Summary of the day: Ukrainian forces initiated a withdrawal from Avdiivka amidst Russian maneuvers aimed at hindering their exit, possibly necessitating Ukrainian counterattacks to ensure an organized retreat. Meanwhile, Germany and France strengthened their support for Ukraine through bilateral security agreements, amidst increasing NATO concerns over Russia’s military threat. Domestically, Russian sentiment towards the Ukraine conflict remains largely indifferent, while reactions to Alexei Navalny’s reported death were subdued. On the battlefield, Russian troops made gains along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, northwest of Bakhmut, and near Avdiivka, as President Putin seeks to reinforce his image as a wartime leader. Additionally, Russian-led courts in occupied Ukraine are imposing severe sentences on Ukrainian POWs, further intensifying the conflict’s severity.
Situation On The Ground And Air
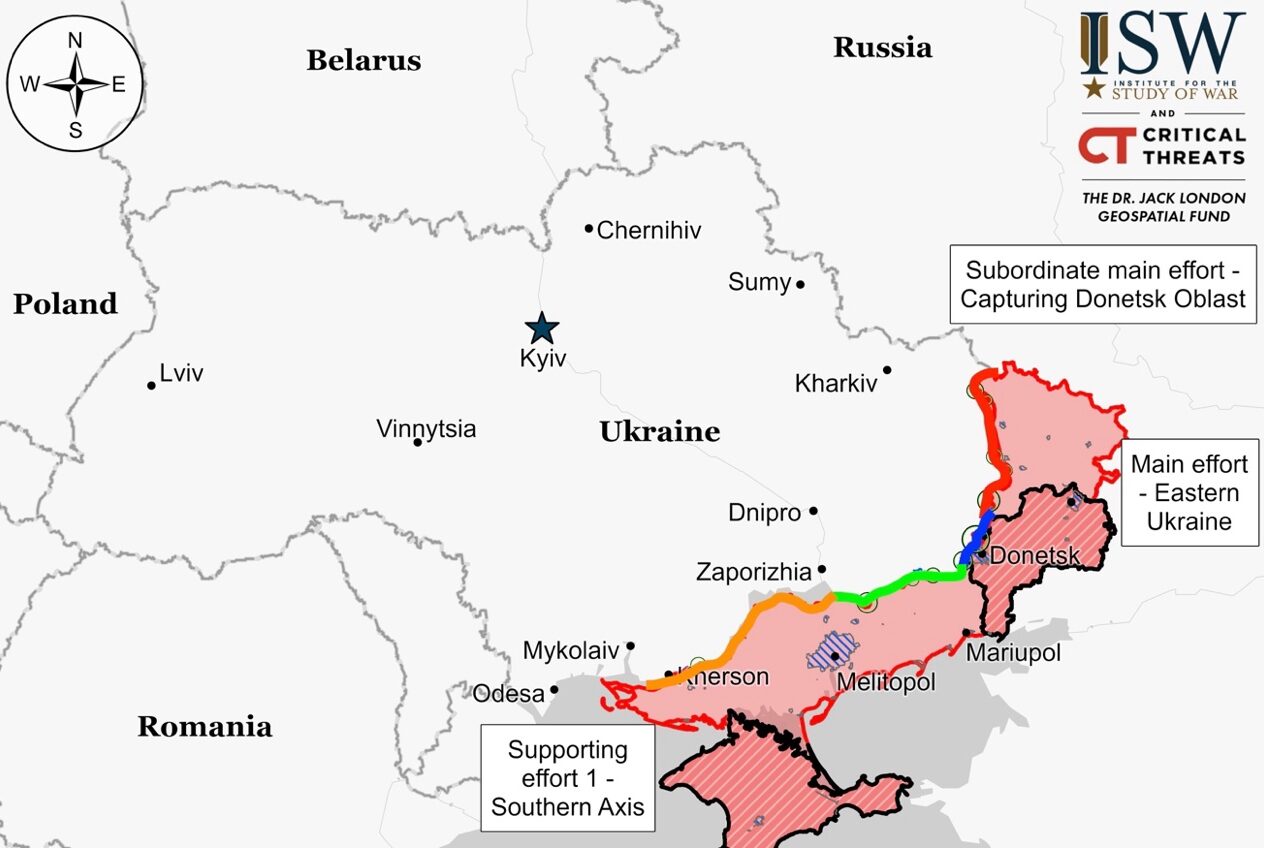
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Russian forces achieved minor advancements along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, with recent geolocated footage indicating progress near Kupyansk, Svatove, and Kreminna. Continued engagements were reported in areas around these locations, with Russian and Ukrainian forces involved in ongoing positional battles. Additionally, reports mention the involvement of Chechen “Akhmat” Spetsnaz forces near Bilohorivka, with tactical counterattacks by Ukrainian troops following initial withdrawals.
Russian forces made advancements in the Bakhmut area, particularly northeast and west of the city, with recent movements reported near Vesele and Ivanivske. Continued positional fighting was noted around these areas and other strategic locations near Bakhmut. The involvement of various Russian military units indicates a concerted effort to push closer to Bakhmut from multiple directions.
Ukrainian forces have strategically retreated from Avdiivka to avoid encirclement by Russian forces, with Commander-in-Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi emphasizing the preservation of personnel over holding the city. The withdrawal follows significant Russian military pressure and advances in the area, and Ukraine is reinforcing its positions to maintain a stable defense. Despite Russian assertions of a disordered Ukrainian pullback, no evidence suggests chaos; instead, the withdrawal appears to be orderly. The conflict for Avdiivka continues, with both sides experiencing heavy losses and ongoing clashes reported. Russian efforts to consolidate gains and encircle Ukrainian forces persist amidst conflicting reports from the front lines.
Ukrainian forces are considering counterattacks to ensure a structured retreat from Avdiivka, aiming to disrupt Russian encirclement efforts. Such counteractions are a strategic move to avoid significant losses and complicate Russian advances. Recent Ukrainian counteroffensives have already weakened some Russian military units, indicating that further Russian advances, especially across open areas towards well-prepared Ukrainian defenses, are likely to be met with heavy casualties.
Russian forces have reportedly made progress southwest of Avdiivka, specifically advancing within Pervomaiske, although there’s no visual evidence to confirm these claims yet. Positional battles are ongoing in the areas around Pervomaiske and Nevelske, indicating a focus of conflict in this sector.
Positional battles were ongoing west and southwest of Donetsk City, specifically near Krasnohorivka, Heorhiivka, Pobieda, and Novomykhailivka.
Russian forces launched unsuccessful attacks southeast and south of Velyka Novosilka, near Prechystivka and Staromayorske, respectively. The reorganized Russian Eastern Grouping of Forces in the Novopavlivka direction comprises a substantial military structure, including nine brigades, 11 regiments, and several tactical units, with one infantry regiment and up to three battalions held in reserve.
Positional battles are ongoing near Robotyne and its surrounding areas, with Russian military presence reported. The Russian 35th Combined Arms Army, incorporating multiple brigades and tactical units, is active in the Orikhiv direction, suggesting a significant military operation. Additionally, the Russian 58th Combined Arms Army, part of the Dnepr Grouping of Forces, displays a formidable structure in the same area, with numerous regiments and battalions, including reserve forces, indicating a strategic focus on this front.
Ongoing positional battles near Krynky involve the Russian Dnepr Grouping of Forces, comprised of a significant military assembly including nine brigades, 19 regiments, and various tactical units, positioned for potential offensive operations in the Dnipro (Kherson) direction and possibly targeting the Crimea and lower Dnipro River areas. This grouping also boasts a formidable array of airborne and naval infantry forces, indicating a strategic emphasis on this front.
Human Cost Of War
Ukraine has successfully repatriated the remains of 58 soldiers through the efforts of various state agencies and with the help of the International Committee of the Red Cross, adhering to the Geneva Conventions’ requirements for a respectful burial. Since the conflict began, around 2,000 soldiers’ bodies have been returned. The soldiers’ remains will undergo forensic examination for identification before being released to their families for burial, a process that remains confidential until the end of martial law.
5 Ukrainian were killed and another 10 were injured in Russian attacks on civilian targets over the last 24 hours:
- Russian military activity in Zaporizhia Oblast resulted in six civilian casualties due to attacks.
- In Kharkiv Oblast, a Russian bombardment resulted in three fatalities, including a teenage girl, and injured two individuals, one being a woman who is in critical condition. The attacks, which utilized two guided aerial bombs, struck the village of Chorne.
- In the Kherson region, a Russian military strike resulted in the death of one individual.
- In Donetsk Oblast, a Russian assault resulted in one fatality and injuries to two individuals. The offensive also caused damage to several structures and civilian infrastructure.
- Russian military operations targeted Mykolaiv, Sumy, and Dnipropetrovsk oblasts, resulting in property damage but no reported casualties.
- Russian forces killed Ukrainian priest Stepan Podolchak in Kalanchak, Kherson Oblast, an area under Russian occupation. Podolchak, known for holding services in Ukrainian and resisting transfer to the Moscow Patriarchate, was kidnapped from his home by Russian forces two days prior to the discovery of his death.
 Aftermath of Russian attack on civilians in Zaporizhia Oblast
Aftermath of Russian attack on civilians in Zaporizhia Oblast
The General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces reported that there were 1210 Russian casualties inflicted over the last 24 hours.
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukrainian officials are emphasizing the pivotal role of technological innovation and the country’s defense industrial base (DIB) in bolstering their war efforts. Deputy Prime Minister Mykhailo Fedorov noted Ukraine’s innovation in drone warfare, while Deputy Defense Minister Ivan Havrylyuk highlighted efforts to develop unmanned systems to reduce human casualties. The National Security and Defense Council Secretary, Oleksiy Danilov, and Defense Minister Rustem Umerov, underscored the importance of mastering new technologies and building sustainable defense capabilities through domestic production and international partnerships.
Ukraine’s Allies
Ukraine secured long-term bilateral security agreements with both Germany and France, enhancing military, political, financial, and humanitarian cooperation through 2034. Germany’s commitment includes over €7 billion in military aid for 2024, with provisions for various defense systems and equipment, while France pledged €3 billion in military assistance for the same year. These agreements signify substantial European support for Ukraine amidst ongoing conflicts.
NATO officials are expressing heightened concerns over Russia’s military threat, with new assessments underscoring the nation’s substantial military capabilities despite losses in Ukraine. The Financial Times highlights that while Russian land forces face degradation, its air and naval assets remain robust, with expectations of force reconstitution within five to six years. This assessment underscores the urgent need for Western defense investments and continued support for Ukraine to thwart any potential Russian aggression towards NATO countries, emphasizing the critical importance of preventing a Russian victory in Ukraine for NATO’s security.
A bipartisan group of U.S. House lawmakers introduced a $66 billion aid package for Ukraine, Israel, and Taiwan after a previous bill was stalled. The new package allocates $47 billion for Ukraine but links funding to domestic border security measures, addressing concerns from House conservatives. President Zelensky has urged Congress to pass the bill, emphasizing the importance of continued support for Ukraine.
Swedish Defense Minister Pal Jonson stated that while Sweden is open to providing modern fighter jets to Ukraine, full NATO membership is a prerequisite. Jonson highlighted Ukrainian interest in Saab JAS 39 Gripen aircraft but emphasized that a decision must align with NATO obligations. Amidst delays in Sweden’s NATO accession, a bipartisan U.S. Senate delegation is set to visit Hungary to advocate for Stockholm’s entry, with Hungarian support being crucial for the ratification process.
Life in Russian Occupied Ukraine
Russian-controlled courts in occupied Ukraine are imposing severe sentences on Ukrainian POWs, with the Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) Supreme Court sentencing seven Ukrainian servicemembers to 25 to 28 years for charges related to artillery strikes. Over 60 Ukrainian servicemembers have received similar sentences in 2024, highlighting a systematic use of legal repression. These actions, deemed violations of international legal standards and the Geneva Convention, are likely methods to demoralize Ukrainians and suppress their national identity in occupied territories.
Russian occupation forces are utilizing educational initiatives as a means of spreading propaganda in territories they control. Denis Pushilin, head of the Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR), emphasized the role of the “Znanie” Society in providing educational opportunities in occupied Donetsk, aligning with a presidential mandate for mass educational organization. This move, reminiscent of Soviet-era intellectual propaganda tactics, aims to “revive” the “Znanie” organization for contemporary purposes, likely to further Russification efforts in the region.
Russian authorities are intensifying their control over media and information in occupied territories, particularly in Kherson Oblast. Vladimir Saldo’s meeting with Russian Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Chernyshenko focused on integrating Russian media projects, including the installation of “Russkiy Mir” television satellites that cover over 80% of Kherson, pushing Russian TV channels as sources of “objective information.” This strategy underscores efforts to dominate the information landscape and shape public perception in occupied areas.
Russia News
The reported death of Alexei Navalny, a prominent figure in Russian opposition politics, has caused a stir within the international community and Russia. Navalny, who had been incarcerated in a penal colony in the remote Yamal-Nenets Autonomous District, was said to have lost consciousness and could not be revived. This announcement, made by the Federal Penitentiary Service, has been met with skepticism by Navalny’s family and colleagues, given the Russian state media’s history of disseminating false information.
Navalny’s imprisonment has been rife with controversy, as he had been serving sentences deemed politically motivated by global human rights entities. He was sentenced to 2.5 years in 2021 and a subsequent 9-year term on fraud charges in 2022. In August 2023, a Russian court imposed an additional 19-year sentence on extremism charges related to his founding of the Anti-Corruption Foundation. These convictions have been internationally criticized as unjust, especially considering Navalny’s prior poisoning with a Novichok nerve agent in 2020, an incident that German medical experts confirmed, and which was linked to Russian state agents.
The response to Navalny’s death within Russia appears muted, with reports indicating that most Russians are largely apathetic, treating the war in Ukraine and issues like Navalny’s death as distant events. In contrast, international figures have voiced their concerns and called for a thorough investigation. NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg expressed sorrow and urged Russia to provide answers regarding Navalny’s death. Yulia Navalnaya, speaking at the Munich Security Conference, called for accountability for Vladimir Putin and his administration, underscoring the need for international support to oppose the Russian regime.
Russian officials, including Vyacheslav Volodin, speaker of Russia’s parliament, have deflected blame, suggesting Western culpability for Navalny’s death without providing substantial evidence. This narrative has been further complicated by the fact that the Kremlin, through spokesperson Dmitri Peskov, has claimed no knowledge of the event.
Independent Russian media like Novaya Gazeta are pushing for transparency, seeking body camera recordings from the medical staff at the penal colony to verify the circumstances of Navalny’s death. This pursuit for truth comes amidst the fear expressed by the Russian Strelkov Movement over the impact of Navalny’s death on potential domestic resistance.
The international community, led by figures like Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba, has renewed calls to confront Putin’s regime, emphasizing the pattern of violence against political dissidents in Russia. Kuleba’s statements highlight the significance of defeating Russia in Ukraine to deter future aggression and hold Putin accountable.
Navalny’s case has long been emblematic of the broader struggle for political freedom and opposition to authoritarianism in Russia. His reported death, therefore, not only resonates as a potential tragedy for his family and supporters but also as a stark reminder of the risks faced by those who challenge the status quo in environments hostile to dissent.
Russian anti-war presidential candidate Boris Nadezhdin lost two legal challenges against his disqualification by Russia’s Supreme Court, effectively barring him from the upcoming presidential election, as announced on Feb. 15. Nadezhdin, who openly opposed Russia’s war on Ukraine, faced disqualification due to invalid signatures collected for his candidacy. Despite his campaign’s setback, Nadezhdin asserted that his effort had raised awareness about opposition to Russia’s current course, although President Putin is still expected to secure a fifth term in the elections scheduled for March 15-17.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian President Vladimir Putin is actively showcasing his leadership in wartime by engaging in activities that highlight his involvement in Russia’s industrial and technological advancements. He toured the “Robot Factory” at the Chelyabinsk Forging and Press Plant and the Stankomash Industrial Park, both key sites in producing industrial robotics and machinery parts. During his visits, Putin reviewed production metrics and engaged with employees and engineering students on topics concerning the development of the Southern Urals and the broader Russian industry.
Russia Allies
Russian forces have fired at least 24 North Korean missiles at Ukraine, according to Prosecutor General Andrii Kostin. These missiles, provided by North Korea since last autumn, have been used in attacks across seven Ukrainian oblasts, resulting in civilian casualties. The U.S. and nearly 50 countries have condemned the transfer and use of these missiles, while South Korea warned of potential further sales of advanced weaponry from North Korea to Russia.
Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko reported the detention of several individuals, including three Belarusians, near the Belarusian-Ukrainian border during a counterterrorist operation. Lukashenko alleged these detainees were planning sabotage activities within Belarus and highlighted that such counterterrorist operations are a regular occurrence along the border.
Russian Narratives for Propaganda
Russian officials Sergei Lavrov and Alexander Lukashevich have reiterated claims blaming the West for instigating Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, framing Russia as a victim of Western aggression to erode support for Ukraine. Lavrov accused the West of manipulating global opinion against Russia’s narrative and undermining President Zelensky’s peace plan. This rhetoric indicates the Kremlin’s concerns about international isolation due to its aggressive actions in Ukraine.
Vyacheslav Volodin, the speaker of the Russian parliament, has blamed Western leaders for Alexei Navalny’s death, suggesting their accusations against Russia are premature without official investigation results. He implicated figures ranging from NATO’s Secretary-General to Western political leaders as being responsible, a claim he made in a Telegram post.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
