Summary of the day: Amidst the backdrop of the two-year anniversary of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, Russian officials and media remained noticeably silent, possibly to avoid highlighting the invasion’s unachieved objectives and substantial personnel losses. Ukrainian officials, on the other hand, emphasized the nation’s 2024 goals, stressing the importance of innovation and Western support, while drone footage revealed Russian forces committing potential war crimes near Bakhmut. Moreover, as Russian forces recorded advances near Bakhmut and Krynky, concerns over the security of Russia’s A-50 radar aircraft and the lack of long-range missiles from Iran were notable, alongside Russia’s continued efforts to recruit Ukrainian citizens in occupied areas into its military, amidst reports of over 28,000 Ukrainian captives in Russian detention.
Situation On The Ground And Air
During a visit to the front lines Ukrainian military leaders Syrskyi and Umerov announced plans to reinforce certain areas of the front, focusing on protection from drone and air strikes. They held detailed analyses and discussions on necessary actions, emphasizing coordination among defense forces. Despite challenging conditions, Ukrainian troops are effectively holding their positions, inflicting significant losses on Russian forces, with a reported total of 409,820 Russian troop casualties since the conflict began.
At the “Ukraine. Year 2024” forum, Ukrainian Deputy Commander-in-Chief Vadym Sukharevskyi clarified that drones are not intended to replace artillery, but to complement and enhance Ukraine’s military capabilities. The forum, marking the second anniversary of Russia’s invasion, focused on Ukraine’s defensive strategies, economic growth, and maintaining sovereignty. Digital Transformations Minister Mykhailo Fedorov also highlighted ambitious plans to significantly boost drone production as part of Ukraine’s asymmetric response to the conflict.
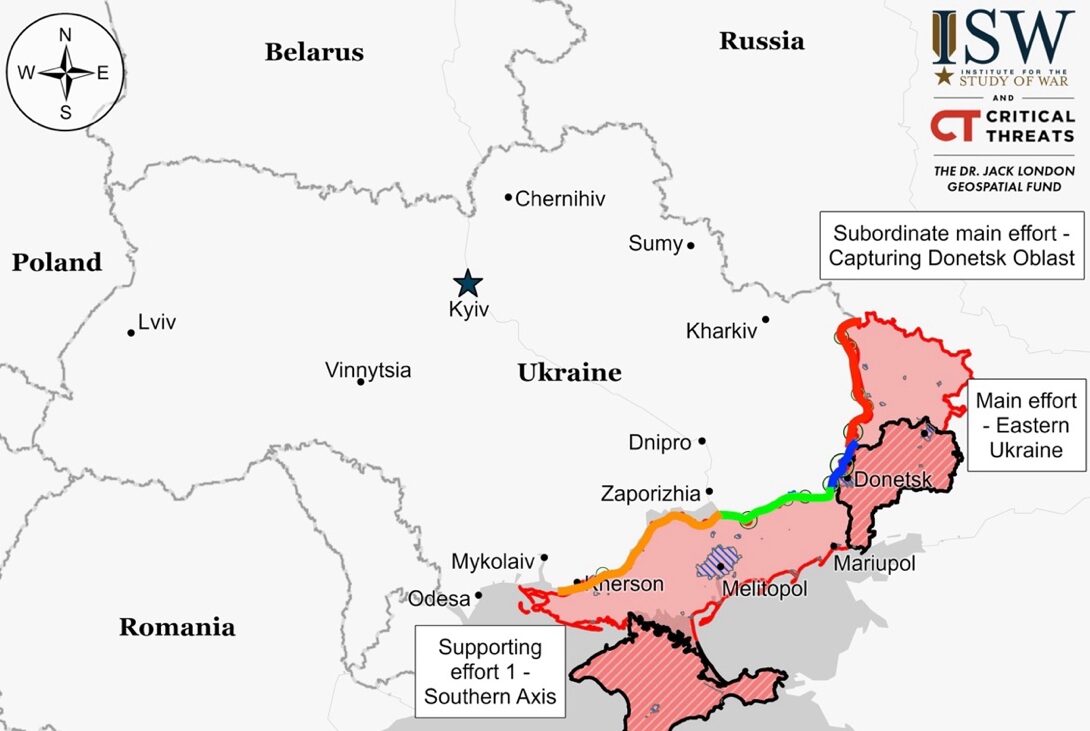
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Positional engagements persisted along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line without any confirmed changes to the frontline. Reports indicated Russian forces made advances west of Kreminna near Yampolivka and Terny, while battles also took place northeast and southeast of Kupyansk, as well as west and south of Kreminna. Due to significant personnel and equipment losses, Russian forces reportedly require two to three days to regroup after each assault in the Kupyansk and Lyman directions, with the Russian “GORB” detachment operating near Bilohorivka.
Russian forces made advancements near Bakhmut, specifically to the north of Ivanivske, west of the city. Positional fighting also occurred in the vicinity of Ivanivske, including areas northwest and southwest of Bakhmut such as Bohdanivka, Klishchiivka, Andriivka, Niu York, and Pivdenne.
Russian forces were reported to have made advances west of Avdiivka, with claims of progress west of Lastochkyne and operations in the area, though no changes to the frontline were confirmed. Ukrainian forces have reportedly repositioned to defensive setups on the western outskirts of Lastochkyne. Despite Russian milbloggers’ claims of capturing Sieverne and Stepove, no visual evidence supports these advancements, with ongoing positional battles noted around Avdiivka and its surrounding areas, involving specific Russian military units.
Ukrainian forces reportedly recaptured some positions southwest of Donetsk City, despite no official confirmation of changes to the frontline. Claims from a Russian milblogger mentioned specific gains near Solodke. Meanwhile, continued positional fighting was reported west and south of Donetsk City, with the Russian forces active near Heorhiivka.
Engagements remained limited along the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border with no changes to the frontline reported. Fighting occurred south of Zolota Nyva and Novodonetske, and near Hulyaipole, with a Russian milblogger mentioning a “strike force” in the area yet to engage in combat, possibly indicating uncommitted tactical reserves.
Russian forces have reportedly made advances within Robotyne, Zaporizhia Oblast, amid offensive operations, with claims of progress in eastern and northern parts of the settlement. Heavy fighting in and around Robotyne has been reported, alongside claims of Russian captures southwest of Verbove. Counterattacks by Ukrainian forces aiming to push Russian troops back and increased Russian activity in the Kamianske sector, with the involvement of specific Russian military units in the area, have also been noted.
Geolocated footage revealed a slight Russian advance along Ostap Vyshnyi Street in Krynky, amidst ongoing positional battles in the area. Despite Russian assertions of fully recapturing Krynky, both Ukrainian and Russian sources indicate continued fighting. The 45th Guards Spetsnaz Brigade and the 337th VDV Regiment of the 104th VDV Division are actively engaged in the vicinity.
Human Costs Of War
President Volodymyr Zelensky warned at the “Ukraine. Year 2024” forum that Russia may be planning a spring or early summer offensive against Ukraine. He emphasized Ukraine’s preparations for potential counteroffensive actions and discussed the importance of U.S. military aid, including the need for more Patriot missile systems to bolster defense and force Russian retreats. Zelensky also highlighted the EU’s leadership and support amidst concerns over delays in U.S. assistance, which are impacting Ukraine’s military readiness on the front lines.
President Volodymyr Zelensky also announced for the first time that approximately 31,000 Ukrainian soldiers have died since the onset of Russia’s full-scale invasion, marking a significant revelation as Ukraine has generally not disclosed casualty figures during the conflict. Zelensky highlighted the gravity of each loss to the nation and mentioned that Russia has suffered around 500,000 casualties, including 180,000 killed. This statement comes amid reports from independent Russian media suggesting different figures for Russian military casualties, and as the United Nations Human Rights Monitoring Mission in Ukraine reports significant civilian casualties and injuries since February 2022, underscoring the profound human cost of the ongoing war.
Drone footage from February 25 depicts Russian forces executing nine Ukrainian prisoners of war near Bakhmut, an act constituting a violation of the Geneva Convention on the Treatment of POWs. This incident, recorded near Ivanivske on Bakhmut’s outskirts, marks the fourth instance of video evidence in two weeks showing Russian forces executing Ukrainian POWs. Such actions are deemed war crimes under international law.
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets in Ukraine caused three deaths and injuring 5 others:
- The Kostiantynivka Central Station in Donetsk Oblast was destroyed in a Russian overnight attack, with Ukrzaliznytsia reporting no casualties as the station was not operational. Local authorities noted this was one of eight attacks in the region, which also resulted in one civilian injury from a blast that damaged nearby residential areas. The Donetsk Oblast Military Administration has launched an investigation into these attacks, which also caused widespread damage to infrastructure, including educational facilities and a church.
- Russian attacks with cruise missiles and drones on Dnipro and Dnipropetrovsk Oblast resulted in injuries to at least four individuals and caused significant damage to residential structures and vehicles.
- Russian shelling in the village of Tiahynka, Kherson Oblast, resulted in the deaths of a 44-year-old man and a 62-year-old woman in their home’s courtyard. Across Kherson Oblast, Russian forces targeted various settlements, causing damage to apartment buildings, residential houses, an educational institution, administrative buildings, and a critical infrastructure object.
- In Nikopol, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, a Russian drone attack targeted a truck, resulting in the death of a 57-year-old man. The drone dropped explosives on the vehicle, leading to the fatal incident and causing additional damage to nearby buildings and vehicles.
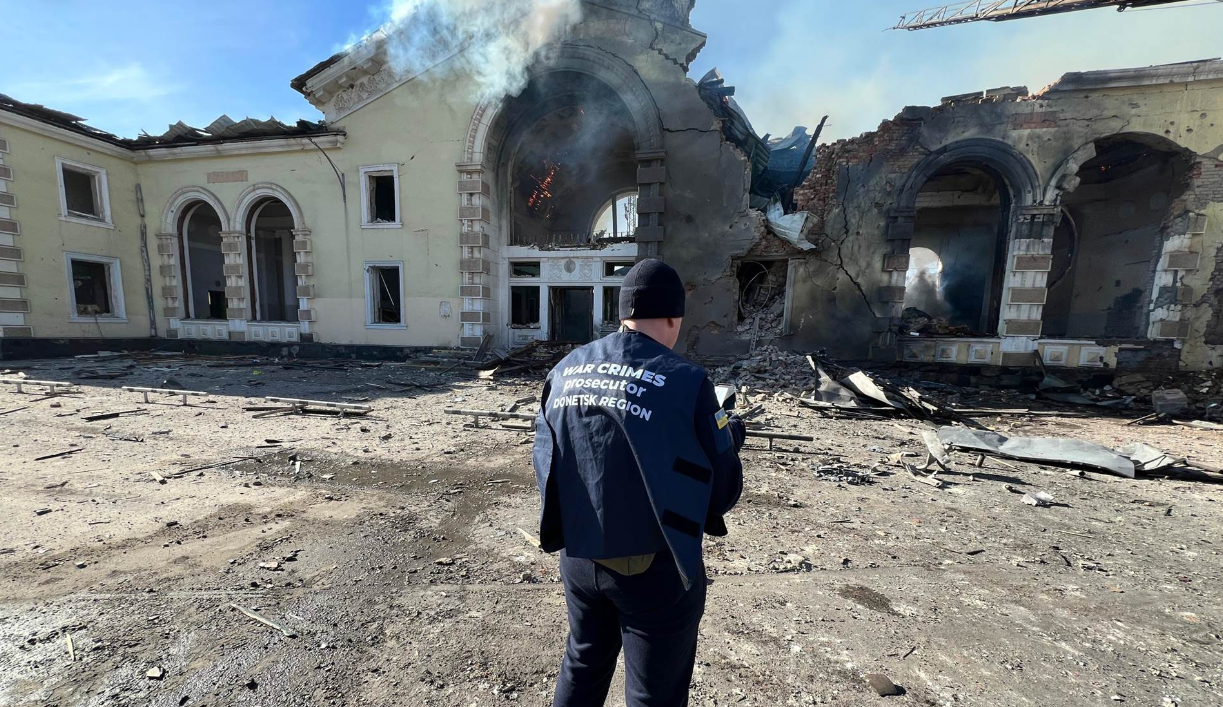 The aftermath of a Russian missile attack on the Kostiantynivka Central Station
The aftermath of a Russian missile attack on the Kostiantynivka Central Station
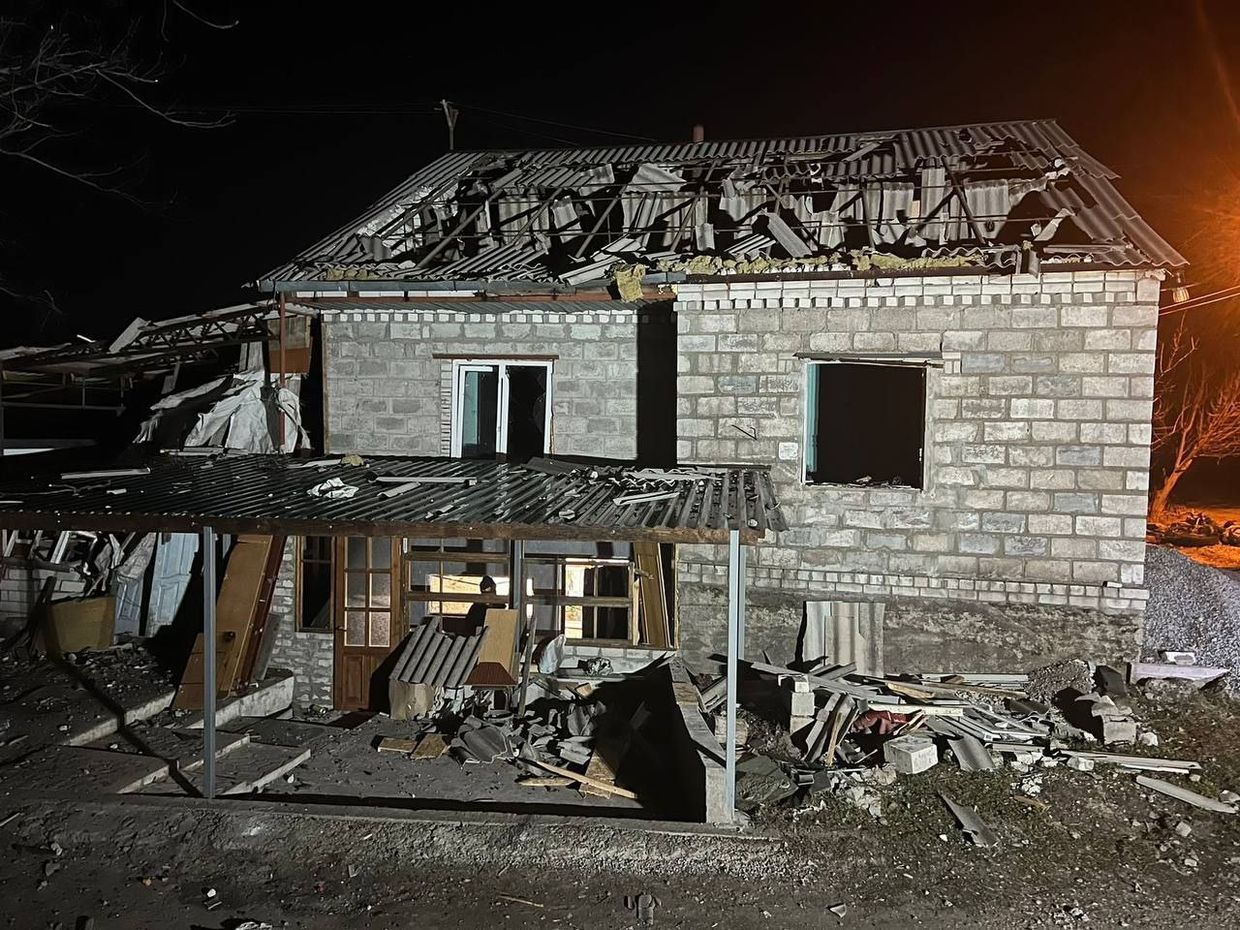 The aftermath of a Russian attack on civilian targets in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast
The aftermath of a Russian attack on civilian targets in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast
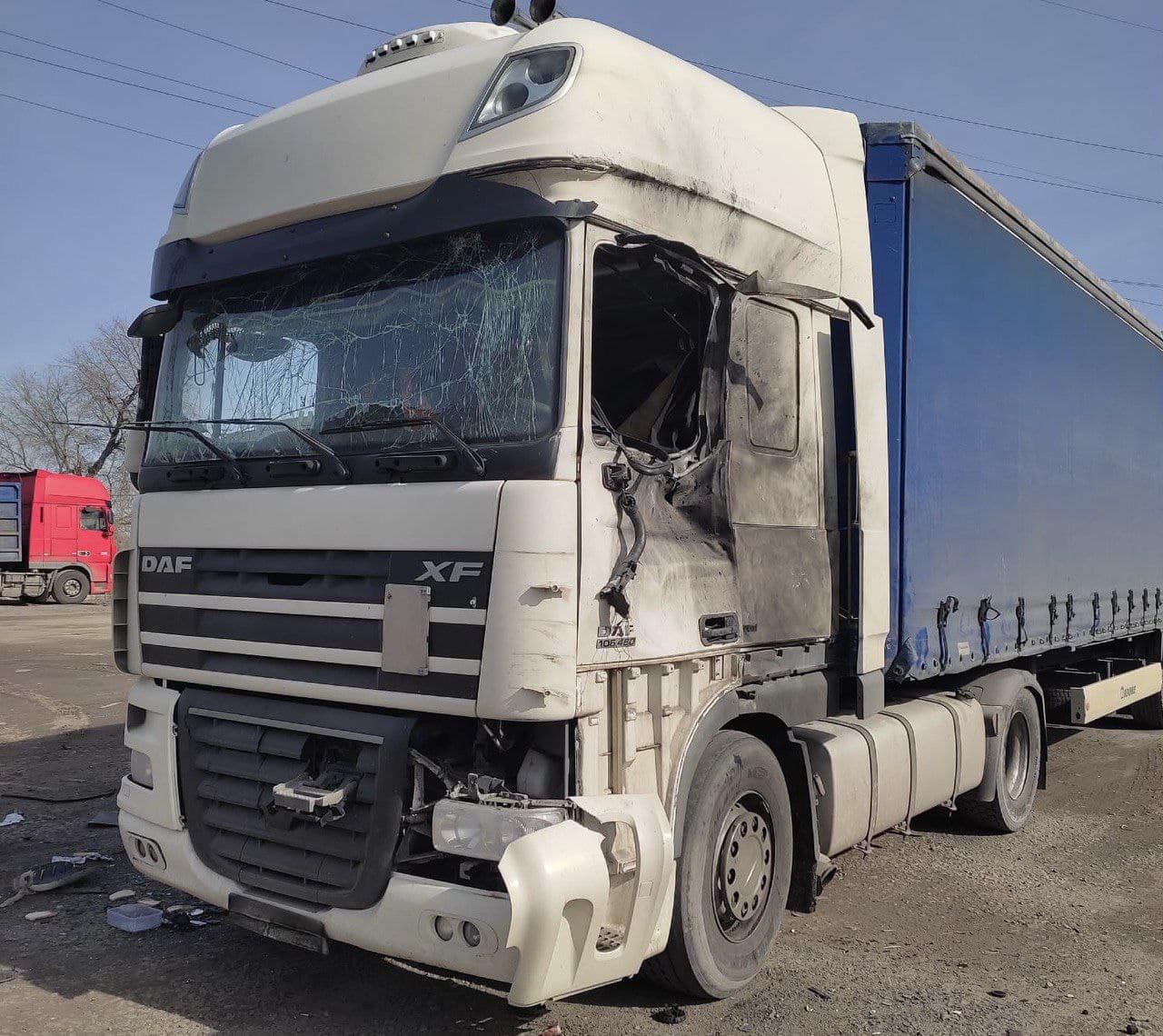 A truck damaged in a Russian attack on Nikopol, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast
A truck damaged in a Russian attack on Nikopol, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast
The General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces reported that 810 Russian forces casualties were recorded in the previous day alone.
Ukraine News
Overnight on February 24-25, Russian forces targeted Ukrainian rear areas with 18 Shahed-136/131 drones. Ukrainian air defenses successfully intercepted 16 of these drones across multiple regions, including Poltava, Kyiv, Khmelnitsky, Mykolaiv, Kirovohrad, Dnipropetrovsk, Zaporizhia, and Kherson oblasts. Additionally, two Kh-31P anti-radar missiles were shot down over Odesa Oblast during the same timeframe.
Ukraine’s military intelligence chief, Kyrylo Budanov, stated at the “Ukraine. Year 2024” forum that Russia’s strategic objectives for 2024, aimed at undermining Ukrainian statehood and securing the borders of Luhansk and Donetsk oblasts, have not changed and are unlikely to be achieved. Budanov highlighted Russia’s failure to meet these goals through military means in the past years and dismissed the possibility of success in 2024.
Ukrainian officials outlined their objectives for 2024, emphasizing innovation and the need for Western support to achieve their goals. Defense Minister Rustem Umerov mentioned Ukraine’s comprehensive yet undisclosed plan for 2024 aimed at significant advancements on the frontline, while President Zelensky discussed reducing Russia’s artillery advantage and the critical role of additional artillery systems for future offensives. Key initiatives also include the formation of an Unmanned Systems Force to enhance drone efficiency and the importance of securing long-range weapons from Western allies, alongside plans for the first Ukrainian Peace Formula Summit in Switzerland and strengthening ties with NATO.
Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba, speaking at the “Ukraine. Year 2024” forum, refuted the notion of ‘Ukraine fatigue’ among allies, challenging the media’s amplification of this unfounded narrative. He praised European countries for their unwavering understanding and swift decisions to support Ukraine but indicated that the U.S. has been less clear about the timing of its future aid. This comes against the backdrop of further European aid confirmed at the Munich Security Conference and delays in U.S. assistance, which have had tangible effects on Ukraine’s defensive capabilities.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine is significantly expanding its defense industrial base (DIB) for 2024, with Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal announcing a tripling of DIB production capacity and a hundredfold increase in drone production. Minister for Strategic Industries Oleksandr Kamyshin echoed this growth, stating a tripling of the DIB in 2023 and plans for a sixfold increase in output for 2024. Additionally, Kamyshin revealed the development of a domestic long-range weapon capable of striking targets up to 700km away, though specific details about the weapon were not disclosed.
Ukraine is on track to achieve the ambitious target of manufacturing 1 million drones annually, as stated by Digital Transformations Minister Mykhailo Fedorov at the “Ukraine. Year 2024” forum. The forum convened to formulate Ukraine’s strategies, particularly emphasizing drone production, which has become crucial for Ukraine’s defense efforts. President Zelensky has also established the Unmanned Systems Forces, a new branch of the Armed Forces, underscoring the importance of drones in military operations and innovation.
At the “Ukraine. Year 2024” forum, Strategic Industries Minister Oleksandr Kamyshin reported a significant increase in Ukraine’s defense capabilities and output, stating a sixfold rise for 2024 compared to 2023 and a tripling of defense production in 2023 over the previous year. Kamyshin discussed the revitalization of Ukraine’s defense industry, noting a shift from survival to efficiency, with plans to expand ground drone usage. The forum, coinciding with the second anniversary of Russia’s full-scale war, brought together top officials to strategize on Ukraine’s military development, economic integration, and sovereignty.
Ukraine’s Allies
Ukraine’s Presidential Office head, Andriy Yermak, at the “Ukraine. Year 2024” forum indicated that Ukraine might invite Russian representatives to a future peace summit following an initial global leaders’ meeting in Switzerland. This primary summit aims to discuss and draft a joint document based on Kyiv’s peace formula to restore Ukraine’s sovereignty. If the initial summit and document are successful, it could serve as a foundation for dialogue with Russia towards achieving a just peace.
On the second anniversary of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, King Charles III commended the resilience and determination of the Ukrainian people facing unprecedented aggression. He highlighted the unprovoked attacks that have entered a tragic third year, resulting in significant civilian casualties, including over 10,000 deaths and nearly 20,000 injuries, as per UN estimates, and the specific impact on children. King Charles, having shown consistent support for Ukraine, did not extend an invitation to Russian President Vladimir Putin for his coronation ceremony and has previously condemned Russia’s actions in Ukraine as a “war of aggression” in statements to international bodies.
Ukraine’s military intelligence head, Kyrylo Budanov, assured that the Russian-controlled region of Transnistria will not be seeking to join Russia, in response to concerns sparked by a warning from the Institute for the Study of War. Budanov dismissed the rumors of a potential referendum for annexation as disinformation and maintained that no such move would pose a problem for Ukraine, which shares a border with Transnistria. Tensions in the region have been monitored closely since the start of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, especially given the Russian military presence established there after the 1991 ceasefire agreement.
Life in Russian Occupied Ukraine
Over 28,000 Ukrainian individuals are detained by Russia, including three OSCE representatives from Donetsk and Luhansk. Ombudsman Dmytro Lubinets notes the difficulty in negotiating their release due to international laws against exchanging civilians and has acknowledged Qatar’s offer to aid in talks. This situation, including detentions often lacking legal process, has been previously reported by the BBC’s Russian Service.
On the night of February 23 to 24, soldiers from the Russian 81st “Medvedi” Volunteer Brigade, reportedly under the influence, violently attacked civilians in a cafe in occupied Chornomorske, Crimea, after a dispute related to the second anniversary of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Surveillance captured the severe assault on several individuals, leading to criminal charges by the FSB against the involved soldiers, as reported by Russian milbloggers. Efforts by Russian authorities to suppress the incident were highlighted when the opposition outlet Vazhnye Istorii sought to identify the soldiers, with the brigade’s ties to the “Redut” PMC and Sergei Aksyonov’s “Crimean People’s Militia” being noted.
Early voting for the Russian presidential election set for March 15-17, 2024, began in occupied Zaporizhia, with similar processes scheduled in occupied Kherson Oblast from February 27 to March 3, according to statements from local occupation authorities. However, the G7 has publicly declared that it will not recognize the legitimacy of these elections or their outcomes in the occupied Ukrainian territories, emphasizing international non-recognition of the voting process in these regions.
Russia News
Russian officials and state media notably avoided discussing the two-year anniversary of the invasion of Ukraine, likely to deflect from the invasion’s failures and significant losses. State TV channels and officials maintained silence or minimal commentary on the anniversary, reflecting an effort to manage domestic perception and maintain public apathy towards the war. This approach aligns with avoiding public backlash and Putin’s considerations on mobilization’s popularity, especially with upcoming elections and force generation needs potentially outweighing public discontent risks.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian efforts to recruit Ukrainian citizens in occupied areas into their military persist, with the Ukrainian Presidential Representative in Crimea reporting the capture of at least 41 Russian soldiers from occupied Crimea, most likely forcibly mobilized Ukrainians. Recruitment activities include the establishment of a mobile military recruitment point in Simferopol and the cancellation of mobilization exemptions for miners in Luhansk Oblast, where medical examinations for potential conscription are set to begin in March 2024. Such forced mobilization actions, particularly in Crimea and occupied Ukrainian territories, potentially violate international law, specifically the Geneva Convention’s stipulations against the compulsory enlistment of occupied residents into the occupying force’s military.
Russian Allies
Ukraine’s intelligence head, Lieutenant General Kyrylo Budanov, reported that Russia has not acquired any long-range missiles from Iran. However, a Reuters article from February 21, citing Iranian sources, claimed Iran supplied Russia with hundreds of short-range ballistic missiles in early January 2024. Despite the lack of visual evidence of Russian forces using these Iranian missiles in Ukraine, there has been a noticeable uptick in military cooperation between Russia and Iran against the backdrop of the ongoing conflict.
Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko has expressed opposition to the Kremlin’s push for deeper integration between Belarus and Russia within the Union State framework. Lukashenko emphasized the strength of Russia and Belarus as independent states over a merged entity, stating that Belarus would “never support” the idea of combining the two countries into one state.
Russian Narratives and Propaganda
The recent loss of a Russian A-50 long-range radar detection aircraft has notably unsettled the Russian information space, underlining the challenges Russia faces in deploying and safeguarding these critical assets. Ukrainian intelligence prepared for two weeks to down the A-50, with Ukraine’s GUR head, Lieutenant General Kyrylo Budanov, hinting at future operations against the remaining six A-50s Russia possesses. Amid skepticism over the official narrative of the A-50’s downing by a Ukrainian Patriot missile, criticism within Russia points to a systemic issue of self-preservation among military personnel, while discussions on alternatives, including adopting less capable systems or seeking acquisitions from China, reflect concerns over the capability gap this loss represents.
The Ukrainian Coordination Center for the Treatment of POWs disclosed an alleged Russian information campaign that aims to undermine trust in Ukrainian authorities by distributing a list on social media. This list falsely claims that Ukrainian POWs are being refused for exchange by their own government, despite Russia not actually proposing these individuals for exchange. The operation has seen participation from several milbloggers, indicating a coordinated effort to spread misinformation.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org.
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com.
