Summary of the day: The conflict in Ukraine saw marginal gains by both Ukrainian and Russian forces in Kursk Oblast, while Russian troops also advanced near Svatove, Pokrovsk, and Donetsk City. Internally, Russia faced growing discontent amid the Ukrainian incursion into Kursk Oblast, as reported by state-owned polling agencies. International developments included Venezuela’s extradition of Colombian fighters to Russia, Hungary deepening its cooperation with Russia, and the reported departure of Russian mercenaries from Burkina Faso to join the fight in Kursk Oblast, highlighting the conflict’s global ramifications.
Picture of the day:
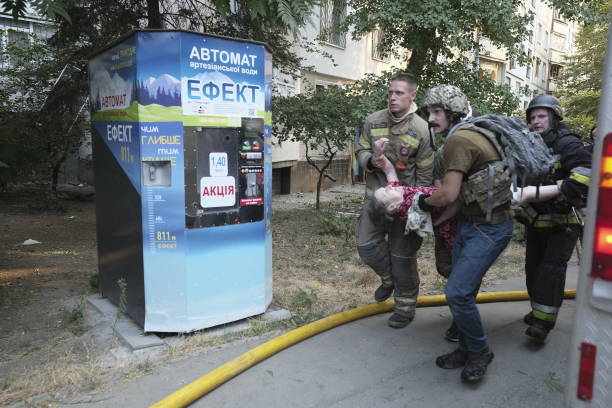 Firefighters carry a elderly woman out of the site of a a Russian guided bomb attack on Ukraine’s northeastern city of Kharkiv. The attack hit a residential building and a playground, killing at least seven people, including a child, and injuring at least 97 more, local authorities said. (George Ivanchenko/Anadolu via Getty Images)
Firefighters carry a elderly woman out of the site of a a Russian guided bomb attack on Ukraine’s northeastern city of Kharkiv. The attack hit a residential building and a playground, killing at least seven people, including a child, and injuring at least 97 more, local authorities said. (George Ivanchenko/Anadolu via Getty Images)
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Russia and Belarus have jointly accused Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania of human rights violations, including fostering Nazism, antisemitism, and Russophobia. This report, published by both countries’ foreign ministries, also claims these Baltic states are suppressing minority rights. Similar allegations have previously been made against other Western countries supporting Ukraine, including Germany, Canada, and Australia. This appears to be part of an ongoing effort by Russia and Belarus to discredit Ukraine’s allies.
Venezuela extradited two Colombian citizens to Russia for allegedly fighting as mercenaries in the Ukrainian military. The individuals were detained in Caracas while traveling from Ukraine to Colombia in July 2024. This marks the first known case of a foreign state extraditing accused mercenaries to Russia, highlighting growing Russian-Venezuelan cooperation and Venezuela’s support for Russia’s war efforts.
Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko had phone conversations with several leaders from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). These included Russian President Vladimir Putin and other high-ranking Russian officials, as well as the presidents of Tajikistan, Azerbaijan, and Uzbekistan. The discussions focused on bilateral relations and the upcoming CIS summit scheduled for October 8, 2024, in Moscow.
The International Criminal Court (ICC) has stated that Mongolia, as a member state, is obligated to arrest Russian President Vladimir Putin during his upcoming visit on September 3. Putin faces an ICC arrest warrant for forcibly transferring Ukrainian children. This visit would be Putin’s first to an ICC member country since the warrant was issued. While Mongolia is required to comply, ICC agreements allow exemptions in certain diplomatic situations. Ukraine has called on Mongolia to arrest Putin, but the Kremlin expresses no concerns about the trip. Mongolia has maintained a neutral stance on Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
An F-16 fighter jet recently delivered to Ukraine crashed on August 26 during a Russian attack, killing pilot Oleksii Mes. Ukraine’s Air Force Commander Mykola Oleshchuk announced that the U.S. has joined the investigation into the crash. A special commission has been established to determine the cause. A U.S. defense official suggested the crash was not due to Russian fire, with pilot error and mechanical failure being considered. The F-16 had successfully shot down four missiles before losing communication.
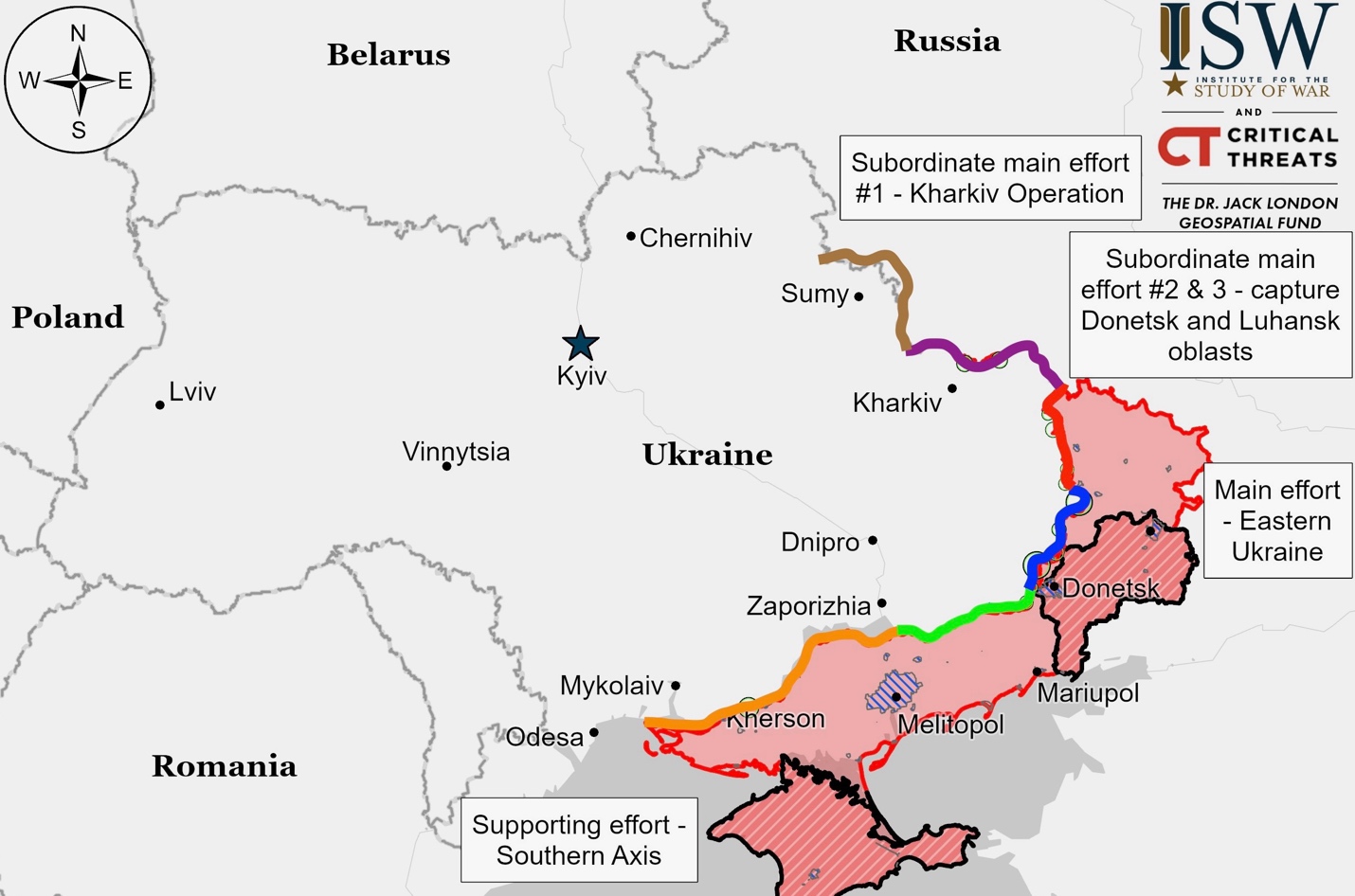
Kursk Front – Initiative Ukraine
Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi reported that Ukrainian troops have advanced 2 kilometers into Russia’s Kursk Oblast, capturing 5 square kilometers of territory. This extends Ukraine’s claimed control in the region to over 1,290 square kilometers and 100 settlements, including the town of Sudzha. President Volodymyr Zelensky confirmed the ongoing offensive, describing it as part of a broader plan for victory. Both Russian and Ukrainian forces reportedly made small advances in the area. Russian sources claim their forces progressed near Korenevo, Olgovka, and Sheptukhovka, while Ukrainian forces allegedly advanced near Cherkasskoye Porechnoye and Nizhnyaya Parovaya. Ukrainian assaults were reported in various locations around Korenevo and Sudzha.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Fighting continued north and northeast of Kharkiv City with Russian forces conducting offensive operations near Lyptsi, Pletenivka, and Vovchansk. Ukrainian forces reportedly repelled Russian attacks near Ohirtseve. Russian attempts to deliver assault groups to Vovchansk were thwarted by Ukrainian defenses. Over 100 Russian personnel from Leningrad Oblast are being sent to the Kharkiv area as reinforcements.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces recently advanced near Svatove, capturing Stelmakhivka and reportedly making progress near Synkivka. The 423rd Motorized Rifle Regiment was credited for seizing Stelmakhivka. Russian sources claim advances west of Pishchane and northwest of Berestove, though these are unconfirmed. Ongoing Russian offensive operations continue along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, including areas northeast of Kupyansk, around Svatove, and near Kreminna. Fighting was reported in multiple settlements including Stepova Novoselivka, Kolisynkivka, Myasozharivka, Tverdokhlibove, Novosadove, and in the Serebryanske forest area.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces continued their offensive operations in the Siversk area without any confirmed changes to the frontline. Attacks were reported east of Siversk near Verkhnokamyanske, southeast near Vyimka and Ivano-Darivka, and south towards Zvanivka.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued their offensive near Chasiv Yar with no confirmed changes to the frontline. The Ukrainian General Staff reported Russian operations around Chasiv Yar and nearby settlements including Kalynivka, Ivanivske, Stupochky, Andriivka, and Klishchiivka.
Toretsk
Russian forces reportedly advanced near Toretsk though no confirmed frontline changes were observed. Russian sources claimed advances in and around several settlements including Druzhba, Pivnichne, Toretsk, Niu York, Yurivka, and Panteleymonivka. Russian forces conducted operations near Toretsk and surrounding areas such as Dachne, Zalizne, Nelipivka, and Sukha Balka.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces advanced near Pokrovsk. They made gains northeast and west of Karlivka, and within southwestern Novohrodivka. Russian sources claimed additional advances in Hrodivka, Karlivka, Halitsynivka, and other nearby areas, though these claims are unconfirmed. Russian offensive operations continued east and southeast of Pokrovsk, targeting several settlements including Zelene Pole, Vozdvyzhenka, Marynivka, and Selydove.
West of Donetsk City
Russian forces continued their offensive west of Donetsk City with no confirmed frontline changes. A Ukrainian brigade reported repelling a large Russian mechanized assault near Heorhiivka, claiming to have destroyed 13 out of 17 Russian armored vehicles. Russian forces also continued operations near Krasnohorivka.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces advanced southwest of Donetsk City. Confirmed advances were made north of Kostyantynivka and northwest of Pobieda. The Russian Ministry of Defense claimed to have captured Kostyantynivka, but some Russian sources suggest Ukrainian forces still hold positions in the northwest of the town. Russian forces continued offensive operations near Kostyantynivka, Vodyane, and Vuhledar.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces reportedly made advances in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border region north of Urozhaine, according to a Russian military blogger. However, these claims have not been independently verified, and no confirmed changes to the frontline in this area have been reported.
Zaporizhia Line
Ukrainian forces reported continued fighting near Robotyne and Mala Tokmachka in western Zaporizhia Oblast with no confirmed frontline changes. A Ukrainian military spokesperson noted reduced Russian activity in the region.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Ongoing combat was reported in eastern Kherson Oblast on August 29-30, with no confirmed changes to the frontline.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched a series of attacks against Ukraine. They fired one Iskander-M missile from Crimea and 18 Shahed drones from various locations. Ukrainian forces successfully shot down 12 drones over several regions, while four others crashed on their own. The attacks targeted civilian infrastructure in Sumy City, port facilities in Odesa, and reportedly energy infrastructure in Poltava Oblast.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky dismissed Lieutenant General Mykola Oleshchuk from his position as Ukrainian Air Force Commander, just days after the first Ukrainian F-16 fighter crashed on August 26, killing top pilot Oleksii Mes. While no official reason was given for Oleshchuk’s dismissal, the timing suggests a possible connection to the crash. Lieutenant General Anatoly Kryvonozhko, previously commander of Ukraine’s Central Air Command, was appointed as the acting Air Force Commander by General Oleksandr Syrskyi. A special commission is investigating the crash, with preliminary reports suggesting it was not due to Russian fire. Zelensky emphasized the need to strengthen Ukraine’s defenses and take care of military personnel, though he did not specify the reason for the dismissal.
Ukraine is preparing for the start of the school year on September 1, with President Zelensky urging for maximum in-person learning where possible. However, Russia’s invasion has severely impacted education, destroying or damaging one in seven schools and forcing 1.6 million children out of education. Only schools with bomb shelters can operate in-person, resulting in about one-third of Ukrainian children attending school physically, one-third learning online, and one-third using a hybrid approach. Ukrainian officials are investing in building school shelters to increase safety. In Mykolaiv, 23 out of 40 schools plan to resume offline education, while Zaporizhzhia is preparing underground schools. The war’s impact on education remains severe, with over 3,500 educational institutions damaged.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 7+ INJURIES: 97+
- Russian forces attacked Kharkiv with UMPB D-30 munitions. The assault killed at least seven people, including a child, and injured 97 others. A 12-story residential building in the Industrialnyi district was hit, causing a fire. The attack also struck the Nemyshlianskyi district, killing a 14-year-old girl. Downtown Kharkiv and the Slobidskyi district were also targeted, damaging buildings. Twenty of the injured are in serious condition, with search and rescue efforts ongoing.
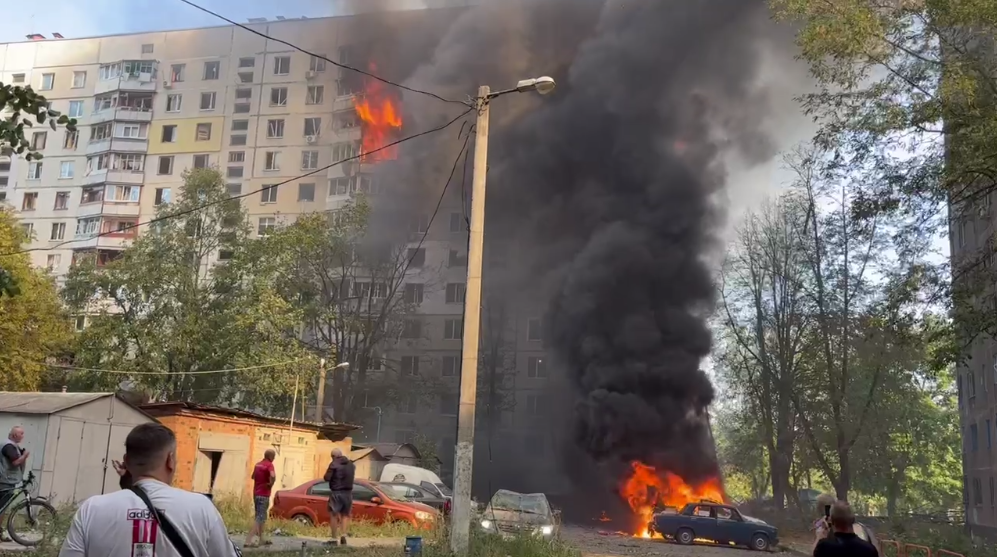 The burning 12-story residential building hit by Russian forces in Kharkiv, Ukraine. (Oleh Syniehubov/Telegram)
The burning 12-story residential building hit by Russian forces in Kharkiv, Ukraine. (Oleh Syniehubov/Telegram)
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine’s Digital Transformation Minister Mykhailo Fedorov announced at the Globsec Forum in Prague that Ukraine is seeking collaboration with weapons manufacturers to develop AI for drone swarms and cost-effective missiles to counter Russian kamikaze drones. Fedorov highlighted the challenges faced by Ukrainian soldiers, including equipment shortages and various types of Russian drones. In response, Ukraine is using a range of drone technologies and is looking to advance its capabilities further. Ukraine has the capacity to produce over three million drones annually but requires financial support from foreign partners. Fedorov emphasized the need for international cooperation in developing new defense technologies to address the evolving challenges of modern warfare.
Ukraine’s Allies
EU member states have differing opinions on Ukraine’s use of European-provided weapons to strike targets in Russia. Some countries, like Estonia and Poland, support lifting restrictions, while others, such as Italy, oppose it. The UK wants to allow Storm Shadow missile strikes into Russia but faces US opposition. These divergent policies complicate logistics for Ukrainian forces, who must navigate different guidelines for weapon use based on their country of origin.
European Union defense ministers agreed to expand the EU Military Assistance Mission for Ukraine (EUMAM), increasing the target from 60,000 to 75,000 trained Ukrainian soldiers by year-end. A coordination center will open in Kyiv. Some EU members are considering sending instructors to Ukraine, despite concerns about potential escalation with Russia. The training primarily occurs in Germany and Poland, but Ukraine has requested in-country training for logistical reasons.
European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen criticized some EU politicians for shifting blame for Russia’s war onto Ukraine, comparing the situation to Soviet aggression in Central Europe. She announced plans for the first EU Defense Commissioner to address security concerns. At the Globsec conference in Prague, Czech President Petr Pavel emphasized the need for long-term support for Ukraine and stronger sanctions against Russia. Both leaders stressed the importance of unity in facing the ongoing conflict, with von der Leyen highlighting Europe’s progress in reducing dependency on Russian energy. The conference, attended by various international officials and experts, focuses on current security challenges, particularly Russia’s war in Ukraine.
Belgium has committed 150 million euros to restore civilian and energy infrastructure in Ukraine’s Kyiv and Chernihiv oblasts. These regions, including the cities of Kyiv and Chernihiv, have faced numerous Russian attacks since the full-scale invasion began. The funds will support reconstruction efforts in education, healthcare, and energy sectors, as well as the building of shelters and backup power systems.
Ukraine and Montenegro are discussing a potential bilateral security agreement. This agreement would join 25 similar pacts Ukraine has already signed with various countries, including the U.S., UK, Germany, and France, aimed at supporting Ukraine against Russian aggression.
Russia News
Recent polls from Russian state-owned agencies show a slight increase in public dissatisfaction with President Putin and authorities amid Ukraine’s incursion into Kursk Oblast. The Public Opinion Foundation reported 28% of respondents expressing dissatisfaction, up from previous months. Putin’s approval rating also dropped to 72.4% according to the Public Opinion Research Center. While these polls may not accurately reflect true public sentiment, they suggest the Kremlin acknowledges rising discontent and may be part of a strategy to address concerns about the Ukrainian incursion.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian mercenaries from the “Bear Brigade” are leaving Burkina Faso to join the fight in Russia’s Kursk region. About 100 of these fighters departed on August 30, as reported by French newspaper Le Monde. The group had been working with Burkina Faso’s military government since May 2024. Their commander, Viktor Yermolaev, confirmed the withdrawal, citing a need to focus on defending Russia. However, an unnamed Western official suggested the departure might be due to payment issues.
Russian authorities are actively promoting military service contracts across the country. In St. Petersburg, they’re advertising in school and kindergarten online groups. Similar promotions are occurring at public events in Kazan, Tatarstan. The Republic of Karelia is offering a one-time payment of 400,000 rubles (about $4,400) for one-year contracts signed between August and December 2024. These efforts aim to encourage voluntary enlistment and avoid a broader mobilization.
Dmitry Rogozin, a Russian-appointed official in occupied Zaporizhia, Ukraine, claims there are enough volunteers to form a full brigade for the “BARS-SARMAT” Detachment. This unit reportedly specializes in robotic and electronic systems. Rogozin’s statement suggests growing interest in this specialized volunteer force within Russian-controlled areas of Ukraine.
A Russian military blogger reported that Defense Minister Andrei Belousov has addressed the issue of former Wagner Group fighters obtaining combat veteran status. Following discussions with military bloggers, Belousov reportedly ordered that ex-Wagner personnel can now apply for combat veteran certificates through the “Defenders of the Fatherland” foundation. This decision potentially affects the status and benefits of former Wagner Group members.
Russia’s Allies
Hungarian Foreign Minister Peter Szijjarto met with Gazprom head Alexey Miller to discuss gas exports and cooperation. Hungary imports over half its gas from Russia, receiving 5.6 billion cubic meters in 2023 through the Turkish Stream pipeline. This meeting, along with Prime Minister Viktor Orban’s recent actions, indicates deepening ties between Hungary and Russia despite ongoing tensions between Russia and the EU.
Chinese banks are reportedly halting transactions with Russia on a large scale, particularly for electronics, due to fears of U.S. sanctions. This development intensified in August, with billions of yuan worth of transactions now suspended. The move comes amid growing U.S. pressure on Chinese and Russian companies supporting Moscow’s aggression in Ukraine. Despite a 121% surge in Russia-China trade since 2021, Chinese banks are now rejecting about 80% of Russian payments in yuan. Additionally, banks in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) have begun blocking transactions from Russian companies for electronic components from China. These actions are creating significant obstacles for Russian-Chinese economic relations, forcing some Russian businesses to seek alternative methods for transactions.
Controlling the Narrative and Russian Propaganda
Russian newspaper publisher Sergei Mikhailov was sentenced to eight years in prison for “spreading fakes” about the Russian Army. The charges stem from his newspaper Listok’s coverage of the Bucha massacre and other Russian war crimes in Ukraine. Mikhailov, detained since April 2022, maintains his innocence, stating he aimed to reveal the truth and protect readers from state propaganda. The court also banned him from journalism for four years. This case is part of a broader crackdown on dissent in Russia since the invasion of Ukraine, with thousands arrested and many jailed. Amnesty International reports that at least 21,000 people were targeted by Russia’s “repressive laws” against anti-war activists in 2023.
Russian State Duma Defense Committee Chair Andrei Kartapolov has issued a warning to European countries. He stated that Russia would respond harshly and immediately if Europe allows Ukraine to use European-supplied weapons to attack targets within Russia. This threat appears to be an attempt to influence Western decision-making regarding military support for Ukraine.
Darya Dolzikova, from the Royal United Services Institute (RUSI), has refuted Russian claims that Ukrainian forces plan to threaten the Kursk Nuclear Power Plant (KNPP). She stated on August 30 that there’s no evidence supporting these Russian allegations. Dolzikova added that Ukraine has no strategic or operational reason to endanger the KNPP, suggesting that Russia’s claims are likely part of an information campaign.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
