Summary: Russian forces executed their second-largest drone and missile strike since the February 2022 invasion began, with Kyiv being a notable target coinciding with EU Commissioner Borrell’s visit, as the conflict with Ukraine intensifies. Amidst this escalation, Dmitry Medvedev issued nuclear threats, likely to dissuade Western support for Ukraine, while domestically, Russia tightened control over information with a new law against “fake” military news. Additionally, Yandex NV announced the sale of its Russian assets for approximately $5.2 billion, as Russia continues to make strategic gains in Ukraine and actively recruits foreign nationals under various guises for its military efforts.
Situation On The Ground And Air
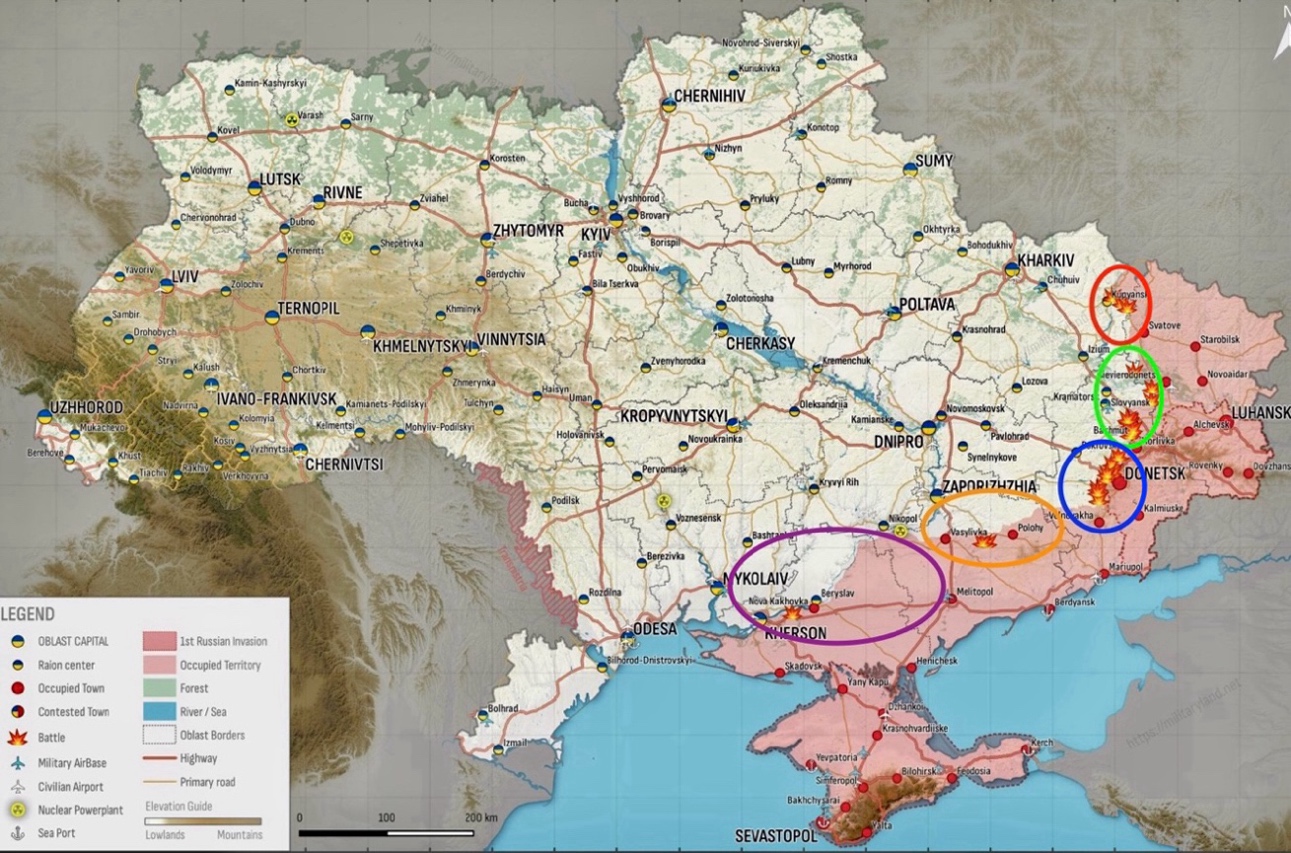
Sloboda Front – Initiative Russia – Target: Recapture Kupyansk
Siversky Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia – Targets: Zherebets River, Siversk, & Chasiv Yar
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia – Targets: Avdiivka, Pervomaiske, Novomykhailivka, & advance from occupied Marinka
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None – Targets: Staromaiorske, Urozhaine, & Robotyne
Dnipro Left Bank Front – Initiative None – Target: Krynky
Despite ongoing positional battles along the Kupyansk line, there have been no significant changes in frontlines, with both Russian and Ukrainian forces engaged in localized skirmishes.
Despite ongoing positional battles along the Svatove-Kreminna line, there have been no significant changes in frontlines, with both Russian and Ukrainian forces engaged in localized skirmishes. Russian claims of tactical advancements near Terny and Bilohorivka lack visual confirmation, and their strategic intentions to control key areas along the Oskil River remain unverified.
The area around Bakhmut saw continued but limited positional engagements, with no significant shifts in the frontline reported. Clashes were noted northwest of Bakhmut near Bohdanivka, west near Ivanivske, and southwest near Klishchiivka. In a related development, Russian forces achieved a minor territorial gain northeast of Niu-York, west of Horlivka, as confirmed by geolocated footage. The Russian Ministry of Defense also stated that Ukrainian assaults were repelled in the northwest Horlivka region.
Russian forces made progress in northern Avdiivka but did not secure any definitive changes in territorial control. Russian milbloggers reported southward advances along Zaliznychnyi Lane in the area, with claims that Russian units executed a tactical maneuver aimed at dividing Ukrainian forces. Ukrainian military observer Kostyantyn Mashovets noted that Russian troops have reached the northern part of a local gardening partnership on the same lane. Russian forces are also said to be pushing west towards the Coke Plant, with efforts to control Hrushevskoho Street, a vital Ukrainian supply route. Claims suggest Russian control over 18-20% of Avdiivka.
Russian troops have achieved tactical advances to the west and southwest of Donetsk City. Verified footage confirms Russian presence in the eastern outskirts of Heorhiivka, just west of Donetsk, with milbloggers asserting Russian control within the settlement. Further footage shows the Russian forces moving into the eastern part of Novomykhailivka on Lenin Street, corroborating reports of Russian entry into the area. Continued positional clashes were also reported in regions west of Donetsk, particularly near Krasnohorivka and Heorhiivka, and to the southwest near Pobieda and Novomykhailivka.
Russian forces have advanced in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border region, with confirmed movements north of Mykilske and near Vuhledar, supported by geolocated footage. Claims from Russian military bloggers suggest further advances towards the Pivdennodonbaska Coal Mine and south of Velyka Novosilka, although not all claims have been visually verified. Ongoing clashes are reported near Velyka Novosilka, with significant Russian military activity, including operations by the 11th Air and Air Defense Forces Army and the 218th Tank Regiment, indicating a continued escalation in the conflict area.
The frontlines in western Zaporizhia Oblast remained stable despite ongoing clashes near Robotyne and Verbove. Ukrainian and Russian sources noted continued positional battles, while a Russian milblogger highlighted Ukrainian drones restricting Russian armored maneuvers in the Orikhiv area and a significant drone shortage for Russian forces.
Amidst ongoing positional conflicts, both Ukrainian and Russian forces achieved territorial gains in the east bank of the Kherson Oblast. Confirmed by geolocated footage released the same day, Ukrainian troops made headway in eastern Krynky, while Russian units advanced in the area’s southern part. Continuous engagements in Krynky were reported by sources from both sides, highlighting the sustained intensity of the conflict in this region.
Human Cost Of The War
In a significant escalation, Russian forces carried out the second-largest drone and missile strike on Ukraine since February 2022, including 64 drones and missiles intercepted by Ukrainian defenses. The attack caused residential damage in Kyiv and involved missiles believed to be of North Korean origin, with some missiles possibly used as decoys. Meanwhile, unconfirmed reports suggest Russia’s unprecedented use of Zircon hypersonic missiles inland. Interior Minister Ihor Klymenko reported that 28 individuals, including a woman rescued from a damaged apartment building, were hospitalized. Additionally, two of the five missiles launched at Kharkiv were identified as North Korean-made, with injuries reported in industrial facilities, prompting international condemnation and calls for an immediate halt to weapons transfers from Pyongyang to Moscow.
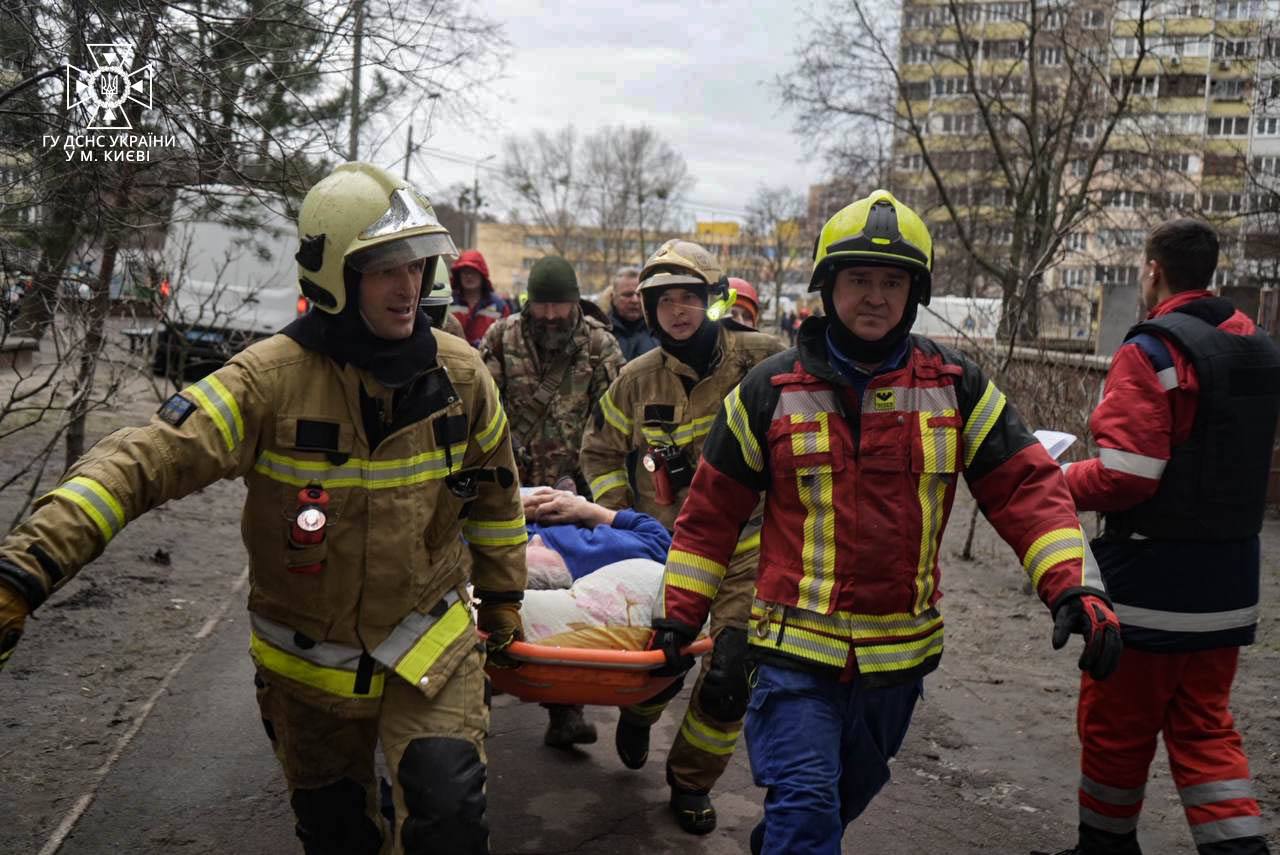

Woman rescued from building in Kyiv
At least 5 Ukrainian civilians were killed and over 56 more injured from Russian attacks over the last 24 hours:
- Explosions in Kyiv resulted in at least four deaths and over 50 injuries, with the city’s military administration confirming the casualties. The Dniprovskyi district experienced significant damage, including injuries to three people, destruction of two high-voltage lines, and disruptions to power and heating infrastructures. Mayor Vitali Klitschko also reported fires in the Holosiivskyi district, affecting vehicles, a repair shop, and an 18-story building, leading to dozens of injuries and evacuations. Interior Minister Ihor Klymenko noted four fatalities under a damaged building’s rubble. Additionally, Kyiv faced temporary water supply issues on its western bank.
- In Kyiv Oblast, Russian attacks damaged numerous houses, apartment buildings, cultural and educational centers, a post office, and vehicles, as reported by the Kyiv Oblast Military Administration. One death and three injuries were reported by regional authorities.
- In Kharkiv, the strikes hit industrial facilities, wounding three people, according to local officials.
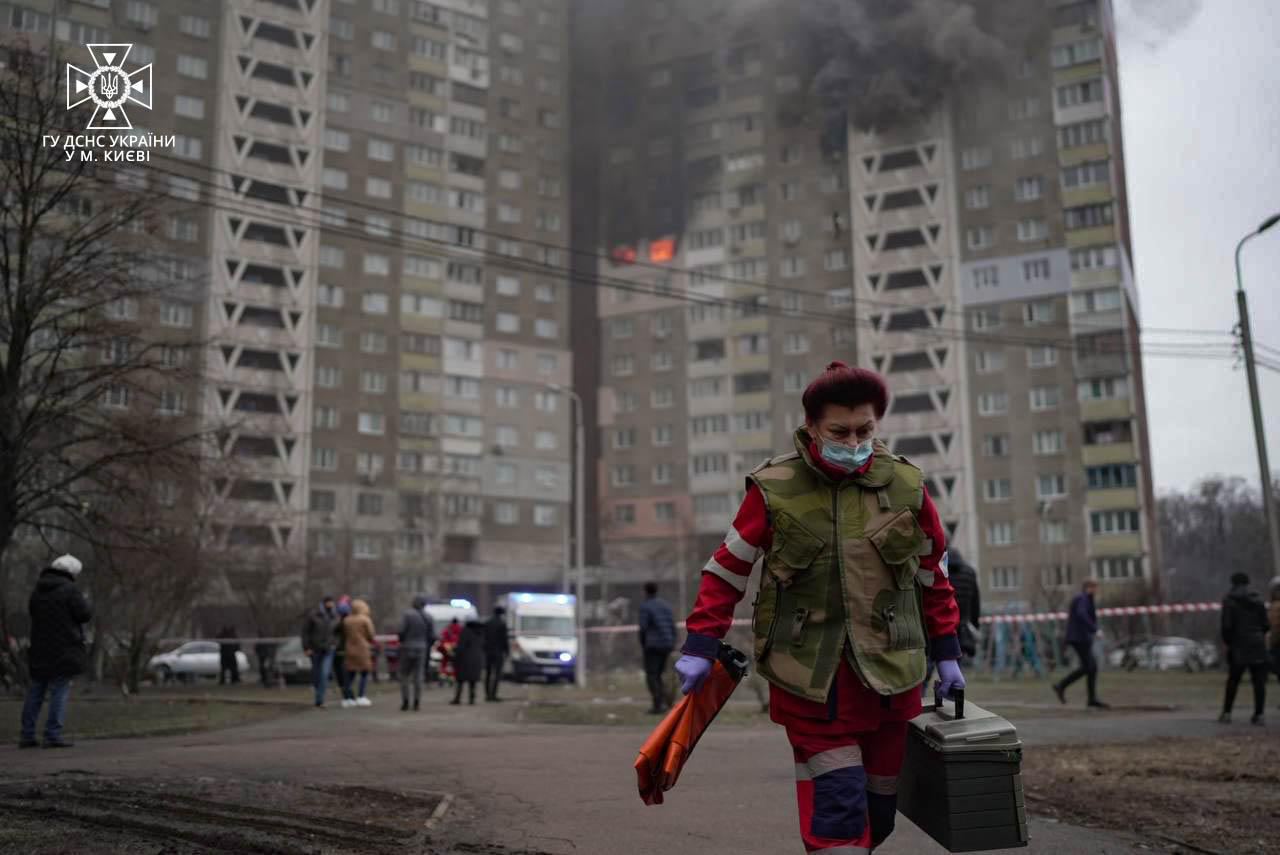 Aftermath of attack on Kyiv
Aftermath of attack on Kyiv
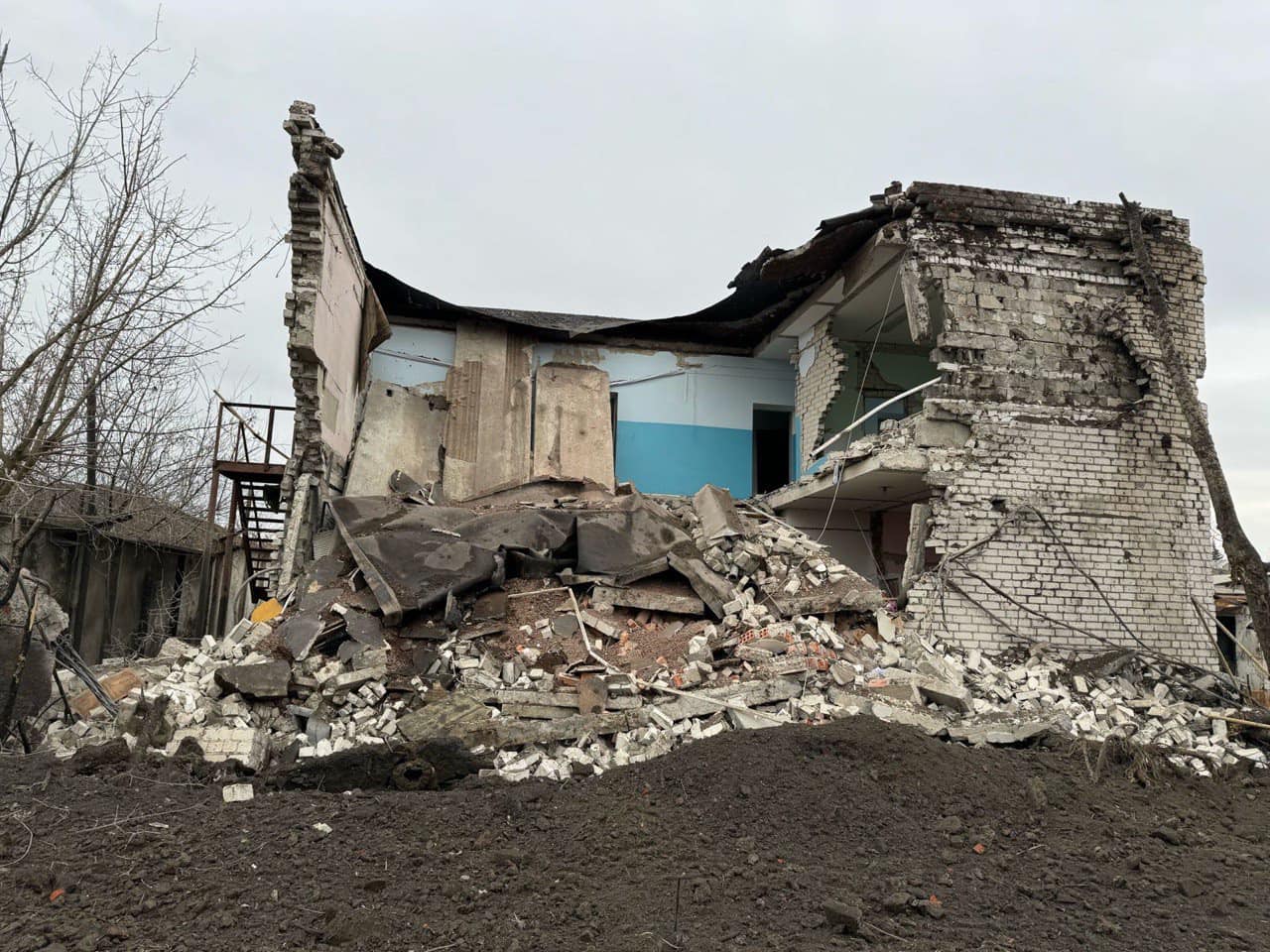 Aftermath of attack on Kharkiv
Aftermath of attack on Kharkiv
Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov reported on Telegram that an attack on Belgorod, located near the Ukrainian border, injured two people and damaged windows in multiple apartments. Gladkov claimed that Russian air defense systems downed seven projectiles, with one person hospitalized due to shrapnel wounds. The Russian Defense Ministry attributed the attack to Ukrainian forces using a multiple launch rocket system, while Ukrainian authorities did not comment on the allegation.
The General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces reported that Russian forces suffered over 890 casualties in the past day.
Ukraine News
President Zelensky and Western leaders, including EU’s Borrell, responded to Russia’s strikes in Ukraine, causing casualties. Zelensky pledged retaliation, emphasizing consequences for terrorists. Borrell highlighted the daily reality of Ukrainians under Russian aggression. US Ambassador Brink emphasized the urgency of security assistance. Presidential adviser Podolyak condemned the attacks as reflective of Russian aggression. Casualty reports from strikes in various Ukrainian cities are ongoing.
A survey by the Razumkov Center, published on Feb. 7, reveals a declining trend in the percentage of Ukrainians who believe the country is heading in the right direction, dropping from a peak of 61% in early 2023. President Zelensky’s proposed leadership reset, amid rumors of Commander-in-Chief Valerii Zaluzhny’s potential dismissal, faces opposition from most Ukrainians. Veterans Affairs Minister Yuliia Laputina’s resignation on Feb. 5 underscores calls for “fresh energy” in government. The survey, conducted from Jan. 19-25, indicates that 41% of Ukrainians view the country’s direction positively, with concerns rising over economic stability, prices, and citizens’ confidence in authorities. Despite challenges, respondents note improvements in defense capability and international reputation, while differing on the timeline for addressing ongoing issues. The survey, conducted among 2,000 Ukrainian adults, excludes Russian-occupied territories and front-line settlements.
Rafael Grossi, Director General of the UN’s nuclear watchdog, visited the Russian-occupied Zaporizhia nuclear power plant in Ukraine’s south on Feb. 7 to assess its safety and operational status, particularly its cooling systems and staffing levels. The plant, Europe’s largest, has been under Russian control since March 2022, facing heightened risks due to its proximity to the frontlines. Grossi noted a significant reduction in staff, from over 10,000 to 2,000-3,000 personnel, posing operational challenges. Despite IAEA concerns and limited access to the plant, Grossi deemed the situation stable but precarious during his tour of the fourth power unit.
Former National Bank Chairman Kyrylo Shevchenko, who fled to Austria from Ukraine in September 2022, is under investigation by Austria’s Economic and Corruption Public Prosecutor’s Office, as reported by Der Standard on Feb. 6. Shevchenko faces charges stemming from his tenure at Ukrgasbank, accused of orchestrating a corruption scheme to embezzle $5.5 million. While Austria rejected Ukraine’s extradition request due to the ongoing war, Shevchenko remains subject to investigation in Austria for breach of trust. Shevchenko claims political persecution and denies the allegations against him. Meanwhile, his asylum application in Austria is pending assessment, a process that could potentially strain relations with Ukraine if approved, according to Der Standard.
Vasyl Maliuk, head of Ukraine’s Security Service (SBU), held a meeting with ambassadors from G7 nations to address concerns regarding the situation surrounding the Bihus.Info editorial office, as reported by the SBU. Maliuk emphasized the SBU’s commitment to defending democratic values and ensuring media independence, particularly amid wartime conditions. The meeting followed parliamentary summons of Maliuk after reports emerged of SBU surveillance on Bihus.Info journalists. The SBU initiated a criminal case into the matter, which is now being transferred to the State Bureau of Investigation.
Ukraine Mobilization and Technology Advances
Ukraine is set to enhance its military with a new unmanned systems force, following an announcement by President Volodymyr Zelensky. Minister of Digital Transformation Mykhailo Fedorov detailed that this unit will introduce a command structure to address challenges in radio frequency planning and electronic warfare (EW), readying three attack drone companies and boasting 67 drone models in its Army of Drones project. Additionally, Fedorov revealed that Ukraine has developed an alternative to the Russian Lancet drone, with combat testing already underway and deployment expected within two months.
Ukrainian lawmaker Yaroslav Zhelezniak announced that Ukraine’s parliament, the Verkhovna Rada, supported an updated bill on mobilization in its first reading. The government aims to enhance the legal framework around conscription to bolster mobilization efforts in 2024. The bill, submitted on Jan. 30 after withdrawing an initial contentious version, outlines transparent rules for the mobilization process and addresses rights of military personnel and conscripts. Key provisions include service exemptions for individuals with disabilities, a reprieve for volunteers before service, and granting annual leave during martial law. The bill also proposes abolishing mandatory conscription for citizens aged 18-24, replacing it with five-month military training, a move criticized by Chief Ombudsman Dmytro Lubinets initially but later supported after discussions with Defense Minister Rustem Umerov.
Digital Transformation Minister Mykhailo Fedorov announced that Ukraine will soon sign contracts for mass-producing attack drones like the Russian Lancet drones. The Lancet, known for its effectiveness against high-value targets, has been widely used by Russia since late 2022. Fedorov highlighted the importance of hitting targets at a 40-kilometer range and emphasized Ukraine’s efforts to accelerate domestic production of drones, aiming to manufacture one million drones this year. President Zelensky’s recent decree established a separate branch of Ukraine’s Armed Forces dedicated to drones, focusing on enhancing drone operations, training, production, and innovation.
Baykar, renowned for its Bayraktar drone utilized by Ukrainian forces in the 2022 invasion, disclosed plans to construct a factory near Kyiv, CEO Haluk Bayraktar informed Reuters on Feb. 6. Having obtained licenses in June 2023, production of combat drones is scheduled to commence in 2025, with a total investment of approximately $95 million. The factory, agreed upon by Kyiv and Ankara in February 2022 and ratified by Ukraine’s parliament in December 2022, is already under construction and expected to employ around 500 individuals. Despite security concerns, Bayraktar asserted unwavering progress in the project.
Ukraine’s Allies
Russia launched its third strike of the year against Kyiv, coinciding with EU High Commissioner Josep Borrell’s visit to discuss ongoing military aid and support for Ukraine. This pattern of timing attacks with high-level foreign visits and international aid discussions suggests a strategic move by Russia. The strikes appear to be aimed not only at military objectives within Ukraine but also at influencing EU and Western perspectives on continuing military support for Ukraine.
Ukraine’s state-owned energy operator, Ukrenergo, reported that the attack did not cause critical disruptions to the energy system. While some damage was reported to power grids in Kyiv and Kharkiv, Ukrenergo stated that its high-voltage power transmission lines are functioning normally. The attack damaged local power grids in Kyiv, leaving around 19,400 consumers and healthcare facilities without electricity, while approximately 1,000 consumers in Kharkiv lost power. Ukrenergo estimated that energy supply would be restored within three to four hours as of 10 a.m. local time.
President Zelensky and EU’s foreign policy chief Borrell met in Kyiv to discuss security cooperation and ammunition deliveries to Ukraine, emphasizing the EU’s ongoing commitment amid Russian aggression. Despite delays, the EU pledged additional financial support, with ongoing discussions on defense assistance. Zelensky urged the EU to prioritize supplying artillery shells, citing critical shortages and Ukraine’s struggle against Russian forces. Amidst concerns over Russia’s increasing military capacity and foreign supplies, Ukraine seeks enhanced EU support. Borrell pledged continued assistance, acknowledging Ukraine’s enduring fight for sovereignty and independence.
On Feb. 6, Canada’s House of Commons approved an updated free trade agreement with Ukraine, with the bill now heading to the Senate for review. Despite opposition from the Conservatives, the deal, supported by the ruling Liberal Party and two other parties, does not include mandatory adoption of a carbon tax for Ukraine, contrary to Conservative concerns. While Conservative leader Pierre Poilievre argues against the bill due to perceived carbon tax implications, he asserts his party’s support for Ukraine and free trade. The original agreement was signed in 2016, and an updated version was signed during President Volodymyr Zelensky’s visit to Canada in September 2023, awaiting ratification by the Canadian parliament.
Ecuador is set to swap Soviet-era military gear for $200 million in US-made equipment, facilitating the US in forwarding this Soviet hardware to Ukraine. The deal includes transferring six Osa-AKM anti-aircraft missile systems, 18 BM-21 Grad MLRS, five Mi-17 helicopters, and numerous anti-aircraft machine guns to the US, which will then supply these assets to Ukraine for battlefield use.
Sweden’s Prosecution Authority announced the closure of its investigation into the explosion and damage to the Nord Stream pipelines, citing lack of jurisdiction. The underwater pipelines connecting Russia to Germany were blown up in September 2022, with ongoing investigations unable to definitively attribute the source of the explosions. While suspicions of Russian involvement persist, Denmark confirmed the presence of a Russian vessel near the site. Although some German investigators suggest Ukrainian involvement, Ukraine denies any role. The German investigation also explores the possibility of Polish involvement, noting hesitancy from Polish authorities to cooperate, although no concrete evidence implicates them. Despite Sweden’s closure, investigations in Germany and Denmark continue.
Life in Occupied Regions
Russian occupation forces are intensifying the militarization of young people in occupied Ukraine, including giving lectures on “countering extremism and terrorism” to instill “patriotism” among Donetsk Oblast schoolchildren. Investigations by Russian opposition media have exposed the involvement of the Russian Investigative Committee and its chief, Alexander Bastrykin, in the deportation of Ukrainian children to Russia, with Bastrykin personally managing their enrollment in Russian military courses. Reports emerged that Russian authorities are further embedding military-patriotic education within occupied Ukrainian schools, utilizing programs like “Lessons in Courage” to indoctrinate youth.
Russia News
The Russian Federation Council passed legislation enabling the government to seize assets from individuals accused of disseminating “fake” news about the Russian military. This move is part of broader efforts to suppress dissent and control the narrative around Russia’s military activities as the country approaches its presidential election in March 2024. The law also targets those convicted of promoting terrorism or extremism and those who advocate for sanctions against Russia. This crackdown follows reports of increasing discontent among relatives of conscripted Russian soldiers over the alleged mistreatment of troops, with the Kremlin seemingly intent on quelling such dissent to project unity and support for the war.
Yandex NV, the Dutch parent company of Russia’s leading internet firm Yandex, announced a deal to divest all its Russian operations, selling them for approximately 475 billion rubles (around $5.2 billion) to a consortium of five Russian companies. The agreement, disclosed on February 5, specifies that at least half of the payment will be made in Chinese yuan. Post-sale, Yandex NV will exit the Russian market, retaining only its international businesses. Despite generating 95% of its 2023 revenue in Russia, as reported by The New York Times, Yandex NV’s move away from Russian activities aligns with what ISW suggests is the Kremlin’s broader strategy to nationalize key companies, thereby tightening its grip on the information space ahead of Russia’s presidential elections in March 2024.
Russian Mobilization and Technology Advances
The Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) disclosed that Russia is actively recruiting Syrian citizens for military mobilization under the guise of employment opportunities as security personnel at oil refineries. According to the GUR, Russia employs “tourist companies” to enlist Syrian civilians for supposed positions in the Sakha Republic. It is reported that approximately 1,000 Syrian recruits are currently receiving specialized urban combat training in Syria, in preparation for their deployment to the Sakha Republic. The GUR further revealed that these individuals are subsequently enticed with offers of higher-paying jobs in the Buryatia Republic, where upon arrival, they are issued Russian passports and conscripted into the military forces. A contingent of these Syrian mercenaries, now holding Russian passports, is stationed in Ulan-Ude, poised to integrate with the Russian 5th Tank Brigade, part of the 36th Combined Arms Army in the Eastern Military District.
Igor Sechin, head of the Russian state oil company Rosneft, is reportedly establishing his own private “Spetsnaz” (special purpose) security force, according to an insider source. This initiative, taking place at Sechin’s golf club in Moscow’s Krylyatskoye Raion, aims to protect Rosneft’s global assets, notably in Africa. Comprised of former Russian National Guard (Rosgvardia) personnel and private security officers, the force is currently two groups strong, each with up to 10 members. Despite efforts, recruitment challenges persist, notably from former Wagner Group members and Ukraine war veterans, deterred by low pay. Sechin plans to expand this force, which started forming in late 2023 and began receiving funding in 2024. This development mirrors a broader trend among Russian state-owned enterprises creating their own security units.
Rostec, a Russian state defense corporation, is currently trialing “Prometheus,” an innovative software and hardware suite capable of transforming manned military vehicles such as infantry fighting vehicles, armored personnel carriers, and tanks into autonomous, remotely operated units. According to a February 6 report by TASS, the Kremlin’s news agency, vehicles outfitted with the Prometheus system can navigate autonomously to designated locations, intelligently selecting the optimal path and circumventing obstacles without human intervention.
Russian Narratives for Propaganda or What Tucker Carlson Will Be Saying Tomorrow
Dmitry Medvedev, Deputy Chairperson of the Russian Security Council, continued his pattern of aggressive rhetoric, suggesting Russia would respond to a hypothetical conflict with NATO using “asymmetric” methods, implying nuclear warfare and warning of an “apocalypse.” This rhetoric aligns with recent Kremlin statements that have rhetorically threatened NATO member states and is perceived as a tactic to deter Western aid to Ukraine. Medvedev’s messages, disseminated through his English language X channel and Russian Telegram, indicate a dual-targeted communication strategy. The narrative, emphasizing NATO’s larger military budget and population, serves to bolster domestic support by portraying NATO as an existential threat, a stance Russia has historically used to justify its actions in Ukraine.
Russian officials persist in blaming the West for the worsening ties between Russia and Western countries, suggesting Western support for Ukraine as the cause, in an effort to deter further Western military aid to Ukraine. This stance overlooks Russia’s own actions, including initiating military conflicts with Ukraine in 2014 and 2022 and issuing threats against the EU and NATO.
Russia’s Allies
Facing Western sanctions, Chinese banks are curtailing transactions with Russian entities. Notably, Zhejiang Chouzhou Commercial Bank, crucial for Russian-Chinese trade, has suspended dealings with Russian and Belarusian clients, a report from Vedomosti on February 6 highlighted. This move, initially targeting goods under sanctions in December 2023, has expanded to a complete stop of transactions over concerns of Western scrutiny. Other Chinese banks are similarly tightening measures, demanding assurances against involvement with sanctioned entities or Russia’s defense sector. Additionally, following the US’s authorization of secondary sanctions, Chinese state-owned banks and Turkish financial institutions have begun reviewing or closing Russian accounts, reflecting a global financial realignment in response to the conflict in Ukraine.
Russian Ambassador to North Korea, Alexander Matseroga, described the current state of Russian-North Korean relations as “unprecedented,” highlighting years of developing “very close mutually beneficial cooperation,” in stark contrast to Russia’s strained ties with the EU and NATO.
The Ukrainian Resistance Center disclosed that the Belarusian Committee of State Security (KGB) has intensified its scrutiny of Ukrainian citizens in Belarus over the last month, conducting more frequent interrogations and searches. According to the Center, these actions aim to recruit Ukrainians as informants for Belarusian special services.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Militaryland.net (maps)
