Summary: It has been confirmed that Russian forces captured Vesele last week near Bakhmut. European Union passes €50 billion military aid package to Ukraine.
Situation On The Ground And Air
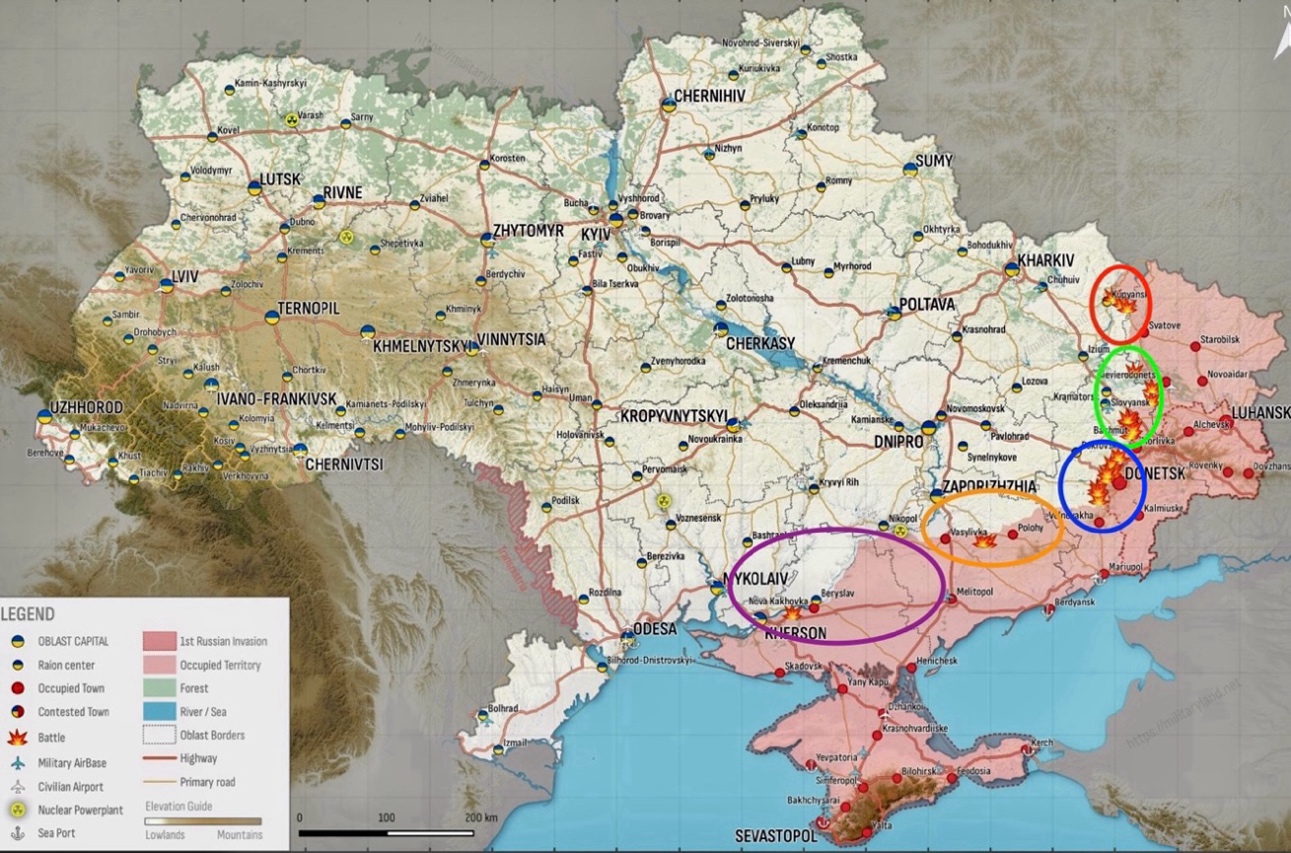
Sloboda Front – Initiative Russia – Target: Recapture Kupyansk
Siversky Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia – Targets: Zherebets River, Siversk, & Chasiv Yar
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia – Targets: Avdiivka, Pervomaiske, Novomykhailivka, & advance from occupied Marinka
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None – Targets: Staromaiorske, Urozhaine, & Robotyne
Dnipro Left Bank Front – Initiative None – Target: Krynky
The frontline along the Kupyansk-Svatove line saw ongoing positional engagements without any confirmed shifts in control. Despite Russian milblogger claims of advancements near Synkivka, there’s no visual evidence to support these assertions. Fighting was reported northeast and southeast of Kupyansk, particularly near Synkivka and Tabaivka.
Near Kreminna, Russian forces were said to have made advances near Terny and Yampolivka, but no changes to the frontline were confirmed. Positional battles persisted west of Kreminna, around Terny, Torske, Yampolivka, and to the south near the Serebrianska forest, Bilohorivka, and Hryhorivka.
Russian forces have achieved a confirmed advance north of Bakhmut, with geolocated footage from February 3 verifying the capture of Vesele, northwest of Bakhmut. This marks the first visual confirmation of Russian Ministry of Defense claims from January 18 regarding the capture of Vesele. The Russian 106th Airborne Division is reported to be active in the vicinity of Vesele.
Meanwhile, near Bakhmut, ongoing positional engagements were reported without any confirmed frontline changes. Despite claims by a Kremlin-affiliated milblogger of minor Russian advances towards Bohdanivka and Ivanivske, west and northwest of Bakhmut respectively, there is no visual evidence to support these advancements. Fighting continues near Bohdanivka, Ivanivske, and to the southwest near Klishchiivka.
Recent clashes near Avdiivka have seen both Ukrainian and Russian forces making tactical gains. Ukrainian troops recaptured positions in southern Avdiivka, while Russian advances were noted in the north, with specific progress along key streets and a northern quarry area. Despite Russian claims of advancing towards Pervomaiske, visual confirmation is pending.
In Avdiivka, Donetsk Oblast, the situation remains tense with ongoing skirmishes, particularly with Russian reconnaissance groups. Russian forces, suffering losses, continue to advance, potentially motivated by the upcoming presidential elections. They have updated their tactics, now including electronic warfare capabilities to counter Ukrainian drones. Vitalii Barabash, the head of Avdiivka’s military administration, acknowledges the severity but maintains that the situation is not hopeless. Ukrainian defense has been robust, repelling numerous attacks. The U.K. Defense Ministry holds a cautiously optimistic view that Avdiivka will sustain its defense in the near term, bolstered by secure supply lines.
Recent geolocated footage confirms that Russian forces made temporary advances near Donetsk City, specifically east and south of Novomykhailivka, during a mechanized assault in late January that ultimately failed. The footage, dated February 3, aligns with Russian milblogger claims of progress up to Novomykhailivka’s eastern outskirts. Despite these movements, ongoing positional engagements have been reported west and southwest of Donetsk City, in areas including Pobieda, Heorhiivka, and Novomykhailivka.
A Russian milblogger highlighted the challenges Russian forces face due to well-prepared Ukrainian defenses near Heorhiivka and the strategic lowland area, as well as nearby Ukrainian artillery positions. These defenses are expected to hinder Russian efforts to push through Heorhiivka towards Kurakhove, indicating a complex and contested battle space in this region.
In the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border region, ongoing positional battles were reported without any confirmed shifts in the frontline. Russian claims of slight advancements near Pryyutne, southwest of Velyka Novosilka, lack visual confirmation. Continued engagements were also noted near Urozhaine and Staromayorske, south of Velyka Novosilka. A Kremlin-aligned Russian milblogger highlighted challenges faced by Russian forces due to Ukrainian mines and drones, restricting operations to infantry assaults supported by artillery and drones.
The western Zaporizhia Oblast saw ongoing positional battles without any confirmed changes to the frontline. The skirmishes were concentrated near Robotyne and to the west of Verbove, which lies east of Robotyne.
In the east bank of Kherson Oblast, near Krynky, positional battles persisted. A Russian military blogger reported that Russian forces in the Kherson direction are focusing on identifying and targeting Ukrainian drone operators. This strategy aligns with recurrent claims by Russian military bloggers about the considerable threat posed by Ukrainian first-person view (FPV) drones to Russian units in the area.
Human Cost Of The War
1 Ukrainian civilian was killed and another 7 injured from Russian attacks over the last 24 hours:
- Russian forces launched an attack on a three-story hotel in Zolochiv, Kharkiv Oblast, using S-300 missiles on Feb. 6. The assault resulted in the death of a two-month-old boy and injuries to three women. The women, aged 21, 28, and 39, were hospitalized with blast injuries and shrapnel wounds. The mother of the deceased child was among the injured. The attack also caused extensive damage to several settlements in Kharkiv Oblast, with reports of strikes on houses, administrative buildings, civilian vehicles, cafes, and shops.
- In Kherson Oblast village of Tokarivka, a 60-year-old man and a 74-year-old woman were injured and hospitalized after an attack.
- In Marhanets, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, a 50-year-old woman and a 63-year-old man were injured by a drone strike. The woman will receive treatment at home, while the man required hospitalization. Additionally, four houses and a car were damaged in Marhanets.
The General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces reported that Russian forces suffered over 1,020 casualties in the past day.
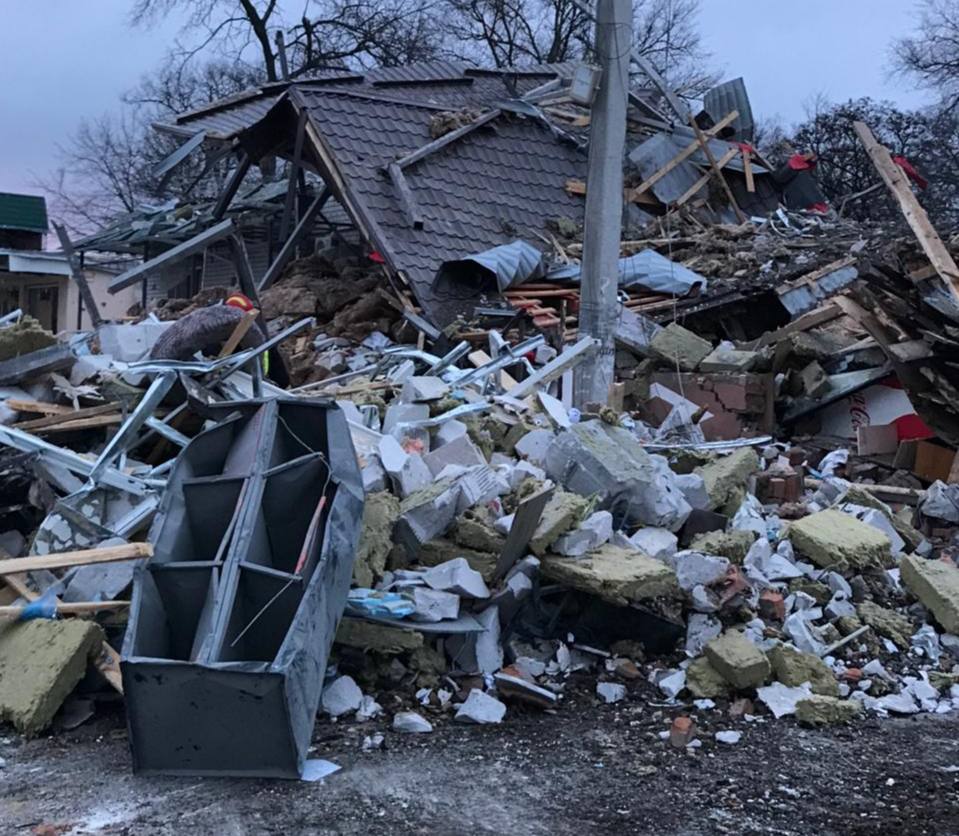 Aftermath of attack on Zolochiv
Aftermath of attack on Zolochiv
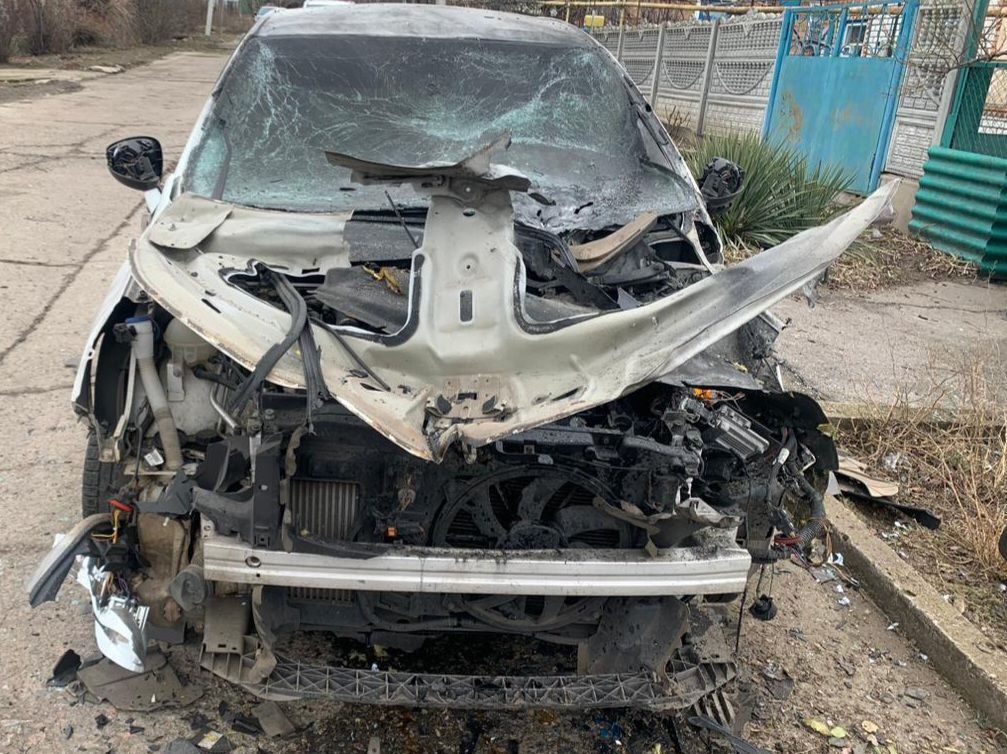 Aftermath of attack on Marhanets
Aftermath of attack on Marhanets
Ukraine News
Ukrainian Special Operations Forces (SOF) have carried out a targeted operation against a key Russian-occupied gas or oil rig in the Black Sea. The platform, illegally seized by Russian forces, was being used to conduct drone attacks and enhance surveillance over the region. The SOF disclosed that the rig was fitted with a “Neva-B” radar system, aiding Russian monitoring of the northwestern Black Sea and tracking surface vessels, highlighting its strategic military importance. The Ukrainian forces’ action included landing on the rig, seizing equipment, and deploying mines, leading to the destruction of the platform’s antenna mast.
The Ukrainian parliament has approved an extension of martial law and mobilization for an additional 90 days from February 14. This decision continues policies first enacted on February 24, 2022, in response to Russia’s full-scale invasion, with repeated extensions over the course of the conflict. The extension, proposed by President Zelensky on February 5, marks the 10th parliamentary vote on martial law since the war’s onset. Martial law restricts Ukrainian men aged 18 to 60, with certain exceptions, from leaving the country due to potential military service obligations.
Ukraine’s President Zelensky established a new military branch for unmanned systems, aiming to bolster defense capabilities. Emphasizing drones’ effectiveness, the move aligns with Ukraine’s 2024 military strategy and calls for increased Western support. This follows efforts for joint weapon production and a UK military aid package, highlighting Ukraine’s focus on modernizing its defense amid ongoing tensions.
Rafael Grossi, Director General of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), visited Kyiv on Feb. 6 before heading to the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant. The plant, Europe’s largest, has been occupied by Russian forces since March 2022. Grossi met with Ukrainian officials to discuss nuclear safety and security. He plans to engage in a dialogue with Russian management at the plant, focusing on water supply issues and long-term plans for reactor restarts.
The High Anti-Corruption Court of Ukraine nationalized assets worth $13 million belonging to sanctioned Russian oligarch Eduard Khudainatov. The move, announced by the Security Service of Ukraine, targeted his share in an oil company amid allegations of ties to Putin’s regime. This action underscores Ukraine’s efforts to combat corruption and sever links with Russian interests amid ongoing conflict.
The investigation into surveillance of Ukrainian investigative outlet Bihus.Info shifts from the Security Service of Ukraine to the State Bureau of Investigation after Bihus.Info reports SBU involvement. The Prosecutor General’s Office announces the transfer, emphasizing the need for a thorough probe into violations of journalists’ rights. SBU Head Vasyl Maliuk vows to ensure media freedom in Ukraine amidst parliamentary scrutiny.
Former Ukrainian Supreme Court chairman Vsevolod Kniaziev, a bribery case suspect, is suspended from working until April 6 by the Supreme Court following his release on bail. Kniaziev, accused of accepting a $2.7 million bribe, paid Hr 18 million bail ($450,000) on Jan. 31, reduced from an initial Hr 107.3 million ($2.8 million). Despite dismissal, he could return as a judge until the suspension.
Ukraine’s Allies
In a significant boost to Ukraine, allies from Europe and Asia are escalating their support with notable initiatives. The European Council, with President Charles Michel at the helm, announced a groundbreaking €50 billion ($54 billion) Ukraine Facility for 2024-2027, aiming for a March 2024 kickoff. Meanwhile, Germany’s Rheinmetall is gearing up to supply Ukraine with a substantial arsenal including artillery shells, tanks, and air defense systems in 2024. South Korea, not to be outdone, is advancing its contributions by contracting with Poongsan to produce long-range artillery shells, continuing its indirect support strategy initiated in early 2023. These concerted efforts reflect a global commitment to bolster Ukraine amidst ongoing challenges.
The European Commission and the International Finance Corporation (IFC) signed a €90 million guarantee agreement to support private sector investments in Ukraine’s reconstruction efforts. This is part of the IFC’s Better Futures Program aiming to mobilize over €500 million across various sectors. The additional investments are crucial for Ukraine’s economy and reconstruction, with estimates suggesting over $400 billion will be needed for full recovery. The agreement aims to rebuild infrastructure, support businesses, and enhance economic resilience, according to officials.
EU Chief Diplomat Josep Borrell has arrived in Kyiv on February 6, emphasizing the European Union’s solid support for Ukraine amidst its struggle against Russian aggression. With $60 billion in aid from the U.S. currently stalled in Congress, the EU’s support, including military, financial, and reform assistance, becomes increasingly vital.
Republicans in the U.S. Senate are poised to block a border deal that includes $60 billion in aid for Ukraine, Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell announced on Feb. 6. Despite months of negotiations, the bill faces opposition, with Republicans demanding concessions on border security. The Senate deal, led by Republican James Lankford, offers significant security assistance to Ukraine alongside aid to Israel and strict border policies. However, McConnell stated that the bill lacks the necessary support to advance, casting doubt on its future. This impasse threatens critical funding for Ukrainian troops, highlighting concerns about ongoing partisan conflicts in Congress.
The US Army plans to boost its domestic production of 155mm artillery shells for Ukraine, targeting an increase from 28,000 to 60,000 shells per month by October 2024, with further hikes to 75,000 by April 2025 and 100,000 by October 2025, contingent on Congressional approval. This expansion includes the construction of a technologically advanced factory in Texas and investments in explosive material production: $600 million for the Holsten Army Ammunition Plant in Tennessee, $93 million for M6 propellant production at the Radford Army Ammunition Plant in Virginia, $650 million for TNT production, and $14 million for a black powder line in Louisiana. These efforts aim to revitalize the US defense industrial base and enhance strategic readiness, while supporting Ukraine’s defense against Russia.
Reuters disclosed on February 6 that Baykar, Turkey’s foremost drone manufacturer, has commenced the construction of a drone factory near Kyiv, Ukraine, destined to produce Bayraktar-TB2 or TB3 drones. According to Baykar CEO Haluk Bayraktar, the construction phase is expected to last approximately 12 months, followed by the installation of machinery and equipment. The facility is projected to employ around 500 individuals and is anticipated to manufacture about 120 drones annually.
Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba met with Portuguese counterpart Joao Cravinho during Cravinho’s two-day visit to Kyiv on Feb. 6. The Portuguese delegation, including Education Minister Joao Costa, arrived on Feb. 5, focusing on Ukraine’s recovery and ongoing conflict. Discussions included Ukraine’s peace formula, NATO and EU accession, and increased military aid from Portugal. Kuleba emphasized the urgent need for artillery shells, as Ukraine faces a critical shortage.
Life in Occupied Regions
The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) is actively working to integrate territories of Ukraine it occupies into its domain and to gain international recognition for its control. On February 6, key figures including Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov, the head of the Russian Center Elections Committee Ella Pamfilova, leaders from the Donetsk and Luhansk People’s Republics, and representatives from the occupied regions of Kherson Oblast, Zaporizhia Oblast, and Crimea convened to discuss opening Russian MFA offices in these territories. Additionally, the Russian MFA is focusing on ensuring the participation of international observers in the upcoming March 2024 presidential elections within these occupied areas. This strategy is viewed as an attempt by Russian authorities to seek international acknowledgment of their annexation efforts, by presenting the involvement of international observers as a form of legitimacy for Russia’s actions in Ukraine.
Russia News
Russian Security Council Secretary Nikolai Patrushev has called for heightened security measures to protect Russia’s strategic facilities amid concerns over threats to infrastructure. During a national security meeting in the Ural Federal Okrug on February 6, Patrushev outlined the need for improved efforts to guard against natural and man-made emergencies, specifically targeting critical and potentially dangerous installations, including those within the defense industrial base and logistic sectors. The emphasis was on bolstering onsite security, investigative capabilities, and threat awareness. Patrushev revealed that authorities thwarted 23 potential “terrorist attacks” in the Urals in 2023, although nine attacks occurred. He also noted an increase in Ukrainian efforts to recruit saboteurs within Russia. Additionally, in response to potential Ukrainian drone strikes, a high alert regime has been activated for ports in Leningrad Oblast, highlighting the ongoing concerns over the security of Russian infrastructure.
Russian oil refineries cut operations by 4% in January 2024 due to increased drone attacks, per Kommersant on Feb. 6. Attacks targeted refineries in several regions, leading to output drops, including a 30% decrease in Tuapse. Rosneft reported a 10% decline, but Bashneft saw a 13% increase. Decreased crude oil exports followed an alleged attack on a Novatek gas plant. Another fire occurred at the Volgograd refinery after a drone incident. Ukrainian authorities haven’t commented on these attacks.
Russian-Israeli relations are set to worsen as Russia adopts a more critical stance towards Israel amidst the Israel-Hamas conflict. The Russian Foreign Ministry criticized and summoned Israel’s new Ambassador to Russia, Simona Halperin, following her interview where she criticized Russia’s delayed condemnation of the Hamas attack on Israel in October 2023, questioned meetings between Russian officials and Hamas in January 2024, and raised concerns over Russia not labeling Hamas as a terrorist organization. The ministry accused Halperin of providing “distorted interpretations” of Russia’s policies, marking a continued decline in diplomatic relations between the two nations.
The Finnish government extends the closure of its eastern border with Russia until at least Feb. 11 due to concerns over migrant influx. The closure, initially imposed in November 2023, aims to prevent migrants, suspected to be pushed by Russia, from entering Finland. Despite ongoing discussions, authorities seek a sustainable solution beyond temporary extensions, as thousands of migrants remain stranded on the Russian side.
Metropolitan Yevgeniy of the Estonian Orthodox Church, affiliated with the Moscow Patriarchate, is leaving Estonia on Feb. 7 as his residence permit was not extended due to accusations of supporting Russian aggression. Estonian authorities cite concerns over his public statements and actions.
A Moscow court ordered the arrest of Boris Akunin, a prominent Russian writer in exile since 2014, citing his criticism of the Ukraine war. Known for historical fiction, Akunin has long opposed Putin’s regime, facing charges of supporting terrorism and spreading “fake news.” The move reflects a crackdown on dissent amid ongoing tensions.
The Insider reports that members of Russia’s GRU created false identities to infiltrate domestic civil society networks and conduct espionage on perceived regime opponents. Alleged agents posed as activists, filmmakers, and journalists, focusing on organizations like the Free Russia Forum and the Moscow Helsinki Group. The report links them to GRU Unit 29155, known for the Novichok poisoning of Sergei Skripal. This revelation underscores Kremlin’s scrutiny of dissent even within Russia, utilizing notorious black ops teams for domestic surveillance.
Russian Mobilization
Russia is set to expand its military education system as part of its efforts to enhance force generation for the future. The Ministry of Defense announced the establishment of a new Suvorov Military School branch in Ulyanovsk, with plans to start enrolling students by September 2024. In a parallel move, the Russian Higher School of Economics is creating the Institute of Military Economics and Strategy, to be headed by retired Admiral Sergei Avakyants, who led the Pacific Fleet until April 2023. Avakyants’ demotion earlier in the year followed a readiness evaluation, amid reports of the Pacific Fleet’s naval infantry’s performance issues in Ukraine. These initiatives reflect the Kremlin’s ongoing efforts to bolster its military capabilities through education and strategic development.
Russian Narratives for Propaganda or What Tucker Carlson Will Be Saying Tomorrow
The Kremlin is accused of preparing for hybrid provocations in the Baltic states and Georgia under the guise of protecting Russian voters abroad. Russia’s Foreign Ministry criticized Baltic nations for not ensuring the safety of Russian nationals voting in the 2024 presidential election, threatening protests over any perceived disruptions. This move, coupled with claims of “Russophobic” campaigns against Russian diplomatic entities, appears aimed at framing any Baltic actions during the election as attacks on Russian expatriates. Additionally, Georgia’s President accuses Russia of launching a hybrid war, including naval expansions in occupied territories. These actions suggest a Kremlin strategy to destabilize its neighbors through information campaigns and territorial provocations.
Russian officials are intensifying claims against Lithuania and Bulgaria, accusing them of promoting pro-Nazi rhetoric and attempting to erase positive Russian history, respectively. These allegations are part of a broader narrative focusing on the removal or relocation of Soviet-era monuments, with Russia’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs Spokesperson Maria Zakharova criticizing Lithuania for “glorifying Nazi collaborators” and the Russian Ambassador to Bulgaria, Mitrofanova, claiming Bulgaria is trying to “erase everything positive about Russia.” These statements appear to set the stage for potential information campaigns against these countries, highlighting ongoing tensions over historical memory and Russia’s influence.
Russian officials are accusing the West of escalating the conflict in Ukraine to justify Russia’s continued military actions and deter Western military support for Ukraine. Sergei Lavrov claims the U.S. and its allies are intensifying tensions to expand their defense industries, while Gennady Gatilov equates Western defense efforts with nuclear escalation, undermining global security. These statements aim to disrupt Western discussions on providing additional military aid to Ukraine, seeking to weaken Ukrainian resistance.
Tucker Carlson has confirmed his upcoming interview with Russian President Vladimir Putin, marking a controversial visit to Russia. Known for his defense of Putin and echoing Kremlin propaganda, Carlson aims to present Putin’s reasons for the invasion of Ukraine, criticizing Western media for failing to convey the “true nature” of the conflict. His visit and the planned interview, a first for an American since the conflict began, have sparked debate, with Carlson accusing the U.S. government of previously blocking his efforts to interview Putin. The move has drawn support from figures like Marjorie Taylor Greene, amidst criticism from Democrats and media.
Russia’s Allies
Hackers from the Prana Network exposed Russia’s substantial expenditure on Iranian drones, revealing a yearly outlay of approximately $4.5 billion. According to leaked data from an alleged Iran Revolutionary Guard front company, Russia spends $193,000 per Shahed-136 drone, with plans to buy 6,000 for about $1.1 billion. Advanced Shahed-238 drones cost Russia $1.4 million and $900,000 per unit, with yearly purchases amounting to nearly $3 billion for both types. Additionally, Russia aims to acquire Shahed-107 reconnaissance drones at $460,000 each, totaling $1.5 billion. A Russian military blogger suggested that local production of Shaheds in Russia might reduce future costs. While the authenticity of the leaked documents is unconfirmed, their content aligns with known aspects of the Iran-Russia drone partnership, highlighting Russia’s significant investment in these drones for use in Ukraine.
Russia is reportedly circumventing international sanctions by unfreezing North Korean assets, facilitating a deal where North Korea supplies missiles and artillery for Russia’s use in Ukraine, according to The New York Times. Intelligence sources indicate Russia has released $9 million of North Korea’s assets, with the transactions linked to North Korea’s procurement of crude oil and evasion of UN sanctions. High-level meetings between Russian President Vladimir Putin and North Korean officials underscore the strengthening military cooperation, which has already resulted in the delivery of a million rounds of artillery ammunition and the deployment of North Korean ballistic missiles by Russian forces. This partnership not only supports Russia’s military actions in Ukraine but also benefits North Korea by providing valuable data for its weapons development programs.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Militaryland.net (maps)
