Summary of the Day:
Russian President Vladimir Putin appears to be shifting away from nuclear threats, focusing instead on Russia’s new Oreshnik ballistic missile as a powerful non-nuclear deterrent. At a Defense Ministry board meeting, Putin emphasized that when used with other conventional munitions, the Oreshnik’s impact could rival nuclear weapons but without radioactive contamination.
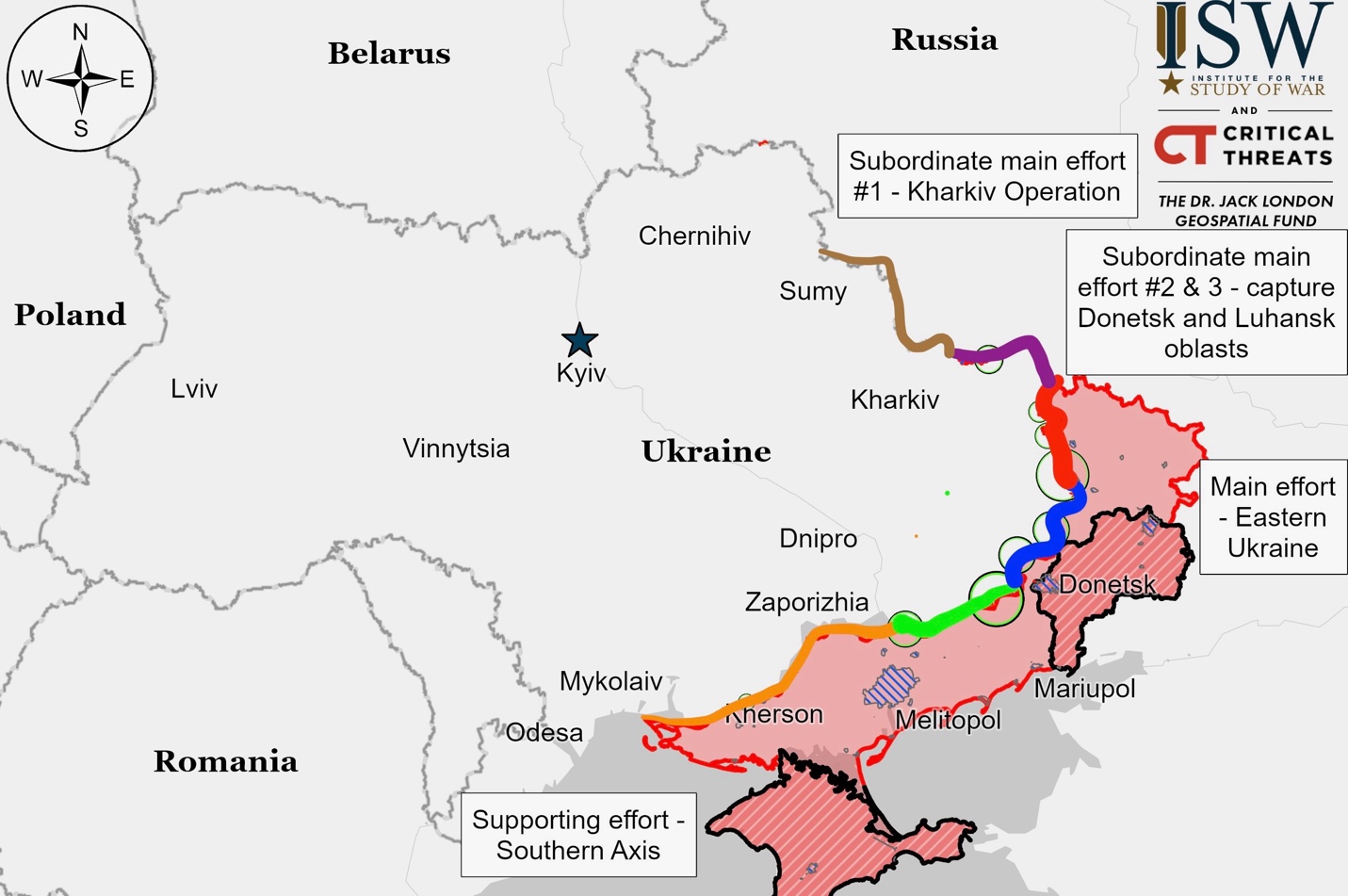
Defense Minister Belousov reinforced Putin’s demands that Ukraine must withdraw from Donetsk, Luhansk, Zaporizhia, and Kherson oblasts before any negotiations. Putin also maintained his stance that Ukrainian President Zelensky is illegitimate, suggesting regime change in Kyiv remains a prerequisite for talks. Belousov reported Russia’s military recruitment of 427,000 volunteers in 2024 barely matches its high casualty rates, which UK Defense Ministry estimates at 1,523 per day in November.
On the battlefield, Russian forces advanced near Chasiv Yar, Kurakhove, and Velyka Novosilka and in Kursk Oblast, while Ukrainian forces regained previously lost positions near Pokrovsk. Putin ordered the creation of new Unmanned Systems Forces to centralize control over drone units, scheduled for completion by third quarter 2025.
In Syria, Russia appears to be orchestrating a major military withdrawal within one month, consolidating forces at coastal bases while negotiating with Hayat Tahrir al Sham (HTS) to maintain its presence at Hmeimim Air Base and Port of Tartus. Ukraine’s intelligence services report Russian forces are evacuating bases near Manbij, Kobani, and Qamishli, with equipment and personnel being transported back to Russia.
Picture of the Day:
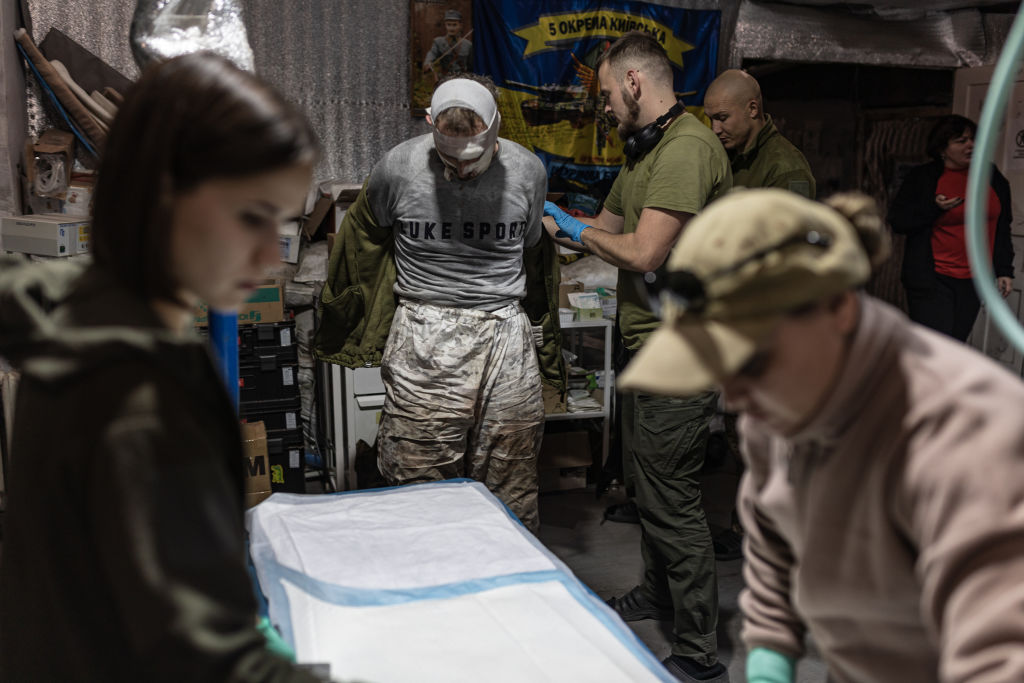 Ukrainian army medics treat a injured Ukrainian soldier in an undisclosed location near the town of Chasiv Yar in Donetsk Oblast. (Diego Herrera Carcedo/Anadolu via Getty Images)
Ukrainian army medics treat a injured Ukrainian soldier in an undisclosed location near the town of Chasiv Yar in Donetsk Oblast. (Diego Herrera Carcedo/Anadolu via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Russian Defense Minister Andrei Belousov announced that Russia must prepare for potential war with NATO within the next decade, citing NATO’s July summit decisions and changing military doctrines. During the same Defense Ministry meeting, President Vladimir Putin accused the West of pushing Russia to a “red line” and threatened to lift all restrictions on weapons deployment if the U.S. places missiles in Europe and Asia-Pacific. These statements follow Russia’s withdrawal from nuclear arms treaties and its recent deployment of the new Oreshnik missile against Dnipro. The mounting tensions are further complicated by NATO’s increased support for Ukraine, including $43 billion in funding and enhanced air defense systems, while Russia claims to have captured 189 Ukrainian settlements this year. This escalating rhetoric and military positioning between nuclear powers raises significant concerns for global stability and peace.
Estonian Prime Minister Kristen Michal is proposing that members of the northern European NATO coalition increase their defense spending to 2.5% of GDP to counter Russian threats, significantly above NATO’s current 2% target. This proposal comes amid growing global security concerns, with Estonia already committing 3.2% of its GDP to defense in 2024. To promote lasting peace, Michal advocates seizing Russian frozen assets and implementing additional taxes on Russian goods to generate approximately 600 billion euros for Ukraine’s reconstruction. This aggressive economic strategy aims to diminish Russia’s capacity for military actions while strengthening Ukraine’s position in Europe and potential NATO membership, representing a significant shift in European defense policy and international peacekeeping efforts.
Following Assad’s overthrow in Syria, Russia faces significant military and diplomatic challenges. Russia is negotiating with Syrian forces, including Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), over its bases at Hmeimim and Tartus, where troops are experiencing food and water shortages. Chechen leader Ramzan Kadyrov made unexpected appeals to HTS on December 15, praising Russia’s support for Syria while requesting HTS’s removal from Russia’s terrorist organization list. Intelligence sources confirm large-scale Russian withdrawals from bases near Manbij, Kobani, and Qamishli, with forces using Il-76MD and An-124-100 aircraft to evacuate troops and equipment to Russia. HTS’s political bureau reported Russia coordinated the evacuation of 400 soldiers from near Damascus.
According to Al Araby al Jadeed sources, Russia plans to completely withdraw from Syria within one month, potentially maintaining only 3,000 troops at its bases. Ukraine’s Foreign Intelligence Service reported on December 15 that Russia is deploying large landing ships from the Baltic and North seas to Syria and chartering additional vessels to evacuate equipment from Tartus port, where satellite imagery confirms Russian vessels have moved offshore. Western officials note Russia may be shifting some naval assets to Libya, potentially seeking port access in Benghazi. The Financial Times revealed Assad had transferred $250 million in cash to Moscow between 2018-19, where his family was purchasing luxury assets, suggesting preparation for this outcome.
The Path to Peace
Putin claimed that Ukraine’s Constitution does not extend presidential powers under martial law, only parliamentary powers, though this misrepresents Ukraine’s actual constitutional provisions. Under Ukraine’s Constitution and martial law legislation, which has been in effect since Russia’s February 2022 invasion, presidential, parliamentary, and local elections cannot occur during martial law, requiring Zelensky to legally suspend 2024 elections. Putin’s false narrative about Zelensky’s illegitimacy, previously dormant since early Summer 2024, aligns with Russia’s long-term efforts to delegitimize Ukraine’s government and sovereignty. The Kremlin has suggested that only Ukraine’s parliament (Verkhovna Rada) is legitimate for negotiations, indicating that regime change in Kyiv is a precondition for any talks. Russia appears unwilling to engage in genuine negotiations unless Ukraine concedes its sovereignty, including the removal of its legitimate government and exclusion from negotiations.
Russian Defense Minister Belousov announced that Moscow plans to seize all of Ukraine’s Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia regions in 2025, reaffirming Putin’s June 2024 territorial demands that required Ukrainian forces to withdraw from these territories, recognize Crimea and Sevastopol as Russian, and abandon NATO aspirations before any peace negotiations; Security Council Deputy Chairperson Dmitry Medvedev echoed these demands on December 12, demonstrating Russia’s expectation to gain control of these territories without Ukraine’s consent and before any peace talks, even though Ukraine currently maintains control of Kherson and Zaporizhzhia regional capitals, while Russia partially occupies Donetsk and Luhansk, which it first invaded in 2014.
At his first post-election news conference at Mar-a-Lago, President-elect Donald Trump addressed the Russia-Ukraine war, expressing his intention to end the conflict and reduce U.S. military aid to Ukraine to encourage peace negotiations, while his national security advisor Mike Waltz announced that Trump’s team is exploring options for permanently ending the war, including potential strategies of delaying Ukraine’s NATO entry in exchange for arms and freezing current front lines, with Trump aiming to bring both sides to the negotiating table and seeking increased European partners’ involvement in regional security; though Trump hadn’t invited Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky to his upcoming inauguration, he noted Zelensky would be welcome to attend, following their recent meeting with French President Emmanuel Macron in Paris on December 7, where Trump called for an immediate ceasefire despite no specific peace plan emerging.
Polish Foreign Minister Radoslaw Sikorski called for Western nations to pressure Russia, not Ukraine, into peace negotiations. Speaking in Brussels as Europe anticipates reduced U.S. support under President-elect Trump’s future administration, Sikorski emphasized that Russia, as the aggressor, should face pressure to negotiate. The EU demonstrated continued support for Ukraine by adopting its 15th sanctions package against Moscow, targeting Russia’s shadow fleet and defense sector.
Ukraine’s Foreign Ministry criticized Hungary’s recent “peacekeeping” statements as unrealistic, particularly addressing Hungarian Foreign Minister Peter Szijjarto’s claim that President Zelensky had declined a Christmas ceasefire proposal. The ministry accused Hungary of advocating for Ukraine’s surrender while maintaining close ties with Moscow and blocking EU military aid to Kyiv.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukraine’s Security Service (SBU) conducted a special operation in the occupied Donetsk region, targeting Russian military depots near the village of Markine. The drone strike destroyed storage facilities containing artillery shells, mortar rounds, tank ammunition, anti-tank missiles, mines, grenades, and other ammunition. The attack triggered a chain of explosions that also destroyed a nearby fuel storage facility.
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative Russia
Russian forces made advances in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast. They captured the settlements of Nechaev and Nizhnyaya Parovaya, with confirmed footage showing Russian movement southwest of Nechaev. Fighting continues across several locations, including near Guyevo, Kremyanoye, Novoivanovka, Plekhovo, and Cherkasskaya Konopelka. Ukrainian forces reportedly launched a counterattack near Novoivanovka, while Russian airborne and naval infantry units remain active in the region.
North Korean forces are experiencing heavy losses in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast, with at least 30 soldiers killed or wounded during operations near Plekhovo, Vorozhba, and Martynovka between December 14-15, along with three others reported missing near Kurilovka; Pentagon spokesperson Major General Patrick Ryder confirmed these casualties, and Ukraine’s Main Intelligence Directorate (HUR) reported that North Korean forces also accidentally killed eight Russian soldiers in a friendly-fire incident, while Russian sources attempt to downplay the casualties and instead promote stories of North Korean successes; North Korean troops, who have been present in Kursk since October in support roles, are reportedly being sent into battle without armored support, and while they are described as well-trained with Soviet weaponry, their effectiveness diminishes significantly when facing heavy losses, leading to reinforcements from North Korea’s 94th Special Forces Brigade.
President Volodymyr Zelensky confirmed Russia’s deployment of North Korean troops in the Kursk region and suggested their potential presence in other areas along the front line, claiming that Russia is attempting to conceal North Korean military casualties by allegedly burning soldiers’ faces after death; Western officials previously reported that over 10,000 North Korean troops had gathered in Kursk Oblast following Ukraine’s surprise incursion in August, with Ukrainian intelligence indicating that at least 30 North Korean soldiers have been killed or wounded since the first reported clashes in early November, marking their first confirmed direct combat engagement.
Ukraine’s intelligence service (HUR) reported a successful sabotage operation at Russia’s Krymsk military airfield in Krasnodar Krai, resulting in the destruction of a Su-27 fighter aircraft and three locomotives. This incident adds to a growing list of attacks on Russian military aviation facilities throughout 2024, including strikes at airfields in Moscow, Chelyabinsk, and Omsk. Russian military observers have criticized these security breaches, noting the apparent lack of basic protective measures at these facilities. The attacks are part of Ukraine’s strategy to disrupt Russian military logistics and infrastructure.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched attacks north and northeast of Kharkiv City near Vysoka Yaruha, Vovchansk, and Tykhe but failed to gain any confirmed territory.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces attacked along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line without confirmed advances. Ukrainian forces reportedly pushed Russians from the west bank of the Oskil River north of Dvorichna, though Russians expanded their position south of there. Ukrainian forces repelled a Russian mechanized assault near Borova, destroying four tanks. Fighting continued near several settlements including Zahryzove, Lozova, Nadiya, Hrekivka, Tverdokhlibove, Novoyehorivka, and Terny, with Russian special forces operating in the Serebryanske forest area.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces attacked near several settlements around Siversk (Bilohorivka, Verkhnokamyanske, Ivano-Darivka, and Vyimka) but failed to make any confirmed advances.
Russian forces launched a large, coordinated battalion-sized mechanized assault near Siversk, Ukraine, on December 14, employing over 400 troops, 30 armored vehicles, 13 buggies, and 60 motorcycles in a three-pronged attack southeast of Vyimka, which failed to make territorial gains despite showing improved coordination of communications, electronic warfare, and drone operations; Ukrainian forces inflicted heavy losses, destroying 15 armored vehicles, 40 motorcycles, and causing up to 400 Russian casualties, including communications specialist Lt. Nikita Korelev, whose death prompted criticism from Russian military bloggers about the misuse of specialized personnel in infantry roles; military observer Yuriy Butusov reported that Ukrainian forces ultimately repelled the attack near Vesele through drone strikes, artillery fire, and close combat, despite Russia’s initial capture of four defensive positions.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued attacking Chasiv Yar and nearby Stupochky but made no confirmed advances. While Russian sources claimed progress in southern Chasiv Yar and at the central Refractory Plant, these claims are disputed even among Russian military bloggers. Ukrainian forces report that Russians are now using small infantry groups rather than large mechanized units, attempting to infiltrate defenses via the Siverskyi Donets Donbas Canal’s pipeline system.
Toretsk
Russian forces made a small, confirmed advance in northern Nelipivka, south of Toretsk. While Russian sources claim additional progress in western Toretsk and near the Tsentralna Mine area, these claims remain unverified.
Pokrovsk
Ukrainian forces recaptured positions in western Shevchenko, near Pokrovsk, though Russian sources claim they later retook these positions. While Russian sources report advances near Myrnohrad, Dachenske, Pushkine, Novotroitske, Novoolenivka, and Ukrainka, only their presence about 2.5 kilometers from Pokrovsk’s southern edge is confirmed.
Kurakhove
Russian forces advanced north of Zorya, northwest of Kurakhove, in a mechanized attack. While Russian sources claim additional advances near Dalne and Shevchenko, these remain unconfirmed. Fighting continues in Kurakhove itself, where Ukrainian forces still control about 27% of the town. Ukrainian military reports that Russian forces are illegally disguising themselves as civilians to infiltrate Kurakhove.
Andriivka
Russian forces advanced west of Uspenivka near Vuhledar during a platoon-sized mechanized assault. Fighting has reached Zelenivka’s outskirts after Russian advances from Sukhi Yaly, though claims of Zelenivka’s capture remain unconfirmed. Russian sources report trapping Ukrainian forces in Hannivka, north of Vuhledar. Combat continues across multiple locations including Uspenivka, Kostiantynopolske, Trudove, Sukhi Yaly, and Zelenivka, with numerous Russian units deployed throughout the area.
Velyka Novosilka
Russian forces made a confirmed advance in southern Novyi Komar, north of Velyka Novosilka, pushing westward along Kosmonavta Komarova Street. While Russian sources claim advances west of Neskuchne and control of half of Novyi Komar, these claims remain unverified. Fighting continues around Velyka Novosilka and nearby settlements including Storozheve, Makarivka, and Novosilka.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian and Ukrainian sources reported no fighting in western Zaporizhia Oblast. While Russian military bloggers claimed their forces were intensifying operations and making slow progress near Orikhiv, these claims have not been independently verified. A Ukrainian military observer noted that Russia has begun moving armored vehicles into the region.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched ground attacks along the Dnipro River in eastern Kherson Oblast, though the frontline remained unchanged. Reports indicate Russian forces are using drones to supply their troops on islands in the Kherson River Delta.
Ukraine News
Russia launched 49 drones against Ukraine from the Kursk and Oryol regions. Ukrainian forces shot down 27 drones across several regions including Chernihiv, Sumy, Cherkasy, Khmelnytskyi, Kharkiv, and Dnipropetrovsk. Electronic warfare measures disrupted 19 additional drones.
Ukraine’s “Grain from Ukraine” humanitarian program, launched in November 2022, has garnered support from over 30 countries and international organizations, accumulating approximately $220 million in funding. President Zelensky announced plans to extend this aid to Syria, providing wheat, flour, and oil to address food security concerns. The program, working with the UN World Food Program, aims to assist countries facing severe food shortages. Zelensky suggests this humanitarian initiative could help build foundations for peace while demonstrating Ukraine’s role in global food security.
Ukraine will not extend its Russian gas transit agreement when it expires on January 1, 2025, Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal announced. While Ukraine is willing to discuss transit of non-Russian gas, this decision particularly affects Slovakia, which still relies on Russian gas supplies through Ukrainian pipelines. Slovakia, along with other EU nations, is now working to secure alternative energy sources, as they collectively need about 15 billion cubic meters of gas next year. This development comes as the EU aims to completely phase out Russian fossil fuels by 2027.
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Colonel Vadym Sukharevskyi, commander of Ukraine’s Unmanned Systems Forces, announced that Ukraine has developed a laser weapon system called Tryzub, capable of downing aircraft at altitudes over 2 kilometers. He also revealed advances in drone technology, including “mother drones” that can carry two FPV attack drones and strike targets up to 70 kilometers behind enemy lines. These developments, along with the serial production of the Palianytsia missile-drone hybrid, mark significant progress in Ukraine’s defense capabilities since Russia’s invasion in February 2022.
Ukrainska Pravda reported that Ukraine has begun serial production of its new Peklo missile-drone hybrid, with nearly 100 units already manufactured. The weapon, which has a range of 700 kilometers and speed of 700 km/h, represents a significant advance in Ukraine’s domestic weapons production. While 70% of components are produced within Ukraine, importing the remaining parts poses a challenge. President Zelensky announced plans to produce 30,000 long-range drones in 2024, prioritizing smaller missiles in contrast to Russia’s larger weapons like the Oreshnik.
Ukraine’s Allies
The EU will expand its military training program (EUMAM) to train 75,000 Ukrainian service members by February 2025, EU diplomat Kaja Kallas announced. The program, which began in October 2022 and operates primarily in Germany and Poland, has already trained 60,000 troops. Additionally, the EU provided Ukraine with 4.2 billion euros in December and will begin monthly payments of 1.5 billion euros in January 2025. During the Foreign Affairs Council meeting, Ukrainian Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha requested increased ammunition, air defenses, and support for Ukraine’s defense industry.
Norway’s Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Stoere announced a $242 million allocation to strengthen Ukraine’s navy and counter Russian threats in the Black Sea. The funding, channeled through Norway’s Nansen Support Program, will focus on improving Ukraine’s minesweeping capabilities to ensure safer maritime passage and protect grain exports. This contribution increases the Nansen program’s total value to $13.2 billion, with Norway currently ranking as the 12th largest aid provider to Ukraine.
The EU has adopted its 15th sanctions package against Russia, targeting Russia’s shadow fleet of oil tankers and military-industrial complex, with EU diplomat Kaja Kallas leading measures that include sanctions on 54 individuals and 30 entities, banning 52 vessels transporting Russian oil above the $60-per-barrel price cap from EU ports, while imposing unprecedented full sanctions on Chinese companies like Xiamen Limbach supplying drone components and microelectronics to Russia, along with companies from India, Iran, Serbia, and the UAE supporting Russia’s military; the package also sanctions those responsible for attacks on the Okhmatdyt children’s hospital in Kyiv and North Korean officials No Kwang Chol and deputy chief Kim Yong Bok following Pyongyang’s troop deployment and combat losses near Plekhovo, Vorozhba, and Martynovka; meanwhile, the Business4Ukraine coalition urges the EU to address three major loopholes: ongoing LNG imports, shadow tanker fleet operations bypassing oil price caps, and refined Russian oil products imported through third countries like India and Turkey, as despite current sanctions reducing Russian fossil fuel revenues by about €3.5 billion monthly, Russia’s crude oil earnings increased by 5% in 2024, enabling a 58% increase in military spending, with the EU having purchased approximately €210 billion in Russian fossil fuels since the invasion began, averaging 468 Euros per EU citizen through November 2024.
Russia News
At a Ministry of Defense board meeting, Russian President Vladimir Putin discussed military developments and highlighted Russia’s new “Oreshnik” ballistic missile, emphasizing its non-nuclear but highly destructive capabilities that could rival nuclear weapons without radioactive contamination when used with other conventional munitions; this shift in messaging away from nuclear threats toward the Oreshnik as a powerful non-nuclear deterrent has been consistent across multiple events, including a November 28 Security Council meeting in Kazakhstan, as Ukraine and Western nations have consistently challenged Russia’s nuclear threats throughout the war.
The Ukrainian Security Service announced charges against Russian Lieutenant General Igor Kirillov for the use of banned chemical weapons in Ukraine, with their investigation revealing over 4,800 cases of chemical weapon use since Russia’s invasion deployed via FPV drones using toxic substances like chloropicrin that affect mucous membranes and force Ukrainian soldiers out of trenches, resulting in the hospitalization of more than 2,000 Ukrainian service members and three deaths; international laboratories confirmed the presence of these banned materials, leading to UK and US sanctions against Kirillov and his unit before he was reportedly killed along with his assistant in Moscow when a device planted on a scooter exploded near their residential building, just one day after Ukraine’s Security Service had sentenced him in absentia.
Defense Minister Andrei Belousov has been appointed to lead the Military Construction Company’s Supervisory Board, replacing Sergei Shoigu amid concerns about corruption, with the Defense Ministry filing 73 lawsuits against the company in August 2024 and several officials facing detention for fraud; in his first board meeting, Belousov emphasized completing pending construction projects including hospitals, while also highlighting Russia’s military modernization efforts in AI, robotics, and quantum computing, claiming the military supply system operated without disruptions in 2024 and acknowledging that Ukrainian strikes on Russian rear areas forced changes in how Russia protects and organizes its storage and logistics bases, with Russian military bloggers praising his candid leadership style in contrast to former Defense Minister Shoigu’s approach, which was criticized for corruption and inefficiency.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1600 765110 |
Tanks +4 9567 |
Artillery +8 21159 |
Arm. Veh. +15 19751 |
Aircraft 369 |
Heli 329 |
Ships 28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Putin ordered the creation of the Unmanned Systems Forces within the Russian military, to be completed by the third quarter of 2025. While Defense Minister Belousov described it as a combat arms branch and Putin called it a separate branch, its exact organization remains unclear. This move appears to be part of Russia’s effort to centralize control over its informal drone units, which could affect the coordination between assault, drone, and artillery elements.
Russia recruited over 427,000 volunteer service members in 2024, averaging about 1,200 recruits daily. However, this recruitment rate barely covers or falls short of Russian casualties, which US Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin reported at 1,200 per day, while UK Defense Ministry noted record-high losses of 1,523 daily casualties in November 2024. Russian opposition outlet Vazhnye Istorii reported lower recruitment numbers based on federal payment data, suggesting a significant gap in the fourth quarter to reach Belousov’s claimed total. These numbers, combined with intensified operations in western Donetsk Oblast, indicate Russia is struggling to maintain adequate force levels without resorting to unpopular involuntary mobilization.
Putin announced plans to begin mass production of the Oreshnik intermediate-range ballistic missile following Russia’s first experimental launch against Dnipro on November 21, which he claimed was in response to Ukraine’s use of Western long-range missiles; while Putin boasts of the missile’s capabilities, including speeds of ten times the speed of sound and alleged inability to be intercepted, experts suggest it may simply be an upgraded version of Russia’s 2011 RS-26 missile, with a former Russian defense engineer indicating that mass production would take years due to technological and bureaucratic challenges.
Rostec, Russia’s state defense company, announced plans to expand Tu-214 airliner production at the Kazan Aviation Plant in 2025. The company began testing new Russian-made components in November 2024.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
