Summary of the day: Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky highlighted the critical shortage of military materiel faced by Ukraine, stressing the necessity for enhanced Western security assistance to counteract an intensified Russian strike campaign and aviation operations. Zelensky also noted that the expected delivery of F-16 fighter jets in 2024 would fulfill only a fraction of Ukraine’s needs for air superiority. Amidst these challenges, Russian forces have achieved advances near Avdiivka and Donetsk City, underscoring the escalating conflict in eastern Ukraine. Additionally, the geopolitical tension extends beyond the battlefield, with the Kremlin issuing threats towards Armenia for its Western engagements and Finland for its NATO membership, alongside internal moves by Russian President Vladimir Putin to rally domestic support for the war effort.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War III
The Kremlin threatened Armenia over its Western engagement and outreach after the loss of Nagorno-Karabakh in September 2023, responding to Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan’s discussions with EU and US officials in Brussels regarding Western support for Armenia’s development. Russia accused the West of stoking geopolitical tension in the South Caucasus, warning of dire consequences for the region’s stability and Armenia’s security and economic future. It criticized Armenia’s potential shift away from Russian alliances and military bases, portraying it as a problematic path that could mirror the challenges faced by Ukraine. Following Armenia’s pursuit of Western security guarantees and contemplation of joining the European Union, the Kremlin escalated its threats, suggesting Armenia’s deteriorating relations with Russia were self-inflicted. Armenia is considering exiting the Russian-led Collective Security Treaty Organization and has sought the withdrawal of Russian border guards from Yerevan International Airport. The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs suggested that Armenia’s policy moves were not of its own making but rather influenced by the West, echoing similar unfounded claims made about Ukraine. This tactic aligns with Russia’s broader strategy of undermining the sovereignty of former Soviet states that aspire for closer EU ties.
The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) has continued its threats towards Finland, criticizing its NATO membership as a loss of foreign policy independence and a move that escalates tensions in the Baltic region. Russian Ambassador to Finland, Pavel Kuznetsov, labeled Finland’s NATO accession as a “destructive course,” suggesting it transforms the region into a potential conflict zone. He warned of Russia’s “adequate” response to any NATO military buildup or nuclear deployment in Finland, accusing Finland of adopting a confrontational stance towards Russia. Despite attributing the breakdown in Russian-Finnish relations solely to Finland, Kuznetsov hinted at the necessity of improving ties due to geographic inevitability, while ignoring Russia’s provocations, including creating a migrant crisis at their border. The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) interprets these threats as part of Russia’s broader strategy to intimidate NATO members and fabricate threats to justify confrontations with the West.
A voice memo, allegedly from Russian State Duma Deputy and former Southern Military District Commander Lieutenant General Andrei Gurulev, was leaked on April 6, suggesting Russia has plans to invade Kazakhstan after its operations in Ukraine. The memo, intended for the Russian State Duma Defense Committee, hinted at a decision already made for such an invasion, motivated by Gurulev’s belief that a recent Ukrainian drone strike in Tatarstan might have originated from Kazakhstan or another Central Asian country. Gurulev has dismissed the leaked audio as fake. This leak follows previous controversies involving Gurulev, including backlash over another leaked recording criticizing Russian military challenges in Ukraine. The authenticity of the leaked plan cannot be confirmed.
Russian military bloggers are spreading claims that US military personnel were involved in recent border raids into Russia, specifically referencing an April 6 video allegedly showing US citizens in combat in Belgorod Oblast. They suggest this video proves US involvement alongside Ukrainian forces against Russia. These claims echo President Vladimir Putin’s March 18 statement that NATO military personnel are present in Ukraine, framing it as a violation of Russia’s “red line” concerning NATO’s involvement in Ukraine.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky, confronting a severe shortfall in military supplies, underlined the critical need for Western security assistance to combat Russia effectively, emphasizing the country’s dire shortage of ammunition and long-range weapons necessary for both defense and counteroffensive strategies. Amidst a significant artillery disadvantage and delayed Western military aid, Ukraine is forced to balance maintaining its current defenses with the preparation for potential counterattacks. Highlighting the importance of air defense, Zelensky pointed to the need for 25 additional Patriot systems to fully protect Ukrainian airspace and prevent Russia from further targeting its weakened defenses and critical infrastructure. Despite past successes in limiting Russian air operations, the need for enhanced long-range air defenses becomes more acute as Russia adapts by launching attacks from greater distances. The anticipated delivery of all promised F-16 jets in 2024 will fulfill only a fraction of Ukraine’s needs to overcome Russian air superiority, as the country also focuses on developing its defenses against guided bombs. Zelensky’s call to global allies through national television underscores the urgency for advanced air defense systems to deter the escalated Russian strikes targeting Ukrainian energy, civilian infrastructure, and, potentially, larger-scale operations against logistics and urban areas, highlighting the vital role of comprehensive security assistance from the West for Ukraine’s robust defense.
Delays in US security assistance are affecting Ukrainian forces’ ability to counter increasing Russian mechanized attacks in eastern Ukraine. Ukrainian military leadership highlighted severe challenges east of Chasiv Yar and west of Avdiivka in Donetsk, where Russia has intensified mechanized and infantry assaults. Despite these challenges, Ukrainian forces have repelled Russian attacks, including a significant engagement where Ukrainian troops destroyed multiple Russian tanks and armored vehicles. The situation underscores the pressing need for continued and timely international support to bolster Ukraine’s defense capabilities amidst ongoing material shortages.
Ukrainian forces neutralized a Russian T-72 tank equipped with multiple electronic warfare (EW) systems, which had been disrupting Ukrainian drone operations at an unspecified front location. This tank, at the forefront of an armored column, interfered with all Ukrainian first-person view drones in the vicinity. A specialized fixed-wing drone equipped with an advanced terminal guidance system was deployed by Ukrainian forces to successfully target the tank. This incident illustrates Russia’s strategy of enhancing their armored vehicles with EW capabilities to defend against Ukrainian drone strikes.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has dispelled the perceived immediate threat of a Russian ground invasion of Kharkiv City, labeling such rumors as false information aimed at causing panic. In an interview, he maintained that Kharkiv remains secure against Russian offensives, even with the uptick in attacks and speculations of a possible ground assault on Ukraine’s second-largest city. Ukrainian military intelligence, dismissing the assault speculations, sees no sign of Moscow preparing for this. Zelensky underscored the strong local defenses in place and proactive measures against Russian disinformation and movements. Additionally, he negated any direct threat from Belarus, citing the establishment of strong northern defenses. Zelensky indicated that the completion of critical defense lines is imminent, with a broader plan to finish additional fortifications within months. This is part of a substantial endeavor to construct 2,000 kilometers of defensive structures, backed by a notable budget from the Ukrainian government for 2024. These preparations come as Ukraine gears up for a potential spring offensive, though there are concerns over the speed of the fortification efforts.
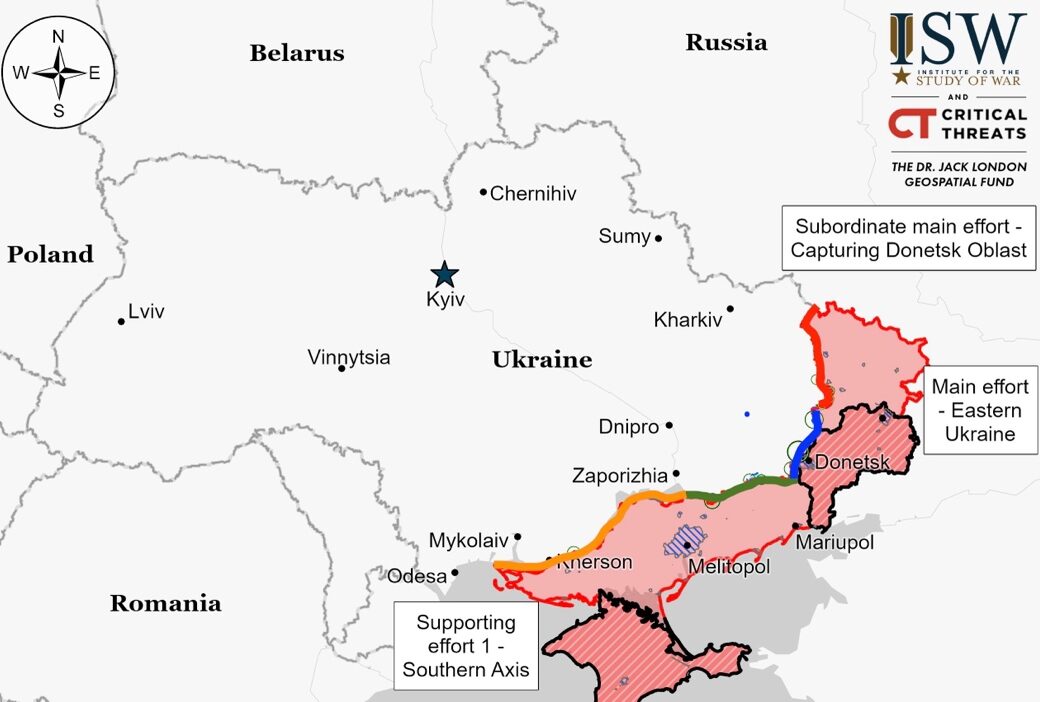
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Ukrainian forces made tactical gains in the Kupyansk and Lyman areas, as confirmed by Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi. These successes occurred amid ongoing battles along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line. Ukrainian troops successfully repelled Russian attacks near Terny and Bilohorivka, despite Russian claims of advancements in these locations.
Russian forces, intensifying their offensive west of Bakhmut towards Chasiv Yar, have not achieved confirmed changes in the frontlines despite assaults northeast and southeast of Chasiv Yar, and claims of territorial gains in the forests. They conducted heavy artillery and airstrikes around Chasiv Yar, with reports of Ukrainian retreats in the Bohdanivka area. Nonetheless, logistical issues and the need for enhanced protection against Ukrainian drone tactics could impede their progress. Continuous clashes around Bakhmut persist, yet Russian claims of northeastern territorial advances lack visual confirmation.
In response, Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi reported fierce battles east of Chasiv Yar, a key area close to previously Russian-captured Bakhmut and Avdiivka. Chasiv Yar’s defense is pivotal as it sits on the route to strategically important cities like Kostiantynivka, Kramatorsk, and Sloviansk. Despite Russian proxies’ claims, Syrskyi affirms Ukrainian forces have successfully rebuffed attacks on Chasiv Yar. The overall front remains challenging as Russia continually deploys armored vehicle-supported assaults aiming for the administrative limits of Donetsk Oblast.
Russian troops made advances west of Avdiivka, executing mechanized assaults southwest of Umanske and taking positions in Pervomaiske and Berdychi. Despite these movements, the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) cannot confirm all claims of Russian progress, such as the clearing of forest areas between Tonenke and Vodyane. Russian military bloggers also reported an airstrike on a dam bridge near Umanske and continued fighting in surrounding areas. The Ukrainian Airborne Forces noted ongoing Russian infantry assaults, with combat vehicles transporting troops to the frontlines. Ukrainian defenders observed Russian attempts to encircle and capture areas around Avdiivka, now facing Ukraine’s fortified defensive positions.
Russian forces made advancements near Donetsk City, specifically moving into the northern and central parts of Novomykhailivka, located southwest of the city. While a claim of further advancement into a southeastern field of Novomykhailivka lacks visual confirmation, ongoing battles continue west and southwest of Donetsk City near Krasnohorivka, Heorhiivka, and Kostyantynivka.
Ongoing positional battles were reported near Staromayorske, located south of Velyka Novosilka, along the border area between Donetsk and Zaporizhia Oblasts.
Battles took place near Robotyne and northwest of Verbove in western Zaporizhia Oblast. Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief, Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi, characterized the Russian actions near these areas as efforts to retake lost territories. Heavy drone usage by both Russian and Ukrainian forces was reported around Robotyne.
Fighting persisted on the east bank of Kherson Oblast, around Krynky. Russian military bloggers reported that on April 5 and 6, Russian troops thwarted several Ukrainian attempts to cross the Dnipro River near Krynky.
Ukrainian Victims Of War
Governor Ivan Fedorov reported that Russian missile strikes on Zaporizhzhia the previous day resulted in four fatalities, including two men and two women, with two succumbing to their injuries in the hospital. Twenty-three others were wounded, with eight hospitalized, including two children aged nine and 17. The attacks caused damage to over 40 structures, among them houses, apartment buildings, a dormitory, and a kindergarten.
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the death of at least 9 people and the injuries to at least 6 others:
- Russian drones attacked Kharkiv, hitting a private home and injuring a 62-year-old man. Two other residents received onsite treatment. Additional drone strikes occurred in the Lozivskyi and Kharkivskyi districts, with no casualties. These incidents are part of a recent escalation in attacks on Kharkiv, including an assault that resulted in at least one death, one injury, and damage to civilian structures.
- Russian forces have attacked a utility facility in the Odesa district, resulting in the death of a civilian worker.
- Russian forces shelled the Kurakhove and Marinka communities in Donetsk Oblast, resulting in five deaths and two injuries. The casualties in the village of Kurakhivka included two fatalities and one injury, while in the city of Krasnohorivka, there were also fatalities and injuries. Among the deceased were a 16-year-old girl and her mother. Russia launched 15 attacks across three districts in Donetsk Oblast.
Ukraine News
Overnight and during the day on April 6, Russian forces launched drone and missile attacks on Ukraine’s civilian, industrial, and agricultural sites. Ukrainian Air Force reported the launch of missiles and drones from various locations, with Ukrainian defenses intercepting the majority. Targets included agricultural businesses in Kherson, and industrial and residential areas in Kyiv, Zaporizhia, Odesa, and Kharkiv, with a humanitarian center in Zaporizhia City also hit. A utility facility near Odesa was attacked with a likely Iskander-M missile. Russia claims it targeted Ukrainian military and defense infrastructure. Amidst these strikes, Ukraine’s Energy Minister stressed the need for enhanced air defenses to protect energy facilities, especially with recent attacks significantly damaging power generation and transmission, affecting about 80% of thermal power plants.
President Volodymyr Zelensky met with U.S. Congress members from both parties in Chernihiv Oblast and stressed the urgency for the U.S. to pass the pending Ukraine aid bill. The $95 billion aid package, approved by the Senate but delayed in the House, is crucial for Ukraine as Zelensky cited the immediate needs of Ukrainian defenders and the impact of Russian aggression, demonstrated by the occupation of Yahidne village where civilians were held captive. He thanked the U.S. for its ongoing support, highlighting the necessity of unfreezing Russian assets for Ukraine’s benefit and aid in arms production. Zelensky underscored the critical situation on the front lines and the importance of timely U.S. defense assistance to prevent further Ukrainian military retreats and to plan effective counteroffensives. The meeting commemorated the second anniversary of the region’s liberation and aimed to reinforce the U.S.’s vital support for Ukraine’s struggle against Russian occupation.
The investigative journalism outlet Slidstvo.Info reported that their journalist, Yevhenii Shulhat, was seemingly targeted by military enlistment officers as payback for his investigative work into Ukrainian authorities. This came after Shulhat, who had been probing into the Security Service of Ukraine (SBU) cybersecurity chief Illia Vitiuk, was approached by uniformed men from an enlistment office, an encounter he captured on video. The outlet suggests this is “revenge” for exposing Vitiuk’s financial activities. Amidst recent scrutiny of the SBU for spying on another investigative media group, this incident raises concerns over freedom of the press and the potential misuse of power within the SBU. The Security Service of Ukraine has stated they are investigating the situation.
Since its opening in August 2023, Ukraine’s Black Sea corridor has facilitated the transport of over 36 million metric tons of goods, exceeding the volume moved by the Black Sea Grain Initiative. Following Russia’s cancellation of the grain deal in July 2023, Ukraine established the new corridor which evolved from a humanitarian passage to a major trade route. Infrastructure Minister Oleksandr Kubrakov reported that 1,286 ships have used the corridor, exporting 25 million metric tons of agricultural products globally. Currently, 135 vessels are queued to ship another 4 million metric tons from ports near Odesa, as efforts continue to match the export levels of 2022.
Ukraine’s Allies
Lithuania has sent a new shipment of M577 tracked armored personnel carriers to Ukraine, as reported by the Lithuanian Defense Ministry. While the exact number of vehicles wasn’t disclosed, this support is part of Lithuania’s significant defense aid to Ukraine, which is among the highest globally relative to its GDP.
Russia News
Ukraine’s military intelligence reported that an oil pipeline in Azov, Rostov Oblast, used to supply oil to tankers at the Azov Sea Port, was destroyed by an explosion overnight. Although a video of the incident was released, the perpetrators were not identified. The explosion halted tanker loading at the port indefinitely, with the pipeline labeled a military asset used for Russia’s war efforts.
The U.K. Military Intelligence reported that Ukrainian attacks might have pressured Russian air defenses into mistakenly shooting down their own aircraft, citing an example from March 28 where a Russian military plane crashed near Crimea due to supposed friendly fire. This incident followed heightened defense readiness after Ukrainian strikes on Russian-occupied Sevastopol. The report suggests such incidents, if confirmed, demonstrate Russian forces’ poor situational awareness and coordination. Additionally, President Zelensky has asserted Ukraine’s right to self-defense with its own weapons in response to U.S. concerns about attacks on Russian facilities. These strikes, notably on military targets and oil refineries, have disrupted a significant portion of Russia’s refining capacity, aligning with reports of considerable Russian Air Force losses in recent months.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ramzan Kadyrov, leader of the Chechen Republic, announced that 3,000 former Wagner Group personnel, including commander Alexander Kuznetsov, will join the Chechen Akhmat Spetsnaz unit, following negotiations and support from the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD). This move signals the MoD’s continued efforts to integrate Wagner forces directly under its command, a process that began in early 2023. The transition of Wagner personnel to the Akhmat Spetsnaz, now under MoD rather than Rosgvardia command, reflects a significant step in the Russian military’s campaign to assert control over private military companies. Despite some Wagner-affiliated groups criticizing the move as a betrayal, and skepticism over the numbers transferring, Kremlin-aligned commentators view this as a positive development for Russian state interests. The integration includes discussions on how to organize an additional 5,000 Wagner personnel within the Russian military, highlighting ongoing efforts to formalize and utilize these forces effectively.
Russian President Vladimir Putin enacted two laws as concessions to Russians supporting the war in Ukraine. One law provides Russian soldiers in Ukraine exemptions from paying interest on consumer loans and offers credit holidays. This follows an earlier law from October 2022, granting mobilized personnel relief from penalties on late payments for various services and debts. These financial incentives aim to recruit more fighters by offering state benefits, despite potential long-term fiscal implications for Russia. Another law amends the Labor Code to protect widows of Russian servicemen from job termination for a year after their spouse’s death, aiming to mitigate criticism from the families of the fallen.
In response to reports of Russia planning to mobilize 300,000 servicemembers by June 1, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky, in an April 6 interview, expressed doubt about Russia’s capacity to meet this target due to potential obstacles such as disciplinary issues and the need for extensive recruit training. He questioned whether the reports referred to Russia’s ongoing volunteer recruitment or a possible formal call-up from the reserves. Zelensky also considered the possibility that the actual number of troops mobilized could exceed the 300,000 figure, following Russia’s earlier conscription of 150,000 citizens. He commented on the insufficient training provided to Russian recruits and the consequent disciplinary concerns. In anticipation, Ukraine is reinforcing its military by focusing on seasoned troops and revising legal frameworks to increase available forces, with new mobilization laws already enacted, including the drafting of 25-year-olds. Zelensky is advocating for the Ukrainian parliament to swiftly approve additional mobilization legislation to bolster the country’s defenses.
Russia is establishing a new volunteer battalion named “Stalinskiye Sokoly” (Stalin’s Hawks) in the Republic of Tatarstan to defend a key facility, possibly in reaction to Ukraine’s drone strikes on the region’s military infrastructure. Recruitment efforts highlight attractive salaries of approximately 261,000 rubles ($2,820) for individuals with air defense experience. Additionally, Russia is actively recruiting foreign fighters to participate in the conflict in Ukraine, offering incentives like a $2,000 signing bonus, a monthly salary of $2,200, and the prospect of Russian citizenship for the recruits and their families, as revealed by Russian opposition sources.
The Russian National Guard’s Press Service announced on April 6 their intention to conscript over 11,000 servicemen in the spring 2024 conscription cycle from April 1 to June 15. They assured that these conscripts would not participate in the conflict in Ukraine and noted an increase in the number of conscripts desiring to serve in the Russian National Guard since 2022.
Russia’s Allies
Russia is utilizing North Korean missiles in its offensive in Ukraine, offering Pyongyang a rare chance to test its weapons in real combat, a U.S. Army Pacific commander, General Charles Flynn, reported. North Korea, now a key military supplier to Russia, has provided a range of military equipment, including ballistic missiles and millions of artillery shells. The U.S. is observing these developments, with concerns that North Korea could gain valuable knowledge from the use of their weapons in the Ukraine war. The U.S. and allies allege that North Korea has sent nuclear-capable ballistic missiles to Russia, with at least 10 confirmed uses in Ukraine, and the Kharkiv Oblast prosecutor reporting nearly 50 instances of such missile use by Russia since the war began.
The United States has been cautioning allies about China’s increasing support for Russia amid the conflict in Ukraine, where China is reportedly providing a range of military aid. President Biden addressed these concerns with President Xi Jinping, warning of consequences for assistance to Russia’s defense sector. This is in the context of China’s “no limits” friendship with Russia, underscored by over $200 billion in trade in 2023, despite international sanctions. Similarly, U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen has issued warnings to Chinese officials regarding the support of Russia’s war efforts. During discussions in Guangzhou with Vice Premier He Lifeng, Yellen highlighted the serious repercussions for Chinese entities that aid Russia. The U.S. has repeatedly urged China to refrain from supplying military aid to Russia and to use its influence to help end the war. These concerns are part of broader security implications, including China’s aid to Russia’s optical equipment production, propellants, and space industry, as reported by Secretary of State Antony Blinken to EU and NATO ministers.
In Slovakia, former Prime Minister Peter Pellegrini, an ally of the Russia-friendly incumbent Prime Minister Robert Fico, won the presidential election with 53.85% of the vote. His victory over the pro-Western opposition candidate Ivan Korcok solidifies Fico’s influence in the country. Pellegrini pledges to keep Slovakia oriented towards peace, not war. He succeeds Zuzana Caputova, who did not seek re-election after threats to her safety. Critics fear Slovakia’s potential pivot away from Western alliances towards Hungary’s populist approach under Viktor Orban. The Slovak president has the power to appoint the prime minister, veto legislation, and nominate judges, with Caputova’s strong support for Ukraine now yielding to a new administration.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
The Kremlin is focusing on training future propagandists, leveraging the effectiveness of its information campaigns. Far Eastern Federal University disclosed that its students engaged with an official from the occupied Donetsk Oblast under the “Heroes Among Us” program. This initiative encourages students to produce compelling propaganda documentaries that support the Kremlin’s justifications for its actions in Ukraine and the occupied territories, including Crimea and the oblasts of Luhansk, Donetsk, Zaporizhia, and Kherson.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
