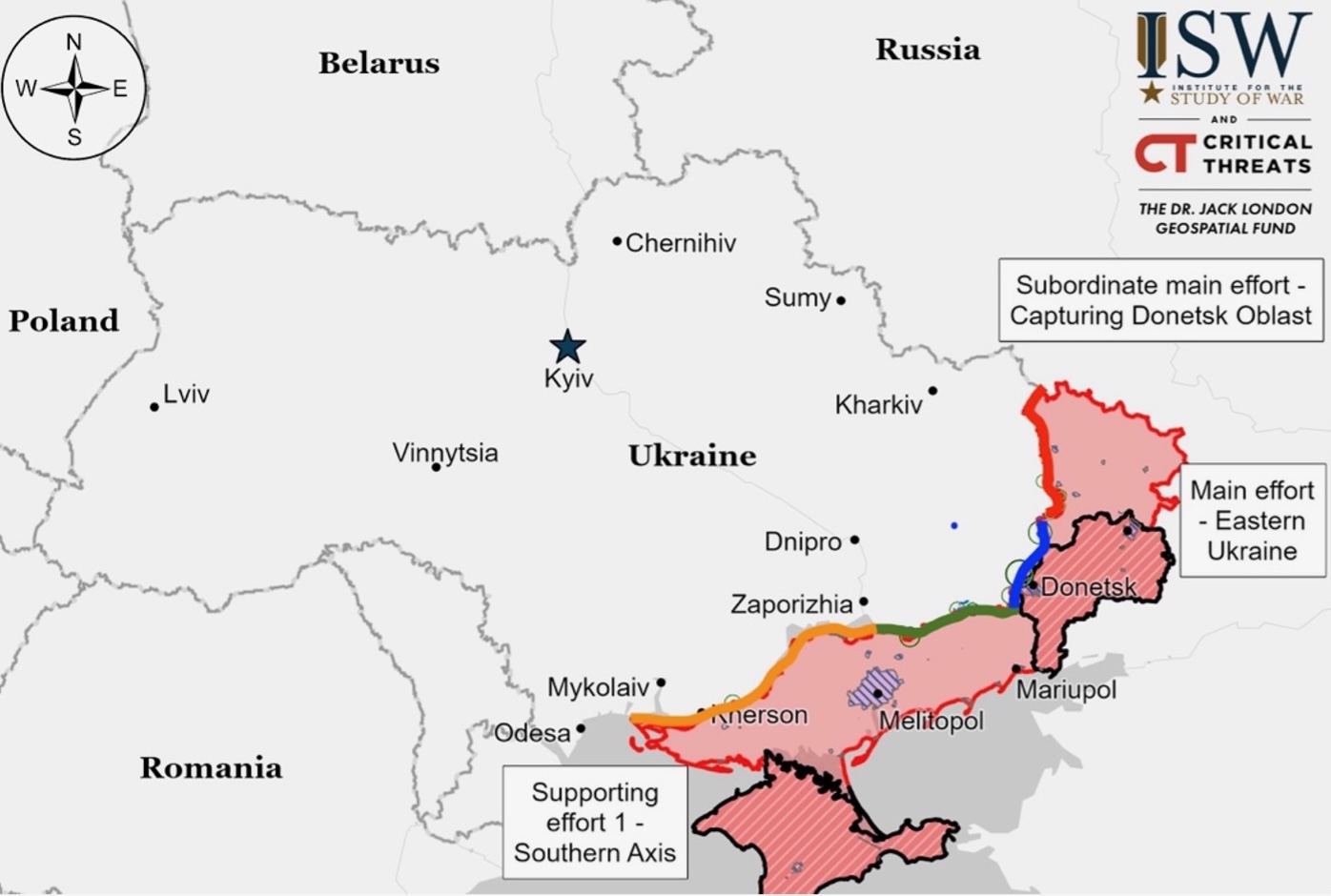
Summary of the day: Russian forces did not make any confirmed advances in the Avdiivka area, marking a pause in their recent activities there. However, increased attacks were reported in the Bakhmut-Chasiv Yar direction, suggesting a possible shift in focus. Meanwhile, Ukrainian forces reportedly conducted an MGM-140 ATACMS strike against targets in occupied Crimea. Internationally, tensions escalated as Tajikistan’s Foreign Minister criticized Russia’s treatment of Central Asian migrants, and former Georgian Prime Minister Bidzina Ivanishvili aligned with Kremlin narratives in his public speech. Additionally, Russian military leadership inspected drone operations in occupied Ukraine, amidst ongoing offensive operations near Kreminna, Chasiv Yar, and Robotyne.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War
A Czech investigation has uncovered that a Russian couple, Nikolay Shaposhnikov and his wife Elena, acted as undercover agents for Russia’s military intelligence, the GRU, orchestrating sabotage activities across the EU since 2014. Their actions included explosions at ammunition depots in the Czech Republic and Bulgaria and the poisoning of a Bulgarian arms manufacturer. The couple, posing as political emigrants in the Czech Republic, gathered military intelligence for Russia and used their hotel in Greece as a base for GRU operatives. Czech authorities found that Elena regularly communicated via email with a GRU commander, providing information that facilitated sabotage against companies deemed harmful to Russian interests. The couple has since avoided questioning by staying outside the Czech Republic, and Nikolay Shaposhnikov died in February following a decline in his health.
Tajik Foreign Minister Sirojiddin Muhriddin criticized Russian authorities for their treatment of Central Asian migrants, particularly from Tajikistan, claiming it violated agreements between the two nations. This response follows increased measures by Russia to control migration after the March 22 Crocus City Hall attack, which have strained relations with Tajikistan. Muhriddin dismissed Russian claims of impartiality post-attack as false, pointing to a targeted negative impact on Tajik citizens. Reports indicate a rise in criminal cases against Tajik migrants and enhanced checks on foreigners entering Russia. Russia’s response suggests an intention to continue these policies despite the diplomatic tensions.
Former Georgian Prime Minister Bidzina Ivanishvili, during his first public speech since announcing his return to politics, echoed Kremlin narratives by claiming that Western NGOs orchestrated Georgia’s 2003 Rose Revolution and controlled Georgian governments until 2012. He accused the West of using Georgia and Ukraine as “cannon fodder” against Russia and criticized Western influence in Georgian politics. Ivanishvili supported Georgia’s “foreign agents” bill, which mandates NGOs receiving significant foreign funding to register as foreign agents, a move aligned with similar Kremlin policies. This bill has faced significant opposition and protests in Georgia. Georgian police used tear gas and water cannons against protesters outside Tbilisi’s parliament. Demonstrators rallied against a proposed “foreign agents” law, likened to Russia’s, which labels organizations receiving foreign funds as such. Riot police clashed with protesters, sparking tensions. The bill, reintroduced by the ruling party, could increase surveillance of funded groups. The European Parliament denounced the legislation. Protests have persisted since April 17, with a government-backed counter-rally on April 29. Former defense minister Tina Khidasheli joined the demonstrators, expressing confidence in their cause.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Oleh Syniehubov, the head of Kharkiv Oblast Military Administration in Ukraine, reported that around 20,000 Russian troops have been stationed on the northern border of Kharkiv Oblast, with a total of about 100,000 troops in the Kupyansk direction for the past ten months. He noted that Russian forces have recently replaced units that lost combat effectiveness and may be preparing to intensify attacks on Ukrainian positions. However, Syniehubov mentioned it is premature to determine if Russia plans to open a new front against Kharkiv City this summer.
Russian sources reported that Ukrainian forces launched a short-range MGM-140 ATACMS missile strike against targets in occupied Crimea overnight on April 29 to 30. The head of Crimea’s occupation administration claimed that missiles aimed at Simferopol were intercepted by Russian air defenses, which allegedly caused cluster munitions to scatter in the area without specifying damage. Additionally, Russian military bloggers reported that between 12 and 15 ATACMS missiles targeting Simferopol and the Dzhankoi airfield were all intercepted. An opposition outlet reported that the strike hit Russian air defense facilities in Crimea, causing a fire and injuring several servicemen. Ukrainian officials have not commented on the incident, and the claims have not been independently verified.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russi
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Positional battles persisted along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line without confirmed frontline changes. While Russian sources claimed advances in Kyslivka, southeast of Kupyansk, only eastern advances are confirmed. Fighting also occurred in areas northwest, west, and southwest of Svatove. Ukrainian military observer Kostyantyn Mashovets reported unsuccessful Russian attacks northeast of Berestove and attempts to advance near Stelmakhivka and Makiivka, involving various units from the Russian military.
Ukrainian forces made slight gains near Kreminna, retaking positions east of Yampolivka. Continued clashes were reported in areas around Kreminna, including west, southwest, and south of the town. Ukrainian advances occurred despite Russian forces pushing Ukrainian troops from positions south of Dibrova.
Ongoing positional battles occurred in the Siversk area northeast of Bakhmut with no confirmed changes to the frontline. Ukrainian forces successfully repelled Russian attacks near Verkhnokamyanske and Rozdolivka, east and south of Siversk respectively.
Russian forces made a strategic advance near Chasiv Yar, capturing territory up to the eastern side of the underground Siverskyi-Donets Donbas Canal south of the town. This movement is part of ongoing Russian efforts to encircle Chasiv Yar, with special operations forces increasing nighttime operations. Russian troops are attempting flanking maneuvers from Bohdanivka and Ivanivske and are deploying reinforcements towards the canal. Initial assaults are typically led by convict units, followed by mechanized or airborne units to secure the newly captured positions. Clashes continue in multiple locations around Chasiv Yar, with Russian aviation also active in the area.
Russian forces did not make any new advances in the Avdiivka area, a shift from previous days, while intensifying attacks in the Bakhmut-Chasiv Yar direction. Ukrainian forces repelled numerous attacks, particularly around Bakhmut, indicating a potential strategic shift by Russian forces. Meanwhile, Russian claims of minor territorial gains near Avdiivka lacked independent confirmation. This activity suggests a possible redistribution of Russian efforts from Avdiivka to areas around Chasiv Yar.
Russian forces are contemplating an advance from north of Avdiivka towards Toretsk, aiming to support operations near Chasiv Yar. This move might necessitate a tactical pause to regroup and strengthen forces. The potential shift to focus on the Stara Mykolaivka-Sukha Balka line reflects challenges in defending the flanks near Ocheretyne. As Russian forces consider advancing north along the H-20 highway to pressure Ukrainian defenses in Toretsk, they might need to reinforce and strategically position additional units, possibly affecting the timeline for their anticipated spring-summer offensive.
There were ongoing positional battles west and southwest of Donetsk City, with no confirmed changes to the frontline. A Russian milblogger claimed that Russian forces made an advance of up to 450 meters near Krasnohorivka, but this remains unverified. The conflict continued in areas west and southwest of Donetsk, notably near Heorhiivka, Paraskoviivka, and Kostyantynivka. Russian troops were active near Novomykhailivka.
Russian forces were reported to have made advances in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border area, though no changes to the frontline were confirmed. A Russian milblogger stated that the Russian 5th Tank Brigade advanced up to one kilometer near Staromayorske, south of Velyka Novosilka, but this has not been visually verified. Reports indicate increased fighting and Russian aviation strikes in the Velyka Novosilka area. Positional battles also continued in the surrounding regions, including near Staromayorske, Urozhaine, Pryyutne, and Novodarivka.
Russian forces have made advances in Robotyne, western Zaporizhia Oblast, with geolocated footage showing the 71st Motorized Rifle Regiment assaulting the area and planting a Russian flag. This footage also captured Russian aircraft flying low, exploiting the absence of Ukrainian air defenses. Although a Kremlin-affiliated milblogger reported that Ukrainian defenses were breached, leading to their withdrawal from Robotyne, the control over the entire settlement is disputed, with the northern outskirts considered a “gray zone.” Caution is advised regarding claims of extensive Russian control in Robotyne. Currently, Russian forces are confirmed to be in the western and southwestern parts of Robotyne, with ongoing fighting near Verbove to the east.
Russian forces attempted but failed to dislodge Ukrainian troops from their positions on the east bank of Kherson Oblast and surrounding Dnipro River islands. According to a Ukrainian military spokesperson, Russian troops attacked Nestryha Island, southwest of Kherson City, but were repelled with losses and forced to retreat. Similar unsuccessful assaults occurred near Krynky, with Russian forces unable to secure their objectives.
Ukrainian Civilian Victims Of War
The casualty count of Ukrainian civilians in the past 24 hours:
DEATHS: 11 INJURIES: 47
- Russian forces launched a ballistic missile attack on Odesa, resulting in three civilian deaths and three injuries. The strike also caused damage to civilian infrastructure. Air raid alerts were issued throughout Odesa on the night of the attack. The injured from the latest attack are currently receiving medical treatment.
- A Russian airstrike targeted the Kyivskyi and Kholodnohirskyi districts in Kharkiv, resulting in at least one death and nine injuries. Initial reports of a second fatality were later retracted. The attack, which involved three UMPB D-30SN glide bombs, damaged residential and administrative buildings, destroying two civilian structures and igniting fires in three garages. Governor Oleh Syniehubov indicated that KAB aerial bombs were likely used in the assault. The State Emergency Service was actively responding to the damages and fires caused by the strike.
- Russia launched a missile attack on Odesa, resulting in five deaths and at least 31 injuries. 23 of those injured remain hospitalized, with eight in serious condition and four, including a four-year-old girl, in critical condition, reported Odesa Governor Oleh Kiper.
- In Donetsk Oblast, an attack on the village of Krasnohorivka in the Pokrovsk district resulted in one fatality and two injuries.
- In the past day, 17 settlements in Kherson Oblast, including the regional center of Kherson, were attacked. The Kherson Oblast Military Administration reported one fatality and one injury from the strikes. Additionally, the attacks resulted in damage to 10 houses, a critical infrastructure facility, an administrative building, a cultural institution, and a car.
- The village of Kupiansk-Vuzlovyi in Kharkiv Oblast was hit by KAB guided bombs, resulting in injuries to a 67-year-old mTop of Forman.
 A firefighter putting out a fire after a Russian airstrike against Kharkiv
A firefighter putting out a fire after a Russian airstrike against Kharkiv
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched a series of strikes on Ukraine. Ballistic missile attacks, likely Iskander-M missiles, targeted Odesa City, resulting in civilian casualties and damage to infrastructure. Additional strikes hit the Odesa Law School and a warehouse in Poltava Oblast. Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson noted challenges in intercepting drones and missiles launched from nearby occupied territories and Russian regions, attributing the difficulty to the short reaction times allowed by the proximity of the launch sites.
Russian forces launched an Iskander missile with a cluster munition warhead at Odesa, killing at least five people and injuring about 30, including children. Ukraine’s Prosecutor General Andrii Kostin stated that the use of such indiscriminate weapons suggests a deliberate Russian strategy to maximize civilian casualties. Fragments from the missile were found spread over a 1.5-kilometer radius. The ongoing investigation aims to hold those responsible accountable. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky called for increased support from international allies to counter these attacks, emphasizing the need for more defensive and offensive weapons to protect and empower Ukraine against continued Russian aggression.
President Volodymyr Zelensky stated that Ukraine would only join NATO after defeating Russia’s full-scale invasion. This declaration was made during a Q&A session at the National Defense University in Kyiv, which coincided with a visit from NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg. Stoltenberg highlighted the ongoing efforts to bring Ukraine up to NATO standards and the need for unanimous consensus among all 32 NATO members before inviting a new country to join. He emphasized the goal of making Ukraine interoperable with NATO forces. Zelensky expressed gratitude to Western partners for their support with air defense systems and other military equipment, noting ongoing challenges and expressing confidence in future enhancements to Ukraine’s air capabilities.
Ukraine’s National Television and Radio Broadcasting Council urged government organizations and officials to cease using Telegram, the country’s most popular messaging app. This advisory followed incidents where Telegram mistakenly blocked three Ukrainian government chatbots crucial for communicating with residents in Russian-controlled areas. The Council emphasized the urgency of discontinuing Telegram for official communications due to security concerns. Despite its widespread use in Ukraine, concerns about the platform’s potential for misuse, including the spread of unregulated information, have led to calls for stricter regulation. Additionally, Telegram’s founder, Pavel Durov, noted recent operational changes for Ukrainian iPhone users due to Apple’s policy updates and past debates over restricting the app to curb military propaganda during the invasion.
Kyiv authorities began dismantling a monument in central Kyiv that commemorated the 1654 Pereyaslav Council treaty between the Cossack Hetmanate and the Tsardom of Muscovy. Erected in 1982 as part of the Soviet-era People’s Friendship Arch, the monument symbolized the “reunification” of Ukraine and Russia. This act is part of Ukraine’s broader efforts to remove Soviet symbols and narratives from public spaces. The dismantling process, involving about 20 parts weighing six to seven tons each, is expected to take several days, with the monument set to be relocated to the Ukraine State Aviation Museum. This move follows the removal of another statue from the complex in 2022 and the Culture Ministry’s recent decision to strip the complex of its historic status.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine will not forcibly repatriate military-aged men from the EU, according to Deputy Prime Minister Olha Stefanishyna in a Deutsche Welle interview. Despite a new provision banning the issuance of identification documents to Ukrainian men aged 18 to 60 abroad, there are no plans for their forced return. The measure aims to manage military registrations rather than immediate mobilization. Ukrainian men can access consular services if registered with conscription offices, though the system’s details are still being finalized. Some neighboring countries, including Poland and Lithuania, have expressed willingness to assist Ukraine in recalling their nationals, but decisions remain pending.
On Ukraine’s Border Guard Day, Interior Minister Ihor Klymenko announced the creation of the State Border Guard Service’s third combat brigade, named “Hart,” meaning “to harden.” This new brigade, composed of veterans who served on Ukraine’s eastern border, reflects the expanded military role of the Border Guard Service, which came under the control of the Ukrainian Armed Forces following Russia’s full-scale invasion in February 2022. The Border Guards have been pivotal in key confrontations since the invasion began, including the defense of Snake Island and Mariupol, and the 2022 counteroffensives in northern territories and Kharkiv Oblast. On the same day, President Volodymyr Zelensky promoted the head of the State Border Guard Service, Serhii Deineko, from major general to lieutenant general.
Ukraine has allocated an additional Hr 15.5 billion ($391 million) to purchase 300,000 drones for its armed forces, announced Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal. This funding complements the Hr 43.3 billion ($1.1 billion) previously designated for 2024, underscoring the country’s strategic emphasis on enhancing its drone capabilities. President Volodymyr Zelensky has prioritized advancing Ukraine’s drone operations as a critical element of the defense strategy against Russia. Moreover, a new branch of Ukraine’s Armed Forces, focused exclusively on drones, was established by a presidential decree on February 6, aimed at boosting drone unit formations, production rates, training, and technological development. Deputy Minister Hanna Hvozdiar noted that Ukraine could potentially produce up to two million drones by year’s end, with a current production capacity of 150,000 drones per month.
Ukraine’s Allies
A Ukrainian delegation, led by the Head of the Presidential Office Andriy Yermak, engaged in the third round of talks with the U.S. on April 29 to discuss a future bilateral security agreement. This meeting follows Ukraine’s broader strategy to forge security agreements with allies amidst the ongoing conflict with Russia. Following the G7’s pledge to support Ukraine’s resistance against Russian aggression, Ukraine has secured similar agreements with nine countries, including the U.K., Germany, and Canada. The recent passage of a $61 billion U.S. aid bill for Ukraine has spurred the negotiation process, with Yermak optimistic about signing a significant security pact with the U.S. soon. Discussions also covered the draft of a bilateral security agreement with Portugal and forthcoming agreements with Nordic and Baltic countries, aiming to enhance Ukraine’s defense capabilities and foster long-term cooperation.
US Defense Secretary Austin urges other nations to provide Ukraine with Patriot air defense systems amid increased Russian strikes on energy infrastructure. Patriots are effective against Russian missiles. Germany pledges an additional system, while Poland and Greece decline. Spain commits to sending Patriot missiles. Ukraine seeks 25 Patriots, focusing on securing seven for major cities.
Donald Trump, in an interview with Time, suggested that the U.S. should curtail aid to Ukraine unless Europe contributes equally. He indicated reluctance to commit to defense assistance for Ukraine if elected in 2024, citing the six-month delay in U.S. aid caused by his influence on the Republican party. Trump argued that Europe should bear more of the financial burden as they are geographically closer to Ukraine. Meanwhile, the U.S. has provided over $67 billion to Ukraine since the invasion began, with $43 billion in military aid. In comparison, Europe has contributed over $96 billion in various supports, surpassing U.S. contributions between summer 2023 and spring 2024. So, since European support far surpasses US support, Donald Trump should continue US support for Ukraine.
The U.S. Senate unanimously passed a bill to ban enriched uranium imports from Russia. President Biden’s approval is expected. The bill prohibits Russian uranium imports through 2040, with exceptions under specific agreements. The House approved the measure in December 2023. The move aims to defund Russia’s war efforts and boost U.S. uranium production.
NATO Secretary General Stoltenberg acknowledges delays in aid to Ukraine, affecting trust in the alliance. He calls for a revamped approach to military assistance coordination. Stoltenberg’s visit to Kyiv coincided with worsening battlefield conditions. He proposes a multi-year plan to clarify NATO members’ contributions. Zelensky states Ukraine will seek NATO membership after defeating the invasion. Stoltenberg affirms NATO’s commitment to help Ukraine align with alliance standards.
French President Emmanuel Macron aims to deepen personal ties with Chinese President Xi Jinping to help end Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Xi’s upcoming visit to France provides an opportunity for Macron to appeal to him to influence Russian President Vladimir Putin. Macron also seeks Chinese investment in France’s electric vehicle battery industry. The visit includes a dinner at the Elysee Palace and discussions in the Pyrenees Mountains. Macron will hold a trilateral meeting with Xi and European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen. Macron has been advocating for European defense and military aid to Ukraine, stressing Europe’s current risks. He previously labeled Russia’s invasion of Ukraine as “existential” for France and Europe.
The Icelandic parliament approved a resolution for long-term assistance to Ukraine from 2024 to 2028. The resolution focuses on supporting Ukraine’s independence, sovereignty, safety of civilians, humanitarian aid, and reconstruction efforts. Iceland’s Foreign Minister initiated the proposal, emphasizing the importance of supporting Ukraine amid Russia’s invasion. Iceland allocated funds for ammunition purchases and equipment for Ukrainian servicewomen in previous years and joined coalitions within the U.S.-led Ukraine Defense Contact Group in 2023.
Latvia approved a new military aid package for Ukraine, focusing on enhancing air defense and intelligence capabilities. The aid includes anti-aircraft guns, surveillance systems, and other essential assets. This support underscores Latvia’s commitment to Ukraine’s defense against Russian aggression. Latvia allocates 0.25% of its GDP annually to provide military aid to Ukraine. Earlier, Riga pledged 392 million euros ($419 million) in military aid. Additionally, Latvia and Ukraine collaborate on joint drone production, with ongoing efforts to strengthen their partnership in defense.
Oslo pledges to increase aid to Ukraine by 7 billion Norwegian kroner ($630 million), focusing on anti-aircraft and artillery ammunition supplies. Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Stoere emphasizes immediate delivery to bolster Ukraine’s defense against Russian attacks on civilian infrastructure. Norway collaborates with allies like Germany and the U.S. to procure air defense systems. The funds will also support a Czech initiative to provide artillery shells for frontline Ukrainian troops. This commitment follows Norway’s earlier allocation of 2 billion Norwegian kroner ($190 million) for Ukrainian aid in January.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
An investigation by Russian opposition outlet Vazhnye Istorii has exposed the involvement of Maria Lvova-Belova, the Russian Commissioner on Children’s Rights, and her sister in the forced deportation of special needs Ukrainian adults to Russia. The report details that four Ukrainian adults from a boarding school in occupied Oleshky, Kherson Oblast were taken to a facility in Penza Oblast, managed by Lvova-Belova’s charity. Despite the support of high-profile Russian figures, including President Putin, one of the deportees expressed a strong desire to return to Ukraine. The Ukrainian Resistance Center highlighted a scheme by Russian authorities to declare these individuals incompetent to transfer their assets to Russian guardians. This act breaches international law, which prohibits the forcible transfer of protected persons from occupied territories.
The Dossier Center reported that high-ranking Russian officials, including Deputy Defense Minister Timur Ivanov, are deeply involved in reconstructing occupied Mariupol. Ivanov, recently arrested on corruption charges, oversaw the Military Construction Company, which managed significant projects in Mariupol, including residential complexes and medical facilities. Following his arrest, these contracts are expected to shift to the Unified Customer company, associated with Deputy Prime Minister Marat Khusnullin, who has been instrumental in allocating construction contracts in occupied Ukraine. This involvement suggests a strategy to tighten Kremlin control over occupied regions and attract Russian investment by rebuilding the very cities they previously destroyed.
Russia News
The General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces reported that Russian forces suffered 1,250 casualties in the past day.
Colonel Abdul Khakim of the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria’s Military Intelligence believes the political situation in Chechnya will not change despite rumors of Chechen leader Ramzan Kadyrov’s fatal illness. Khakim argues that Kadyrov is not an independent political figure and real change would require an overhaul of the entire Russian power structure. He dismisses the possibility of significant shifts with Kadyrov’s potential successors, suggesting they would merely continue Moscow’s influence. Even with Kadyrov’s death, Khakim does not foresee organized uprisings in Chechnya, as there are no current leaders capable of instigating such revolts. Meanwhile, Kadyrov’s reported illness, pancreatic necrosis diagnosed in 2019, is believed to be incurable and worsening. Khakim remains committed to rebuilding Ichkeria’s armed forces and governance structures for eventual independence.
Europe’s reliance on Russian fertilizer is growing, mirroring its past dependence on Russian energy, warns Yara International’s CEO. Despite efforts to reduce reliance on Russian energy, EU imports of Russian urea fertilizer doubled in 2023. Russian fertilizer producers benefit from fewer restrictions and lower costs. Holsether cautions against overlooking the geopolitical implications of this dependency on food production.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian officials, including Deputy Prime Minister Denis Manturov and Deputy Defense Minister Ruslan Tsalikov, visited a drone testing site in occupied Ukraine. The Russian Ministry of Defense stated that they are developing drones capable of firing various ammunitions and performing reconnaissance in adverse weather conditions.
Oleg Zhukov, Chief Designer at the Russian “Geran” Research and Production Enterprise, reported to TASS that Russian forces are deploying the “Abzats” mobile anti-drone system with AI capabilities at the frontline. The system autonomously navigates and uses electronic warfare technology to disable drones without human intervention.
Russia’s Allies
A U.N. sanctions committee report, viewed by Reuters, confirmed that debris from a missile strike in Kharkiv on January 2 originated from a North Korean Hwasong-11 series ballistic missile. This incident aligns with statements from Ukrainian and U.S. officials that Russia has been utilizing North Korean missiles in its attacks on Ukraine. The strike in Kharkiv resulted in at least three deaths and numerous injuries. Inspectors found that the missile fragments did not match Russian-made models, underscoring North Korea’s role as a significant weapons supplier to Russia, despite U.N. sanctions prohibiting such transactions. Concerns are growing over Russia’s reciprocal support to North Korea, potentially enhancing its military capabilities, including ballistic missile and nuclear technology.
A private company linked to Belarusian leader Alexander Lukashenko is constructing a lavish home in the mountains near Sochi, Russia. The property, in the elite resort town of Krasnaya Polyana, spans over 97,000 square meters. Documents reveal Lukashenko’s involvement in transferring ownership from Belarus to his associates. The land, once Belarusian, was exchanged with Russia in 2009. It was sold in February 2022 to a newly formed Russian entity. Plans for the residence include various luxury facilities. Investigators speculate Lukashenko seeks refuge outside Belarus amid political turmoil.
Russian Narratives and Propaganda
Reports indicate that likely Russian sources are disseminating false information about an emergency at the Khmelnitsky Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) in Ukraine. This misinformation campaign, detailed by Ukrainian nuclear operator Energoatom on April 30, falsely claims increased radiation levels in Khmelnitsky and Rivne oblasts, aiming to undermine Ukrainian authorities and create panic among the population. This tactic also seeks to support Russian assertions that Ukraine poses a risk to the safety of the Russian-occupied Zaporizhzhia NPP.
Russian milbloggers are spreading misinformation to provoke panic in Ukraine, falsely claiming that widescale evacuations are occurring in Kharkiv City in anticipation of a Russian offensive. The Ukrainian Ministry of Reintegration has identified these claims as part of a Russian information campaign, noting that Russia is manipulating Ukrainian media reports to further these false narratives.
Alexander Dugin, a Russian ultranationalist ideologue, promoted a false narrative in an interview with an American TV personality on April 29, claiming that the West is targeting Russia due to its defense of “traditional values.” Dugin described this Western stance as “Russophobia.” His comments align with Kremlin efforts to falsely position Russia as a defender of Christianity, culture, and conservative values, despite Russia’s record of repressing religious institutions and employing ultranationalist ideology to support its invasion of Ukraine and opposition to the West.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
