Summary of the day: President Zelensky shared about the limitations of using drones in defending Ukraine’s troops and called on more Western support of artillery systems. He also shared his concerns about the lack of sufficient air defense systems as Ukrainian city’s come under increased attacks. He shared concerns about a possible invasion of Kharkiv city in the summer and the difficulty Ukraine would have as it would force them to divert troops from other parts of the frontlines to defend the city. Meanwhile, the Ukrainian Verkhovna Rada’s adoption of provisions from the draft mobilization law aims to enhance the sustainability of the nation’s mobilization efforts in the long term. On the Russian side, advances near Avdiivka and the capture of Ivanivske highlight ongoing military operations, while the introduction of a bill that could facilitate the deployment of Russian Federal Penitentiaries Service employees to Ukraine signals an intensification of Russia’s mobilization efforts. Amid these dynamics, international attempts to negotiate peace, including Switzerland’s announcement of hosting a global summit, are met with Russian disinterest, indicating a complex and protracted conflict scenario.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War
Amid efforts to distance Armenia from Russia, Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov downplayed tensions, announcing a future meeting between Russian President Putin and Armenian Prime Minister Pashinyan to discuss bilateral relations. Peskov emphasized Russia’s view of Armenia as an ally, confident in resolving issues through dialogue. However, Pashinyan noted the relationship is not at its best, indicating a shift from historical ties to more realistic relations amidst dissatisfaction with Russia’s support over Nagorno-Karabakh and a growing Armenian interest in Western cooperation. Armenia’s participation in upcoming regional summits and events, including the Eurasian Economic Union summit and Putin’s inauguration, remains uncertain. Additionally, Armenia is reconsidering an agreement on broadcasting Russian state television, following the blocking of programs by Russian propagandist Vladimir Solovyov.
The European Union announced plans to provide lethal military aid to Moldova, aiming to bolster its defense amid rising tensions with Russia. Moldova, an EU candidate country, has received non-lethal military support in the past. However, recent developments, including a bilateral defense deal with France and increased EU funding, signal a shift towards more robust military assistance. This move comes amidst concerns that the conflict in neighboring Ukraine could spill over into Moldova via the separatist region of Transnistria, currently occupied by Russian troops.
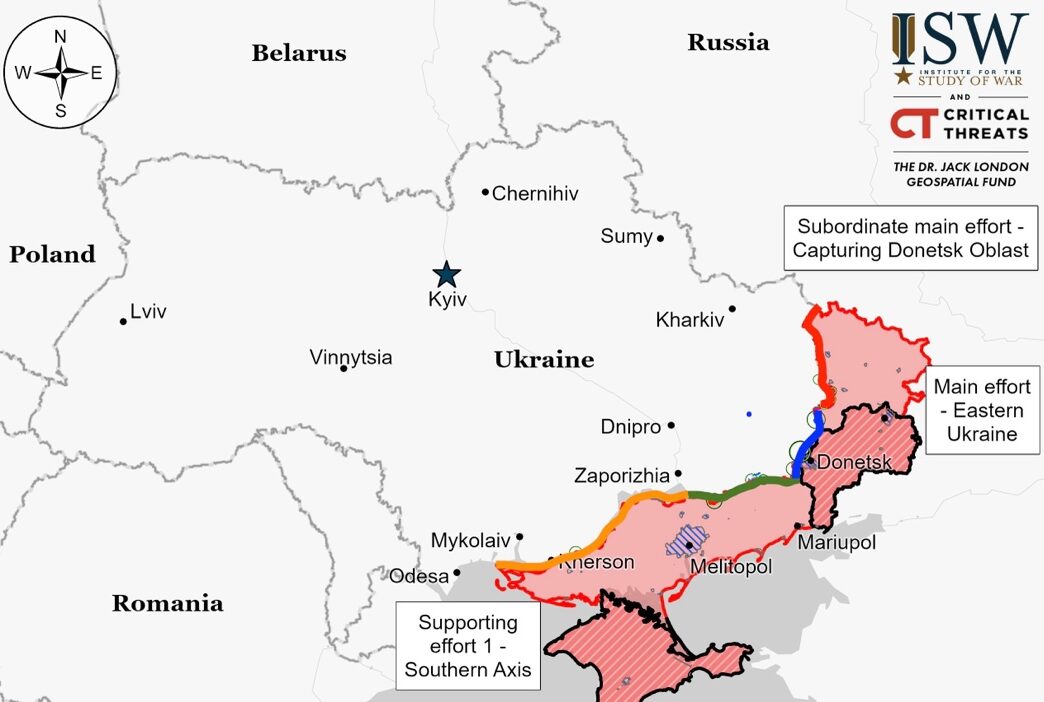
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukraine’s use of drones has been effective but cannot fully offset a critical shortage of munitions, including air defense and artillery systems. Ukrainian President Zelensky highlighted that while drones are being produced domestically, they cannot replace the need for more substantial defense equipment. Despite their success in targeting Russian tanks, drones alone are insufficient to maintain the frontlines without support from artillery and infantry. Electronic warfare and armored vehicle enhancements also challenge drone effectiveness. The U.S. European Command (EUCOM) warned of a significant Russian artillery advantage, stressing the urgency for continued Western military aid to Ukraine. Delays in aid force Ukraine to prioritize defense strategies, impacting their ability to launch counteroffensives and defend territory effectively.
Zelensky highlighted the critical shortage of air defense systems in Ukraine, noting their inability to be replaced by drones amidst intensified Russian strikes, particularly against Kharkiv City. This situation forces Ukraine to reallocate scarce air defense assets to protect strategic locations, further stretching limited resources. The US has approved a $138 million sale to repair and upgrade Ukraine’s HAWK air defense systems but acknowledges this alone won’t change the military balance. Zelensky also mentioned the need for additional Patriot systems to effectively cover all Ukrainian territory. The US European Command warned of Ukraine’s imminent shortage of missiles for existing launchers, emphasizing the necessity of continued US support to prevent battlefield advantages from shifting to Russia.
During his visit to the Kharkiv region’s frontline on April 9, President Zelensky addressed concerns about potential Russian ground offensives targeting Kharkiv City. He stressed that such an attack could strain Ukraine’s already limited resources, potentially necessitating the diversion of forces from critical fronts. Zelensky also discussed ongoing efforts to fortify positions near Sumy City in anticipation of potential Russian advances. While an immediate offensive on Kharkiv seems improbable, Russian military maneuvers suggest a potential summer attack, enabled by their strategic flexibility along the frontline.
A Russian military helicopter crash occurred on the western coast of occupied Crimea. Ukrainian sources confirm the crash of a Russian Ka-27 helicopter, while Russian military sources claim a Mi-24 helicopter crash to technical issues, and Russian military bloggers suggesting a friendly fire incident by Russian air defenses might be the cause. Search operations for the crew are being conducted with additional helicopters and a Raptor boat involved. In response to the incident, Russian forces are increasing coastal air patrols to preempt potential threats. The Ka-27, a Soviet-era helicopter intended for anti-submarine warfare and based at Kacha airfield in Crimea, is utilized by the Russian Black Sea Fleet to counter Ukrainian naval drones and landing crafts. The exact cause and details of the recent crash remain unverified.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Positional battles continued along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line without changes to the frontline. The fighting occurred near several villages and towns along this line. A Ukrainian military observer noted that the Russian 47th Tank Division has almost finished moving from the Lyman area to the Kupyansk area, with significant deployment near Kupyansk. Meanwhile, a geolocation group reported that between December 10, 2023, and April 10, 2024, Russian forces lost 102 to 107 armored vehicles near Terny, showing the intensity of the conflict in that area. These developments indicate ongoing and intense military engagements without significant territorial gains.
Russian state media reported that Ukrainian shelling near Kreminna resulted in the death of Yevgeny Polovodov, a press service officer for the Russian Ministry of Defense’s Western Grouping of Forces and injured two others with him.
Positional battles were ongoing near Bakhmut and other areas northeast of it, without any confirmed territorial changes. Despite a Russian claim of advancing two kilometers towards Vyimka, southeast of Siversk, there’s no visual proof to support this. The fighting also took place near Verkhnokamyanske, Vyimka, and Rozdolivka.
Russian forces have taken control of Ivanivske and are pressing their offensive east of Chasiv Yar. Recent geolocated footage shows Russian advancements along the Bakhmut-Chasiv Yar highway, indicating the likely full capture of Ivanivske following a significant mechanized assault. While similar attacks were observed on April 4, the exact timing of these territorial gains is uncertain. Claims of Russian progress near Hryhorivka and a Ukrainian withdrawal from northeast of Kalynivka are yet to be visually confirmed. Fighting continues around Chasiv Yar, including in the areas of Bohdanivka, the Novyi district, and near Klishchiivka and Andriivka.
Russian forces made slight advances northwest of Avdiivka, with geolocated footage showing gains near Berdychi. Russian military bloggers also claimed progress near Novokalynove, Umanske, and Netyalove, including taking control of part of Semenivka, although these claims lack independent verification. The area continues to see heavy fighting, particularly around Novokalynove, Novobakhmutivka, Berdychi, Semenivka, Umanske, Pervomaiske, and Vodyane.
Russian forces carried out company-sized mechanized assaults west of Donetsk City, particularly near Krasnohorivka, using a considerable number of armored vehicles. Despite these efforts and claims of advancements, including into central Krasnohorivka, there are no confirmed changes to the frontline. Ukrainian forces reportedly destroyed seven Russian armored vehicles during assaults on April 8 and 9. Russian military bloggers also claimed gains south of Novomykhailivka. However, these advances have not been independently verified. Fighting continues in areas west and southwest of Donetsk City.
Ongoing positional battles took place in the area along the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border, specifically south of Velyka Novosilka near Staromayorske and Urozhaine, and southeast of Vuhledar near Mykilske.
There were continued positional battles in western Zaporizhia Oblast. A claim by a Russian military blogger about Russian forces making slight advancements northwest of Verbove, east of Robotyne, lacks visual confirmation. The engagements persisted near Robotyne and in the area northwest of Verbove.
Ukrainian forces have targeted several Russian command posts on the east bank of Kherson Oblast amidst ongoing battles. The Ukrainian General Staff mentioned repelling Russian attacks near Krynky. A Russian Telegram channel, linked to Russian special services, reported a Ukrainian drone strike on a command post of the Russian 205th Motorized Rifle Brigade near Kakhovka on April 5, and a HIMARS strike on another Russian command post near Olhyne on April 6, resulting in three Russian casualties, one injury, and damage to two vehicles. These claims have not been independently verified.
Ukrainian Victims Of War
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the death of at least 9 people and the injuries of 17 others:
- Russian forces launched an attack on the Odesa area resulting in four fatalities, including a 10-year-old girl, and injuring 14 others. The attack, involving Iskander-M ballistic missiles damaged transport infrastructure and trucks. The strike also targeted a gas station, posing further explosive risks.
- Russia conducted airstrikes on Lyptsi, Mala Danylivka, and Vovchansk in Kharkiv Oblast, resulting in at least three civilian deaths and three injuries. The attacks caused fires in local shops and a pharmacy, potentially trapping people under rubble. A 14-year-old girl and two women, aged 43 and 59, were among the fatalities, with two others injured in Lyptsi. In Vovchansk, a 34-year-old man sustained a shrapnel wound from the airstrikes, with the local health center being destroyed in the attack.
- Following a Russian strike on Kostiantynivka, Donetsk Oblast, on April 9, Ukraine’s State Emergency Service discovered two more bodies under the rubble of an apartment building, bringing the death toll to three. The strike partially destroyed a two-story building, resulting in one death and two injuries initially reported. Subsequent rescue efforts revealed the bodies of a 43-year-old woman and a 13-year-old boy. The attack also damaged 27 houses, three high-rise buildings, two infrastructure facilities, and an administrative building.
 The aftermath of the Russian attack on the city of Kostiantynivka
The aftermath of the Russian attack on the city of Kostiantynivka
Ukraine News
Over April 9 and 10, Russian forces launched drone and missile attacks across Ukraine, targeting Odesa Oblast with two guided missiles and deploying 17 drones and three missiles from Crimea. Ukrainian air defenses successfully intercepted most of these, downing both missiles targeting Odesa and 14 drones over Mykolaiv and Odesa oblasts. Additionally, a Russian missile was shot down over Zaporizhia Oblast. The assaults aimed at energy and infrastructure facilities in Odesa Oblast caused damage to an energy facility, with Russian sources claiming hits on a railway bridge and another facility near Odesa City.
The Security Service of Ukraine (SBU) arrested a woman near Odesa suspected of disrupting military conscription and collaborating with Russia. She allegedly posed as a displaced person and was associated with a pro-Russian blogger named Shariya. The SBU claims she cooperated with Russian intelligence through her family members. Evidence was found on her devices. She faces up to 12 years in prison if convicted.
A survey by the Razumkov Center revealed that nearly half of Ukrainians would trust a political party led by military figures after the war. Trust in the military remains high, with 71% having full trust. Following the dismissal of ex-top commander Valerii Zaluzhnyi, President Zelensky’s trust rating reportedly decreased by around 5%. When asked about the source of a trusted political force post-war, most cited the military, followed by volunteers, intellectuals, civil society organizations, existing political parties, and business.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
The Ukrainian parliament recently passed significant provisions of a draft mobilization law to strengthen Ukraine’s long-term mobilization capabilities. These provisions include allowing the mobilization of convicts and increasing penalties for avoiding mobilization. Although a provision limiting active service to 36 months was removed, the Ministry of Defense plans to address service conclusion and personnel rotation separately. These measures aim to bolster the Ukrainian military’s ability to replenish and form new units. However, the effectiveness of these efforts hinges largely on continued support and resources from Western allies. The bill introduces new provisions for demobilization under specific conditions and offers loan benefits for contractors. However, it eliminates the clause on demobilization after 36 months of service, drawing criticism from some military members. The decision to drop the demobilization raised concerns among the military community. The bill also allows citizens with minor criminal convictions to serve in the military, excluding those convicted of serious crimes. The proposal could potentially release 50,000 former convicts and 26,000 current inmates for military service. The bill must undergo a second reading and presidential approval before becoming law.
A toll-free hotline is now available for Russo-Ukrainian war veterans seeking assistance. The hotline offers phone consultations and various services, including psychological support. The hotline offers common referrals for legal, medical, and financial assistance, as well as help with obtaining combat experience status and disability benefits.
Ukraine’s Allies
Kyiv’s new National Security chief, Oleksandr Lytvynenko, met with NATO’s representative, Karen McTear, to discuss Ukraine’s presence at NATO headquarters and the upcoming NATO summit in Washington. They emphasized the importance of increased support for Ukraine. While Ukraine’s NATO membership is supported, no specific timeline has been given.
Germany sent a new shipment of military aid to Ukraine, including artillery shells, drones, and armored vehicles. This follows a 500-million-euro aid package announced in March. The latest delivery includes various weapons and equipment such as ammunition, rifles, reconnaissance drones, and mine-clearing tanks. Germany has emerged as one of Ukraine’s top military donors, providing significant support second only to the U.S.
Switzerland aims to provide 5 billion Swiss francs ($5.5 billion) for Ukraine’s economic recovery by 2036.
Ukraine’s parliament ratified an updated free trade agreement with Canada. The original agreement, signed in 2016, removed most customs duties on mutual trade. The updated deal, signed during President Zelensky’s visit to Canada in 2023, aims to modernize trade relations. Despite controversy in Canada, particularly regarding carbon pricing, the agreement aims to strengthen economic ties between the two countries.
President Zelensky met with Lithuania’s Defense Minister Laurynas Kasciunas in Kyiv, marking Kasciunas’s first foreign trip since taking office. Zelensky thanked Lithuania for its ongoing support and discussed security commitments between the two countries. They also addressed Lithuania’s contributions to Ukraine’s defense, including its leadership in demining efforts and financial support for ammunition initiatives.
The EU Court of Justice lifted sanctions against Russian billionaires Mikhail Fridman and Petr Aven, ruling that the EU failed to prove their involvement in actions undermining Ukraine’s sovereignty. The decision marks a setback for EU efforts to penalize individuals linked to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Fridman and Aven, prominent figures in Alfa Group, had been sanctioned since February 2022. Their businesses faced scrutiny for alleged ties to Russian military operations in Ukraine.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Russian officials are pressing international bodies to affirm their claims that Ukraine is targeting the Russian-occupied Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP) with strikes. Maria Zakharova, spokesperson for the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs, accused Ukrainian forces of systematically attacking the ZNPP. Additionally, Russia’s Vienna mission appealed to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) to denounce Ukraine for alleged damage to the plant. These actions seem aimed at leveraging Russia’s control over the ZNPP to gain international recognition and legitimize its occupation of the facility and Ukrainian territory.
Experimental Tsirkon hypersonic ballistic missiles were launched at Kyiv on Feb. 7 and March 25 from modified Bastion-P coastal defense systems in occupied Crimea. Due to their speed and mobility, Ukraine’s air defenses struggle to detect them. The Ukrainian General Staff has sought public assistance through social media and Telegram channels to locate these weapons, calling it “the people’s intelligence for the elimination of the Tsirkon hypersonic missiles.” They ask residents or contacts in Crimea to share information and images of Bastion systems and associated personnel. This is the first time such public assistance has been requested, indicating the seriousness of the threat and the importance of neutralizing these launchers to protect Ukrainian cities.
Russia News
Ukraine’s Armed Forces General Staff reported 830 casualties among Russian forces in the past day.
Russia announced an investigation into Burisma, a Ukrainian gas company linked to Hunter Biden, for allegedly financing terrorism after a mass shooting in Moscow. Despite ISIS claiming responsibility for the attack, Russian officials attempt to tie it to Ukraine. U.S. National Security Adviser dismissed the accusation as baseless. Hunter Biden’s association with Burisma has fueled Republican allegations of unlawful profiting, which have been widely debunked. These allegations were central to former President Trump’s impeachment charge.
A Moscow court upheld a nearly $50 million fine against Google’s Alphabet for failing to remove content Russia considers discrediting its armed forces and promoting extremism. Google’s legal battles with Russia began before the war, with fines totaling over $300 million for similar offenses. Russia’s crackdown on free speech extends beyond war-related content to include LGBTQ-related information, with penalties for sharing such content including fines and imprisonment.
Alexander Bastrykin, head of Russia’s Investigative Committee, stated Russia has no economic need for foreign labor, contradicting President Putin’s justification for the country’s migration laws aimed at addressing a future labor shortage. Bastrykin, speaking at a legal forum, highlighted concerns over migrant crime and cultural assimilation, suggesting that migrants should either serve in the military or return home. This stance diverges from Putin’s recent acknowledgment of the necessity for foreign labor to counteract Russia’s impending labor deficit. The internal conflict within Russian leadership illustrates a tension between nationalist sentiments and practical economic needs, with the Kremlin unlikely to adopt anti-migrant policies that could exacerbate labor shortages and impact military mobilization efforts.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
A group of Russian lawmakers has proposed a bill that could enable the deployment of Russian Federal Penitentiaries Service (FSIN) employees to Ukraine without their consent, as part of Russia’s increasing efforts in crypto mobilization. The bill suggests that FSIN staff could be sent on compulsory “business trips” or transferred to different units with new duties. This move comes amid acknowledgments from FSIN Director Arkady Gostev that out of 1,600 former FSIN employees sent to fight in Ukraine since the war began, 156 have died.
The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) is integrating the newly established 49th Separate Air Assault Brigade into the 58th Combined Arms Army (Southern Military District). This brigade is being equipped with BMP-3 infantry fighting vehicles to enhance its capabilities in breaking through Ukrainian defenses. This development is part of Russia’s broader military reforms, which include the formation of air assault brigades within ground forces.
The Simbirsk Design Bureau, a Russian drone developer, announced on April 4 that it is manufacturing 300 “Piranha” FPV drones daily. Production has been localized to two facilities in Ulyanovsk Oblast. These drones can carry payloads up to five kilograms and are equipped with rotating thermal imaging cameras.
Russian forces are reportedly using more Krasnopol laser-guided artillery munitions, driven by ramped-up production and a greater deployment of reconnaissance drones.
Russia’s Allies
Russian President Vladimir Putin and Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko are scheduled to hold bilateral talks in Moscow on April 11 and 12.. Additionally, Russia and Belarus have launched four projects aimed at developing and manufacturing precision machine tools domestically, reducing their dependence on Western-made equipment subject to sanctions.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
Russia has expressed disinterest in participating in meaningful peace negotiations regarding the conflict in Ukraine, even as Switzerland announces plans to host a global peace summit on June 15 and 16, inviting over 100 countries to discuss peace proposals. The Russian Embassy in Switzerland dismissed the summit, stating that discussions about Ukraine without Russia’s participation are pointless.
Ukraine’s Special Services (SBU) revealed that the Kremlin plans to accuse Vasyl Maliuk, head of the SBU, of organizing an attack on Crocus City Hall, making him a primary target. Putin reportedly holds a grudge against the SBU for strikes on the Crimean bridge and the use of Sea Baby drones against Russian ships, alongside SBU’s disruption of Russian operations in Ukraine. To bolster these accusations, detained Tajiks, allegedly tortured after the Crocus City Hall attack, will be said to have Maliuk’s business cards. On March 22, an attack at Crocus City Hall in Moscow left 143 dead, with ISIS claiming responsibility. Despite Putin’s acknowledgment of radical Islamist involvement, he accused Kyiv of facilitating the attackers’ escape, a claim Ukraine denies. Russian claims of Western and Ukrainian involvement lack evidence. Internal sources suggest Putin may use the incident to boost support for the war against Ukraine, despite skepticism within his circle. The US had warned Russia of potential extremist threats to the concert hall, with Russian officials acknowledging the warning but describing it as vague.
Russian officials are using disputes over the custody of Ukrainian children in the EU to deflect from their forced deportation of Ukrainian children. Maria Zakharova of the Russian MFA claimed, without basis, that Ukrainians are seeking Russian help to regain custody of their children taken by EU countries, alleging lack of support from Ukrainian embassies. This controversy stems from differences in EU and Ukrainian laws regarding parental guardianship documentation, leading to EU social services taking custody of Ukrainian children. Ukraine is actively challenging these custody cases in EU countries.
Pro-Kremlin bloggers are making unfounded claims about Ukrainian forces using or preparing to use chemical weapons near Klishchiivka, Donetsk Oblast, to potentially justify Russian use of such weapons. Despite these allegations, there’s no evidence to suggest Ukraine is employing chemical weapons in this area. Conversely, there have been consistent reports, including from Ukrainian and Western sources, about Russia’s use of chemical weapons in the conflict. The bloggers’ narrative appears aimed at diverting attention from Russian actions and legitimizing their own potential use of chemical weapons, with one prominent blogger suggesting Russia could mimic the alleged actions of Ukraine.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
