Summary of the day: President Putin ordered the production and deployment of nuclear-capable short- and intermediate-range missiles, likely to influence Western decision-making. Ukrainian forces reportedly struck Russian targets including an oil depot, a microelectronics plant, and a military unit. StratCom reported that Ukrainian forces have damaged or destroyed over 30 Russian military aircraft in the first half of 2024. In troop movements, Ukrainian forces regained lost positions near Vovchansk and Kreminna, while Russian forces advanced near Chasiv Yar. A Russian opposition outlet estimated that over 71,000 Russian men died in the Ukraine war in 2022 and 2023, based on Federal State Statistics Service data.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian StratCom reported that their forces have damaged or destroyed over 30 Russian military aircraft in the first half of 2024, including various fighter jets, bombers, and specialized aircraft. While some incidents, such as the downing of A-50 radar planes and a Tu-22M3 bomber, have been independently confirmed, not all claims have been verified. These losses have temporarily constrained Russian aviation activities, but Ukraine still struggles to contest the air domain fully. Ukrainian officials continue to emphasize the need for additional air defense assets and advanced fighter aircraft to achieve air parity with Russian forces, who currently exploit Ukraine’s air defense limitations to conduct widespread glide bomb strikes along the frontline.
Using Federal State Statistics Service (Rosstat) data, the Russian opposition outlet Vazhnye Istorii estimated that over 71,000 Russian men died in the Ukraine war during 2022 and 2023. This estimate was derived by comparing pre-war male to female mortality ratios to the actual rates during the war years. Similarly, another outlet, Meduza, using the same method, estimated a minimum of 64,000 Russian male war deaths in the same period.
Satellite imagery analysis by German news outlet Suddeutsche Zeitung (SZ), using AI, shows significant losses of Russian tanks and armored vehicles in the Ukraine war. Reviewing imagery from 2021 to 2024 of 87 military sites, SZ noted drastic reductions in vehicle storage, including one base that reduced from 857 tanks in April 2021 to nearly empty by June 2024. The International Institute for Strategic Studies suggests Russia has about 3,200 tanks, most in poor condition. Additionally, a report by the Royal United Services Institute indicates Russia’s plan to produce 1,500 tanks and 3,000 armored vehicles in 2024, with 85% being refurbished from storage.
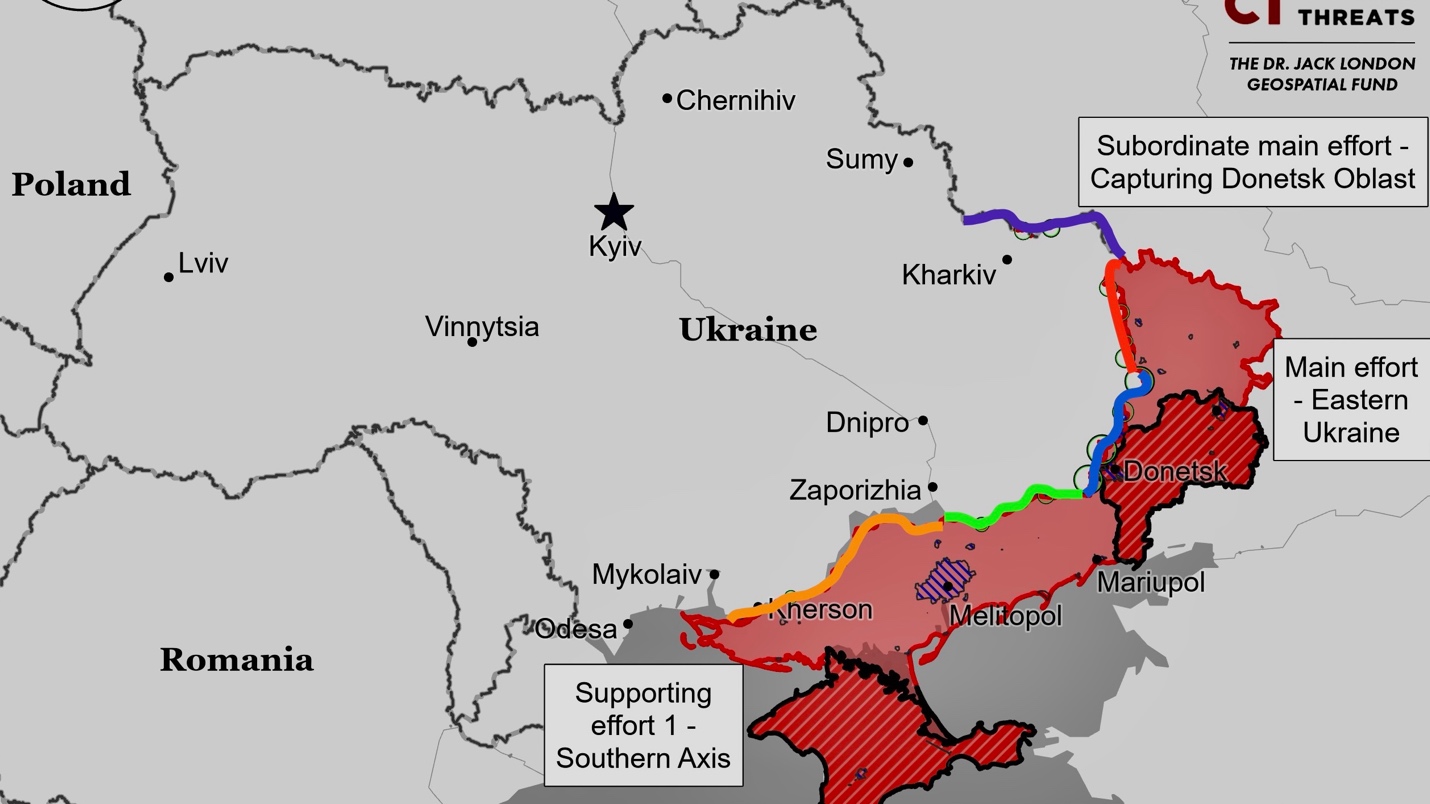
Kharkiv Front – Initiative None
Ukrainian forces recaptured positions in central Vovchansk, northeast of Kharkiv City. A Ukrainian drone commander reported that the situation in northern Kharkiv Oblast has stabilized since June 12, with no significant Russian progress. Russian forces are using both poorly trained “Storm” assault units and regular units, quickly replenishing losses despite heavy casualties. Fighting continued near and within Vovchansk. Russian engineering units are reportedly attempting remote mining operations in the area.
A Ukrainian source claimed that Russian forces may have lost almost the entire 83rd Airborne Brigade in the Kharkiv direction due to losses and refusals to fight. However, this claim is likely exaggerated. Ukrainian officials previously reported that Russia attempted to withdraw combat-ineffective elements of the 83rd Brigade from the Kharkiv area. While the brigade likely suffered significant losses, it’s unlikely to be completely destroyed. Part of the brigade was previously reported operating near Chasiv Yar, and it’s unclear how much of the unit was transferred to the Vovchansk direction.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Ukrainian forces regained previously lost positions south of Kreminna and east of Terny along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line. Military observer Kostyantyn Mashovets reported that Ukrainian forces advanced about 1.5 kilometers near Terny and Yampolivka while Russian forces were focused on operations towards Borova. Mashovets stated that several Russian units were likely regrouping to resume offensive operations in the area when Ukrainian forces counterattacked and recaptured these positions.
Russian forces reportedly advanced along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, but these claims remain unconfirmed. A Russian milblogger claimed advances near Stepova Novoselivka and in the Serebryanske forest area. Russian forces continued offensive operations in multiple locations along this line, including near Synkivka, Petropavlivka, Stelmakhivka, Pishchane, Kruhlyakivka, Andriivka, Nevske, Makiivka, Kopanky, Hrekivka, Torske, Terny, and the Serebryanske forest area.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces intensified offensive operations in the Siversk direction, with no confirmed frontline changes. The Russian Ministry of Defense claimed to have seized Rozdolivka, south of Siversk, but this remains unconfirmed. Russian milbloggers reported conflicting information about the status of Rozdolivka. The Ukrainian General Staff noted increased Russian offensive activities in the area. Russian forces attacked multiple locations around Siversk, including Bilohorivka, Verkhnokamyanske, Spirne, Ivano-Darivka, Vyimka, and Rozdolivka.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces recently advanced to the concrete plant in Kanal Microraion, easternmost Chasiv Yar, indicating their continued presence in the town. This contradicts earlier Ukrainian claims of pushing Russian forces out of the area. Small Russian infantry groups can enter and advance within the microraion but struggle to establish lasting positions. Russian forces also claimed a foothold in central Kalynivka, north of Chasiv Yar. Offensive operations continued near Chasiv Yar, its eastern microraions, Ivanivske, and Klishchiivka.
Toretsk
Russian forces carried out offensive operations near Toretsk without significant frontline changes. Claims from Russian milbloggers suggest minor territorial gains near the area, but these are not officially confirmed.
Avdiivka
Russian forces conducted offensive operations around Avdiivka, with no confirmed changes to the frontline. Claims by Russian milbloggers mention minor territorial advances in the northwest and west of Avdiivka. Key locations involved include Vozdvyzhenka, Novooleksandrivka, and Yasnobrodivka. Ukrainian military sources report Russian military reinforcements in the region.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces continued offensive operations west and southwest of Donetsk City, with no confirmed frontline changes. Claims from Russian milbloggers suggest limited advances in Krasnohorivka and near Kostyantynivka, approaching a major highway. Specific areas of operation include Krasnohorivka, Heorhiivka, Paraskoviivka, and Vodyane.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces did not launch ground attacks in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area.
Zaporizhia Line
Russian forces continued ground attacks near Mala Tokmachka in western Zaporizhia Oblast, with no confirmed changes to the frontline. Claims of an advance near Zahirne lack visual confirmation.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Fighting persisted in east Kherson Oblast, particularly near Krynky and the Antonivsky roadway bridge, with no changes to the frontline confirmed. Claims suggest Russian control in Krynky, with Ukrainian forces holding positions in basements.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched limited missile strikes on Ukraine, targeting Odesa City with a likely Iskander-M missile armed with cluster munitions and conducting an unspecified strike against Dnipro City.
Russian missile strikes have critically damaged the Burshtyn Thermal Power Plant, rendering it irreparable. Over 12 missiles have targeted the plant, with at least five strikes on the region’s energy infrastructure between March 22 and June 1.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
IAEA Director General Rafael Grossi reported that an external radiation monitoring station 16 kilometers from the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant was destroyed by strikes from unspecified actors. While the station is not critical to the plant’s function, its destruction represents a further erosion of the plant’s safety measures.
Following a Ukrainian missile incident injuring over 150 beachgoers in occupied Sevastopol, Russian authorities are enhancing civilian warning and protection measures. Sevastopol’s occupation head, Mikhail Razvozhaev, announced the adoption of a new “Ballistika” warning system, requiring civilians to shelter within two to three minutes, and the establishment of 600 temporary shelters on beaches. Additionally, fines for blocking civilian access to shelters during air raids have been increased to 300,000 rubles (about $3,500). Despite the ongoing conflict and use of Crimea for military operations, Russian authorities continue to promote the region as a tourist destination, maintaining open beaches without adequate safety measures.
Russian officials are actively working to assimilate occupied Ukrainian regions into Russia’s legal, social, and informational frameworks. President Vladimir Putin emphasized the need to raise living standards in these areas to align with Russian federal levels. Furthermore, Kherson Oblast’s occupation head, Vladimir Saldo, discussed with Russian Deputy Presidential Administration Head Eldar Gaifutdinov on June 27 the expansion of communication and broadcasting infrastructure in Kherson Oblast to bolster Russia’s “informational front” in the ongoing “hybrid war with the West.”
Russian authorities are intensifying efforts to Russify and militarize Ukrainian children in occupied regions, aiming to suppress Ukrainian national identity and culture. On June 27, Yevgeny Balitsky, the occupation head of Zaporizhia Oblast, reported sending 70 Ukrainian schoolchildren to Russia’s “Zarnitsa 2.0” military-patriotic game, designed to foster a “love for the [Russian] Fatherland” and teach military and sports skills. Additionally, Petro Andryushchenko, an advisor from Mariupol, revealed that over 16,500 Ukrainian children have been compelled to join Russian military-ideological groups like Yunarmiya. Ivan Fedorov, Head of the Ukrainian Zaporizhia Oblast Military Administration, also stated that Ukrainian children are being sent to Moscow under vacation schemes to publicly support Russia’s military actions and visit military sites.
Russia News
Ukrainian forces reportedly conducted several strikes in Russia. A drone hit an oil depot in Tambov Oblast, starting a fire at the Transnefteprodukt “Nikolskoe” station. In Bryansk Oblast, Ukrainian forces allegedly struck a military unit in Karachev and the “Kremniy El” microelectronics plant in Bryansk City, which produces components for military equipment. Bryansk’s governor claimed Russian forces suppressed a drone over Bryansk City, with debris damaging an administrative building. The Russian Ministry of Defense reported destroying 12 drones over Bryansk Oblast but didn’t mention the Tambov Oblast incident.
President Putin ordered the production and deployment of nuclear-capable short- and intermediate-range missiles, following the US withdrawal from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces (INF) treaty in 2019. Putin claimed this decision was in response to US violations, citing two 2024 military exercises with the Philippines and Denmark involving Typhon Medium Range Capability launchers. This move is part of Russia’s broader strategy to discourage Western military aid to Ukraine and influence decision-making. The US had previously withdrawn from the INF treaty due to Russian violations involving 9M729 missiles. Despite Putin’s claims, the cited exercises involved launchers with limited threat to Russia due to range constraints. His condemnation aligns with China’s earlier criticism of the Philippine exercise, possibly appealing to China, North Korea, and Vietnam in efforts to create a new “Eurasian security architecture.”
Russian opposition journalist Mikhail Zygar reported that many Russian elites who initially opposed the war in Ukraine have shifted to supporting it, believing Russia is now prevailing. This change is attributed to Russia’s slow but steady battlefield gains, Ukraine’s munitions disadvantage, and perceived reduction in Western aid to Ukraine. Some elites reportedly view a Russian victory as necessary to prevent Russia’s collapse. This shift aligns with Putin’s strategy of gradual advances and attrition warfare.
Russian officials are calling for harsher criminal punishments, likely in response to recent terrorist attacks in Dagestan. Investigative Committee Head Alexander Bastrykin suggested lifting the moratorium on the death penalty for certain cases, despite the Constitutional Court deeming it inadmissible under the current constitution. Justice Minister Konstantin Chuychenko proposed a bill to make forced labor the main punishment for over 65 crimes, claiming it’s more humane and reduces recidivism. Bastrykin also called for stricter migration policies, citing spreading migrant crime. These calls for harsher measures follow the March 2024 Crocus City Hall attack and the June 23 Dagestan attacks.
Russia may be creating a shadow fleet to transport liquefied natural gas (LNG) and bypass Western sanctions. Bloomberg reports that a Dubai-based company has acquired at least eight vessels in the past three months, with Russia granting four permissions to traverse Arctic waters in Summer 2024. Some vessels list their insurers as “unknown,” a tactic used by tankers carrying Russian oil to avoid the G7 price cap. This development comes as the EU’s latest sanctions package prohibits EU entities from providing reloading services for Russian LNG in EU territory for transshipment to third countries.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Sri Lankan Foreign Minister Tharaka Balasuriya met with Russian officials on June 27 to address issues related to the recruitment of Sri Lankan nationals by the Russian military. Discussions included compensation for Sri Lankans harmed during service, the option for early contract termination, and the formation of a committee to support currently serving Sri Lankans. Following a June 11 meeting with Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov, both nations agreed to halt the recruitment of Sri Lankan citizens into the Russian military.
Select Russian milbloggers claim to have influenced Defense Minister Andrei Belousov’s decision to enhance social benefits for Russian military personnel. Following a June 10 meeting with Belousov, these milbloggers reported that he directed the Ministry of Defense to improve social support for veterans from the Donetsk and Luhansk regions who served before the 2022 annexation. This interaction is seen as an effort to secure milbloggers’ loyalty and portray Belousov as a responsive leader.
Russian officials, led by First Deputy Prime Minister Denis Manturov, are prioritizing innovation in the defense sector to support military efforts in Ukraine. At the “ERA” military innovation forum, Manturov stressed the need for rapid development of new man-portable weapons, close combat arms, and airfield-based drones, urging that these be finalized within days. The meeting, which included Deputy Defense Minister Colonel General Yunus-Bek Yevkurov and other military and defense industry leaders, also highlighted collaboration among the Ministry of Defense, government bodies, defense industries, and the “Popular Front” social movement to maintain a technological edge in drones and electronic warfare systems.
Russia’s Allies
Belarus has reportedly deployed a Polonez multiple rocket launch system (MLRS) battalion to its border with Ukraine, citing a “difficult situation” and as part of a surprise readiness check, according to the Belarusian Ministry of Defense. Additionally, the Belarusian State Border Committee reported shooting down a drone, allegedly from the pro-Ukrainian Russian Volunteer Corps, near the border in Gomel Oblast on June 26.
At the Forum of Regions of Belarus and Russia held in Belarus, officials and business representatives from both countries discussed enhancing bilateral economic cooperation. Russian President Vladimir Putin highlighted efforts to integrate new technologies and develop knowledge-intensive industries and agriculture. Russian Ambassador to Belarus, Boris Gryzlov, announced that over 100 contracts are expected to be signed during the forum, involving more than 80 Russian federal subjects in trade and economic interactions with Belarus. Additionally, Belarusian and Russian parliamentarians explored cooperation opportunities in agro-industrial and light industries.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) continues to falsely accuse the United States of involvement in a Ukrainian strike on occupied Sevastopol, Crimea, suggesting it could lead to direct NATO-Russia confrontation. They claim the U.S. aids Ukraine in targeting Crimea. On June 23, the Russian MoD attributed responsibility for the strike to the U.S., alleging assistance in target designation. Additionally, the MoD admitted that a Russian air defense interceptor misdirected the missile, causing it to detonate over a civilian area. Defense Minister Andrei Belousov has directed the Russian General Staff to develop responses to what he calls Western “provocations.”
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
