Summary of the day: US officials continue to clarify the policy on Ukraine’s use of US-provided weapons against Russian targets, but communication remains unclear. Western artillery ammunition has arrived at the Ukrainian front, though insufficient to match Russian artillery. Russian attacks have severely damaged Ukraine’s energy grid, leading to further constraints. Ukrainian intelligence reports 550,000 Russian military personnel in occupied regions and near the border. Russian forces advanced in multiple areas, including southeast of Kupyansk and west of Avdiivka. The Kremlin seeks to centralize control over private military companies by granting them legal veteran statuses.
These updates will be shorter until the end of July and will only use the Institute for the Study of War as a source while we are on holiday visiting family and friends. We will be back to our normal coverage again starting on July 22, 2024.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Russian investigative outlet The Insider and Moldovan outlet Little Country revealed that former Moldovan Chief of the General Staff Igor Gorgan acted as an agent for the Russian General Staff’s Main Directorate (GRU). Leaked Telegram messages show Gorgan reported on Moldovan internal affairs and Ukrainian defense visits since 2019 to his handler, Colonel Alexei Makarov. Gorgan’s cooperation with the GRU began during his NATO mission in 2004. He provided information on Moldovan military capabilities and politics, aiding Russia’s efforts to destabilize Moldova and hinder its European Union accession.
Russian officials claim Armenia’s distancing from Russia is due to Western influence. Deputy Foreign Minister Mikhail Galuzin stated that Armenia is reducing interactions with Russia’s Foreign and Defense Ministries under Western pressure, which he says threatens Armenia’s sovereignty. He alleged that the West aims to destabilize regions around Russia and disrupt the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). The Kremlin has threatened Armenia with consequences if it does not re-engage with the CSTO and align with pro-Kremlin policies.
Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Secretary General Zhang Ming announced that Belarus will become a full member at the upcoming SCO summit in Astana, Kazakhstan, in July.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
US policy on Ukraine’s use of US-provided weapons against Russian targets remains unclear. National Security Spokesperson John Kirby stated Ukraine can shoot down Russian aircraft in Russian airspace if they pose an imminent threat. However, the definition of “imminent threat” and overall policy remains vague. This ambiguity impacts Ukraine’s defense against Russian glide bomb attacks. Russian forces continue intense bombings from their airspace. The lack of clear US policy prevents deterring Russia’s strikes on Ukraine. US officials cannot confirm if Ukraine has used US-provided weapons to strike Russia since restrictions were loosened on May 30. However, an unnamed US senator and Western official told the Associated Press that Ukraine has used these weapons “in recent days.” Geolocated footage from June 1 or 2 shows a likely Ukrainian HIMARS strike on a Russian S-300/400 air defense system in Belgorod Oblast.
Western artillery ammunition has begun arriving for Ukrainian forces near Vovchansk, northeast of Kharkiv City, but in limited quantities. Ukrainian soldiers report that Russian forces still maintain a five-to-one artillery advantage. Ammunition is “trickling” in but not at a scale to challenge the Russian munitions dominance. The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) notes that it will take time for the Western-provided weaponry to have a significant impact on the frontline, as Russian forces aim to make gains before US military assistance arrives in full.
A Ukrainian intelligence source reported that around 550,000 Russian military and paramilitary personnel are in occupied Ukraine and near the border. This includes about 32,000 law enforcement personnel like Rosgvardia and FSB, with the rest being military. The figures likely include both combat and support staff. Ukrainian Ground Forces Commander estimated 510,000 to 515,000 Russian personnel in May. Russian President Putin previously claimed 617,000 personnel in the combat zone, which includes staging areas within Russia.
Ukrainian intelligence reported that Russian forces are gathering near Grayvoron, Belgorod Oblast. President Zelensky had previously mentioned Russian preparations for new offensives near the Ukrainian border, specifically around the Grayvoron-Borisovka-Proletarsky area. This region allows for potential attacks towards Zolochiv and Bohodukhiv in Kharkiv Oblast or towards Sumy Oblast. Despite warnings, Kharkiv officials noted no significant Russian strike group presence as of June 1. The concentration near Grayvoron could facilitate attacks in multiple directions.
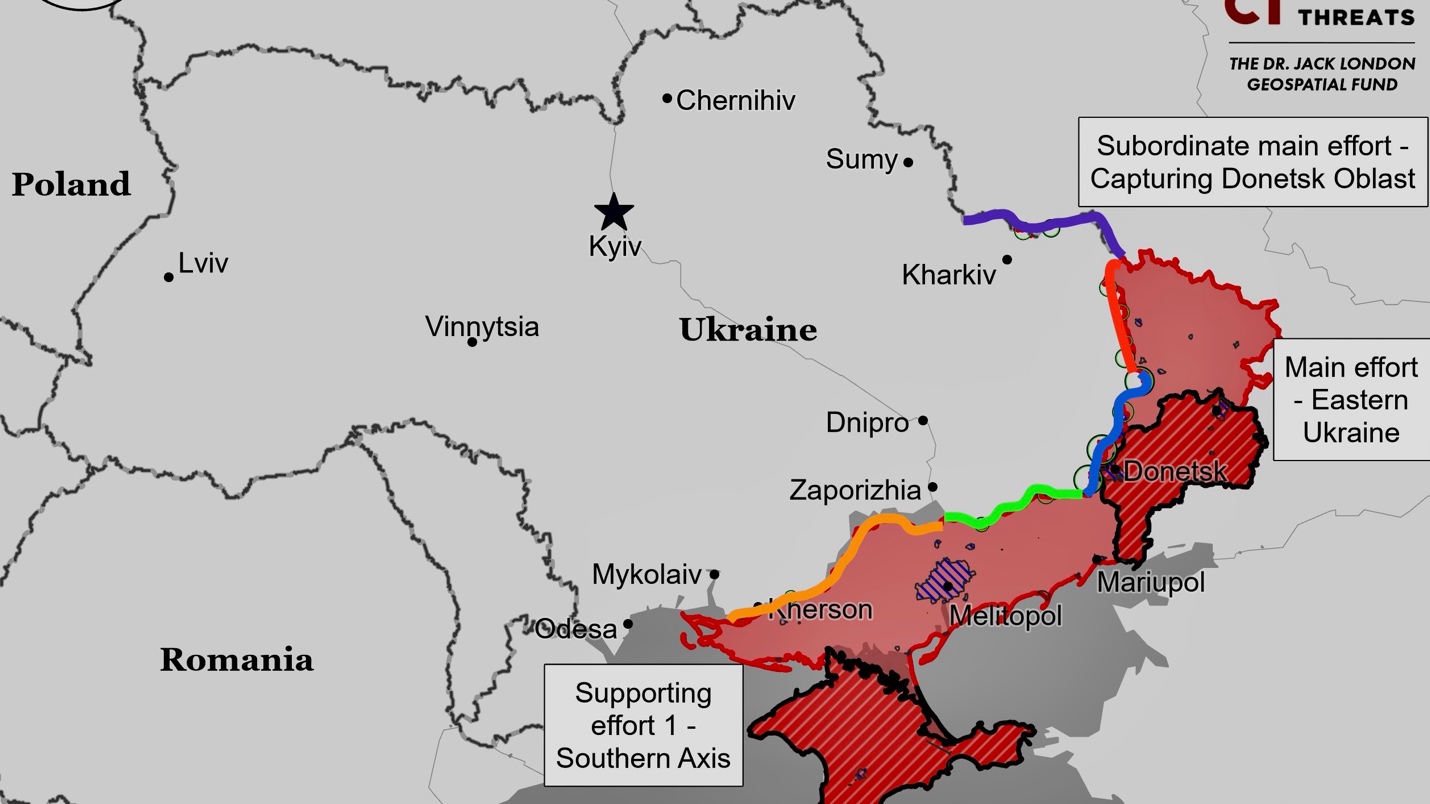
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Lyptsi
Russian forces continued attacks near Lyptsi, but no changes to the frontline were confirmed. Ukrainian forces repelled Russian assaults, according to the Ukrainian General Staff. Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi reported that Russian efforts are focused north of Kharkiv City, particularly on Lyptsi and Hlyboke.
Vovchansk
Fighting continued near and within Vovchansk on June 5 without confirmed changes to the frontline. Ukrainian forces aim to inflict maximum losses on Russian troops, prevent gains, and gradually reclaim territory. Russian sources claimed increased Ukrainian counterattacks, and Vovchansk City Military Administration Head Tamaz Gambarashvili noted that Ukrainian forces have retaken unspecified positions within the town. Ukrainian forces control central and eastern Vovchansk, while Russian forces hold much of the northern part.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces advanced southeast of Kupyansk, targeting areas along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line. Geolocated footage shows advances near Ivanivka and southwest of Novoselivske. Russian sources claim further advances towards Andriivka, though unconfirmed. Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi noted Russian efforts to break Ukrainian defenses from two directions. Fighting continued in multiple areas around Kupyansk, Svatove, and Kreminna, including near Synkivka, Stepova Novoselivka, Stelmakhivka, Druzhelyubivka, Novoyehorivka, Cherneshchyna, Nevske, Yampil, and the Serebryanske forest.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces continued their offensive in the Siversk direction but made no confirmed advances. The Ukrainian General Staff reported Russian assaults near Bilohorivka, Verkhnokamyanske, Vyimka, and Rozdolivka. A Russian milblogger claimed advances near Verkhnokamyanske, but this remains unconfirmed. Russian forces are reportedly operating near Rozdolivka.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces have advanced north and southeast of Chasiv Yar. Geolocated footage from June 4 shows advances along Lisova Street in eastern Kalynivka, with claims of further progress by Russian milbloggers. Footage from June 1 shows minor advances northeast of Andriivka. Ukrainian forces repelled a reinforced Russian attack near Kurdyumivka. Increased Russian attacks have been reported in eastern Chasiv Yar, penetrating some Ukrainian positions. Russian forces continue offensive operations near Kalynivka, Ivanivske, Bila Hora, Klishchiivka, and Andriivka.
Avdiivka
Russian forces advanced west of Avdiivka. Geolocated footage shows progress across the Umanske-Netaylove road. Russian milbloggers reported advances up to 1.5 kilometers in the Karlivka area, moving towards Umanske and Yasnobrodivka. Claims of advances near Novooleksandrivka are unconfirmed. Heavy fighting continues near Sokil and Ocheretyne. Russian troops are pushing towards Novoselivka Persha with recent assaults involving armored personnel carriers.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces advanced southwest of Donetsk City. Geolocated footage showed progress near Solodke, and Russian sources claimed advances in Paraskoviivka and Kostyantynivka. Unconfirmed reports suggest possible control over Heorhiivka. Ukrainian forces repelled attacks near Heorhiivka, and heavy fighting continues near Krasnohorivka, Paraskoviivka, and Vodyane.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces continued ground attacks in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia area but made no confirmed advances. They attacked near Urozhaine, Staromayorske, and Zolota Nyva. Reports claimed Russian advances in northern Staromayorske, though unverified. Russian forces are operating in Staromayorske, and other units are active near Rivnopil and Urozhaine. Russian operations aim to divert Ukrainian forces from the Novomykhailivka-Kostyantynivka area.
Zaporizhia Line
Positional engagements continued in western Zaporizhia Oblast without confirmed changes to the frontline. A Russian source claimed forces advanced 400 meters northeast of Robotyne, but this is unverified. Fighting also occurred near Robotyne, east towards Verbove, northeast near Mala Tokmachka, and northwest near Mali Shcherbaky.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Fighting continued in eastern Kherson Oblast. Geolocated footage shows Russian forces holding positions north of Oleshky near the Antonivsky bridge. Clashes occurred near Krynky and on islands in the Dnipro River Delta. Russian sources claimed a lack of boats and motors is hindering their operations and evacuation efforts in the delta.
Ukraine News
Russian missile and drone strikes have severely damaged Ukraine’s energy grid, reducing its power generation from 55 to below 20 gigawatts. Over half of Ukraine’s power capacity is affected, with recent strikes causing significant losses. Ukraine faces increased energy constraints, especially in summer 2024, as consumption rises. Russia aims to further degrade Ukraine’s energy infrastructure and warfighting capabilities. The European Union Ambassador to Ukraine highlighted the extensive damage, and officials expect the energy system to struggle significantly due to ongoing attacks.
Russian forces conducted drone and missile strikes on Ukraine. They launched 27 Shahed-136/131 drones, and Ukrainian forces shot down 22 over Mykolaiv, Kherson, Dnipropetrovsk, Sumy, and Poltava. A drone strike caused a fire at an industrial facility in Poltava Oblast. Additionally, Russian missiles hit civilian infrastructure in Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi near Odesa.
Kharkiv City Mayor Ihor Terekhov reported that Russian attacks on Kharkiv City tripled in May 2024 compared to April. In May, Russian forces launched 37 guided glide bombs, 25 missiles, 12 Shahed-136/131 drones, and three lancet loitering munitions against the city.
Russia News
President Putin demoted former First Deputy Speaker Andrei Turchak on June 4, appointing him governor of the Altai Republic to remove untrusted political and military figures. This significant downgrade from his Moscow position likely stems from his ties to the late Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin, conflicts with the Russian Ministry of Defense, poor execution of Kremlin initiatives, and involvement in local political intrigues. Turchak’s blunt briefing in February 2023 about military failures, influenced by Wagner’s complaints, and his support for Major General Ivan Popov, further strained his standing with Putin.
The Kremlin-appointed Russian Human Rights Council (HRC) recently discussed migration policy, highlighting Russia’s need to attract migrants to address labor shortages while appeasing its anti-migrant ultranationalist base. The June 4 meeting considered initiatives like mandatory Russian language tests for migrant children and social adaptation centers. Some proposed stricter measures, like banning labor migrants from bringing families. These policies target mainly Central Asian migrants and reflect a balancing act between economic reliance on migrant labor and catering to anti-migrant sentiments.
Chechen Republic Rosgvardia Head Adam Delimkhanov accused State Duma Deputy Chairman Vladislav Davankov of attempting to divide Russian society by proposing a bill to ban religious clothing that covers the face. Delimkhanov argued that this violates the Russian Constitution’s guarantee of religious freedom and criticized the bill for targeting Muslim attire like the hijab, which does not cover the face. Davankov defended the bill, citing parental concerns and a previous court ruling. This conflict underscores tensions between Chechen autonomy and Russian state control over Islamic practices.
Gazprom, Russia’s state-owned gas company, believes it won’t recover the gas sales lost after the invasion of Ukraine. A report commissioned by Gazprom projects that by 2035, its annual gas exports to Europe will be about a third of pre-invasion levels. A new pipeline to China is expected to help but will only handle a fraction of the lost European volume. This loss in gas sales, combined with Western sanctions, limits Russia’s revenue streams, even as it circumvents oil price caps to fund its war efforts.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian President Vladimir Putin announced that Sergei Shoigu, Alexei Dyumin, and Dmitry Medvedev will work to boost Russia’s defense industrial capacity. Shoigu, the former Defense Minister, now has a role like Dyumin and Medvedev, indicating a demotion. Shoigu will also work with foreign countries to procure necessary materials. Dyumin, appointed to the board of defense conglomerate Rostec, is tasked with supplying the military with weapons and equipment. Their roles in expanding the defense industry may be largely nominal.
The Kremlin has likely authorized the Crimean branch of the “Defenders of Fatherland” state fund to grant legal veteran statuses to combatants in Russian private military companies (PMCs). Vladimir Tregub, head of the Crimean branch, confirmed that these combatants are now receiving veteran documentation. This move appears to be part of an effort to centralize control over irregular forces in Ukraine. Tregub also mentioned efforts to address denied state compensation for injured PMC combatants through medical evaluations.
On June 1, Putin tasked the “Defenders of Fatherland” fund with supporting PMC combatants and all personnel who have fought in Ukraine since 2014. He emphasized that all Russian personnel involved in the Ukraine war must receive government support, including PMC members. This marks a shift from Putin’s previous stance of not acknowledging PMCs. The move is likely part of an effort to legally recognize PMCs, starting with a scripted interaction with a Redut PMC fighter during his December 2023 press conference.
Russian Minister of Science and Higher Education Valeriy Falkov announced that 70 Russian universities are creating programs to train students in operating unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for civilian roles. He stated that Russia needs around one million specialists, including UAV operators, engineers, and developers, to work in forest protection, emergency response, and agriculture. This initiative aligns with Russia’s broader strategy to encourage students to join UAV training programs to support the war effort in Ukraine.
An investigation by Russian independent outlet Lyudi Baikala found that one-third of volunteers from Irkutsk Oblast and the Republic of Buryatia killed in Ukraine were former prisoners. Analyzing over a thousand obituaries, they discovered 334 deceased volunteers had criminal records, with many having served time for murder. The actual number of deceased Russian convicts who volunteered is likely higher. Since the full-scale invasion of Ukraine began, Russia’s prisoner population has decreased by 86,000.
A source in the Russian shipbuilding industry informed TASS that the Project 677 “Velikiye Luki” submarine will join the Baltic Fleet by the end of 2024. This submarine, a cruise missile carrier, will be equipped with Kalibr cruise missiles.
A Russian milblogger reported that the Russian defense industry has failed to deliver promised military equipment to troops in southern Ukraine. Despite spending 20 trillion rubles ($224.6 billion), new T-14 Armata tanks, heavy infantry fighting vehicles, “Boomerang” APCs, S-60 and “Altius” drones, 2S35 “Koalitsiya-SV” guns, “Tornado-S” and “Uragan 1M” rocket launchers, and “Peresvet” laser weapons have not reached the frontlines. The milblogger suggested investing in “Lancet” drones, credited with aiding Russian counterbattery efforts in Ukraine.
A former “Storm Z” instructor countered claims about the effectiveness of “Lancet” drones, stating they weigh only 25 kilograms and lack sufficient payload to destroy Ukrainian equipment. He mentioned that while “Lancets” can temporarily disable equipment, multiple drones might be needed to inflict serious damage. He also noted that Russian forces often hit Ukrainian decoys due to poor sensors on their reconnaissance and loitering munitions.
Russia’s Allies
Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko visited the Irkutsk Aviation Plant in Russia, likely to discuss Belarusian support for the Russian aviation industry. He toured facilities for assembling aircraft, including Su-30 SM fighters and MC-21 passenger planes. The General Director of the Russian United Aircraft Corporation mentioned that Belarusian enterprises might receive orders worth 3 to 5 billion rubles annually. Lukashenko also talked with Irkutsk Oblast Governor Igor Kobzev about increasing trade between Belarus and Irkutsk Oblast.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
Russian President Vladimir Putin met with international news agencies at the St. Petersburg International Economic Forum (SPIEF). He focused on internal US politics, aiming to downplay the threat Russia poses to the US and to discourage American support for Ukraine.
The Ukrainian Resistance Center reported that Russian propagandists are manipulating search engine algorithms to display Russian propaganda to residents in occupied Ukraine. Typically, Ukrainian language searches lead to independent Ukrainian resources, but Russian propagandists are creating Ukrainian language versions of their news platforms. This tactic ensures that residents using Ukrainian search terms encounter Russian propaganda in their language.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
