Summary of the day: Ukrainian forces made marginal advances near Sudzha during ongoing operations in Kursk Oblast. Despite Russian materiel advantages, Ukrainian officials emphasized their ability to leverage tactical and technological advantages. US President Biden announced a new military assistance package for Ukraine following a call with President Zelensky. In other developments, Ukrainian forces reportedly conducted a drone strike on an oil depot in Rostov Oblast, while Russian forces advanced near several key locations including Kreminna and Donetsk City. Additionally, a hostage situation unfolded at a penal colony in Volgograd Oblast, prompting criticism of Russia’s prison system from milbloggers.
Picture of the day:
 Zhenya Dove, an activist and volunteer from Kherson who is based in Edinburgh, explores the sunflower fields in East Lothian, Scotland. The sunflower is the national flower of Ukraine and a symbol of peace. August 24th is Ukraine’s Independence Day. (Jane Barlow/PA Images via Getty Images)
Zhenya Dove, an activist and volunteer from Kherson who is based in Edinburgh, explores the sunflower fields in East Lothian, Scotland. The sunflower is the national flower of Ukraine and a symbol of peace. August 24th is Ukraine’s Independence Day. (Jane Barlow/PA Images via Getty Images)
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
China and Belarus agreed to strengthen security and economic ties during Chinese Premier Li Qiang’s visit to Minsk on August 22. The countries plan to improve cooperation in finance, energy, and industrial supply chains. This visit followed Li’s trip to Russia, as both Belarus and China remain key allies of Moscow amid Western sanctions. Belarus recently joined the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, a Eurasian group led by Russia and China. The two countries also conducted joint military drills near Ukraine’s border in July. While China claims neutrality in Russia’s war against Ukraine, it continues to strengthen ties with Moscow.
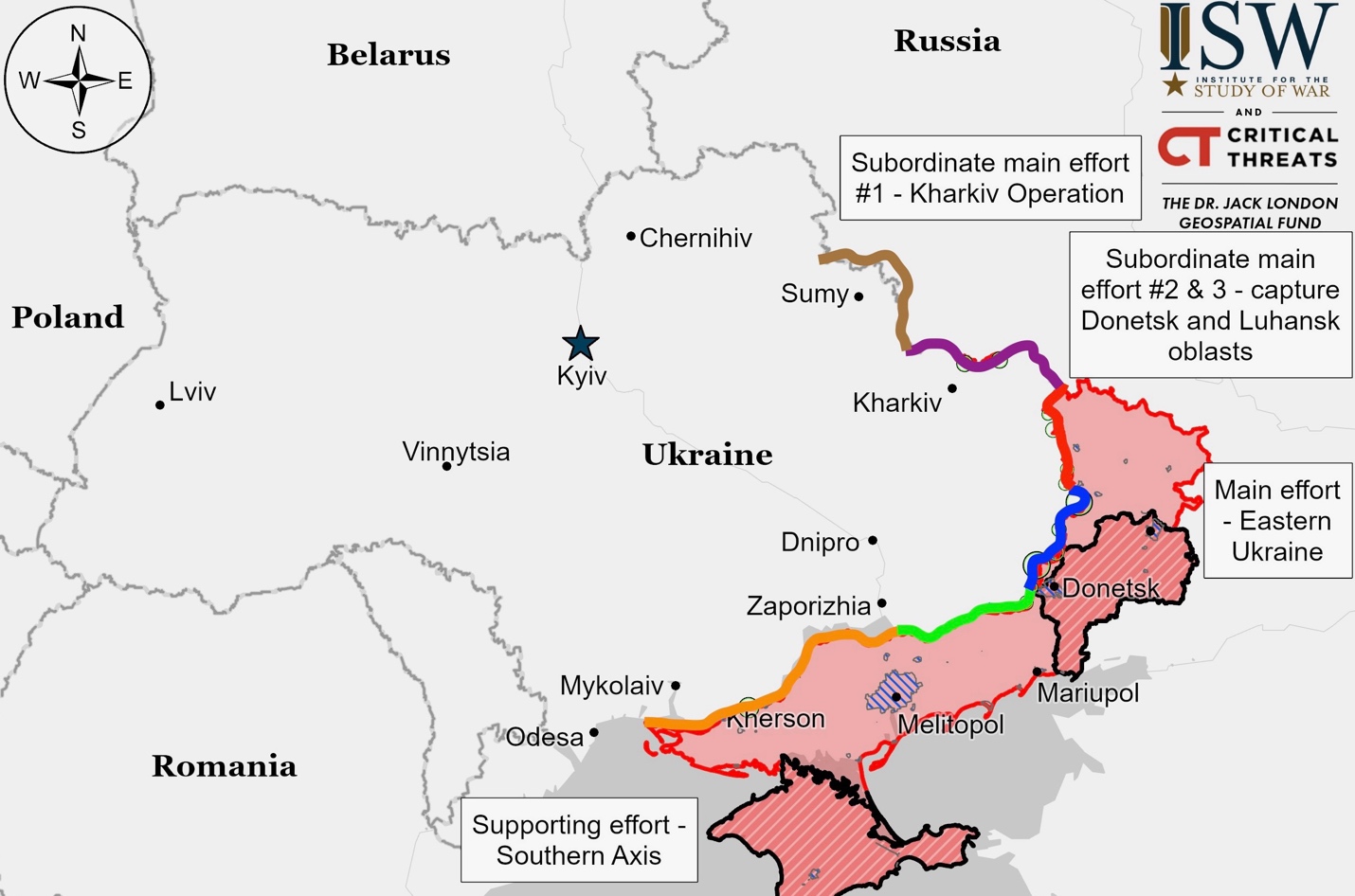
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian officials say they’re using tactics and technology to counter Russia’s materiel advantages. Ukraine claims to have destroyed significant amounts of Russian equipment since February 2022. They note that precise Western artillery systems help offset Russia’s numerical advantage. Ukraine is also increasing its use of drones to inflict losses on Russian forces more cost-effectively.
Ukrainian forces destroyed the “Konro Trader” ferry in Russia’s port of Kavkaz on August 22, as confirmed by the Ukrainian Navy and satellite imagery. The attack also caused possible damage to nearby vessels and railroad tracks. This was the last functioning ferry at the port, with two others already out of service. The vessel, used for transporting fuel and weapons to Russian forces, was carrying 30 fuel tankers when struck. The destruction potentially disrupts fuel supplies to occupied Crimea and complicates Russian logistics, forcing consideration of alternative fuel transport methods across the Kerch Strait. The Kerch ferry crossing, a key supply route, has been halted as a result. This attack is part of Ukraine’s ongoing efforts to target occupied Crimea and nearby areas, including ferry crossings between Crimea and Krasnodar Krai, aiming to disrupt Russian military logistics in the region.
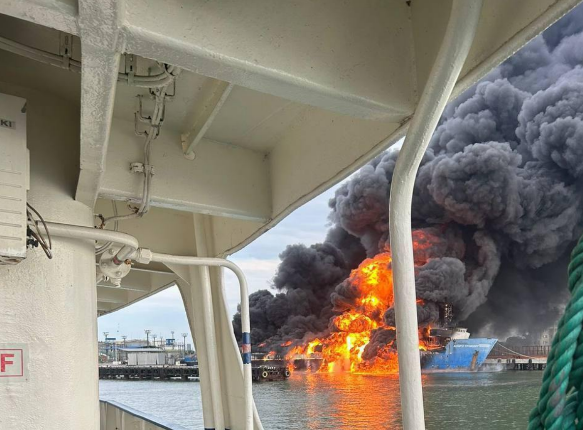 The footage purporting to show a burning ferry in the Kavkaz port in Russia’s Krasnodar Krai. (Astra/Telegram)
The footage purporting to show a burning ferry in the Kavkaz port in Russia’s Krasnodar Krai. (Astra/Telegram)
Kursk Front – Initiative Ukraine
Ukrainian forces made small advances near Sudzha in Kursk Oblast. They progressed in southern Russkaya Konopelka and possibly north of Martynovka. Fighting was reported near Samoryadovo and Kozyrevka. Russian sources claimed to have retaken Spalnoye and Krupets, but the situation remains unclear. Clashes occurred near Aleksandrovka and Korenevo. Fighting continued along the Kursk Oblast front.
Ukrainian forces are reportedly attempting to capture a women’s penal colony in Malaya Loknya, Kursk Oblast, Russia. This facility has been used to hold Ukrainian prisoners of war, including over 50 military and civilian women in 2022. The capture could help document Russian war crimes against POWs. Former prisoners reported physical abuse and humiliation at the facility.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative None
Russian forces continued attacks north and northeast of Kharkiv City with no confirmed frontline changes. Unverified Russian claims of advances near Vovchansk emerged, while reports surfaced of an unsuccessful Ukrainian assault near Hlyboke. Small Ukrainian attacks were noted near Ohirtseve and Hatyshche. Russian ground assaults occurred near Hlyboke, Starytsya, Vovchansk, and Tykhe.
Ukrainian President Zelensky reported that Ukrainian forces are gradually pushing Russian troops out of Kharkiv Oblast. The 3rd Separate Assault Brigade launched a counterattack, advancing nearly two kilometers into the front-line area. While Russia initially gained ground in May, their offensive has since stalled with heavy losses reported. Ukrainian forces claim to have damaged Russian positions and logistics, potentially impacting their effectiveness despite large reserves in the area.
Ukrainian military spokesperson Colonel Vitaly Sarantsev reported that Russia has moved some troops from the Kharkiv area to Kursk Oblast. Despite this, Russian forces still have enough soldiers to continue attacks near Kharkiv. Sarantsev mentioned possible Russian reinforcements coming to Kharkiv but noted this needs confirmation. Russian activity has decreased in some parts of the Kharkiv region. These troop movements suggest Russia is prioritizing its response to Ukrainian actions in Kursk Oblast over its offensive in northern Kharkiv Oblast.
Vitaly Ganchev, head of the Russian-installed administration in occupied Kharkiv Oblast, claimed that Russian forces control about 50 settlements in the region. Independent analysis confirms Russian advances or claims of control in 57 settlements. Ganchev stated that 13 to 14 settlements are part of a Russian “sanitary zone” in northern Kharkiv Oblast, which aligns with observations of Russian control in 14 northern settlements.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces advanced northwest of Kreminna and continued attacks along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line. They gained ground in eastern Makiivka and conducted offensive operations near several settlements, including Synkivka, Petropavlivka, Hlushkivka, Stelmakhivka, Andriivka, Lozova, Druzhelyubivka, Novosadove, Nevske, Torske, and Terny.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces attacked near Siversk. Offensives occurred northeast at Bilohorivka, east at Verkhnokamyanske, and southeast at Vyimka and Spirne. No confirmed frontline changes. A Russian source claimed 1km advance near Vyimka, but this is unverified.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces attacked near Chasiv Yar. Offensives occurred at Kalynivka, Ivanivske, and Chasiv Yar itself. Russian sources claim advances near Ivanivske, Klishchiivka, and in eastern Chasiv Yar, but these are unconfirmed. No verified frontline changes.
Toretsk
Russian forces advanced in southeastern Toretsk. They attacked near Toretsk, Pivnichne, Druzhba, Nelipivka, and Niu York. Claims of further advances in eastern Toretsk and a 750×800 meter push are unconfirmed.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces advanced west of Orlivka and in eastern Novohrodivka near Pokrovsk. They attacked multiple settlements including Vozdvyzhenka, Zelene Pole, Hrodivka, Kalynove, Ptyche, Mykolaivka, Mykhailivka, and Karlivka. Additional Russian claims of advances remain unconfirmed. Reports suggest Russia has reinforced the Pokrovsk area while moving some troops from eastern Ukraine to Kursk Oblast.
Ukrainian forces have withdrawn from positions southeast of Pokrovsk, Donetsk Oblast, to avoid Russian encirclement. Russia is focusing efforts in this area after failing in Kharkiv Oblast. Pokrovsk, a key logistical hub, faces evacuation calls as Russian troops approach within 10 km. Ukrainian units withdrew to “preserve the lives of servicemen.” Poor training of new recruits may affect Ukraine’s ability to hold positions.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces advanced southwest of Krasnohorivka near Donetsk City. They attacked Heorhiivka and Krasnohorivka. Ukraine claims to have destroyed one tank and five infantry fighting vehicles during the assault.
Russian forces attacked near Kostyantynivka, Vodyane, Volodymyrivka, and Vuhledar southwest of Donetsk City. Claims of advances near Kostyantynivka and north of Paraskoviivka are unconfirmed. No verified frontline changes.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian and Ukrainian forces clashed near Rozdolne and Urozhaine in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border region. These battles are part of ongoing military operations in eastern Ukraine.
Zaporizhia Line
A Russian military blogger reported ongoing battles in western Zaporizhia Oblast. Ukrainian sources did not confirm this claim.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Russia claims its airborne forces stopped a Ukrainian attempt to land on an island in the Dnipro River Delta, Kherson Oblast.
Ukraine News
Russia launched 2 ballistic missiles from Voronezh and 16 drones from Krasnodar and Kursk. Ukraine shot down 14 drones over several regions. Russia also struck Bohuslavka in Kharkiv Oblast with glide bombs. (Russian War Crimes)
On August 22, Ukraine’s nuclear operator Energoatom reported that the Russian-occupied Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant in Enerhodar was disconnected from an external power line due to Russian shelling, leaving only one connection to Ukraine’s power grid. Energoatom warns of potential emergencies if the remaining line is damaged. The plant has experienced multiple blackouts since its occupation in March 2022. The International Atomic Energy Agency reported “deteriorating” nuclear safety after a drone strike near the facility. Russia has accused Ukraine of planning attacks on nuclear plants, while Ukraine claims Russia is creating panic with provocations at the Zaporizhzhia plant.
Germany and the U.S. have issued travel advisories warning of potential increased Russian attacks on Ukrainian cities, especially Kyiv, on August 24, Ukraine’s Independence Day. Both countries urge their citizens to avoid travel to Ukraine or leave if already there. Russia has historically intensified attacks during Ukrainian national holidays.
Ukraine plans to resume electricity exports on August 25 during surplus periods, mainly from solar power. This follows recent energy shortages due to Russian attacks on infrastructure and a July heatwave. Exports will not occur during peak consumption. DTEK, Ukraine’s largest private energy company, lost 90% of its capacity from Russian attacks but aims to recover 60-70% by October.
Ukraine’s Allies
The Pentagon has affirmed ongoing US support for Ukraine’s battlefield needs, including defense against Russian cross-border attacks in areas like Kursk Oblast. President Biden announced a new $125 million military aid package following a conversation with Ukrainian President Zelensky. This assistance includes air defense missiles, anti-drone systems, HIMARS ammunition and rockets, artillery shells, anti-armor weapons (such as TOW missiles, Javelins, and AT-4 systems), medical equipment, mine-clearing tools, and various types of ammunition for small arms and demolitions. Biden reaffirmed U.S. support for Ukraine, stating Russia will not prevail. The U.S. now allows Ukraine to use American-supplied weapons to strike Russian targets near the Kharkiv Oblast border but prohibits strikes deeper inside Russia with long-range weapons like ATACMS.
The U.S. imposed new sanctions against nearly 400 entities in Russia and other countries for supporting Moscow’s war effort. The sanctions target networks in China, Switzerland, Turkey, and the UAE that help Russia evade restrictions. They also affect Russian technology and defense companies, as well as entities involved in chemical and biological weapons programs and the metals and mining sector. The U.S. aims to disrupt Russia’s military-industrial supply chains and limit its ability to fund and equip its invasion of Ukraine.
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi visited Ukraine, the first such visit since 1992. Modi and Ukrainian President Zelensky signed four bilateral cooperation agreements covering medicine, agriculture, humanitarian relations, and culture. They also issued a joint statement supporting peace in Ukraine based on international law and agreed to strengthen strategic partnership, trade, and defense collaboration. The visit included a commemoration of Ukrainian children killed in the war. This meeting suggests a potential shift in India’s stance towards Ukraine, despite India’s historically close ties with Russia, which have been maintained since the invasion began in 2022.
Latvia is sending its largest batch of 1,400 drones to Ukraine, completing a program that provided 2,700 drones in total. This is part of the international drone coalition, led by Latvia and the UK, which aims to supply Ukraine with crucial UAV capabilities. Latvia has invested about 20 million euros in the coalition this year. The alliance includes nine countries in total, supporting Ukraine’s defense efforts. Meanwhile, Ukraine plans to produce at least 1 million drones domestically in 2024.
Norway will finance the production of 155mm artillery shells in Ukraine, developed by Nammo (Nordic Ammunition Company). This agreement allows for licensed production in Ukraine, speeding up ammunition delivery to Ukrainian troops. The move addresses Ukraine’s shift to NATO-standard artillery and its urgent need for shells to counter Russian aggression. Nammo, a Norwegian-Finnish company, has received a license to transfer shell production technology to Ukraine. The company has also increased production at its Swedish and Finnish plants to support Ukraine’s defense efforts.
Ukraine banned Russian oil company Lukoil from using the Druzhba pipeline for crude oil transit, aiming to reduce Kremlin’s war funding. Hungary and Slovakia, which receive Russian oil through this pipeline, criticized the decision. However, the European Commission found no cause for concern, as oil deliveries continue and Ukraine confirmed that transit to these countries is unaffected. The EU is monitoring the situation and encouraging member states to reduce dependence on Russian fossil fuels. Ukraine’s Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal denied that the ban violates the EU-Ukraine Association Agreement and called Hungary’s and Slovakia’s reactions “politicized and manipulative.”
Russia News
Ukrainian forces reportedly conducted another drone strike on an oil depot in Proletarsk, Rostov Oblast, following a previous strike on August 18. Satellite imagery suggests a Ukrainian strike on August 22 may have destroyed or damaged Russian fighter aircraft at Marinovka airbase in Volgograd Oblast. A Russian milblogger criticized the use of light hangars for inadequate protection of aircraft.
A drone attack in Russia’s Voronezh Oblast caused a fire and explosions. The Russian Telegram channel Astra reported the explosion occurred at an ammunition depot in Ostrogozhsk. No casualties were reported. This attack is part of Ukraine’s ongoing efforts to target Russian military infrastructure and oil industry in the region. Voronezh Oblast borders Ukraine’s partially occupied Luhansk Oblast.
Four Islamic State-affiliated inmates from Uzbekistan and Tajikistan took 12 hostages at IK-19 prison (Penal Colony No. 19) in Surovikino, Volgograd Oblast, Russia, claiming revenge for Muslims detained after the March 2024 Crocus City Hall attack. The incident occurred during a disciplinary meeting and resulted in five deaths, including three prison employees, before Rosgvardia snipers killed the attackers. Four employees were hospitalized, and the prison head may have been among the hostages. President Putin held a Security Council meeting during the crisis, while local authorities restricted access to messaging platforms in nearby regions. Russian military bloggers criticized the prison system and migration policy, claiming IK-19 was known for corruption and expressing concerns about prisoner radicalization. The incident prompted calls for prison reform and stricter measures against extremism, with the Volgograd Oblast Prosecutor’s Office announcing inspections. This event, along with a similar incident in Rostov-on-Don in June 2024, challenges the Kremlin’s claims of effectively combating domestic extremism.
One year after Yevgeny Prigozhin’s death in a plane crash, the Wagner Group’s personnel has drastically reduced from 50,000 to about 5,000, according to UK intelligence. The group, once pivotal in Russia’s Ukraine invasion and the Battle of Bakhmut, now operates mainly in Belarus and Africa, particularly Mali. Many senior leaders have taken positions in Russian military and government organizations. The group’s diminished presence follows Prigozhin’s failed rebellion against the Kremlin two months before his death.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian authorities are reportedly pressuring conscripts to deploy to occupied Crimea. Documents suggest officials are forging consent forms from reluctant conscripts to free up soldiers for combat in Ukraine. This tactic aims to increase available manpower for frontline operations.
Russian military recruitment ads promise large bonuses to new contract soldiers. One offer includes a $21,000 signing bonus and $57,000 annual salary. Recruiters also offer $547 to those who bring in new recruits. These tactics aim to boost enlistment for the war in Ukraine.
Russia plans to upgrade Yak-52 trainer aircraft to combat drones. The new Yak-52V2 will have improved electronics, radar, and electronic warfare systems. This modification aims to expand the aircraft’s capabilities beyond training to include counter-drone operations.
Russia’s Allies
South Africa blocked the transfer of 50,000 artillery shells to Poland, fearing they might be sent to Ukraine. Poland had ordered these 155mm shells from Denel Munition, a subsidiary of German arms manufacturer Rheinmetall. The agreement was terminated on August 20, 2023, due to supply issues. Poland needs at least one million such shells for defense but can only produce 30,000 annually. To address this shortage, Poland is seeking supplies from South Korea and considering building a domestic factory. Meanwhile, Rheinmetall is planning to construct at least four production plants in Ukraine, including an ammunition factory ordered by the Ukrainian government.
Controlling The Narrative and Russian Propaganda
Russia is using propaganda to discourage Western support for Ukraine following a Ukrainian incursion into Kursk Oblast. Russian officials claim the US is preparing to allow strikes on Russian territory and compare the incursion to World War II events. They accuse the US of supporting “terrorism” and allege Ukraine is targeting a nuclear power plant. Russia also criticizes foreign journalists reporting from Kursk with Ukrainian military escorts.
On the anniversary of the 1939 Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, Russia’s Foreign Ministry deflected blame for Soviet actions. They claimed the West forced the USSR to sign with Nazi Germany, ignoring subsequent Soviet invasions of Poland, Finland, Moldova, and the Baltics. This narrative attempts to rewrite history, downplaying Soviet expansionism during World War II.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
