Summary of the day: On March 27 and 28, the World Russian People’s Council, orchestrated by the Russian Orthodox Church Moscow Patriarchate (ROC MP), endorsed a document to unify Kremlin narratives, aiming at expanding nationalist ideology amidst the war in Ukraine and Russia’s expansionist aspirations. The ROC MP declared the conflict a “holy war,” marking a significant shift in how Russian authorities have previously described the invasion. Concurrently, Russian forces have made tactical gains near Bakhmut, Avdiivka, and Donetsk City, as well as in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, against a backdrop of Ukraine facing materiel shortages due to delays in Western security assistance. This situation is compounded by Russia’s expansion of its strike campaign against Ukraine’s infrastructure to include hydroelectric plants, and efforts to consolidate control over occupied areas, including crackdowns on the Crimean Tatar minority.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War III
Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov criticized Armenia for allegedly distorting history and straining relations with Moscow, as tensions escalate following Armenia’s discontent with Russian actions in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict. Armenia’s Prime Minister threatened to leave the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) if security concerns aren’t addressed. Lavrov accused Armenian leadership of pushing toward a rift with Russia. He condemned NATO’s involvement in the South Caucasus and claimed Western interference aims to disrupt regional stability. Despite Armenia’s recent overtures to the West, Russia insists the West is provoking Armenia’s shift away from Moscow. Russian officials are criticizing Armenia’s move away from Russia, using rhetoric similar to what has been previously applied to Ukraine. The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs claims the Russian military base in Gyumri is essential for Armenia’s sovereignty, mirroring Putin’s stance on Ukraine. The Russian Ambassador to Armenia warns of significant harm to bilateral relations if Armenia does not show the political will to maintain its ties with Russia.
Ukraine’s Interior Ministry has placed Vitaly Ignatiev, the chief negotiator for Moldova’s Russian-controlled Transnistria region, on its wanted list. Ignatiev, who holds Ukrainian and Russian citizenship, faces accusations of undermining Ukraine’s territorial integrity and collaborating with occupying forces. Despite summons from the Security Service of Ukraine (SBU), Ignatiev remains in Transnistria. The region, bordering Ukraine’s Odesa Oblast, has been occupied by Russian troops since the 1990s. President Zelensky discussed the situation with Moldova’s President Sandu, emphasizing Russia’s destabilizing role.
Romania’s Defense Ministry reported finding drone fragments near the Ukrainian border, indicative of spillover from Russian attacks on Ukraine. These fragments, discovered on Great Braila Island close to Reni, Ukraine, highlight ongoing concerns over Russian drone strikes near Romanian territory. President Klaus Iohannis has stated such incidents, though not intentional attacks on Romania, are unacceptable. Romania has responded by enhancing border security, including building air raid shelters and deploying drone defenses. Additionally, Turkish F-16s in Romania were activated following a Russian strike on Odesa in February 2024.
NATO’s Military Committee Chair, Lieutenant Admiral Rob Bauer, stated that there are no signs of an imminent Russian attack on a NATO member but cautioned about future threats. While immediate danger is low, Bauer emphasized the need for NATO to enhance readiness. Concerns arise as Western leaders, including Polish President Andrzej Duda and Danish Defense Minister Troels Lund Poulsen, suggest potential Russian aggression against NATO within a few years. Despite acknowledgement of equipment and manpower shortages, NATO aims to bolster its defenses. Bauer highlighted NATO’s principles of resilience and collective security under Articles 3 and 4, with cyber activities also considered potential triggers for NATO response under Article 5.
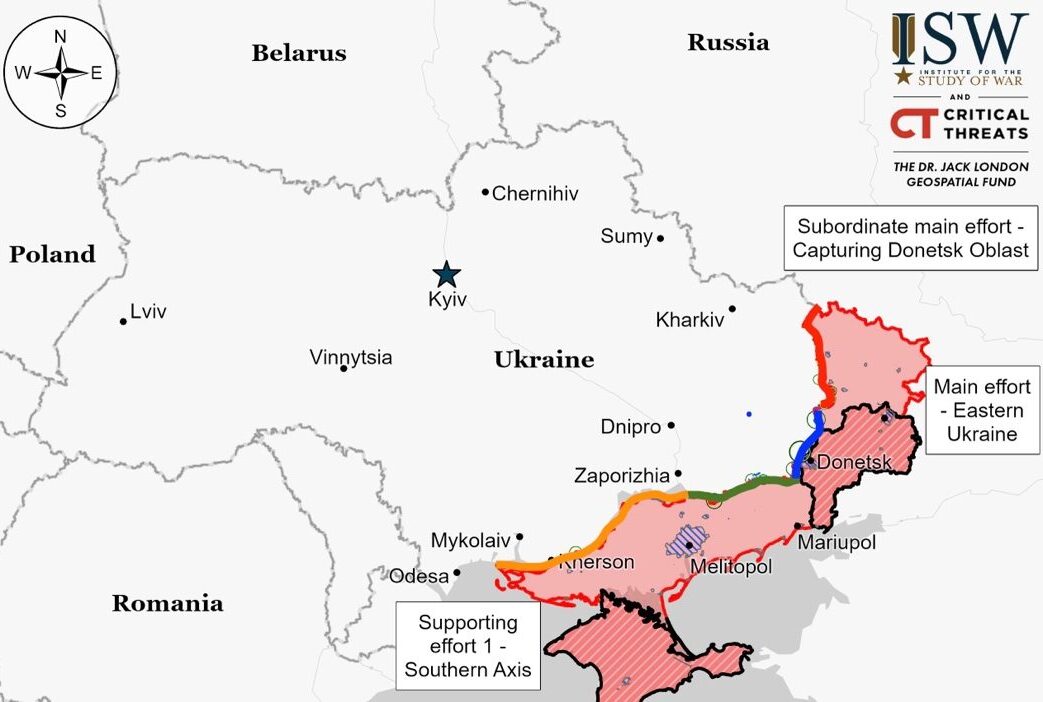
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief, Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi, highlighted that delays in Western security aid are limiting Ukrainian military actions, forcing a defensive strategy due to material shortages. This has particularly affected Ukraine’s ability to defend key locations like Avdiivka, Donetsk Oblast, where Russian forces overcame Ukrainian defenses in mid-February 2024, largely due to a lack of artillery ammunition and air defenses. Despite these challenges, Ukrainian forces have demonstrated effectiveness in operations when adequately equipped, such as using HIMARS to target strategic locations and conducting successful counter-offensives in Kharkiv Oblast and against the Russian Black Sea Fleet. Syrskyi emphasizes the critical impact of timely and consistent Western military support for Ukraine’s ability to plan and execute significant operations. Additionally, Ukraine is reallocating personnel from non-combat to front-line roles to address manpower shortages, though this measure falls short of fully overcoming the deficit in material support.
Commander-in-Chief of Ukraine’s Armed Forces, Oleksandr Syrskyi, warned that any Russian ground offensive against Kharkiv, Ukraine’s second-largest city, would disastrously fail for Moscow. Amid increasing Russian missile and air strikes on Kharkiv, Ukraine is bolstering its defenses and preparing for all eventualities. Syrskyi emphasized Ukraine’s readiness, highlighting extensive fortification efforts and the successful prior experience in the region, which previously led to significant Russian setbacks. Despite being outnumbered, Ukrainian forces leverage drones and high-precision artillery to maintain a strategic edge, ensuring Russian forces remain vulnerable. Syrskyi also pointed out the current challenges, including a significant ammunition disparity favoring Russia, yet underscored the effectiveness of Ukraine’s precision strikes against enemy positions.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
On the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna frontline, fighting continues without any shifts in territory. Russian forces, numbering around 100,000 in the Kupyansk and Lyman areas, are undergoing weekly rotations due to losses. They are bolstering their presence and attempting to advance towards Kupyansk, focusing their efforts near Bilohorivka and Terny without success. No Russian sabotage groups have been detected crossing into Ukraine from Russia, and there are no signs of an imminent attack on Kharkiv City.
Russian forces made slight progress west of Bakhmut, with geolocated footage showing advancements within Ivanivske. Claims of further advances in Bohdanivka remain unverified. The area continues to see ongoing clashes, particularly around Chasiv Yar, Ivanivske, Klishchiivka, and Andriivka. Ukrainian forces highlight the growing threat from Russian drones, which are increasingly used for reconnaissance.
Russian troops have slightly advanced in areas northwest and west of Avdiivka, with recent positional battles ongoing. Geolocated footage shows minor gains north of Krasnohorivka and south of Nevelske. Russian military bloggers report gradual progress near Tonenke. Clashes continue around Semenivka, Berdychi, Umanske, Pervomaiske, and Nevelske.
Russian forces have made slight advancements southwest of Donetsk City, with ongoing skirmishes reported. Recent geolocated footage shows minor progress north of Novomykhailivka. Claims from Russian military bloggers suggest Russian forces made advances in central Novomykhailivka, with further movements reported along Tsentralna and Haharina streets in Heorhiivka. The area continues to witness positional engagements, especially around Krasnohorivka, Heorhiivka, and Vodyane.
Russian forces have made slight gains in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, with ongoing clashes reported. Recent footage shows minor advancements south of Urozhaine. The fighting continues near Staromayorske and north of Pryyutne.
In western Zaporizhia Oblast, ongoing skirmishes were reported near Robotyne and northwest of Verbove, with no shifts in the frontline.
Ongoing positional battles were reported in east Kherson Oblast, likely near Krynky.
Ukrainian Victims Of War
Ukraine has returned the bodies of 121 soldiers for burial, as reported by the Coordination Headquarters for the Treatment of the Prisoners of War. The soldiers, primarily from Luhansk and Donetsk with two from Zaporizhzhia, will be given to their families after identification. This repatriation, part of ongoing efforts involving various Ukrainian agencies and aided by the International Committee of the Red Cross, adheres to the Geneva Conventions’ standards for a dignified burial. Over 2,100 soldiers have been repatriated in the last two years. This news follows President Zelensky’s recent acknowledgment of the loss of approximately 31,000 Ukrainian soldiers since the invasion began.
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the injuries to at least 11 people:
- Russian missiles struck Odesa, resulting in at least five injuries, including three children. While Ukrainian air defenses intercepted the missiles, the falling debris caused the casualties. The injured, including a 12-year-old, were hospitalized with non-life-threatening injuries.
- Russia initiated a significant assault on Ukraine, causing damage to energy infrastructure and injuring six individuals in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast.
 Aftermath of Russian Attack on Civilian Businesses in Odesa
Aftermath of Russian Attack on Civilian Businesses in Odesa
Ukraine News
Russian forces intensified their strikes on Ukrainian critical infrastructure on the night of March 28 to 29, notably targeting the Kaniv and Dniester Hydroelectric Power Plants, causing damage and power outages in multiple oblasts across central and western Ukraine. This strategic shift towards targeting energy facilities marks a significant escalation in aggression. Despite successful interception by Ukrainian air defenses, downing 84 of 99 attacking drones and missiles, the strikes inflicted injuries on at least six people and signified an elevated risk not only to Ukraine but also to neighboring Moldova due to the Dniester plant’s close border proximity. These developments come amid Western hesitance to provide Ukraine with advanced military aid due to fears of Russian reprisal, although Russia continues to escalate its attacks, such as the previous significant strike on the Dnipro Hydroelectric Power Plant on March 22, showing a willingness to intensify its offensive regardless of Ukrainian defensive actions or potential Western responses. President Zelensky, condemning the attacks, stresses the deliberateness of the Russian strategy and its broad repercussions.
President Volodymyr Zelensky of Ukraine believes that reclaiming territories occupied by Russia since the 2022 invasion could force President Vladimir Putin into negotiations. Zelensky argues that a Russian withdrawal would undermine Putin’s domestic support and open avenues for dialogue without solely relying on military means. Despite initial peace talks, Ukraine insists on full military withdrawal for negotiations, a stance reinforced after Russia’s annexation attempts in 2022. Zelensky’s peace plan demands Russian troop withdrawal and addresses war crimes and security issues, but Russia has dismissed this plan and declined participation in a forthcoming peace summit in Switzerland. Amidst warnings of a potential Russian offensive, Zelensky maintains that Ukraine’s situation has stabilized but acknowledges the possibility of future challenges.
President Volodymyr Zelensky, in an interview with the Washington Post, defended Ukraine’s right to strike Russian oil refineries as self-defense, despite U.S. concerns about potential impacts on global oil prices. Zelensky highlighted the use of Ukrainian drones for these attacks, asserting that Ukraine has the autonomy to use its own weapons. These strikes, including a significant one on March 17 that targeted 12 Russian refineries, are in retaliation for Russian assaults on Ukraine’s infrastructure, causing widespread damage and power outages. Zelensky questioned the limitations on Ukraine’s defensive actions, emphasizing the right to respond to Russian aggression.
President Zelensky chaired Ukraine’s first National Security and Defense Council meeting since Secretary Oleksiy Danilov’s dismissal. Zelensky outlined five priorities, including enhancing the ability to forecast national security factors. The council coordinates security efforts and its decisions are enacted by presidential decrees. Danilov was replaced by Oleksandr Lytvynenko. Zelensky emphasized the importance of sanctions policy and cybersecurity.
President Zelensky appointed Oleksiy Danilov, former National Security and Defense Council secretary, as the new Ukrainian ambassador to Moldova, replacing Markо Shevchenko. Danilov was dismissed on March 26 after over four years in office. Zelensky also approved Oleh Ivashchenko as the head of Ukraine’s Foreign Intelligence Service. Valerii Zaluzhnyi, former Armed Forces commander, was approved as the next Ukrainian ambassador to the U.K. Zelensky emphasized the need for leadership reset, hinting at more personnel changes beyond the military.
President Zelensky dismissed Andrii Smirnov and Oleksii Dniprov as deputy heads of the Presidential Office. They were replaced by Iryna Mudra and Olena Kovalska, respectively. The reason for the changes was not provided. Zelensky announced these moves as part of a broader personnel reshuffle.
The State Bureau of Investigation announced charges against an officer for negligent homicide and misappropriation of arms in connection with the death of Major Hennadii Chastiakov last November. Chastiakov died when a grenade, received as a gift, exploded at his home near Kyiv. The suspect allegedly provided the grenades without disclosing their authenticity. The accused, reportedly Oleh Timchenko, could face up to 15 years in prison if convicted.
Ukraine’s Allies
In March, Ukraine is set to receive its largest financial aid package from international allies since its independence, totaling over $9 billion. This support includes 4.5 billion euros from the European Union, $1.5 billion from the World Bank, $880 million from the IMF, $1.5 billion from Canada, and $230 million from Japan. Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal highlighted the importance of these funds for critical budget needs. Looking ahead to 2024, Ukraine anticipates over $30 billion in aid to cover its budget deficit, with contributions expected from the IMF, EU, U.S., and other nations. The 2024 state budget forecasts revenues of around $45 billion against expenditures of $85 billion, planning for significant external borrowing and government bonds to manage a deficit of $40 billion.
Ukraine secured a $1.5 billion loan from the World Bank, supported by guarantees from Japan and the U.K., to aid its state budget, economic recovery, and essential social and humanitarian needs. Japan and the U.K. provided guarantees of $984 million and $516 million, respectively. This financial assistance is part of a larger effort, with the World Bank mobilizing over $41 billion for Ukraine, of which nearly $35 billion has been disbursed. The funding comes in response to Ukraine’s extensive recovery needs, estimated at $486 billion due to the ongoing conflict.
Belgium approved a 100 million euros ($107 million) assistance package for Ukraine, supporting F-16 fighter jets through an international coalition. The coalition, initiated by the U.S., Denmark, and the Netherlands, aims to bolster Ukraine’s Air Force. Last October, Belgium committed to providing F-16s and pilot training. Other countries like the Netherlands, Denmark, and Norway have also pledged to supply jets. Ukraine may receive the first F-16s from Denmark this summer, with estimates suggesting up to 60 jets could be delivered.
Poland’s Foreign Minister Sikorski announced that artillery shell transport for Ukraine, secured through the Czech-led initiative, is underway. The initiative plans to deliver millions of rounds, with shipments potentially starting in April or June. Sikorski didn’t disclose Poland’s contribution but hinted at doubling it. Ukraine faces ammunition shortages, with the EU providing half of its promised shells. The U.S. offered some aid, but further assistance is delayed due to stalled congressional approval.
U.S. Joint Chiefs of Staff Chairman Charles Brown stated on March 28 that the risk of escalation from supplying Ukraine with long-range Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles has decreased. The U.S. delivered older ATACMS models with a 165-kilometer range to Ukraine in October 2023, but has not provided newer versions capable of reaching about 300 kilometers. Recent Ukrainian drone attacks on Russian targets and Russia’s restrained response have led the Pentagon to reassess the escalation risk of sending these weapons. Despite the delivery of shorter-range ATACMS, which have notably impacted the conflict, Ukraine seeks newer, longer-range variants. The U.S. and other Western nations remain cautious, weighing the potential for escalation with Russia.
The U.S. Commerce Department advised around 20 American companies to halt shipments of materials abroad to prevent them from potentially being used in Russian weapons. This action aims to curb sanctions evasion and prevent Western components from aiding Russia’s attacks on Ukraine. The move follows President Biden’s executive order warning of sanctions for companies inadvertently doing business with Russia. The Commerce Department urged companies to cease shipments to certain parties to reduce the risk of transshipment to Russia. Specific consequences for non-compliance were not disclosed.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine’s commander-in-chief, Oleksandr Syrskyi, announced a significant reduction in the previously estimated mobilization need from 500,000 to an unspecified lower number, aiming to ensure adequate defense capabilities. This adjustment reflects the need for troop rotation and rest, especially given the physical and psychological toll of prolonged combat. The majority of mobilized individuals undergo training before deployment, with few exceptions directly sent to the front. Amendments to the mobilization law are underway, proposing changes including lowering the enlistment age and introducing basic military training for adults, with basic military service set to replace conscript service. The updated mobilization bill, which has seen over 4,000 amendments since its first reading, outlines service durations and introduces military training in higher education from 2025.
The National Security and Defense Committee reviewed over 4,000 amendments to a mobilization bill, aiming to update conscription laws. Lawmaker Yaroslav Zhelezniak expects the bill to proceed to the plenary hall in two weeks without delays. The proposed changes include mobilization from age 25 to 60 and basic military training instead of conscription. Initial estimates suggested mobilizing up to 500,000 conscripts, but the number has since decreased.
Life In Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Russian occupation forces are intensifying their crackdown in occupied Ukraine, notably targeting the Crimean Tatar minority. Recent reports show the Russian Federal Security Service arresting a Crimean Tatar man, accused of terrorism. This arrest is part of broader efforts to suppress Crimean Tatar and Ukrainian identities. Following the March 22 Crocus City Hall attack, Russian authorities are also scrutinizing Tajik and Uzbek nationals. Over 10,000 Ukrainian civilians are reportedly detained in occupied territories and Russia, highlighting aggressive measures to solidify control.
Ukrainian partisans in occupied Melitopol, Zaporizhia Oblast, executed a bombing on March 22, as reported by Ukraine’s Main Military Intelligence Directorate. The attack resulted in the death of 20 Russian personnel and the destruction of two Kamaz trucks and a UAZ Patriot SUV.
Russian authorities are actively repairing and developing transportation and industrial facilities in occupied Ukraine to bolster their military efforts and cement long-term control. In 2023, they fixed 300 kilometers of roads in Kherson Oblast and plan to build a railway linking Rostov-on-Don to Crimea, passing through Berdyansk, Melitopol, and Kherson. Additionally, new rail lines are being constructed in Donetsk Oblast. Meanwhile, the use of the Kerch Strait railway bridge for military logistics has ceased. Russia is also establishing numerous military training camps and bases across occupied territories. In Luhansk Oblast, Russian forces are coercing the sale of 11 coal mines, aiming to enhance their defense industry and tighten their grip on the region.
In occupied Crimea, Russian forces mistakenly shot down their own Su-27 fighter jet amid heightened alertness, as stated by Ukraine’s Navy spokesperson, Dmytro Pletenchuk. The incident, reported by Russian officials in Sevastopol on March 28, involved the jet crashing off the Crimean coast due to friendly fire from Russian air defenses after taking off from the Belbek airbase. The pilot ejected safely and was rescued. Pletenchuk attributed the mishap to the “human factor” in the rush for combat readiness, noting the incident reflects Russia’s significant recent air force losses, including over a dozen warplanes.
Russia News
Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov has rejected Ukraine’s peace proposal, stating discussions cannot be based on President Zelensky’s 10-point plan, which demands Russia’s withdrawal from occupied areas and addresses issues like territorial integrity, POW release, and punishment for war crimes. Lavrov criticized Western politicians for supporting Zelensky’s plan and confirmed Russia’s non-participation in a planned peace summit in Switzerland, despite over 160 countries being invited to discuss restoring Ukraine’s sovereignty. Lavrov criticized U.S. foreign policy and dismissed attempts to separate arms deals from the conflict as undiplomatic.
Following the March 22 attack at Crocus City Hall, the Kremlin has effectively pressured the messaging app Telegram into ramping up efforts to censor extremist content. Telegram’s CEO, Pavel Durov, announced on March 28 that the platform had started blocking posts and users advocating for terrorism since March 24, impacting tens of thousands of potential messages and users, particularly in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. Additionally, Telegram plans to introduce features allowing users to restrict who can message them privately, emphasizing the app’s stance against violence. Despite Telegram’s independence from Russia and Durov’s previous departure over censorship disputes, the Kremlin, which stated it does not intend to block Telegram, expects further compliance, highlighting its influence over digital platforms regardless of their geographic ties.
The Russian FSB claims to have foiled a terrorist attack in Stavropol Krai, detaining three suspects from Central Asia. They allegedly possessed explosive materials. The FSB’s announcement follows a recent attack near Moscow, with Russia blaming Ukraine despite ISIS claiming responsibility. The U.S. Embassy in Russia had issued prior warnings about potential attacks in Moscow.
Russia’s Allies
Russia vetoed a United Nations Security Council resolution to extend a panel monitoring North Korea’s adherence to UN sanctions, with China abstaining from the vote. This move breaks the consensus normally seen since the panel’s establishment in 2009. Russia’s actions, described as serving its own interests, aim to prevent scrutiny of its relationship with North Korea, especially as it seeks North Korean military supplies for use in Ukraine. Russia and China had proposed introducing “sunset” clauses that would automatically end some sanctions unless renewed, suggesting these nations are working to ease pressure on North Korea. This veto is seen as part of broader efforts by Russia to shield its transactions with North Korea, including potential sanctions evasion, from international oversight.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
The Russian Defense Ministry is gearing up for its 2024 spring conscription cycle, starting April 1 across all federal subjects, excluding some northern areas due to bad weather. This cycle aims to conscript 130,000 individuals, including regions in occupied Ukraine, with the dispatch of conscripts to assembly points beginning April 15. A portion of these conscripts will undergo specialized training within military and training units. Despite forming special units for research and development tasks, Russia insists conscripts will not be deployed to combat or war-related duties in occupied Ukraine, aiming to avoid domestic backlash from conscript casualties. However, conscripts have been utilized for border security roles, and there are plans to potentially deploy them in support roles along Russia’s southern border to allocate more experienced troops elsewhere. Additionally, there are indications of plans to expand crypto-mobilization efforts during this cycle.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
The Russian Orthodox Church Moscow Patriarchate (ROC MP), closely linked to the Kremlin, has endorsed a document at the World Russian People’s Council aiming to deepen nationalist ideology amid Russia’s war in Ukraine and broader expansionist goals. This initiative, likely in coordination with Kremlin efforts, positions the Ukraine conflict as a “holy war” for national and civilizational defense, advocating for the inclusion of ethnic Ukrainians and Belarusians within a broader Russian identity. The ROC MP also promotes traditional family values and a revised migration policy to address Russia’s demographic challenges, suggesting a future of national rejuvenation based on increasing birth rates and repatriating “compatriots.” This ideological stance not only aims to consolidate Russian national identity but also seeks to legitimize aggressive policies against Ukraine and potentially other neighbors under the guise of defending the Russian people and Orthodox Christianity.
The Russian Investigative Committee alleges it has proof of Ukraine’s involvement in the March 22 Crocus City Hall attack, aiming to boost domestic support for the war in Ukraine. This claim is being pursued by a special department focused on investigating war crimes and acts of Nazism, indicating a Kremlin strategy to use legal channels to validate its accusations against Ukraine. However, the Institute for the Study of War maintains that the Islamic State was responsible for the attack, with no credible evidence linking any other parties to the incident.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
