Summary of the day: Ukrainian intelligence warns of an intensifying Russian offensive in the coming months, while diplomatic interactions continue as Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov meets with Chinese officials, raising concerns about China’s support for Russia’s military efforts. Allegations of prohibited chemical weapons use by Russian forces and drone strikes on a nuclear power plant underscore the escalating nature of the conflict. Amidst these developments, Ukraine addresses internal challenges, including reports of intimidation within its Security Service. On the battlefield, both sides report advances and continued fighting, highlighting the complex dynamics of the Ukraine-Russia conflict.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War III
The German Air Force intercepted a Russian II-20 aircraft over the Baltic Sea for flying without a transponder, essential for safe air traffic. This incident adds to a series of Russian military activities close to NATO airspace, including past intrusions by missiles into member-states’ territories. NATO has responded by increasing its defensive presence around Ukraine, with instances of Polish and French jets also scrambling to intercept or track Russian aircraft in recent months. These actions reflect heightened vigilance by Western nations due to the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian intelligence, led by chief Kyrylo Budanov, forecasts a Russian offensive targeting the Donbas region in late spring or early summer, with specific moves toward Chasiv Yar and Pokrovsk in Donetsk Oblast. This comes as current activities of Russian forces are noted near Chasiv Yar. Ukraine is actively seeking more support from Western allies, including artillery, ammunition, and Taurus cruise missiles from Germany, to withstand this anticipated military push. President Zelensky has also expressed concerns about a major Russian offensive potentially launching around late May or June, aligning with Budanov’s projections. However, this assessment is somewhat at odds with NATO intelligence, which suggests that without further large-scale mobilization, Russia might not embark on such a large-scale offensive imminently. Reports of a potential Russian ground offensive against Kharkiv have been rejected by Ukraine as a Russian psychological operation, despite intensified attacks, with Zelensky stating Kharkiv’s preparedness to face such an event. Observations confirm an uptick in Russian assault activities, underscoring the effects of delayed Western military aid on Ukraine’s ability to defend itself. Zelensky and other Ukrainian military leaders underline the pressing need for timely aid, essential for planning successful counteroffensives and ensuring national defense, pointing out strategic difficulties due to the postponement of aid.
Russian forces are accused of regularly using prohibited chemical weapons, including CS gas, against Ukrainian positions, violating the Chemical Weapons Convention. Investigations reveal near-daily attacks with chemical agents aimed at causing panic and exploiting Ukrainian defenses. Reports include the use of chlorine and other harmful substances, with Ukrainian forces documenting over 1,400 instances of chemical weapon use by Russia from February 2023 to March 2024. Russian military admissions of using CS gas in attacks have been noted, highlighting a systematic approach to chemical warfare in the conflict.
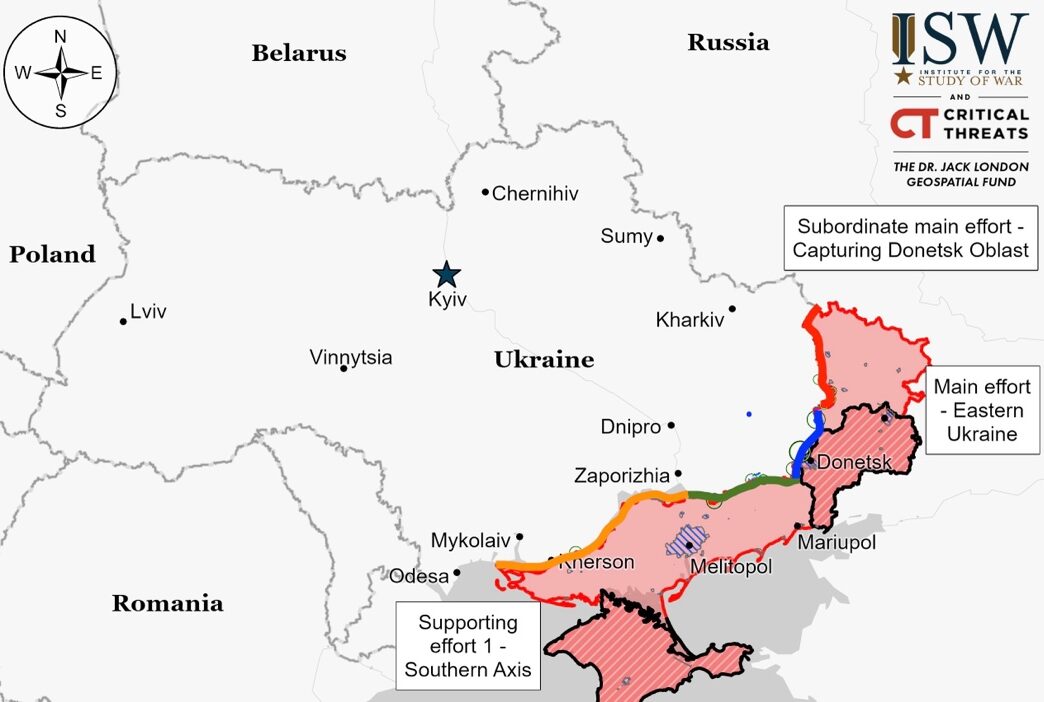
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Battles continued around Kreminna, with Ukrainian forces reporting the destruction of 11 Russian armored vehicles near Terny. Russian military bloggers note shifts in Russian troop deployments in the area and a significant increase in glide bomb strikes in Kharkiv Oblast, highlighting intensified Russian aerial attacks there.
Ukrainian forces successfully repelled multiple Russian attacks in the area northeast of Bakhmut, including near Spirne, Vyimka, Rozdolivka, Fedorivka, and Vesele.
Russian forces reportedly made advances near Bakhmut but did not alter the frontline significantly. Claims of capturing Bohdanivka are disputed, with ongoing fighting reported. Russian paratroopers are said to be pushing in Chasiv Yar’s outskirts, though no visual proof exists. Fighting continues around Bakhmut, with Ukrainian and Russian units engaging in various sectors. Ukrainian analysis highlights aggressive Russian attacks near Ivanivske and attempts to maneuver around Klishchiivka, indicating a continued focus on strategic positions in the area.
Russian forces advanced near Avdiivka capturing significant parts of Pervomaiske, southwest of the city. This progress is supported by geolocated footage and assessments. Fighting continues around Avdiivka, with engagements reported in several nearby locations, indicating ongoing conflict in the region.
Russian forces are reported to have made advances southwest of Donetsk City, with ongoing battles in the region. Claims of progress in Novomykhailivka are yet to be visually confirmed. Fighting persists west and southwest of Donetsk City, notably near Krasnohorivka, Heorhiivka, Pobieda, and Novomykhailivka.
Ongoing battles took place in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area without altering the frontline. Fighting occurred near Staromayorske and Urozhaine, south of Velyka Novosilka.
Battles in western Zaporizhia Oblast near Robotyne and Verbove didn’t change the frontline, despite Russian claims of gains northwest of Verbove, including a push towards a key highway. These claims lack visual confirmation. Reports also suggest Russian airborne forces’ involvement in the area.
Russian forces increased small group assaults in Kherson Oblast’s east bank, targeting Ukrainian positions in Krynky from various directions. These efforts failed to dislodge Ukrainian forces, leading Russia to revert to fewer assaults. Despite these tactics, positional battles persisted in the area.
Ukrainian Victims Of War
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the death of 4 people and the injuries to 7 others:
- In Zaporizhzhia Oblast’s Hulyaipole, a Russian Grad rocket attack killed two men and a woman, left another civilian wounded and hospitalized. The victims were found under the debris of a destroyed house.
- A Russian attack in Kharkiv hit an industrial zone and a central park, injuring five and damaging 13 buildings, educational facilities, cafes, dormitories, a hotel, and cars. Preliminary reports suggest two guided bombs were used in the strike.
- In Kupiansk, Kharkiv Oblast, a Russian bomb destroyed two floors of an apartment building, killing an 85-year-old woman found under the rubble.
- Russian forces launched 40 attacks on Sumy Oblast, injuring one person through artillery shelling in the village of Myropillia. Various weapons, including mortars, rockets, tanks, and grenade launchers, were used, and drones dropped explosives on three communities. Bilopillia, close to the Ukraine-Russia border, was hit by 33 explosions.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched a missile and drone attack against Ukraine on the night of April 6 to 7, firing from Luhansk, Crimea, and Cape Chauda. Ukrainian defenses successfully intercepted all drones over Kharkiv, Dnipropetrovsk, and Poltava. A missile strike damaged port facilities in Odesa, while drone strikes in Kharkiv hit civilian infrastructure, including a fuel warehouse and an aviation school.
Russian missiles struck Kharkiv in the morning, injuring at least one person and hitting four locations, including a private house, with the exact targets undisclosed. Following two hours later, another attack occurred with unreported details. Kharkiv, close to the Russian border, has seen an increase in such assaults, including a double-tap strike on April 6 that killed seven and injured 11 with S-300 missiles. Recent attacks have heavily damaged the city’s energy infrastructure, leaving Kharkiv with significant power outages. Despite this, metro services, halted on April 5, have since resumed. Over 20,000 buildings in the city have been destroyed in the conflict since February 2022.
Ukraine’s Energy Minister stressed the urgent need for advanced air defense systems to protect the country’s energy facilities from intensified Russian missile and drone strikes. Such attacks have significantly damaged Ukraine’s power generation and transmission infrastructure, with key hydroelectric plants targeted. President Zelensky has called on international partners for modern air defenses, as Ukraine faces a tangible shortage, especially near frontline areas. While full damage assessments are pending, the cost could be in the billions, with substantial losses already to private energy capacities. As summer peak demand approaches, Ukraine is also seeking replacement energy equipment and urging conservation to prevent a repeat of past blackouts.
Donald Trump has suggested he could swiftly end the war in Ukraine by convincing Kyiv to give up Crimea and parts of Donbas to Russia, according to the Washington Post, without detailing the peace strategy. Contrary to Trump’s assertions, President Zelensky of Ukraine insists on not surrendering territory for peace and has proposed a peace plan calling for Russian troop withdrawal and a tribunal for war crimes. Meanwhile, Trump, who may be the Republican nominee for the U.S. presidency, has been non-committal about future defense aid to Ukraine. Russia continues to dismiss peace negotiations, and Ukraine is dealing with ammunition shortages despite substantial U.S. support held up by congressional disputes. Russian peace talk proposals from 2022 reveal demands that would significantly weaken Ukraine’s defense capabilities.
Ukraine’s Prosecutor General’s Office is investigating a video that appears to show Russian soldiers shooting unarmed Ukrainian POWs in Kherson Oblast, a potential war crime violating the Geneva Convention. The video, shared on Russian Telegram channels, depicts a member of the Russian Armed Forces firing at the unmoving Ukrainian servicemen. Ukraine’s Ombudsman has reported the incident to the UN and the Red Cross, stating that such acts are systematic and calling for international response. Over 128,000 victims of war crimes have been documented in Ukraine as of March 18.
Ukraine’s military chief condemned and launched an investigation into allegations that the Security Service of Ukraine (SBU) intimidated a journalist probing SBU corruption by issuing a draft summons. This action follows a report by Slidstvo.Info about potential SBU efforts to silence a journalist investigating the agency’s cybersecurity department. This incident highlights Ukraine’s ongoing battle against wartime corruption and the commitment to transparency and accountability, supported by a strong network of NGOs.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
The Odesa military enlistment office is investigating an incident where a 14-year-old boy was allegedly detained and beaten by men in military uniforms in Pryozerne village. The incident, reported by local media and involving the boy being forcibly taken and then released upon verification of his age, is under official review with law enforcement involvement. Amid efforts to mobilize more troops after heavy battles in 2023, this case adds to the scrutiny over mobilization practices in Ukraine, where past abuses by military officers have been reported. Ukraine is also considering new legislation on mobilization, reflecting the country’s ongoing challenges with conscription during the war.
Ukraine’s Allies
International donors, including the U.S., Switzerland, Norway, the EU, and Japan, have contributed over $700 million for mine clearance in Ukraine, where nearly a third of the country is mined. This funding will support demining efforts from 2022 to 2027. Mines have caused civilian casualties and hindered military operations. With the largest landmine stockpile, Russia has contributed significantly to the issue. Ukraine is coordinating demining with experts and emergency services through dedicated working groups for strategic collaboration.
Lithuania has proposed dismantling its inactive power stations to supply Ukraine with parts to repair energy infrastructure damaged by intensified Russian attacks. This response comes after Ukraine’s Prime Minister sought help from post-Soviet states for spare parts compatible with Soviet-era equipment.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) confirmed that the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP), Europe’s largest nuclear facility, sustained three direct strikes to its main reactor containment structures, the first incident of its kind since November 2022, but assured that these did not compromise nuclear safety, even though there was damage and one casualty. IAEA Director General Rafael Grossi highlighted the global risks associated with such attacks, reiterating that no one benefits from targeting nuclear facilities. The agency, which has been monitoring the plant since September 2022, was made aware of a drone explosion at the site but has not attributed it to any party. Concurrently, Ukraine’s military intelligence, which has refuted any involvement in the explosion, pointed to Russian false flag operations as the likely cause and condemned the dangerous conditions stemming from Russian troops and weapons presence, along with the mining of facilities at the ZNPP, a plant under Russian occupation since March 2022. Ukrainian military intelligence spokesperson Andrii Yusov has called for the withdrawal of Russian forces from the ZNPP to bring operations back in line with international safety standards.
Russia News
Ukraine’s military intelligence reports that a Ukrainian drone strike on April 5 damaged seven Russian aircraft at the Yeysk airbase, including fighter jets, transport planes, and an amphibious Be-200 Altair, used for various missions including firefighting and search and rescue. The attack, which also targeted a power station, is part of a series of recent Ukrainian strikes on military and industrial sites in Russia, leading to heightened Russian air defense measures.
The UK’s Defense Ministry reports that Russia’s daily military casualties in Ukraine have decreased to 913, coinciding with fewer attacks in the past month. Factors include a pause after the costly Avdiivka offensive and the intent to lower casualty announcements during elections. Russian forces have averaged 658 casualties daily since February 2022, with an upward trend each year. Ukraine’s General Staff reports a total of 447,510 Russian troop losses since the invasion began, including 820 in the last day, but this figure hasn’t been independently verified. Ukrainian President Zelensky has cited 180,000 Russian deaths, while independent Russian media outlet Mediazona, with BBC Russia, has confirmed 49,281 deaths. NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg estimated over 350,000 Russian troop losses, with U.S. officials suggesting over 315,000 killed or injured.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Nikolai Doluda, a top Cossack leader, stated that over 30,000 Cossacks are engaged in combat in Ukraine, integrated within Russian motorized rifle units. He mentioned that nearly all of Russia’s 13 Cossack groups have created volunteer units for the fight.
Reports from Russia highlight issues within its military, including drunkenness, extortion, and fratricide. An incident involved six soldiers from the 164th Motorized Rifle Brigade in Luhansk Oblast torturing and killing a fellow soldier over a personal vendetta. This brigade faces problems with an extortion ring exploiting the unit’s prevalent drunkenness to abuse and extort money from colleagues.
Oleg Ryazantsev of Rostec reported that Russian forces deployed the Pantsir-M naval air defense system for the first time in Ukraine, successfully intercepting a Storm Shadow missile aimed at a Russian vessel. The Cyclone Karakurt-class corvette, part of the Black Sea Fleet, is noted as the only ship equipped with this system.
Russia’s Allies
Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov is set to engage in talks with his Chinese counterpart, Wang Yi, on April 8-9 in China, addressing bilateral cooperation and the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, which Russia labels the “Ukrainian crisis.” Amid Western concerns about China’s expanding role in supporting Russia’s military, particularly regarding geospatial intelligence, NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg and U.S. officials have pointed out China’s contribution to Russia’s defense sector, supplying components for tanks, missiles, and satellite imagery. These developments could significantly influence the dynamics of the conflict in Ukraine. As Russia becomes more isolated from the West because of its aggression in Ukraine, it has tightened its alliance with China, underlined by their “no limits” partnership declared shortly before Russia’s full-scale invasion. Concurrently, the United States is alerting its allies to China’s escalated backing of Russia, including sharing geospatial intelligence useful in warfare. In a further display of the two countries’ close relations, Russian President Vladimir Putin is scheduled to meet Chinese President Xi Jinping in China this May.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
Russian officials continue to promote false narratives about the 2014 conflict in Donbas, portraying it as a Ukrainian insurrection rather than a result of Russia’s military actions. Despite evidence of Russia’s orchestration, spokespeople and state media claim the unrest was a local response to a supposed US-backed coup in Ukraine, misrepresenting the invasion as a defense against external aggression. This misinformation aims to obscure Russia’s initial aggression and its goals in Ukraine.
Russian officials claim Ukraine targeted the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP) with drone strikes, causing minor damage but no critical harm or casualties. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has been informed but did not assign blame, emphasizing the need for all parties to avoid jeopardizing nuclear safety. Russia’s allegations aim to draw international condemnation towards Ukraine and seek to use their control over the ZNPP to gain legitimacy for their occupation, both of the plant and Ukrainian territory.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
