Summary of the day:
The world watched as the gears of war continued to turn in Eastern Europe. The conflict in Ukraine, now well into its second year, saw a significant development as Iran, in a bold move, delivered hundreds of short-range ballistic missiles to Russia. This transfer marked a deepening of the strategic alliance between Tehran and Moscow, further complicating the geopolitical landscape.
In Washington, United States Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin addressed the ongoing conflict, asserting that no single weapon system would dramatically alter the course of the war. His words, however, were met with skepticism from some quarters, who argued that such a stance underestimated the impact of advanced weaponry and the critical importance of long-range strike capabilities for Ukrainian forces.
As these debates raged, Ukraine’s allies gathered at Ramstein Airbase in Germany, pledging additional military aid to the beleaguered nation. Yet, even as promises of support were made, the specter of delay loomed large, with much of the promised assistance not slated for immediate delivery.
On the front lines, a grim reality unfolded. Reports began to surface of Russian forces executing surrendering Ukrainian soldiers, a stark reminder of the brutality of this conflict. Meanwhile, in the diplomatic arena, Russian officials engaged in a calculated effort to legitimize their occupation of the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant during talks with the International Atomic Energy Agency.
The day’s events also saw shifts on the battlefield. Russian forces managed to regain ground in Kursk Oblast, while Ukrainian troops made advances near Pokrovsk. These movements, though seemingly small in the grand scheme, represented the ebb and flow of a war that had become a grueling test of endurance for both sides.
As night fell, the conflict’s impact on the information landscape became ever more apparent. The Russian government continued its efforts to tighten control over its domestic information space, while simultaneously honing its capabilities for information operations on global social media platforms. This battle for hearts and minds, fought in the digital realm, underscored the multifaceted nature of modern warfare.
Picture of the day:
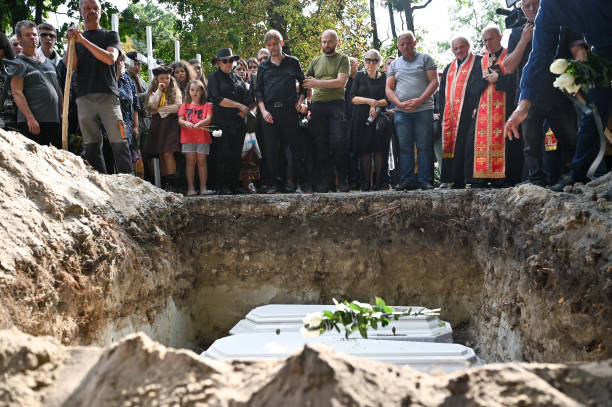 People attend the funeral ceremony of 7-year-old Emilia Bazylevich,18-year-old Daryna Bazylevich, 21-year-old Yaryna Bazylevich, and 43-year-old Yevgenia Bazylevich, who died during Russian shelling on the morning of Sept. 4 in Lviv. The entire family died, except for the children’s father. (Olena Znak/Anadolu via Getty Images)
People attend the funeral ceremony of 7-year-old Emilia Bazylevich,18-year-old Daryna Bazylevich, 21-year-old Yaryna Bazylevich, and 43-year-old Yevgenia Bazylevich, who died during Russian shelling on the morning of Sept. 4 in Lviv. The entire family died, except for the children’s father. (Olena Znak/Anadolu via Getty Images)
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Tensions in Eastern Europe escalated as Russia pursued a two-pronged strategy of diplomatic pressure and cyber warfare. Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov made statements challenging the 1995 Dayton Accords, which had brought peace to Bosnia. Peskov claimed the agreement’s foundations were eroding and Serb interests were being violated, offering Russia’s support to Serbia and Republika Srpska on the international stage. This move was seen as part of Moscow’s ongoing efforts to destabilize the Balkans and undermine regional peace agreements.
Simultaneously, new information emerged about Russia’s cyber capabilities. Russia’s Military Intelligence Agency (GRU) Unit 29155, previously known for physical attacks in Western countries, was revealed to have a sophisticated cyber arm operational since 2020. The United States responded by charging five Russian intelligence officers and one civilian for cyber-attacks against Ukraine and multiple NATO countries. Estonia also issued arrest warrants for three individuals involved in attacks within its borders.
The Dutch Military Intelligence Agency warned that the Netherlands could be a potential target due to its logistical support for Ukraine. These cyber operations aimed to disrupt Western aid to Ukraine by targeting government systems and critical infrastructure across NATO and EU countries.
This coordinated campaign of diplomatic maneuvering in the Balkans and advanced cyber warfare against NATO allies highlighted Russia’s multifaceted approach to undermining Western support for Ukraine and sowing discord within European alliances. The revelations underscored an escalation in Russia’s cyber warfare capabilities and its persistent efforts to destabilize NATO and EU countries supporting Ukraine.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Alarming evidence emerged of Russian forces systematically executing surrendering Ukrainian soldiers along the frontline. CNN released footage of such incidents near Pokrovsk in Donetsk Oblast and in Zaporizhia Oblast. Ukraine’s Prosecutor General Andrii Kostin reported investigating 28 execution incidents since February 2022, resulting in 62 Ukrainian soldiers’ deaths. Ukrainian intelligence documented 15 similar cases since November 2023, with increasing frequency in 2024.
These executions, occurring across various Russian units and front sectors, violate the Geneva Convention. UN sources suggest these actions could amount to crimes against humanity. Ukraine’s Ombudsman Dmytro Lubinets appealed to international organizations, emphasizing the gravity of these war crimes.
Reports indicate that Russian commanders may have ordered the killing of Ukrainian servicemen to deter surrenders. Intense battles near Pokrovsk, a key logistics hub, and similar incidents near Toretsk highlight the widespread nature of these atrocities. This disturbing trend has added a new, horrifying dimension to the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict, raising serious concerns about adherence to international humanitarian law.
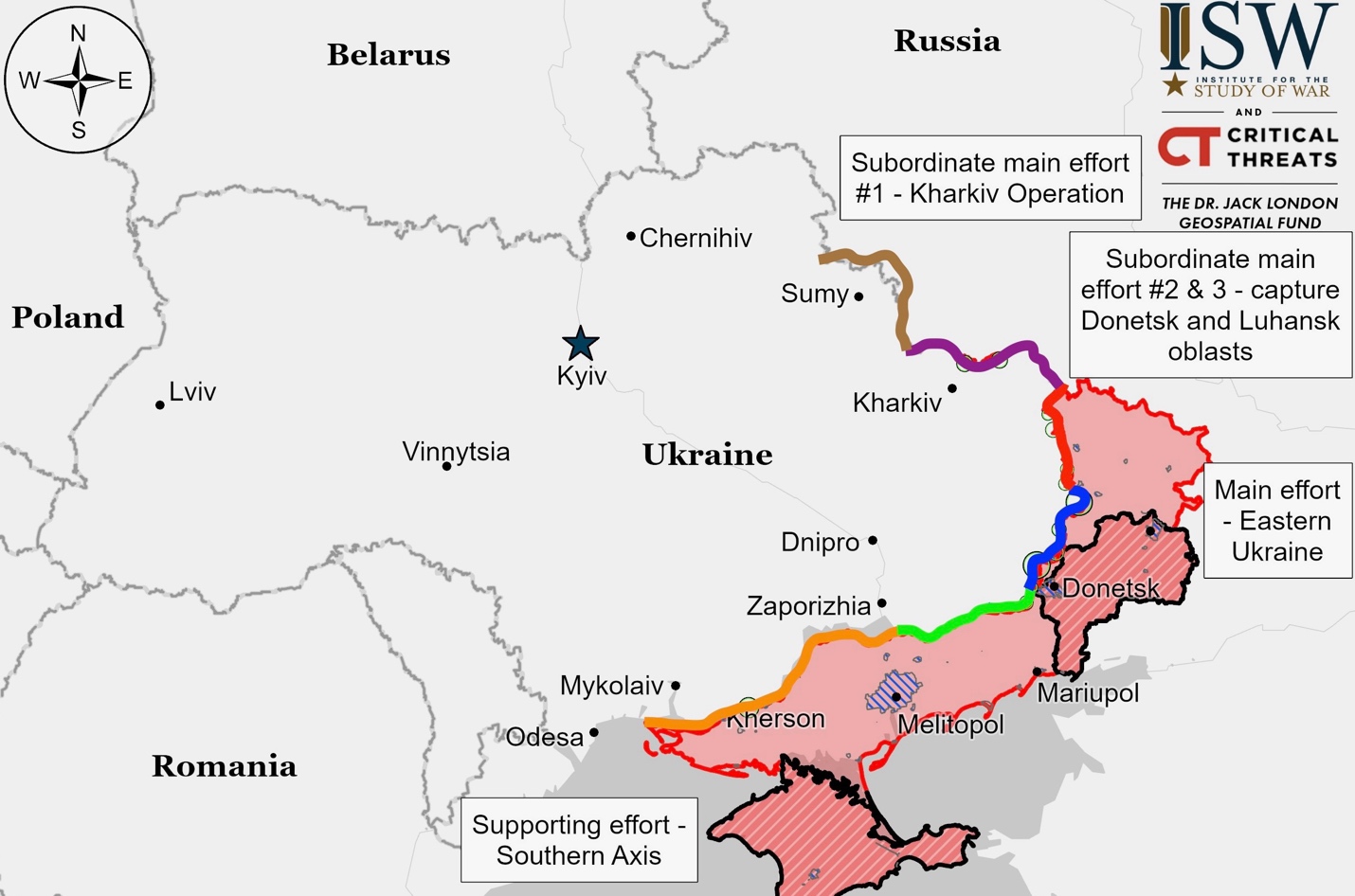
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Ukrainian forces made substantial gains in Russia’s Kursk Oblast, with President Zelensky announcing control over 1,300 square kilometers and 100 settlements. This incursion, which began on August 6, reportedly resulted in 6,000 Russian casualties and reduced threats to Ukraine’s Sumy region. Simultaneously, Russian forces regained some positions near Zhuravli in Kursk Oblast, while Ukrainian forces launched assaults around Korenevo and Sudzha.
On the international stage, US Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin downplayed the impact of specific weapons as “game changers” for Ukraine. However, Senator Mark Kelly of Arizona called for reevaluating restrictions on Ukraine’s use of American weapons to strike inside Russia, highlighting the ongoing debate over Western military assistance.
The conflict’s dynamics were further complicated by Ukraine’s limited long-range strike capabilities, contrasted with Russia’s expanding deep strike abilities through procurement from Iran and North Korea. This imbalance has given Russia an advantage in maintaining sanctuary space within its borders for offensive operations against Ukraine.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces continued ground attacks north and northeast of Kharkiv City with no confirmed advances. Offensive operations targeted Hlyboke, Vovchansk, Starytsya, and Hatyshche. Russian sources claimed to repel Ukrainian counterattacks in several areas.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian sources claim advances northeast and southeast of Kupyansk, but these remain unconfirmed. Russian forces reportedly pushed near Pishchane, Stelmakhivka, and Synkivka. Ukraine reports ongoing Russian offensives in various areas, including Synkivka, Hlushkivka, Andriivka, Novoyehorivka, Terny, and Dibrova. A Ukrainian soldier noted Russian infantry groups launching attacks while exhausted and poorly equipped.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces continued offensive operations in the Siversk area without confirmed advances. Ground attacks were reported near Verkhnokamyanske, Spirne, and Vyimka.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued offensive operations near Chasiv Yar with no confirmed advances. Russian sources claimed progress in Kalynivka and west of Klishchiivka. Attacks were reported near Hryhorivka, Ivanivske, Bila Hora, Predtechyne, Ivanopillia, Klishchiivka, and Andriivka.
Toretsk
Recent footage confirms Russian advances in and around Niu York, south of Toretsk, though Ukrainian forces claim to have regained some control. The Russian Ministry of Defense reports capturing Pivnichne. Fighting continues near Toretsk, Nelipivka, Oleksandropil, Panteleymonivka, and Leonidivka. Ukrainian counterattacks have reportedly begun near Toretsk and Niu York.
Pokrovsk
Ukrainian forces regained positions in southwestern Halytsynivka and western Mykhailivka, southeast of Pokrovsk. Russian sources claim advances in Lisivka and near Ukrainsk. The Russian Ministry of Defense reports capturing several settlements, including Ptyche and Karlivka.
West of Donetsk City
Russian forces continued offensive operations west of Donetsk City with attacks reported near Krasnohorivka and Heorhiivka. A Russian military blogger claimed advances in northern Krasnohorivka, but this remains unconfirmed. No changes to the frontline have been verified. Another blogger alleged an unsuccessful Ukrainian counterattack near Maksymilyanivka.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces continued offensive operations southwest of Donetsk City targeting areas near Kostyantynivka, Staromayorske, Vuhledar, and Vodyane. No confirmed changes to the frontline were reported.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
There were no reports of fighting along the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area from either Russian or Ukrainian sources.
Zaporizhia Line
Ukrainian officials reported Russian attacks near Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast. Captain Dmytro Lykhovyi stated that small Russian infantry groups typically launch one to two daily attacks, with recent increases in airstrikes across southern Ukraine.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Positional engagements continued in the east bank area of Kherson Oblast.
Ukraine News
Russia intensified its military campaign against Ukraine with a series of coordinated attacks. The Ukrainian Air Force intercepted 27 out of 44 Shahed drones, while also facing Kh-59 and Kh-31P missiles. A particularly devastating strike occurred in Pavlohrad, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, where five Iskander-M/KN-23 ballistic missiles injured 61 people and damaged residential areas.
Concurrently, Ukraine braced for potential mass attacks on its energy infrastructure. Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal warned of Russia’s preparations, reminiscent of last year’s strikes that caused widespread blackouts. DTEK, Ukraine’s largest private energy provider, cautioned about possible severe power limitations, potentially leading to up to 20 hours of daily blackouts in worst-case scenarios.
Amidst these external pressures, internal political changes unfolded in Ukraine. The government agreed to dismiss Zakarpattia Oblast Governor Viktor Mykyta, pending presidential approval. This decision was part of a broader government reshuffle, which included the appointment of Oleksii Kuleba as deputy prime minister for Ukraine’s restoration and minister for community and territorial development.
These events highlighted the multifaceted challenges facing Ukraine, from defending against Russian aggression to maintaining critical infrastructure and managing internal political dynamics.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 2+ INJURIES: 69
On a harrowing day in Ukraine, Russian forces launched devastating attacks on two locations. In Pavlohrad, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, a brutal assault left at least one dead and 64 injured, including five children. The victims ranged from 4 to 86 years old, with three in serious condition. The attack caused widespread damage, including a fire in a high-rise apartment building.
Simultaneously, Russia struck Krasnopillia in Sumy Oblast with three guided aerial bombs. This attack claimed the life of a 66-year-old woman and injured five others, including two teenagers. Fifteen homes were damaged in the assault.
These coordinated strikes underscored the ongoing intensity of the conflict and its tragic impact on civilian populations across Ukraine, highlighting the urgent need for improved air defense systems and international support.
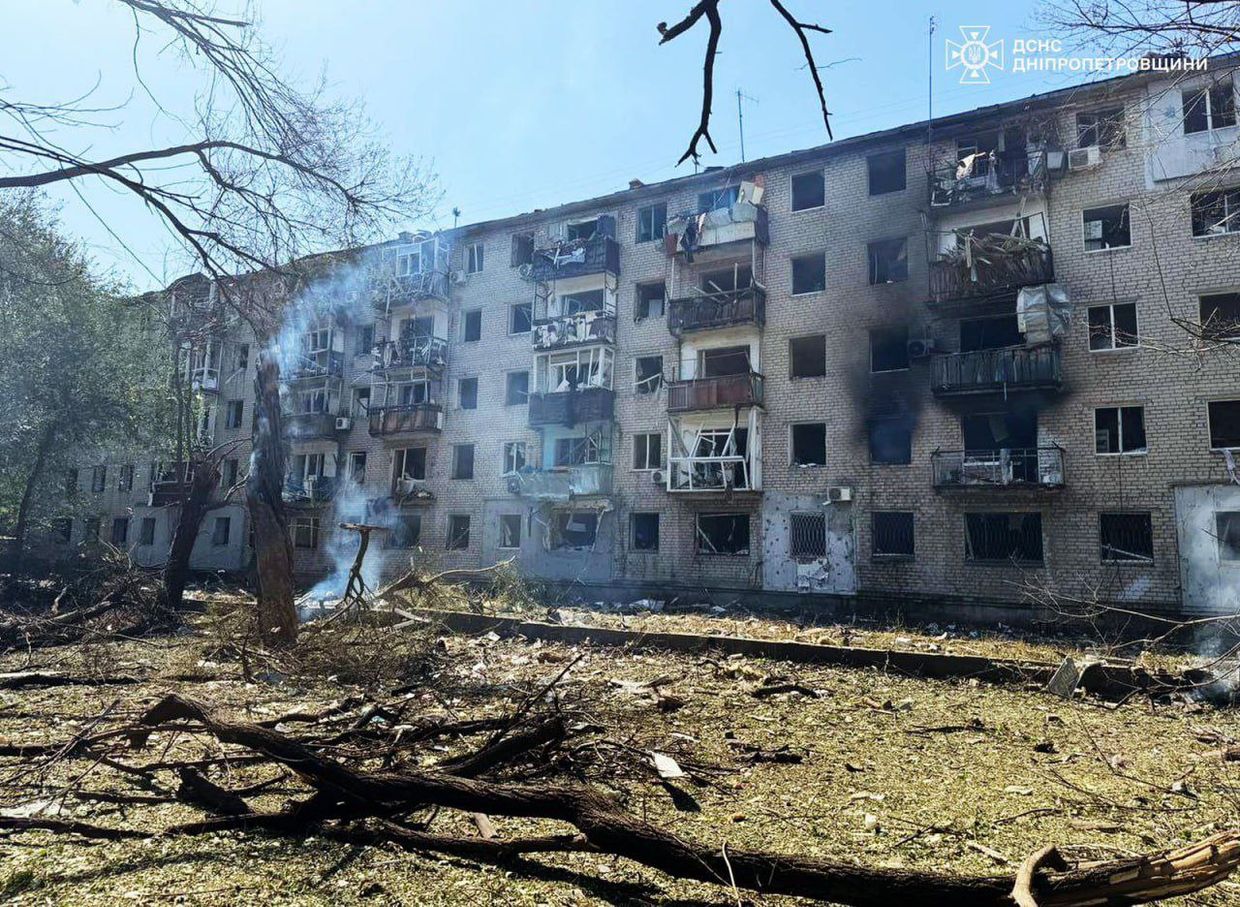 A residential building damaged in a Russian attack against Pavlohrad, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Ukraine. (State Emergency Service/Telegram)
A residential building damaged in a Russian attack against Pavlohrad, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Ukraine. (State Emergency Service/Telegram)
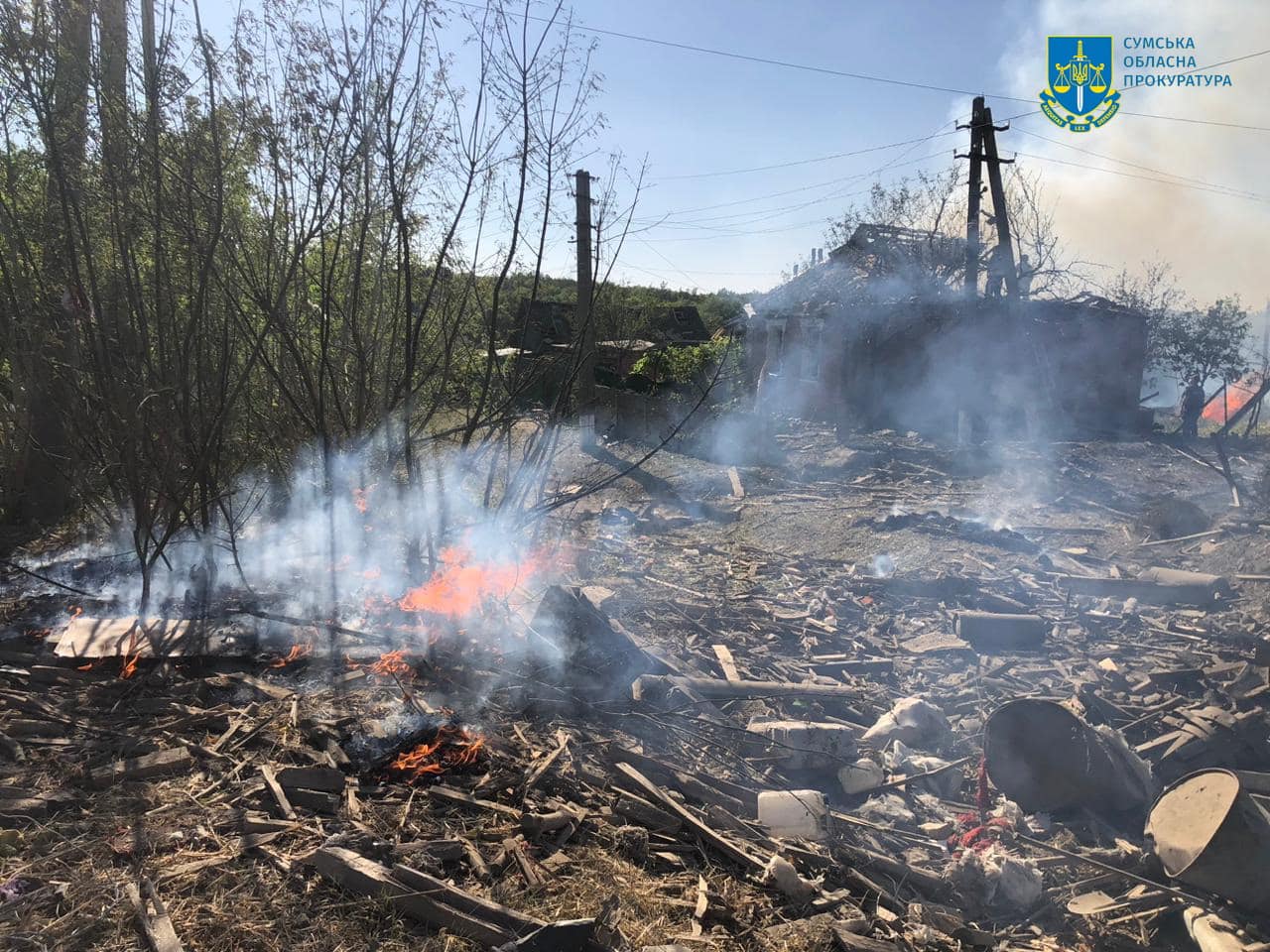 The remains of rubble after a Russian KAB guided aerial bomb struck the community of Krasnopillia in Sumy Oblast. The attack killed one woman and injured five others, including two teenagers. (Sumy Oblast Prosecutor’s Office/Facebook)
The remains of rubble after a Russian KAB guided aerial bomb struck the community of Krasnopillia in Sumy Oblast. The attack killed one woman and injured five others, including two teenagers. (Sumy Oblast Prosecutor’s Office/Facebook)
Ukraine’s Allies
The 24th Ukraine Defense Contact Group meeting in Germany became a pivotal moment in the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict. President Zelensky attended, urgently requesting more air defenses and long-range missiles as Ukraine faced continued Russian aggression, including recent strikes on Poltava and Lviv that resulted in civilian casualties.
The meeting galvanized Western support, with multiple nations pledging substantial military aid. The United States announced a $250 million package comprising missiles, ammunition, and defense systems. The UK committed to providing 650 Lightweight Multirole Missiles worth $213 million. Germany pledged 12 Panzerhaubitze 2000 howitzers and 77 Leopard 1A5 tanks, while Canada offered rocket motors, warheads, and F-16 pilot training support. Other allies, including the Netherlands and Spain, also made significant commitments.
Notably, Lithuania pledged 10 million euros to purchase Ukrainian-made Palianytsia missile-drones, supporting Ukraine’s domestic defense industry. This followed Denmark’s precedent of directly purchasing Ukrainian-made weapons for donation.
Concurrent with military aid, the European Union announced a $44 million humanitarian package to repair Ukraine’s energy infrastructure before winter, addressing the aftermath of Russian attacks on power facilities.
On the diplomatic front, the U.S. imposed new sanctions on Russia’s Arctic LNG 2 project, targeting two vessels and two entities to curb Russian fossil fuel revenues. Meanwhile, the Biden administration urgently worked with Congress to preserve $6 billion in expiring Ukraine assistance, highlighting ongoing challenges in maintaining consistent support.
These developments unfolded against the backdrop of Ukraine’s recent incursion into Russia’s Kursk Oblast, where it claimed control of about 100 settlements, and Russia’s continued advance on Pokrovsk in Donetsk Oblast. The multifaceted nature of the aid – from military equipment to humanitarian support and economic sanctions – underscored the complex, ongoing efforts to support Ukraine while pressuring Russia on multiple fronts.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Russian officials met with Rafael Mariano Grossi, the Director General of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), in Kaliningrad Oblast. The discussions centered on nuclear safety concerns, with Russia accusing Ukraine of posing threats to both the Zaporizhzhia and Kursk Nuclear Power Plants. This move appears to be part of a broader Russian strategy to legitimize their occupation of the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP) and the surrounding oblast, while simultaneously attempting to undermine Western support for Ukraine’s activities in Kursk Oblast.
By maintaining control over the ZNPP, Russia is leveraging its position to force interactions with the IAEA, seeking international validation for its occupation of Ukrainian territory. In a related development, President Vladimir Putin signed a decree that assigns counterterrorism operations in the Sea of Azov to an operational headquarters located in occupied Simferopol. This decree grants the headquarters authority to plan and manage counterterrorism efforts in the sea, though it excludes specific areas such as the Kerch Strait and Taganrog Bay ports.
Russia News
The toll of Russia’s ongoing military campaign in Ukraine continues to mount, with recent data shedding light on the composition of the casualties. A joint tracking effort by BBC Russian Service and Mediazona has identified 68,011 Russian military deaths since the conflict began in February 2022. This grim tally reveals a stark breakdown of the fallen: volunteers account for the largest share at 20%, closely followed by convict recruits at 19%, while mobilized personnel represent 13% of the identified losses.
These figures suggest that more Russian volunteers have lost their lives in the conflict than either convicts or mobilized troops. However, it’s crucial to note that these numbers likely understate the true extent of the casualties. The actual death toll is believed to be higher, and the proportions among different categories of personnel may vary from what has been identified thus far.
This data provides a sobering glimpse into the human cost of the war, highlighting the diverse backgrounds of those who have perished and raising questions about Russia’s military recruitment and deployment strategies. As the conflict persists, these figures serve as a stark reminder of the ongoing sacrifice and the complex demographics of those on the front lines.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian state-owned enterprises have stepped up their involvement in military recruitment efforts, aligning their hiring practices with the nation’s war efforts in Ukraine. In a strategic move, intermediary recruiters are now dangling the prospect of future employment in these state companies as an incentive for individuals to sign contracts with the Defense Ministry.
The recruitment drive extends beyond potential hires, with some state companies actively encouraging their current workforce to enlist. To sweeten the deal, they’re offering substantial financial incentives, with bonuses reaching up to 1.9 million rubles (approximately $21,000) for those who heed the call to arms.
Perhaps most striking is the approach taken by Moscow Metro, a crucial component of the capital’s infrastructure. Reports suggest that the transit authority has implemented a policy of hiring exclusively those who commit to military service. This stringent requirement has not come without consequences, as the Metro now grapples with worker shortages in essential specialties.
These developments highlight the increasing entanglement of Russia’s civilian sector with its military ambitions, blurring the lines between state employment and military service. As the conflict in Ukraine continues, this trend raises questions about the long-term implications for Russia’s workforce and the operational capacity of its state-owned enterprises.
Russia’s Allies
As tensions in Ukraine continue to escalate, a significant development has emerged in the form of Iranian support for Russia’s military efforts. U.S. and European officials report that Iran has delivered hundreds of short-range ballistic missiles to Russia, fulfilling a contract signed in December 2023. While the exact type of missiles remains unclear, they may include Ababil and Fateh-360 models.
This delivery marks a deepening of the Iran-Russia strategic partnership, which has been growing since the onset of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022. The collaboration extends beyond military aid, encompassing economic and political dimensions as well. Iran stands to gain financially from these weapon sales and seeks advanced military technology in return, including Su-35 fighter jets and potential support for its cyber capabilities and missile programs.
Russia is expected to deploy these Iranian missiles in the coming months, targeting Ukrainian energy infrastructure, military installations, and civilian areas. This strategy aims to destabilize Ukrainian society and disrupt its defense industry. The move comes as Russia has already intensified its attacks using Iranian-made Shahed drones and North Korean ballistic missiles.
In response to this escalating situation, the U.S. and European countries are preparing sanctions against Iran. The G7 countries are also expected to issue a condemnation of Iran’s actions. Meanwhile, the international community remains vigilant, closely monitoring these developments and their potential impact on the conflict.
Adding another layer to the complex web of international involvement, an insider source has revealed that a drone detection and suppression system, previously touted by Rosgvardia (Russian National Guard) as domestically produced, is actually manufactured by a Chinese company, Shenzhen Skyfend Technology. This discovery has reportedly led Russian authorities to launch a smuggling investigation, further complicating the geopolitical landscape surrounding the conflict in Ukraine.
Controlling the Narrative and Russian Propaganda
In a series of events highlighting the complex interplay of information control, national identity, and international perception in Russia, the Kremlin’s efforts to shape its narrative both domestically and abroad have come under scrutiny.
Russian censor Roskomnadzor briefly published, then quickly retracted, a draft procedure to implement a new law deanonymizing Telegram channels. This proposed measure, based on legislation signed by President Putin in August, would require social media accounts with over 10,000 followers to provide personal information to the government. The sudden withdrawal of the draft, ostensibly due to a technical error, suggests potential sensitivity to backlash from ultranationalist online communities, particularly military bloggers who voiced concerns over their safety.
Despite this setback, the Kremlin signaled its continued intent to control Russia’s information space. Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov justified censorship during wartime and emphasized the need for Russian media to compete with international outlets. This stance indicates that while the specific regulations have been temporarily shelved, similar measures may be pursued in the future.
Simultaneously, President Putin has taken steps to bolster Russian national identity and ideology. The creation of the “Rossiya” National Center in Moscow, led by Sergei Kiriyenko, aims to showcase Russian achievements, strengthen national identity, and develop youth skills. This initiative is likely to be used as a platform to influence both domestic and foreign perceptions of Russia, potentially including promoting claims on annexed Ukrainian territories.
On the international stage, the US Department of Justice revealed ongoing efforts to counter Russian influence campaigns known as “Doppelganger,” also directed by Kiriyenko. These operations use fake news websites and “sleeper” social media channels to spread pro-Russian narratives, aiming to reduce Western support for Ukraine and influence elections. The “Morning Dagestan” Telegram channel, allegedly linked to antisemitic riots in Dagestan, exemplifies Russia’s developing capabilities to trigger real-world events through online information operations.
Adding to the complex narrative surrounding Russia’s actions, a controversial documentary titled “Russians at War” by Russian-Canadian filmmaker Anastasia Trofimova has sparked debate at the Venice Film Festival. The film, which attempts to humanize Russian soldiers fighting in Ukraine, has been criticized for potentially echoing Russian propaganda narratives. Its funding by the Canada Media Fund and scheduled screening at the Toronto International Film Festival have further fueled the controversy, with Ukrainian filmmakers expressing concerns about misrepresentation of the war’s reality.
These events collectively underscore the ongoing struggle over information control, national narrative, and international perception as Russia continues its actions in Ukraine and beyond.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
