 weapons: one Iskander-M ballistic missile, four cruise missiles, and 92 drones. Ukrainian forces intercepted 62 drones and all four cruise missiles across multiple regions including Odesa, Kyiv, Kharkiv, and Sumy. A Russian missile struck civilian infrastructure in Sumy, while falling debris damaged residential areas in Kyiv, injuring four people and damaging several private homes and vehicles. In Kharkiv City, 25 people were injured when a strike hit a 12-story apartment building. In Odesa, drone attacks killed one person and injured nine others, damaging residential buildings and causing fires. Of the injured in Kyiv, one victim is in serious condition, while two others are in moderate condition.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 4 INJURIES: 55
Russian forces launched drone and missile attacks on Kyiv and its surrounding region overnight. While air defenses intercepted all targets, falling debris damaged six houses and four cars in Kyiv Oblast, and injured four civilian drivers who were hospitalized. One driver is in serious condition, two are in moderate condition, and one suffered minor injuries. The air raid lasted nearly 10 hours.
Russian forces attacked twelve border communities in Sumy Oblast causing 129 explosions across the region and injuring eight civilians. The attacks targeted Sumy, Khotin, Yunakivka, Bilopillia, Krasnopillia, Velyka Pysarivka, Novoslobidske, Putyvl, Shalyhyne, Druzhbivka, Seredyna-Buda, and Znob-Novhorodske. Five people were injured in Krasnopillia where public buildings and homes were damaged, while three were injured in Sumy from a ballistic missile strike. Bilopillia, located 8 kilometers from the Russian border, faced the heaviest assault with 65 explosions recorded.
A Russian attack in the Kramatorsk district of Donetsk Oblast resulted in two deaths and six injuries. The assault damaged multiple civilian structures, including five high-rise buildings, nine houses, and two administrative buildings.
A Russian mass drone attack on Odesa Oblast killed one person and injured eight others, with a 91-year-old woman suffering acute stress. The assault damaged residential buildings, shattered school windows, and caused gas pipe explosions in Odesa city.
Russian forces attacked 16 settlements in Kherson Oblast, including Kherson city, resulting in one death and three injuries.
A Russian aerial bomb struck a 12-story apartment building in Kharkiv’s Saltivskyi district, injuring 25 people and causing significant damage, Mayor Ihor Terekhov reported. In Kharkiv Oblast, Russian shelling injured a 19-year-old man in Kozacha Lopan village and damaged residential buildings.
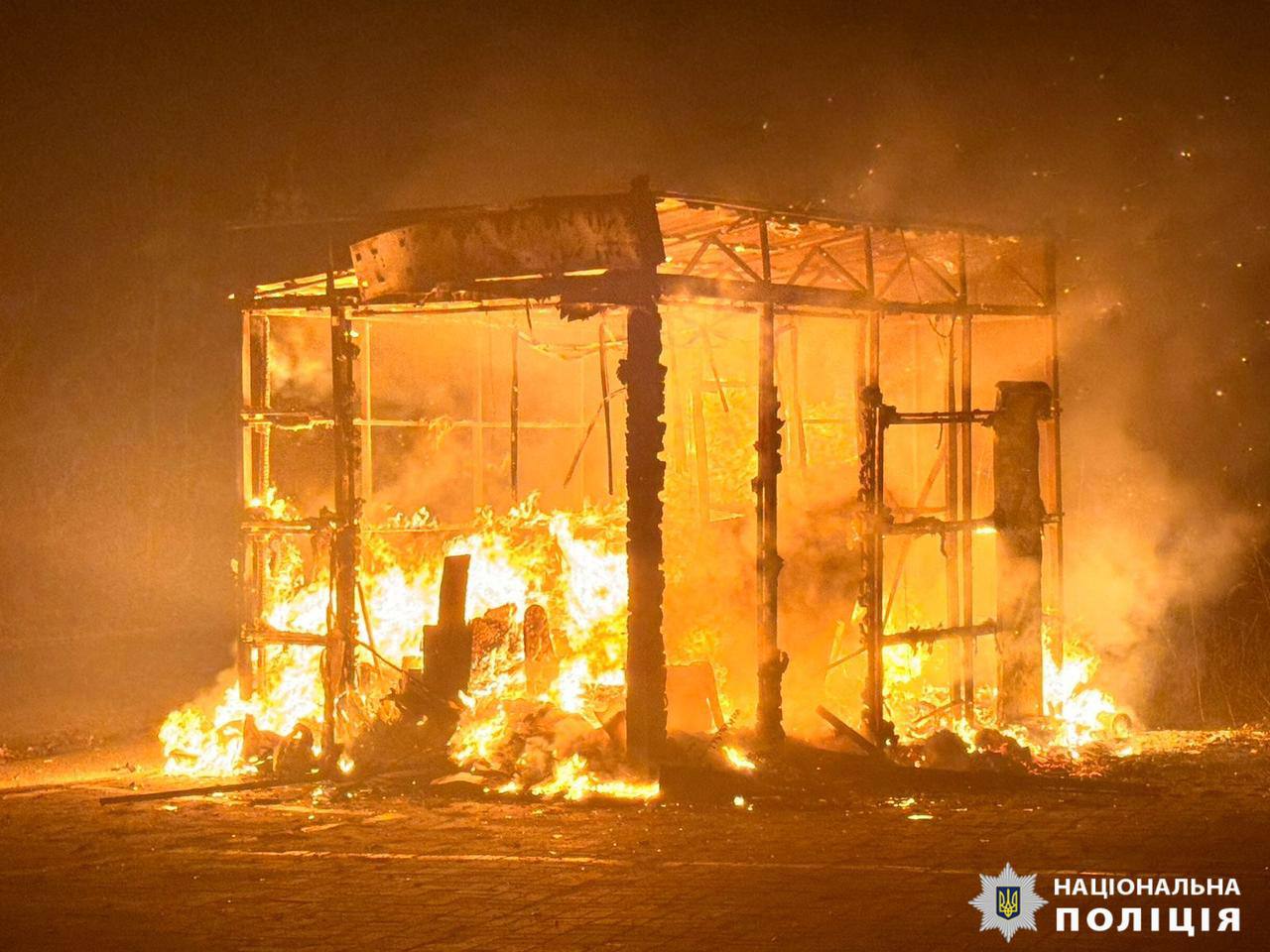 The aftermath of the Russian attack against Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine. (Kyiv Oblast Regional Police / Telegram)
The aftermath of the Russian attack against Kyiv Oblast, Ukraine. (Kyiv Oblast Regional Police / Telegram)
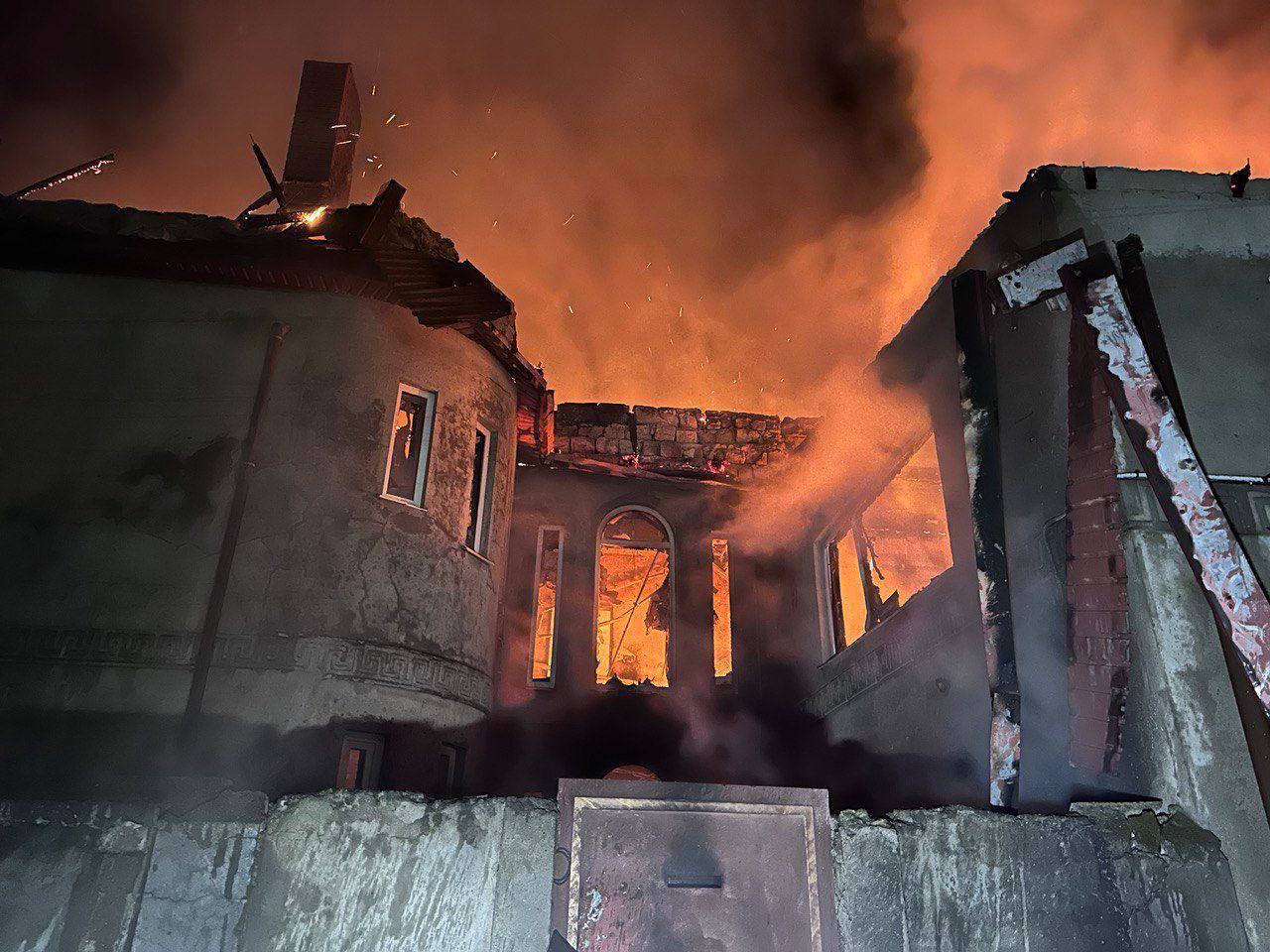 The Russian military launched a mass drone attack on southern Odesa Oblast. (Odesa Oblast Governor Oleh Kiper / Telegram)
The Russian military launched a mass drone attack on southern Odesa Oblast. (Odesa Oblast Governor Oleh Kiper / Telegram)
Ukrainian Allies
G7 nations along with South Korea, Australia, and New Zealand issued a joint statement expressing “grave concerns” over North Korea’s military involvement in Russia. Zelensky has called for stronger international action and permission to use Western long-range weapons to target North Korean troop gatherings on Russian territory, warning that without adequate response, Russia might significantly increase its deployment of North Korean forces.
Reuters reports that the Biden administration has authorized U.S. defense contractors to work in Ukraine to maintain and repair American-supplied weapons. These contractors will be stationed away from the front lines and will not engage in combat. The Pentagon confirmed plans to deliver the full $6 billion in military aid to Ukraine before January 20. The contractors’ presence aims to help Ukrainian forces maintain U.S.-provided weapons systems more efficiently.
The World Bank announced a new $750 million support package for Ukraine on November 7, adding to the $37 billion in budget support received since February 2022. The funds, part of the SURGE project, will support institutional reforms needed for EU accession. World Bank Eastern Europe director Bob Saum praised Ukraine’s ability to maintain state services despite wartime challenges, while Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal expressed gratitude for the continued international support.
Estonia’s Frankenburg Technologies will provide air defense missiles to Ukraine for testing, Ukraine’s Defense Ministry announced on November 8. The missiles, designed to counter drones at altitudes up to 2 kilometers, will be delivered in coming months. Company CEO Kusti Salm met with Ukraine’s Deputy Defense Minister Anatolii Klochko to discuss the tests, with potential for future missile production in Ukraine if trials succeed. This initiative follows a 10-year bilateral security agreement signed in June 2023, where Estonia committed to providing Ukraine with €100 million in defense aid this year and pledged 0.25% of its GDP annually for military support through 2027.
Axios reported that Elon Musk joined a recent 25-minute phone call between President Volodymyr Zelensky and U.S. President-elect Donald Trump, where Musk pledged continued Starlink satellite support for Ukraine and Trump expressed general support for Kyiv. Following the call, Zelensky indicated they agreed to maintain dialogue and strengthen cooperation, though concerns persist about the future of U.S. military support to Ukraine under the incoming administration. Musk, who initially helped Ukraine in 2022 by providing Starlink communication terminals, later restricted their use for strikes against Russian forces. The Wall Street Journal previously reported that Musk has maintained regular contact with Russian President Vladimir Putin and Kremlin officials since late 2022, though Musk claims he spoke with Putin only once in 2021 about space matters. The Ukrainian Presidential Office has not commented on these reports.
Germany will still provide most of its €4 billion pledge to Ukraine despite its government crisis, according to budget committee sources. Following Chancellor Olaf Scholz’s dismissal of Finance Minister Christian Lindner and the coalition’s collapse, the country now faces a potential minority government. The aid package was already reduced from €8 billion in 2024 to €4 billion in 2025. While Scholz wanted to increase Ukraine support to €15 billion by suspending debt limits, Lindner opposed this move. Despite the political turmoil, committed funds can still be disbursed under provisional budget management, ensuring continued support for Ukraine.
The Guardian reports tensions have emerged between Ukraine and the UK since Labour’s rise to power in July, primarily due to Prime Minister Keir Starmer’s hesitancy to supply additional Storm Shadow missiles, which Ukraine uses to strike Russian military targets in Crimea. During their recent meeting at the European Political Community Summit in Budapest, Starmer assured President Zelensky of Britain’s “unwavering” support, but made no concrete commitments on missile supplies. Ukrainian officials expressed frustration over Starmer’s postponed visits and the appointment of Jonathan Powell as national security adviser, viewing these developments with concern, especially as they coincide with Russian advances in eastern Ukraine and increased missile attacks.
Russia News
Russian President Putin has acknowledged a critical labor shortage in Russia, particularly in the construction industry, which needs at least 250,000 additional workers. While currently employing half a million people, the construction sector could absorb another 600,000 workers. Despite this urgent need, Putin emphasizes that migrants must speak Russian, be well-educated, and comply with Russian laws and traditions before being welcomed. This stance highlights a challenging balance between Russia’s desperate need for foreign workers and domestic concerns about migrant assimilation. The situation is further complicated by widespread anti-migrant sentiment among Russians, particularly toward Central Asian workers, even as the country relies heavily on this workforce to address its labor shortages.
Russia’s war economy is creating an unusual economic shift, with workers in military-related industries now earning more than double the national average salary (about 100,000 rubles or $1,025 monthly). In regions like Tatarstan and Bashkortostan, manufacturing wages have increased by 66% since 2021, primarily due to military production demands. However, experts suggest this wartime economic boost is unsustainable long-term.
Swedish retail giant Ingka Group has completed its exit from Russia with the sale of its last asset – a 180,000-square-meter IKEA distribution warehouse in Esipovo, near Moscow, to Russian businessman Robert Uzilov. The company had suspended operations in Russia and Belarus in March 2022 following the invasion of Ukraine, gradually selling its assets including factories to Luzales and Slotex, 14 Mega shopping centers to Gazprombank, and its Khimki Business Park headquarters to KLS-Khimki. The sale was approved by Russia’s Foreign Investment Commission and followed government guidelines requiring a discount and mandatory budget contribution.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1660
707540 |
Tanks +5
9238 |
Artillery +23
20249 |
Arm. VEH +36
18697 |
Aircraft
369 |
Heli
329 |
Ships
28 |
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Belgorod Oblast is now recruiting women into its volunteer defense unit BARS-Belgorod, with Governor Gladkov announcing three recent female enlistments. This follows a pattern of Russian forces recruiting women from prisons and occupied Ukrainian territories, possibly indicating significant personnel shortages in the Russian military despite traditional restrictions on women in combat roles.
Russia is emphasizing its drone warfare capabilities, with footage showing a Serbian volunteer receiving specialized training at the “Republican Center of Unmanned Systems” in occupied Donetsk Oblast. The center, opened in early 2022, focuses on drone operations training, marking a shift from earlier practices where drone pilots were reportedly reassigned to infantry units.
Russian sources report upgraded versions of their TOS-1A “Solntsepek” and TOS-2 “Tosochka” thermobaric artillery systems, claiming improvements in firepower, range, armor, and automation. These enhanced systems are said to match Iskander missile capabilities.
Controlling the Narrative and Russian Propaganda
Russian prosecutors seek a six-year sentence for Ukrainian-born pediatrician Dr. Nadezhda Buyanova for allegedly criticizing Russia’s actions in Ukraine during a patient visit. The case stems from claims by a soldier’s ex-wife that Buyanova made anti-Russian statements, which the doctor denies. This case is part of a broader crackdown on dissent in Russia that has led to thousands of arrests since the Ukraine invasion began, with Amnesty International reporting at least 21,000 people were targeted under anti-war laws in 2023 alone.
Russia is using cartoons as a new propaganda tool to promote its war effort, according to Yevgeniy Golovchenko, a political communication expert at the University of Copenhagen. The Rybar Telegram channel, which has over a million followers, produces cartoon series like “Odnazhdy” that portray Russian soldiers as heroes while depicting Ukrainian forces negatively. These cartoons, supported by Russia’s Ministry of Defense, are part of a broader propaganda campaign targeting younger Russians through various media, including schools, art exhibitions, and social media. The effort is part of Russia’s comprehensive strategy to control information, which includes state-controlled TV channels, censorship laws, and the blocking of Western social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
