Summary of the day: Russian cyber operations targeted Ukraine’s information systems amid their slowed military advance in Avdiivka, with the aim of destabilizing morale. Concurrently, Ukraine’s air defense downed two Russian aircraft as the White House contemplates bolstering Ukrainian long-range missile capabilities. Amidst this, Russia has facilitated the resettlement of its diaspora, while the UAE has tightened financial operations with Russian entities, and Armenia maintains its stance against Russia’s actions in Ukraine. On the ground, Russia has seen troop progress near Donetsk City and western Zaporizhia Oblast and has reportedly recruited over 53,000 military personnel since the start of the year.
Situation On The Ground And Air
Rosgvardia, the Russian National Guard, has increased its presence in Belgorod Oblast by deploying additional elements. This redeployment, overseen by Colonel General Alexander Lapin and Commander Igor Turchenyuk, is strategically positioned north of Belgorod City, focusing on the area stretching from Syrtsevo to Dmitriyevka along the E105 highway, but not extending to the international border with Ukraine.
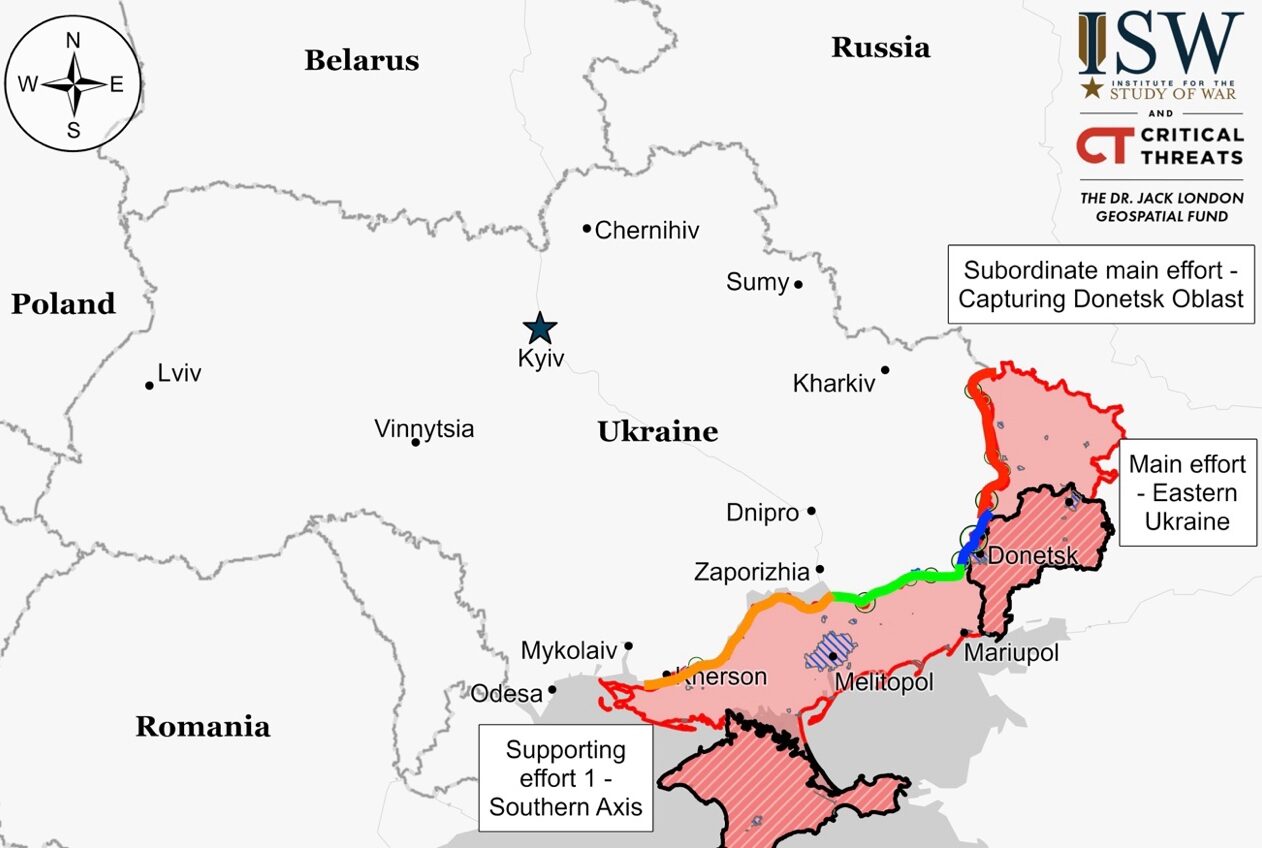
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Positional engagements persist along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line without significant territorial changes. These engagements are concentrated in areas northeast and southwest of Kupyansk, as well as west and south of Kreminna. Russian forces are reportedly intensifying their offensive operations near the Zherebets River, reinforcing their positions to establish defensive lines near Terny and Torske, and preparing for further offensive actions.
President Volodymyr Zelensky visited the command post of the 14th Separate Mechanized Brigade in the northeastern Kupyansk sector, a key logistics area previously occupied by Russia and currently facing increased pressure from Moscow’s forces. During the visit, Zelensky discussed logistical needs, drone warfare, and electronic countermeasures with Brigade Commander Lieutenant Colonel Oleksii Trubnikov, and awarded commendations to soldiers for their service. He expressed gratitude and encouragement, emphasizing the importance of health, camaraderie, and victory for Ukraine.
Positional battles persisted near Bakhmut with Russian forces reportedly making a 0.6-mile (1km) advance near Ivanivske, to the west of Bakhmut. The conflict extends to areas northwest, west, and southwest of Bakhmut, involving intense engagements near Bohdanivka, Ivanivske, Klishchiivka, Andriivka, and Pivdenne. Russian military units alongside Chechen forces, are actively engaging in these regions, with Russian efforts focusing on frontal assaults and flank attacks around Bohdanivka.
Russian forces have consolidated control over Avdiivka, capturing key positions like the Avdiivka Coke Plant, with Ukrainian forces acknowledging their strategic retreat. Conflicting reports persist about the extent of territorial gains beyond Avdiivka, reflecting the fluid and contested nature of the conflict. Despite Russian claims of encirclement, evidence suggests that Ukrainian troops managed a coordinated withdrawal, highlighting the contrasting narratives from both sides of the war.
Ukraine’s Third Assault Brigade narrowly avoided encirclement in Avdiivka and retreated before the city’s fall to Russian forces on February 17. The withdrawal, commanded by Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi, aimed to save troops from entrapment amid escalating attacks. Deputy Commander Maksym Zhorin disputed allegations of abandoned brigade soldiers, while inquiries into reported prisoner captures are ongoing.
After the Russian capture of Avdiivka, the pace of their offensive has slowed, with reports of decreased attacks and military activity as forces regroup and conduct clearing operations. Ukrainian defense has shifted to a pre-prepared and multi-tiered fortification line, potentially causing Russian forces to pause operations or require reinforcements to continue effectively. While reserves are available, there has been no observed movement towards Avdiivka, and Ukrainian spokespeople suggest Russian troops might soon be redeployed to different frontlines.
Russian forces made a slight advance north of Marinka, near Donetsk City, amid ongoing battles in the region. This move is part of a broader pattern of continuous engagement both to the west and southwest of Donetsk City, with notable activity near Heorhiivka, Pobieda, and Novomykhailivka.
Positional battles are ongoing in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, notably near Staromayorske and Prechystivka, south and southeast of Velyka Novosilka, respectively.
Russian forces have made advances near Robotyne and intensified their offensive operations in the western Zaporizhia Oblast as of February 19. Claims from Russian military bloggers indicate progress to the western and southern outskirts of Robotyne, with ongoing battles reported within the settlement, though these claims lack visual confirmation. Ukrainian and Russian military units are actively engaged in this area, with Russia employing small group tactics and increased indirect fire and air strikes, while Ukrainian forces counter with limited armored support.
Ukrainian forces successfully countered at least 16 Russian military attacks in the eastern part of Kherson Oblast, demonstrating resilience against ongoing aggression. The Russian military, aiming to preserve their armored vehicle resources, is reportedly focusing on infantry assaults in this area, according to Ukrainian military officials.
Human Costs Of War
The Russian military reneged on its promise to evacuate and assist wounded Ukrainian soldiers at the Zenit strongpoint in Avdiivka, instead shooting five of them. Despite efforts to negotiate through organizations for prisoner exchanges, Russian forces executed the wounded soldiers, including identified members Andrii Dubnytskyi, Ivan Zhyntnyk, Heorhii Pavlov, Oleksandr Zinchuk, and Mykola Savosik.
Sumy Oblast suffered 252 instances of shelling across 54 attacks by Russian forces, injuring four individuals. The assaults, involving mortars, artillery, tanks, drones, and grenade launchers, targeted nine communities, and led to hospitalizations in the village of Novoslobidske. Bilopillia, a town near the Ukraine-Russia border and home to approximately 15,600 people pre-war, bore the brunt of the attacks with 70 explosions.
Ukraine News
Ukrainian forces downed two Russian jets, a Su-34 and a Su-35S, amid a reported recent surge in Ukrainian air defense successes against Russian aircraft in eastern Ukraine. These shootdowns add to the two Su-34s and one Su-35 downed over Donetsk Oblast on February 17, and another Su-34 on February 18. Despite a brief period of Russian air superiority during their offensive in Avdiivka, Ukrainian air defenses have reasserted themselves in the region.
Ukrainian Air Force successfully intercepted and destroyed four Shahed-136/131 drones launched by Russian forces from Belgorod Oblast towards Kharkiv Oblast. Additionally, Ukrainian defense units shot down a Kh-59 missile near Kryvyi Rih in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, showcasing effective aerial defense against Russian missile and drone attacks.
President Volodymyr Zelensky has criticized the delay in Western military aid, stating that Russian forces are exploiting this to their advantage, particularly in the heavily contested frontlines. As Ukraine contends with significant territorial losses like the recent fall of Avdiivka, the U.S. House of Representatives is stalling on a $95 billion aid bill, with $60 billion earmarked for Ukraine, due to disagreements including issues at the U.S. southern border. Amidst these delays, Zelensky and European leaders are calling for immediate increased support, with some European countries signing bilateral security agreements with Ukraine to enhance defense against Russian advances.
Ukraine’s Digital Transformation Minister, Mykhailo Fedorov, announced collaboration with SpaceX to disable Russia’s use of Starlink satellite terminals in Ukraine’s occupied territories, seeking a solution that doesn’t compromise Ukraine’s drone operations. Despite SpaceX founder Elon Musk denying any sales to the Russian military, Fedorov suggested the terminals are acquired via intermediaries in third countries. The aim is to develop a nuanced strategy that allows Ukrainian forces to maintain connectivity while blocking Russian access, with discussions ongoing on implementing an effective algorithm.
The former abbot of the Dormition Cathedral in Kherson has been charged with treason by the Security Service of Ukraine for supporting the Russian occupation and collaborating with the occupiers. Having fled to Russian-held territory before Kherson’s liberation, he now serves in an eparchy illegitimately established by the Russian Orthodox Church. He is accused of providing ideological support to Russia and receiving benefits in exchange, including the use of confiscated property, and efforts are being made to bring him to justice.
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukrainian defense companies, in collaboration with European counterparts, are actively producing and delivering ammunition to support Ukraine’s military efforts. Specifically, Ukrainian Armor announced that it has dispatched a consignment comprising thousands of 122 mm artillery shells, manufactured in partnership with an unnamed Eastern European ammunition firm, to the Ukrainian armed forces.
Ukraine’s Allies
European officials are preparing for the possibility of former U.S. President Donald Trump’s re-election and his indicated withdrawal from NATO commitments, with concerns heightened by his comments on reducing support for alliance members not meeting defense spending targets. Some suggest forming a pan-European security framework that could stand independently if U.S. support wavers, while others propose strengthening the U.S. focus on China in exchange for continued backing of NATO and Ukraine. At the Munich Security Conference, U.S. Senator J.D. Vance, a Trump supporter, argued for a reduced European reliance on American defense, suggesting a shift in focus to China and not ruling out diplomacy with Russia, despite Western skepticism of Russia’s readiness for genuine peace talks.
The White House, pending Congressional approval for security assistance to Ukraine, is considering providing Ukraine with long-range ATACMS missiles as part of upcoming military aid packages. The US had previously supplied Ukraine with a shorter-range version of ATACMS, which Ukraine used effectively in strikes last October, though not in sustained campaigns. Additionally, the US is ready to send artillery systems and ammunition to Ukraine to enhance their counterbattery capabilities and disrupt Russian logistics.
President Joe Biden expressed willingness to meet with U.S. House Speaker Mike Johnson to discuss the $60 billion Ukraine security aid bill that’s facing challenges in the Republican-led House, following its Senate passage. Johnson has been a vocal opponent of the bill and has sought multiple personal meetings with Biden, which Republican House Majority Leader Steve Scalise asserts Biden has previously declined. Biden, addressing the matter, indicated his openness to a meeting if Johnson has substantive contributions to the discussion.
President Joe Biden is contemplating additional sanctions against Russia following the death of Russian opposition leader Alexei Navalny in a penal colony, with the cause of death being debated as either due to harsh conditions or intentional murder.
Ukraine is expected to receive its first F-16 fighter jets by June, as reported by Foreign Policy magazine, with confirmation from Lithuania’s Defense Minister and an unnamed European official. The jets, provided by the Netherlands, Denmark, Norway, and Belgium, are part of a support package that includes maintenance, modernization, and financing, according to Ukraine’s Air Force spokesperson Yurii Ihnat. Efforts are underway to adapt Ukraine’s infrastructure for the F-16s, including building reinforced storage and enhancing air defenses, despite the challenges and time required for comprehensive preparation.
Japan commits 1.25 billion euros ($1.34 billion) to aid Japanese investors in Ukraine and announces an additional 15.8 billion yen ($105 million) in grants for recovery efforts, as revealed during the Japan-Ukraine Conference for Economic Growth and Reconstruction in Tokyo. The conference, attended by a Ukrainian delegation led by Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal, saw the signing of 56 cooperation and reconstruction documents and discussions on key issues, including mine clearance, infrastructure support, and leveraging frozen Russian assets for Ukraine’s benefit. This financial support is part of Japan’s broader contribution of approximately $8 billion to Ukraine since the conflict began, showcasing Japan’s significant role in Ukraine’s ongoing recovery and reconstruction efforts.
Canada will provide Ukraine with over 800 SkyRanger R70 drones, valued at $70 million, as part of a military aid package worth 500 million Canadian dollars, announced Defense Minister Bill Blair. These drones, equipped for surveillance, reconnaissance, and carrying payloads, are part of Canada’s commitment to support Ukraine’s defensive needs amid the ongoing conflict with Russia.
Ukraine’s Infrastructure Minister Oleksandr Kubrakov urgently discussed the border protests with Poland’s National Security Bureau chief Jacek Siewiera, as blockades disrupt transport and are deemed a security threat amidst the war with Russia. The protests by Polish farmers, initially aimed at trucks due to grievances over Ukrainian imports and the EU’s Green Deal, have escalated to hinder bus travel, trapping women and children fleeing the conflict. With six crossings still blocked and thousands of trucks queued, the protests are set to expand, potentially including farmers from other European countries, raising concerns over the treatment of Ukrainians at the EU border.
Geert Wilders, leader of the Dutch far-right Party for Freedom, criticized Ukrainian refugees for seeking free housing, healthcare, and jobs in the Netherlands, despite his party’s inability to form a government after winning 37 seats in the November 2023 elections. Wilders, known for his anti-immigration stance and pro-Russia comments, described the Netherlands as “the village idiot of Europe” for accommodating refugees. This controversy arises as Dutch refugee facilities, especially in Utrecht, near capacity, amidst debates on extending temporary protections for Ukrainian refugees in the EU until March 2025.
Life in Russian Occupied Ukraine
Russian officials have returned 11 Ukrainian children from territories under Russian control and Russia itself back to their families in Ukraine. Maria Lvova-Belova, the Kremlin’s Children’s Rights Commissioner, confirmed that the children were repatriated from various locations including occupied Zaporizhia Oblast, Mariupol in Donetsk Oblast, Luhansk City, Simferopol in Crimea, and Krasnoyarsk City in Russia, with the assistance of Qatari mediation.
Ukrainian authorities successfully facilitated the return of two families and an additional child from areas of Kherson Oblast under occupation to regions controlled by Ukraine.
Russian authorities, under the guise of vacation programs, continue to forcibly relocate children and their families from occupied Ukrainian territories to Russia. Leonid Pasechnik, head of the self-proclaimed Luhansk People’s Republic, disclosed a collaboration with the Russian organizations “We Don’t Abandon Our Own” and the “We Are Together” Foundation, arranging a two-week stay in Sochi, Krasnodar Krai, for the offspring of deceased Russian military members. Accompanying the children on this trip to Sochi will be their mothers and grandmothers.
Russian occupation forces are actively manipulating election processes in occupied Ukrainian regions for the March 16-17 Russian presidential vote, deploying teams to oversee and ensure voting result falsifications. These groups aim to prepare civilians for participation by March 10, utilizing an online voting system that does not require Russian passport verification, in regions such as Kherson and Zaporizhia Oblasts. Claims of significant support for President Putin among voters in these areas are being promoted, amidst intensified efforts by Russian officials to fabricate voter turnout figures.
Russia News
Yulia Navalnaya, widow of the late Russian opposition leader Alexei Navalny, vowed to carry on her husband’s legacy in a video after his death on Feb. 16 in a penal colony, which she attributes to an act by Vladimir Putin. Global leaders have condemned Putin for Navalny’s death, with debates on whether it was due to prison conditions or deliberate murder, while Navalnaya accuses the Russian government of hiding his body to erase evidence of foul play involving Novichok, a nerve agent. Despite this, the Russian authorities are denying the family access to Navalny’s remains, claiming a need for chemical examination. The EU’s top diplomat, Josep Borrell, has expressed condolences and indicated potential sanctions against Russian officials responsible for Navalny’s death, proposing to rename the EU’s Global Human Rights Sanctions Regime in Navalny’s honor.
Maksim Kuzminov, a Russian helicopter pilot who defected to Ukraine in 2023, was found dead in Spain, as reported by Ukrainska Pravda, and confirmed by Ukraine’s military intelligence. After landing an Mi-8 helicopter in Ukraine, Kuzminov was promised a reward, security, and new identity documents by Ukrainian authorities. His defection, supported by his family who joined him in Ukraine, was featured in a Ukrainian documentary where he encouraged other Russian pilots to defect and provided insights into Russian military operations. Kuzminov, who had recently moved to Spain, was found shot in his apartment, with a burned-out car nearby, suggesting foul play.
The Russian government has simplified the resettlement process for “compatriots” abroad, removing the need to demonstrate Russian-language proficiency for several categories of individuals, including former citizens and those with Soviet or Russian Empire ties. This move aligns with a presidential decree aimed at aiding compatriots from “unfriendly countries” and is consistent with President Putin’s expansion of the “Russkiy Mir” concept to include those connected by language, history, and culture, reflecting Russia’s broader imperialistic ambitions, and potentially justifying territorial claims.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Dmitri Medvedev announced that over 53,000 military personnel have been recruited by the Russian Ministry of Defense since the start of 2024, marking a continuation of the recruitment efforts which saw 42,000 personnel enlisted between November and early December 2023. This claim is further contextualized by the Ukrainian GUR’s estimate that Russia is recruiting approximately 30,000 personnel monthly, indicating a sustained and significant effort to bolster Russian military ranks amidst ongoing conflicts.
The initiative to incorporate ex-Wagner Group members into Rosgvardia’s ranks has reportedly stalled. Reasons for the pause remain unclear, with personnel initially earmarked for these units redirecting to other volunteer formations. This development follows a recent legislative change in December 2023, permitting Rosgvardia to establish volunteer groups, suggesting a strategic shift or reevaluation within Russian paramilitary organization efforts.
Russia has initiated the nationalization of Western-owned enterprises, aiming to bolster its defense industrial capabilities. President Vladimir Putin decreed the transfer of all shares of the Ulyanovsk Machine Tool Plant, owned by the German firm Gildemeister Beteiligungen GmbH (part of DMG Mori), to Russia’s Federal Property Management Agency. This action comes after the plant ceased operations in 2022, post the commencement of Russia’s full-scale military actions in Ukraine.
Russian Allies
During his visit to Hungary, Chinese Public Security Minister Wang Xiaohong offered long-term security support to Budapest, marking an expansion of their relationship beyond economic cooperation. This move aligns with Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban’s strategy of cultivating closer ties with authoritarian regimes, including China and Russia, despite concerns from EU and NATO partners. The agreement, focusing on combating terrorism and transnational crimes and including security capacity building under the Belt and Road Initiative, may increase tensions between Hungary and Western nations, especially as Hungary shows reluctance to support Ukraine against Russia and delays NATO initiatives.
Hungarian Foreign Minister Peter Szijjarto announced that Budapest will not block the EU’s 13th sanctions package against Russia, following negotiations that ensured the sanctions would not harm Hungary’s interests. This decision comes despite previous reports of Hungary’s hesitation due to the inclusion of Chinese companies in the sanctions list and continues Hungary’s pattern of supporting EU sanctions after securing national interest exemptions. Szijjarto reiterated criticism of the EU’s sanctions strategy but affirmed Hungary’s participation in the upcoming package targeting nearly 200 entities aiding Russia’s war efforts.
Emirati banks have started restricting transactions with Russian entities and are closing accounts held by Russian citizens, prompted by the risk of triggering Western secondary sanctions. This crackdown began in September 2023 and has been acknowledged by the Russian government as a manageable issue, suggesting local connections could mitigate the impact. The move follows global trends, with US pressure leading to increased scrutiny of Russian firms in the UAE, and similar actions taken by Chinese and Turkish banks against clients connected to sanctioned Russian entities.
Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan, speaking at the Munich Security Conference, declared that Armenia does not align with Russia on its invasion of Ukraine. He cited the Alma-Ata Declaration, which upholds the territorial integrity of CIS member states, amidst a period of strained Russian–Armenian relations and increasing Kremlin criticism of his policies.
Russia has likely influenced Ecuador’s decision not to provide Soviet-era military equipment to Ukraine, using trade dynamics as leverage. Initially, Ecuador planned to exchange $200 million worth of Soviet-era weapons for modern arms with the US, a move announced by Ecuadorian President Daniel Noboa in January. However, following Russia’s partial lifting of its ban on Ecuadorian bananas—a significant export item for Ecuador—on February 16, Ecuadorian Foreign Minister Gabriela Sommerfeld declared that Ecuador would abstain from sending military equipment to nations engaged in international conflicts.
Russian Narratives for Propaganda
Russian cyber actors targeted Ukrainian media to spread panic about Avdiivka’s seizure, posting false reports on hacked social media accounts to demoralize Ukraine. The State Special Communication Service of Ukraine noted these cyberattacks on February 18. Following this, the Russian MoD’s false narratives about Ukrainian forces’ withdrawal from Avdiivka were designed to foment distrust against Ukrainian leadership.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org.
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com.
