Summary of the day: Russian financial, economic, and military indicators suggest the nation is gearing up for a potential large-scale conflict with NATO, with preparations likely happening faster than Western analysts anticipated. This includes structural reforms within the military to enhance Russia’s long-term conventional capabilities, alongside continuing the conflict in Ukraine. Additionally, Ukrainian forces conducted a drone strike against a Russian airbase, reflecting a pattern of limited but impactful asymmetric warfare. Furthermore, confirmed Russian troop advances were made near Kreminna and Donetsk City, highlighting ongoing military aggression in the region. Concurrently, pro-Russian narratives in Moldova’s Gagauzia region suggest Russia’s broader strategy to destabilize neighboring countries, mirroring tactics used prior to the invasion of Ukraine.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Russian Threats and Actions Beyond Ukraine
As Russia continues to set the stage for an invasion of Moldova and the Baltic States, and its threats of punitive actions against Armenia, I will include this new section as Russia prepares for World War III to report on their aggressive postures towards other potential targets.
Russia’s military and economic strategy is positioning the country for a potential large-scale conflict with NATO, signaling a shift in focus from the current conflict in Ukraine to more significant long-term confrontations. Despite potential economic strains from sanctions, Russia is preparing for growth that could surpass G7 countries, indicating a robust financial approach to sustaining increased defense spending. Defense Minister Shoigu has elaborated on military advancements, with the formation of an army corps, a motorized rifle division, and plans for further expansion by the end of 2024, despite concerns over manpower and resources. The recent appointment of Lieutenant General Andrei Bulyga as Deputy Defense Minister for logistics support underlines a commitment to enhancing military logistics, viewed as a step to bolster long-term conventional military strength.
In a geopolitical context, Polish and Danish officials, alongside NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg, have expressed apprehension over an expedited timeline for potential Russian aggression towards NATO, highlighting the need for vigilance and preparedness within the alliance. With President Putin’s attention on economic and military growth following his recent election victory, there is a distinct drive to distance from the oligarchic wealth accumulation of the post-Soviet era. Instead, there’s a focus on cultivating a “new elite” among those proving their loyalty on the frontlines, as Russia aims to establish a more self-reliant and potent war economy.
This comprehensive posture, underscored by the ISW’s analysis, emphasizes not only the direct military enhancements but also the broader economic and societal transformations as Russia gears up for a conflict that may have wider global implications beyond Ukraine. Despite Putin’s denials of plans to attack NATO, the systematic military restructure and economic preparations underscore a readiness for possible direct engagement, with the timeline contingent on Russia’s strategic allocation of resources towards these ends.
Russia declared that U.S. spy satellites launched by private firms like SpaceX could be targeted militarily in response to their role in American military initiatives. This statement follows reports of SpaceX’s collaboration with the U.S. National Reconnaissance Office to create a satellite network under a significant contract. The Russian Foreign Ministry flagged these satellites as potential military targets. SpaceX, while often involved in geopolitical tensions, particularly with its Starlink internet during the Ukraine invasion, has denied providing its technology to the Russian military. The use of Starlink by Russian forces has led to a U.S. congressional inquiry and efforts by Ukraine to prevent such use in occupied regions. SpaceX’s CEO Elon Musk, initially praised for supporting Ukraine with Starlink, has faced criticism for his recent comments on the war and assistance to Ukraine.
In Moldova’s Gagauzia region, officials are echoing narratives similar to those Russia used before its invasion of Ukraine, suggesting Kremlin efforts to destabilize Moldova. Gagauzia’s Governor, Yevgenia Gutsul, seeks “protection” from Russia, demanding rights for a better life, market access for Gagauzian products in Russia, and lower gas prices, while emphasizing Gagauzia’s loyalty to Moldova under certain conditions. This stance mirrors Russia’s prior accusations against Ukraine regarding the Minsk Agreements and adds to tensions within Moldova, including with the breakaway region of Transnistria, where recent alleged drone strike footage was called a fake by Moldova’s Interior Minister, aimed at spreading panic. These developments indicate a broader Kremlin strategy using hybrid warfare tactics to undermine Moldovan sovereignty and stability.
Ukraine’s Main Military Intelligence Directorate reported that Russia is intensifying efforts to discredit Ukraine and Western countries in the Middle East. This involves a strategic information campaign using Russian intelligence networks, propaganda tools, and diplomatic missions. Specifically, the Russian Embassy in Cairo, Egypt, has been tasked with spreading anti-Ukrainian and anti-Western disinformation. This initiative is part of Russia’s broader strategy to maintain its influence in the Middle East amid ongoing conflict in Gaza and its expanding cooperation with Iran.
Russian officials, including Security Council Deputy Chair Dmitry Medvedev, have issued threats against France’s consideration of deploying military personnel to Ukraine, warning of potential French casualties and political backlash within France. Medvedev’s comments, shared in French on social media, aim to influence French public and political opinion against such actions. French President Emmanuel Macron has discussed the idea of sending Western troops to Ukraine as part of a broader strategy to enhance security assistance to the country, though he notes the current situation does not demand such measures. Despite Russia’s threats, it has not taken significant action in response to previous Western security assistance to Ukraine.
Situation On The Ground And In The Air in Russian War On Ukraine
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
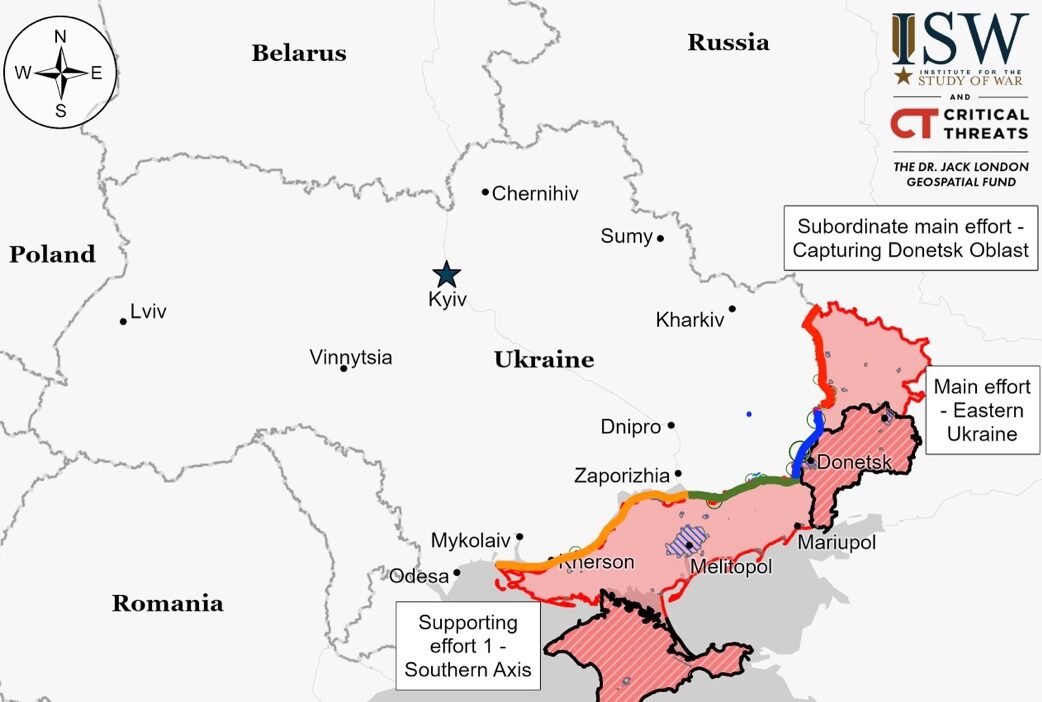
Russian forces achieved gains west and south of Kreminna, despite Ukraine’s Ground Forces repelling a significant assault in the Lyman area. Geolocated footage highlighted Russian advancements towards Terny and showed Ukrainian counterstrikes damaging Russian armored units, although the extent of Russian losses is unclear. Further footage indicated Russian progress near Zolotarivka, south of Kreminna. Continuous battles were reported in areas around Kupyansk, Kreminna, including near Synkivka, Terny, Bilohorivka, and Zolotarivka.
There were no significant changes in the frontline around Bakhmut, despite ongoing battles in various areas. Clashes were reported northeast, northwest, west, and southwest of Bakhmut, involving different locations such as Rozdolivka, Vesele, Spirne, and others. Russian forces were specifically noted to be active west of Bakhmut near Chasiv Yar. Additionally, a Russian military blogger reported an unsuccessful Russian attack near Oleksandropil, aiming to approach Kostyantynivka from the southwest and adjust the frontline away from Horlivka-Donetsk City.
Fighting continued near Avdiivka with no significant shifts in frontlines reported. Clashes were noted in areas northwest, west, and southwest of Avdiivka, including Berdychi, Semenivka, Orlivka, and others. Russian claims of having cleared Orlivka and advances near Pervomaiske and Tonenke lack visual confirmation. Additionally, Russian sources allege control over key Ukrainian supply routes between Berdychi, Orlivka, and Umanske, but these claims also await verification.
Russian troops achieved progress west and southwest of Donetsk City, with battles ongoing in the vicinity. Footage confirms Russian advances near Heorhiivka and Novomykhailivka. Despite these gains, fighting continues, particularly near Krasnohorivka and Heorhiivka to the west, and Novomykhailivka to the southwest of Donetsk City. Reports suggest Ukrainian counterattacks have diminished Russian control in Krasnohorivka, though Russia maintains positions on its southern outskirts. Russian military units are active near Marinka and Krasnohorivka.
No significant changes occurred at the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast frontline, despite ongoing battles. The Ukrainian General Staff noted Russian attacks near Vuhledar and Velyka Novosilka were repelled.
The frontlines in western Zaporizhia Oblast remained unchanged despite ongoing clashes, particularly around Robotyne and Verbove. A Russian military blogger highlighted a lack of electronic warfare capabilities across Zaporizhia’s frontlines.
Fighting persisted in the east bank of Kherson Oblast, particularly around Krynky. Reports indicate Ukrainian forces remain active near the Antonivsky bridge in Oleshky’s northern dacha areas.
Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu announced the formation of the “Dnepr River Flotilla,” a naval unit aimed at enhancing Russia’s combat capabilities in the Dnepr region. This move marks the first confirmation of such a flotilla in the current context, historically known for its roles in various wars. The flotilla is expected to play defensive roles against Ukrainian actions and potentially aid Russian offensive operations across the river. Although its exact size and capability remain unspecified, its presence necessitates strategic adjustments from Ukraine, particularly in resource allocation amidst ongoing military challenges.
Human Cost Of War
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the death of 7 people and injuries to 21 others:
- Early on March 21, a Russian missile attack on Kyiv injured 13 people, including an 11-year-old girl, and caused extensive damage to residential areas, a kindergarten, businesses, and infrastructure. Mayor Vitalii Klitschko reported hospitalizations and ongoing damage assessments, while Serhii Popko noted the impact on the Shevchenkivskyi district. Despite the launch of 31 missiles, including ballistic and cruise missiles from Russian territories, Ukraine’s air defenses successfully intercepted all. The attack triggered multiple explosions across Kyiv, with damages to apartment buildings, educational facilities, and vehicles, leading to evacuations and firefighting efforts. Additional missile debris caused injuries and property damage in Kyiv Oblast.
- A Russian attack on Kharkiv, utilizing a Kh-35 anti-ship missile, resulted in five civilian deaths. Originally designed for naval targets, the missile caused significant damage to an eight-story building and ignited a large fire at a local factory, affecting 10,000 square meters. Kharkiv Oblast Governor Oleh Syniehubov noted that eight civilians were injured.
- A Russian attack on a civilian vehicle in Kherson Oblast resulted in the deaths of two men, both approximately 40 years old, on the road between the villages of Antonivka and Sadove.
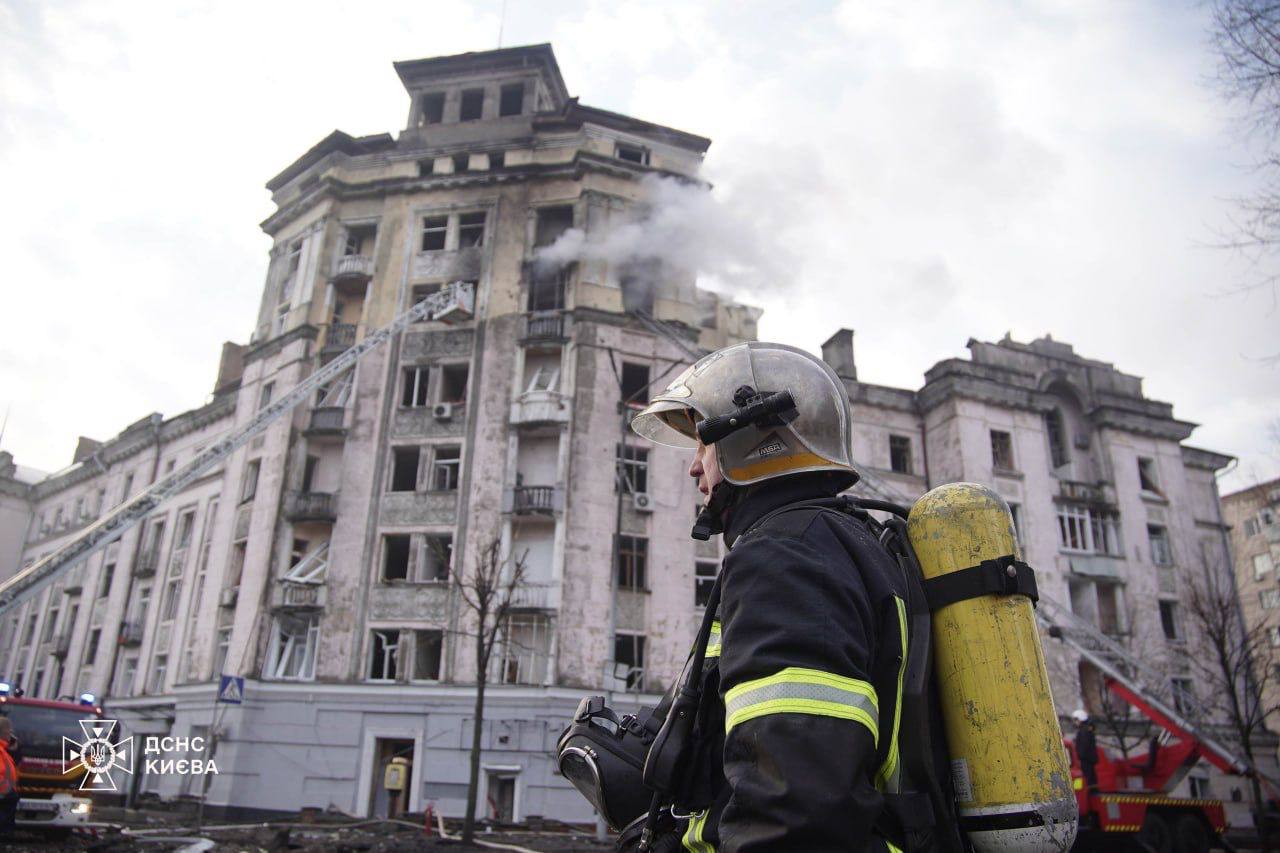 The aftermath of a Russian missile attack against Kyiv
The aftermath of a Russian missile attack against Kyiv
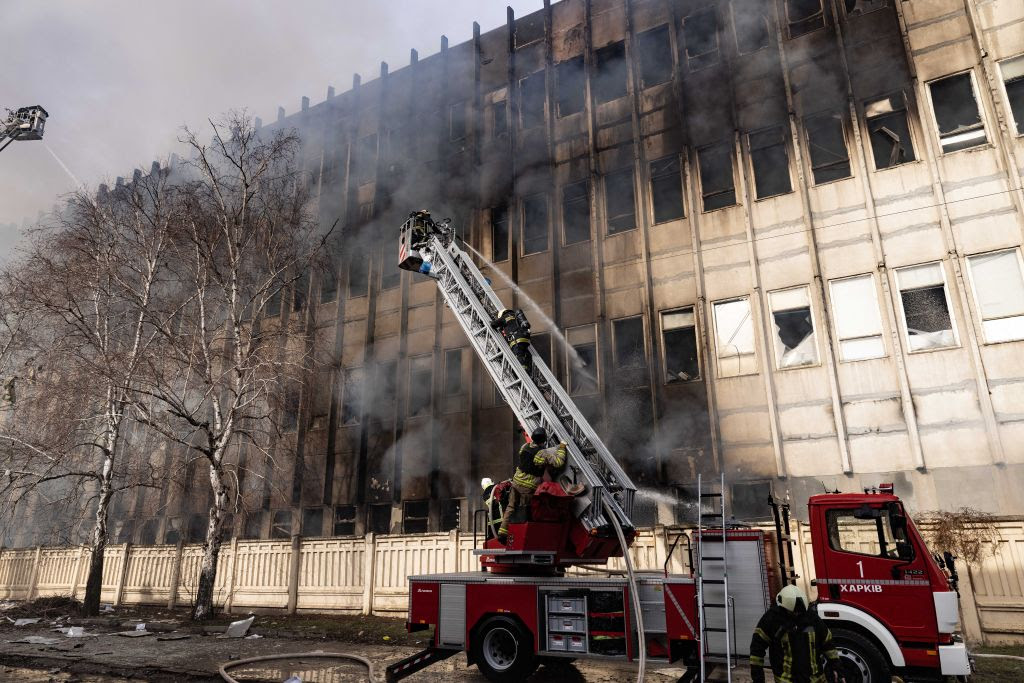 Fire extinguishing efforts continue as fire breaks out after a Russian shelling on an industrial building in Kharkiv
Fire extinguishing efforts continue as fire breaks out after a Russian shelling on an industrial building in Kharkiv
The General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces reported that 700 Russian forces suffered casualties in the past day.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched missile strikes on Kharkiv City using an unspecified number of missiles and targeted Kozacha Lopan in Kharkiv Oblast with two S-300/S-400 missiles.
Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal has presented the Ukraine Facility Plan to the European Commission, outlining reforms necessary for receiving €50 billion in aid from the EU over the next four years. The plan, pivotal for Ukraine’s EU path and financial stability, covers reforms in public administration, anti-corruption, and various economic sectors. The first funding tranche was received on March 20, following the EU’s approval of the Ukraine Facility in February, which includes €33 billion in loans and €17 billion in grants for various programs, including defense, migration, and emergency aid. Ukraine now awaits the plan’s approval and the full activation of the program.
Ukraine is set to rename five cities and 104 villages with Russian or Soviet-era names, part of an ongoing decommunization initiative and a response to the Russian invasion. This decision, announced by lawmaker Roman Lozynskyi, follows a 2015 ban on Soviet symbols and a 2023 law against geographic names linked to Russian figures or events. Notable changes include renaming Chervonohrad to Sheptytskyi, honoring a local bishop, and Pavlohrad to Matviiv, reflecting its Cossack heritage. The city of Brovary will adjust its spelling to align with Ukrainian orthography. The proposals await final approval from Ukraine’s Parliament.
Ukraine is removing its ‘International War Sponsors’ list from its corruption prevention agency’s website following concerns from representatives of several countries. The list aimed to pressure businesses to exit Russia but lacked legal weight. The information will now be reviewed by an interdepartmental group to decide on further action. Diplomatic partners raised issues about the lack of regulatory framework and negative impacts on decisions to counter Russian aggression. The Justice Ministry also highlighted legal concerns. The list included around 50 multinational companies operating in both Ukraine and Russia, prompting dissatisfaction among international partners.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine plans to open 27 new recruitment centers in major cities and regional centers by mid-2024 to enhance military mobilization efforts. Two centers already operational in Lviv and Zaporizhzhia provide information and application support for those interested in joining the Ukrainian Armed Forces. Unlike traditional enlistment offices, these centers focus on consulting and transparency about military roles, considering candidates’ professions, experiences, and health conditions. Staffed by civilian employees, the centers aim to streamline the recruitment process and are part of a broader government initiative to modernize mobilization, as a new draft law on the issue is considered by parliament. The Zaporizhzhia center, for instance, offers positions in various military branches, without the staff having the authority to issue military summons.
Ukraine’s Allies
The European Commission provided Ukraine with 4.5 billion euros ($4.8 billion) as the first part of its macro-financial assistance. This aid is part of the larger Ukraine Facility approved by the EU in February, which includes 33 billion euros ($36 billion) in loans and 17 billion euros ($18.6 billion) in grants. Josep Borrell, the EU’s top diplomat, announced the payment and highlighted discussions within the European Council to expedite Ukraine’s path to EU accession.
Lithuania pledged 35 million euros (about $38 million) to the Czech initiative for purchasing artillery shells for Ukraine, according to Prime Minister Ingrida Simonyte. The initiative aims to address Ukraine’s critical ammunition shortages. Czech Prime Minister Petr Fiala stated that the initiative has secured the purchase of 300,000 shells and received commitments for 200,000 more. The shells could begin reaching Ukraine by June.
The Netherlands will supply 150 million euros ($164 million) worth of munitions for Ukraine’s F-16 jets, announced Dutch Defense Minister Kajsa Ollongren. The munitions will be sourced directly from the industry. Additionally, a contract for new intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) drones worth around 200 million euros ($218 million) was secured. Ollongren’s visit to Ukraine included discussions with President Zelensky on enhancing Ukraine’s air defense and providing artillery, armored vehicles, and UAVs. The Dutch delegation also witnessed the impact of Russian airstrikes during a visit to Dnipro.
During his surprise visit to Kyiv on March 20, U.S. National Security Adviser Jake Sullivan assured that the United States remains committed to delivering a $60 billion aid package to Ukraine, despite hurdles in the Republican-controlled House of Representatives. Sullivan’s visit aimed to reaffirm U.S. support amidst concerns about wavering commitment. The aid package, part of a larger $95 billion funding approved by the Senate in February, awaits House approval. House Republicans, led by Speaker Mike Johnson, have stalled its progress, citing priorities at the southern border. Sullivan expressed confidence in eventual bipartisan support and emphasized ongoing U.S. assistance to Ukraine. While no timeline was provided, Sullivan dismissed the need for an alternative plan.
Democratic Senator Joe Manchin warned during a summit on March 19 that the U.S. failure to pass continued aid for Ukraine could lead to catastrophic consequences, calling it potentially “the worst atrocity in history.” Despite the Senate passing the aid bill in February, House Speaker Mike Johnson has stalled its progress. Manchin emphasized the urgency of providing assistance to Ukraine and highlighted the dire implications of inaction. The ongoing impasse over aid has already been linked to Ukraine’s loss of the city of Avdiivka in February.
Pentagon spokesperson General Pat Ryder clarified that the $300 million U.S. aid package announced earlier in March was a one-time allocation sourced from savings of other contracts. This aid, primarily comprising artillery rounds and GMLRS rockets, aims to support Ukraine amid a Congressional impasse delaying further assistance. Ryder stressed that it doesn’t replace the pending $60 billion aid package awaiting Congressional approval. While urging passage of the larger aid bill, Ryder highlighted ongoing U.S. support for Ukraine’s defense strategy and training. He ruled out deploying U.S. troops to Ukraine but affirmed the U.S.’ commitment to deterring Russian aggression.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
The UN reported widespread international law violations by Russia in occupied Ukrainian territories, creating a severe climate of fear through unlawful detention, torture, and other oppressive measures. The UN’s human rights office documented these abuses based on over 2,300 interviews, highlighting Russia’s impunity in targeting those seen as opposing the occupation. Efforts to control information, suppress free expression, and coerce Ukrainian citizens into adopting Russian citizenship were noted, along with the pillaging of homes and businesses. The report urges Russia to cease its aggression and withdraw, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive approach to accountability and support for Ukraine from the international community. Additionally, during Russia’s presidential election in the occupied areas from March 15-17, there were reports of forced voting, with the EU declaring the election results “null and void.”
Denys Kostev, showcased by Russia to endorse the deportation of Ukrainian children, revealed he was coerced into supporting the narrative under threats of violence. Nearly 20,000 Ukrainian children have been reportedly taken by Russia since February 2022, with Ukraine recovering only around 400. Kostev, an orphan, was moved from Kherson to Crimea and featured in pro-Russian propaganda. He admitted to participating due to fear for his safety and refuted sharing information with Russian security agents. Despite false promises of educational opportunities by Russian officials, Kostev managed to leave for Germany, with Russian authorities not hindering his departure.
Russia News
Ukrainian intelligence conducted a drone strike on a Russian air base in Saratov Oblast, part of ongoing efforts causing limited damage to Russian military and economic targets. Although the exact impact at the Engels air base remains unverified, Russia reported the destruction of four Ukrainian drones without damage. These strikes, including those on oil refineries, are disrupting Russia’s oil refining capacity significantly, affecting up to 11% of its capacity and leading to price surges, though export levels and domestic fuel prices remain largely stable for now. Additionally, these actions are stretching Russia’s air defense resources, with plans to deploy more air defense systems to protect strategic facilities. Ukraine’s drone strategy underscores its capability to exert asymmetric pressure on Russia, highlighting vulnerabilities within Russian military and economic systems.
The governor of Russia’s Belgorod Oblast reported an attack on the region, including the city of Belgorod, with the air defense system activated. The authenticity of these claims has not been independently verified, and Ukraine typically does not acknowledge attacks within Russia. This incident follows reports of anti-Kremlin militia engagements in the area. The governor stated that one man was killed by debris, two others were injured, and there was damage to residential buildings, vehicles, schools, and kindergartens, although no educational institution casualties were reported. Additionally, seven houses and two cars were damaged in an airstrike in the village of Razumnoye. Overnight drone attacks were also claimed in Belgorod and Saratov oblasts, including Engels city, with no reported casualties or damage according to the local governor.
Russian reports suggest a decrease in pro-Ukrainian cross-border raids into Belgorod and Kursk regions. According to the Russian Ministry of Defense and a Kremlin-affiliated military blogger, Russian troops have expelled volunteer forces from Kozinka in Belgorod and are currently securing the area. However, some Russian military bloggers report ongoing attacks by pro-Ukrainian forces near Kozinka.
Russian President Vladimir Putin has directed the Federal Security Service (FSB) to locate and punish Russian citizens fighting for Ukraine, including those in groups like the Freedom of Russia Legion, the Siberian Battalion, and the Russian Volunteer Corps. This order follows incidents of these groups making cross-border raids into Russia. Putin, drawing historical comparisons to Russians who sided with Nazi Germany during World War II, insists on tracking these individuals indefinitely, emphasizing a history of Russian security efforts to target perceived traitors beyond its borders.
New International Criminal Court (ICC) President Tomoko Akane expressed confidence in Putin facing justice for war crimes in Ukraine, citing a Chinese proverb. The ICC issued arrest warrants for Putin and Russian officials for forced deportations of Ukrainian children. Akane, elected on March 11, also addresses conflicts in the Middle East. Additionally, arrest warrants were issued for two Russian military commanders for strikes on Ukrainian infrastructure.
Russia has collected $385 million from an ‘exit tax’ on foreign companies departing the country, a figure that has already surpassed annual expectations 17-fold. This tax was introduced after many Western businesses withdrew from Russia following the invasion of Ukraine, aiming to discourage financial contributions to the Russian war effort. The departure process includes government approval, discounted sales, and a tax of at least 10% on the sale value.
The Kremlin criticized the International Olympic Committee (IOC) for barring Russian and Belarusian athletes from the Paris Olympics’ opening ceremony due to competing as Individual Neutral Athletes (AIN). Russian foreign ministry spokeswoman accused the IOC of racism and neo-Nazism, denouncing the decision as discriminatory. Ukraine has advocated for a complete ban on Russian and Belarusian athletes from the games.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Since the beginning of 2024, the Russian Central Military District has trained over 100 drone operators for missions in Ukraine, highlighting ongoing efforts to enhance drone capabilities. However, the number of trained operators appears limited given the extensive use of drones by both Russian and Ukrainian forces, suggesting potential training challenges within the Russian military.
The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) is implementing a new system to streamline benefits for veterans. Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu announced that electronic identification cards will be issued to Russian veterans, following a government order signed on March 16. These cards will enable veterans to access various payments and privileges from the MoD, federal and regional authorities, and banks. So far, the MoD has received 70,000 applications for these electronic cards.
TASS reported that the Russian company HiderX has supplied “invisibility suits” to Russian forces in Ukraine. These suits, designed to evade detection by Ukrainian thermal imaging, are lightweight at about 350 grams, pocket-sized, and crafted using a unique chemical composition based on Russian technology.
Russia’s Allies
The U.S. has reported at least 10 instances of Russia using North Korean missiles in attacks on Ukraine, with North Korea emerging as a significant arms supplier to Russia. This includes ballistic missiles and over 3 million artillery shells. Contrary to these reports, the Kharkiv Oblast prosecutor’s office claims nearly 50 North Korean missiles have been used since the invasion began, indicating a larger scale of involvement. North Korea’s contributions also reportedly include at least 10,000 containers of weaponry, surpassing earlier estimates. This partnership raises concerns about North Korea benefiting from the conflict, possibly gaining valuable insights and compensation for their military support. Notably, the use of North Korean missiles by Russia was confirmed in attacks on Zaporizhzhia and Kharkiv, with investigations ongoing for additional cases.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
