Summary of the day: Troop advances were noted as Russian forces made confirmed progress near Bakhmut, Avdiivka, and Donetsk City. Additionally, various Russian military actions and strategies were highlighted, including limited cross-border incursions by pro-Ukrainian Russian volunteer corps and discussions between Lithuanian and French authorities regarding support for Ukraine. Amidst these developments, the US announced emergency military aid valued at $300 million for Ukraine, reflecting ongoing international efforts to address the conflict. Meanwhile, the Kremlin’s actions, such as personnel changes in defense and enforcement of Russian federal law in other countries, continue to draw scrutiny and discussion within the global community.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
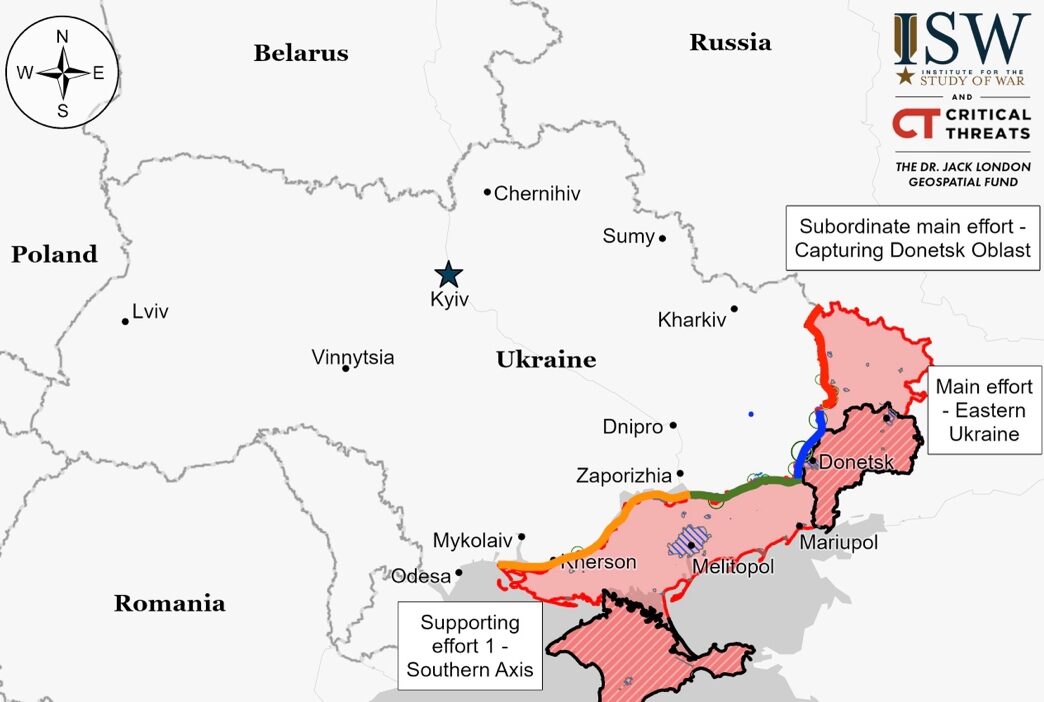
Situation On The Ground And Air
The New York Times reported that Russian and Ukrainian forces have different strengths and weaknesses in electronic warfare (EW). Russian forces have more EW equipment but lack uniform distribution, leaving armored vehicles vulnerable to Ukrainian drone strikes due to the absence of mounted EW gear. Meanwhile, Ukraine’s defense industry allows civilian companies to supply drones, fostering innovation and adaptability. This dynamic has led to an ongoing “arms race” between the two sides, with each side constantly seeking new technologies to gain an edge. As both sides innovate and adapt, variations in capabilities are expected across different areas of the frontline, presenting opportunities for tactical advantage.
The US Office of the Director of National Intelligence’s 2024 Annual Threat Assessment stated that Russian President Vladimir Putin believes Russian forces have hindered Ukrainian attempts to reclaim territory, noting finite US and Western support for Ukraine. The assessment indicates Russia avoids direct military conflict with the US or NATO but engages in sub-threshold activities globally. While Russia poses threats to NATO, full-scale war isn’t Putin’s current aim. US aid is crucial for Ukraine’s defense against Russia’s sustained ammunition procurement from North Korea and Iran. This aid includes essential military equipment like tanks, air defense systems, and long-range strike systems.
Governor Oleksandr Prokudin stated that it will take at least two years to de-mine Ukrainian-controlled territory in Kherson Oblast west of the Dnipro River. Ukraine faces a significant mine threat, endangering around six million lives, according to Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal in October 2023. Only one-third of liberated territory in Kherson Oblast has been surveyed, with over 155,000 mines or explosives found. Currently, more than 1,000 sappers and de-miners are working in the area, supported by de-mining equipment donated by Western allies. Some Western officials are considering sending military personnel to assist in de-mining operations in Ukraine.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Positional engagements continued along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line without confirmed frontline changes. Russian forces reportedly advanced slightly near Synkivka and pushed Ukrainian forces back in a forest area east of Yampolivka. Fighting persisted in various areas, with Russian forces reportedly active in the Kupyansk direction. Ukraine’s Internal Ministry reported a guided aerial strike destroying an apartment building in Kupyansk.
Recent footage suggests marginal Russian advances north of Klishchiivka, southwest of Bakhmut. Positional engagements persist east of Chasiv Yar, Ivanivske, and west of Bakhmut. Contrary to claims, Ukrainian forces reportedly maintain positions in western Ivanivske.
Geolocated footage suggests recent Russian advances east of Nevelske and Pervomaiske, near Avdiivka. The Russian Ministry of Defense claims full control of Nevelske, but visual evidence and some Russian sources contradict this. Positional engagements persist in various areas around Avdiivka. Russian forces are reportedly active in the Pervomaiske area.
Recent geolocated footage shows Russian forces advancing west and southwest of Donetsk City. Limited advances were observed along the H-15 highway, south of Marinka, and on the northeastern outskirts of Novomykhailivka. Ukrainian forces are conducting rotations in the Tavriisk direction. Positional engagements persist west and southwest of Donetsk City. Russian artillery units are reportedly active near Heorhiivka.
Positional engagements persisted along the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border. Ukrainian military officials reported Russian forces resuming assaults in this area, focusing on Staromayorske and Urozhaine, south of Velyka Novosilka.
Positional engagements persisted in western Zaporizhia Oblast with no confirmed frontline changes. Battles occurred near Robotyne and Verbove, east of Robotyne. Ukrainian forces reported Russian pressure in the Robotyne area, but assaults have lessened.
Positional engagements persisted in the east bank of Kherson Oblast near Krynky with no frontline changes reported. Ukrainian forces stated that Russian assaults continue without armored vehicle support, aiming to wear down Ukrainian troops rather than achieve tactical objectives. Various Russian units, including airborne, territorial defense, naval infantry, mobilized, and “Z” assault elements, are observed operating in the Kherson direction.
The Ukrainian Air Force conducted a successful strike on the Russian Mechanik Pogodin tanker near the occupied Kinburn Spit, Mykolaiv Oblast. The tanker, previously used by Russian forces for surveillance and electronic warfare, was washed ashore after the destruction of the Kakhovka Hydroelectric Power Plant. According to the Ukrainian Navy, the Mechanik Pogodin qualifies as a military target under international law due to its role in enemy intelligence activities.
Human Cost Of War
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the death of 5 people and injuries to 55 others:
- A Russian attack on Kryvyi Rih in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast caused a fire in a residential building, resulting in four deaths and injuring 44 people. Three missile hits were recorded, with one hitting a nine-story building. Rescue operations ended, with nine people rescued from the rubble.
- A Russian attack on Hlushkivka village in Kharkiv Oblast resulted in one death and three injuries. Additionally, Russian aircraft bombed Kupiansk city overnight, causing property damage but no casualties.
- Russia launched an artillery attack on Hulyaipole village in Zaporizhzhia Oblast, injuring two women aged 63 and 77. They received first aid and were taken to the hospital by the police. Further details are awaited.
- Russian forces launched 82 attacks on Sumy Oblast, hitting 14 communities. Five children were injured in Velyka Pysarivka, and one man was wounded in Myropillia. The attacks involved mortar, artillery, drones, bombs, rocket launchers, and mines, causing at least 383 explosions. Velyka Pysarivka bore the brunt with 130 explosions.
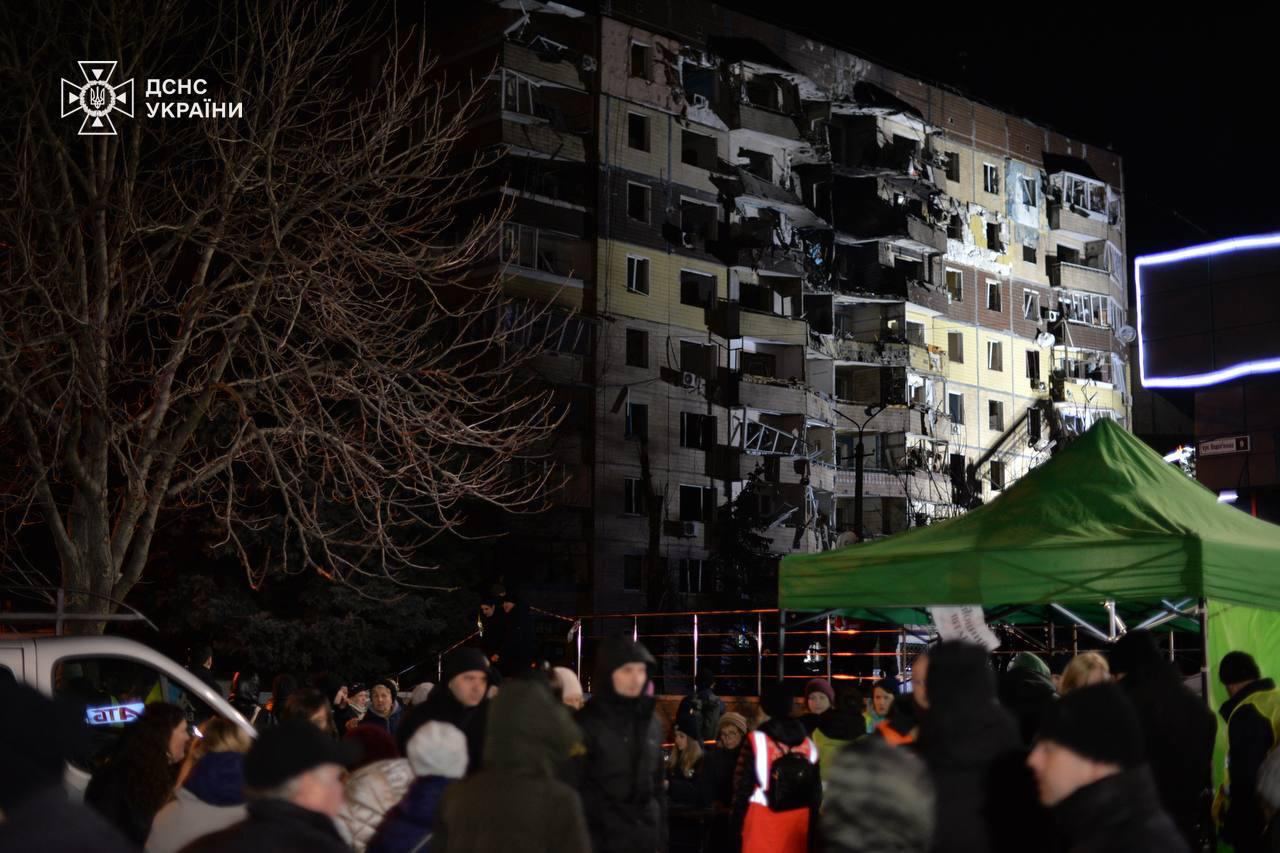 The aftermath of a Russian attack against Kryvyi Rih
The aftermath of a Russian attack against Kryvyi Rih
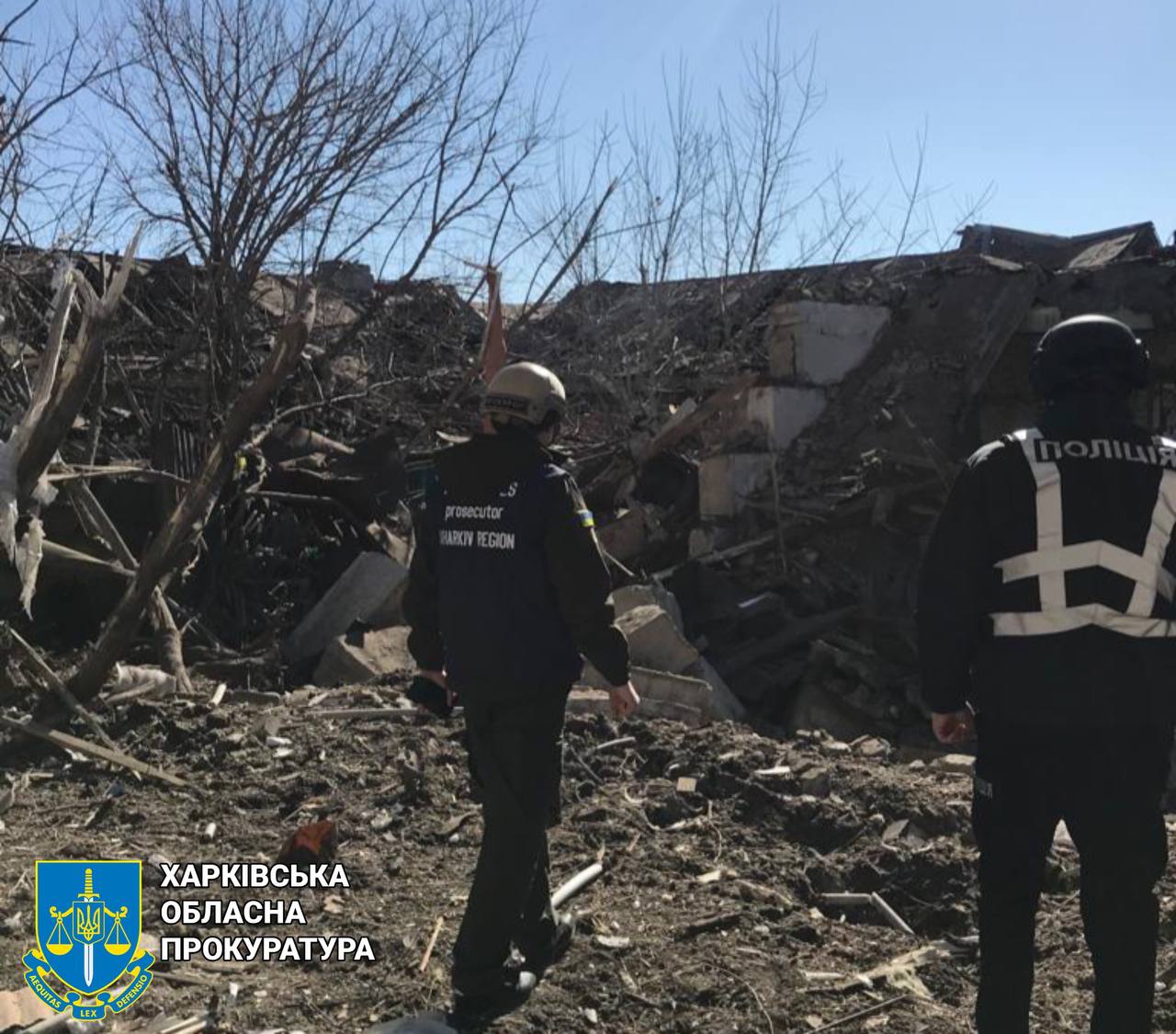 Aftermath of the Russian attack on Kupiansk district in Kharkiv Oblast
Aftermath of the Russian attack on Kupiansk district in Kharkiv Oblast
Ukraine News
The Ukrainian General Staff reported 22 Shahed-136/131 drones launched by Russian forces at Ukrainian targets. Ukrainian forces downed 17 drones, with eight in Kherson, Mykolaiv, and Dnipropetrovsk oblasts. Targets hit included a hotel in Kharkiv Oblast and an infrastructure facility in Kremenets, Ternopil Oblast. Ukrainian authorities also reported downing a Russian Kh-59 missile over the Black Sea. Additionally, Russian forces struck Selydove, Donetsk Oblast with six S-300 missiles, injuring two civilians.
The European Commission proposed a draft framework for accession talks with Ukraine and Moldova. Ukraine fulfilled all recommended reforms. The framework outlines negotiation principles and procedures. The European Council will review the proposal, and upon approval, negotiations will officially commence.
The State Bureau of Investigation (DBR) has launched a criminal case against Vitalii Shabunin, head of the Anti-Corruption Action Center, based on a court decision in Kyiv, as reported by RFE/RL. Allegations include document forgery and evasion of military service. Shabunin denies the accusations, citing his voluntary military service at the war’s onset and claiming impossibility of document forgery due to electronic processing. He sees the cases as part of a targeted campaign by a presidential deputy chief of staff he criticized previously. The Anti-Corruption Action Center, co-founded by Shabunin in 2012, is a prominent Ukrainian NGO dedicated to fighting corruption.
A poll by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology (KIIS) found that 81% of Ukrainians oppose the use of Russian as an official language in their region or as a state language. The survey, conducted in February 2024, reflects a shift in attitudes towards the Russian language since the start of the 2022 invasion. In 2019, only 8% of respondents opposed teaching Russian in schools, but by 2023, this number rose to 52%. Only 7% would support Russian as an official language in their region, and 3% want it as Ukraine’s second state language. Opposition to Russian language use in official communication has risen in the eastern regions, from 3% in 2015 to 40% in 2024. Anton Hrushetskyi, the executive director of KIIS, highlighted that younger Ukrainians now strongly advocate for the unified state and official status of the Ukrainian language. The poll surveyed 1,052 adults across Ukraine, excluding areas under Russian occupation.
Ukrainian soldiers can now preserve their reproductive cells for free under a law signed by President Volodymyr Zelensky. Passed by parliament in November 2023, the law allows soldiers to store cells to have children in case of injury or death. The stored cells can be used even after the soldier’s death, provided they arrange legal affairs to be recognized as the parent. Cells will be stored free for at least three years post-death, and soldiers can choose to have them destroyed after death. A certified will is necessary for using the cells for assisted reproductive technologies. This law follows other changes, including legalizing medical cannabis for veterans with PTSD and patients with serious illnesses.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine plans to manufacture mobile robots for various battlefield tasks, including mining, demining, drone operation, and casualty evacuation, announced by Digital Transformation Minister Mykhailo Fedorov. The aim is to reduce human involvement in combat, particularly due to critical ammunition shortages and Russia’s numerical military advantage. Fedorov described the robots as a significant development in warfare, like the impact of drones. Currently, there are 140 registered robotic systems, with 96 successfully tested, on the Brave1 platform. Ukraine aims to scale up production and deploy the robots swiftly, like its approach with drones. Both Ukrainian and Russian armies are utilizing remote-controlled technologies on the battlefield, with Ukraine already deploying robotic turrets at the frontline.
Ukraine’s Allies
Ukraine and the EU signed a transitional financing agreement worth 6 billion euros ($6.5 billion), part of the EU’s larger 50-billion-euro ($55 billion) support plan. The EU’s four-year Ukraine Facility, approved in February, includes 33 billion euros ($36 billion) in loans and 17 billion euros ($18.6 billion) in grants. The transitional financing will provide 4.5 billion euros ($4.9 billion) in March and 1.5 billion euros ($1.6 billion) in April, pending evaluation by the European Commission. Finance Minister Serhii Marchenko expressed gratitude for the support, noting that it will cover urgent budget needs until the final approval of the Ukraine plan for the Ukraine Facility. Upon full approval, an additional 1.9 billion euros ($2.1 billion) in unconditional financing will be available for Ukraine.
The Danish Defense Ministry announced a new military aid package for Ukraine worth 2.3 billion kroner ($336 million). It includes Caesar self-propelled artillery systems, mortars, and ammunition. This marks Denmark’s 16th aid delivery since Russia’s invasion began. Danish Foreign Minister Lars Lokke Rasmussen emphasized the importance of supporting Ukraine in its fight for freedom. Denmark ranks fourth globally in military aid to Ukraine and second in terms of GDP percentage.
US National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan announced a $300 million emergency military aid package for Ukraine. The funding comes from cost-saving measures in Pentagon contracts, but it’s considered a one-time solution. This aid is separate from the $4 billion presidential drawdown fund for Ukraine. It will provide ammunition for a few weeks, but Sullivan stressed the need for additional, timely aid.
Czech Prime Minister Petr Fiala reported that the Czech-led initiative secured “non-binding commitments” for an additional 200,000 artillery shells for Ukraine, in addition to the confirmed purchase of 300,000 rounds. Fiala emphasized Czechia’s active role in European security policy. The initiative aims to address Ukraine’s critical ammunition shortages.
Lithuanian and French authorities plan to meet in Paris soon to discuss ramping up support for Ukraine. Lithuanian President Nausėda aims to strengthen NATO’s eastern flank and boost European defense production. Discussions may include sending Western military personnel to Ukraine, challenging Russia’s influence over aid decisions.
The French National Assembly approved a security agreement between France and Ukraine signed by Presidents Macron and Zelensky in February. It pledges 3 billion euros ($3.2 billion) in military aid. The vote, with 372 in favor, is the first Assembly vote on the Ukraine conflict. Far-left parties opposed, while far-right abstained. France has committed over 3.8 billion euros ($4.1 billion) in security aid to Ukraine. Macron may consider further support, even military involvement.
Lithuania seized the first Russian-registered car under new rules requiring re-registration in Lithuania. The vehicle, an Audi Q7 worth €41,000 ($45,000), was caught at the Medininkai border crossing. The driver, a Moldovan citizen, was unaware of the new regulations. The car may be confiscated, possibly for transfer to Ukraine. Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia banned Russian-registered vehicles in September 2023.
U.S. House Democrats initiated a discharge petition to force a vote on a $95 billion foreign aid bill for Ukraine, which includes $60 billion for Kyiv. The petition requires 218 signatures from both parties. Another petition by Republican Brian Fitzpatrick aims for a vote on military aid for Ukraine, Israel, and Taiwan. Discharge petitions are rarely successful. Republican House Speaker Mike Johnson has resisted calls to bring the bill to a vote, possibly influenced by former President Trump. Alternatives for Ukraine aid funding are being explored.
Cardinal Pietro Parolin, the Vatican’s secretary of state, stated on March 11 that for peace in Ukraine, Russia must stop its hostilities. This came after criticism of Pope Francis for suggesting Ukraine negotiate peace with Moscow. Parolin clarified that negotiating courage doesn’t mean surrender. President Volodymyr Zelensky viewed the call for a ceasefire as reinforcing Russian military capabilities. German Chancellor Olaf Scholz disagreed with the Pope, affirming Ukraine’s right to self-defense.
Life In Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Russian occupation forces are handling the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP) improperly and unsafely. Energoatom Head Petro Kotin reported Russian attempts to connect the ZNPP to the Russian power system and the dismissal of 400 Ukrainian workers responsible for safety. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Director Rafael Grossi expressed concern about the ZNPP’s long-term stability but noted that the current staff can manage its shutdown state.
Russian Presidential Administration Deputy Head Sergei Kiriyenko visited occupied Avdiivka, Donetsk Oblast with Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) Head Denis Pushilin. They inspected the Avdiivka Coke Plant, with Kiriyenko expressing intentions to restore it, claiming the damage isn’t as severe as at the Azovstal Metallurgical Plant in occupied Mariupol. Kiriyenko’s frequent visits suggest financial interests in building industrial capacity in occupied Ukraine. They also met commanders of the 114th Motorized Rifle Brigade, credited by Putin for seizing Avdiivka on February 17, with units still active in the area.
Russia News
The Russian Defense Ministry stated that it shot down 25 Ukrainian drones over its territory overnight. The drones were allegedly downed in various regions, including Moscow Oblast and Voronezh. While Kyiv hasn’t directly claimed responsibility, Ukrainian military intelligence commented on the reported attacks. Russian authorities have reported a rise in drone strikes targeting multiple regions in recent weeks.
Anti-Kremlin armed groups, including the Freedom of Russia Legion and the Siberian Battalion, crossed into Russia from Ukraine to conduct combat operations. The Freedom of Russia Legion claimed control of Tyotkino village in Kursk Oblast, stating Russian forces had fled. Ukrainian military intelligence confirmed the units consist of Russian citizens aiding Ukraine against Russian invaders. The Russian Defense Ministry reported thwarting a Kyiv attempt to breach the border but did not directly address the armed groups. Ilya Ponomarev claimed the militia entered Belgorod and Kursk oblasts for a joint operation. Both groups posted videos on social media. The Freedom of Russia Legion aims to free Russia from Putin’s dictatorship, while the Siberian Battalion urged Russians to boycott the upcoming presidential elections. This is not the first such incursion; similar actions occurred in May 2023.
A Russian military transport plane, an Il-76, crashed in Ivanovo, central Russia, reportedly killing all 15 aboard. The crash occurred shortly after takeoff, with the engine catching fire. No external interference is confirmed.
Navalny’s former chief of staff, Leonid Volkov, was physically assaulted near his home in Lithuania, as reported by Navalny’s spokesperson Kira Yarmysh. Volkov, residing in Lithuania since 2020, faced an attack where someone broke his car window, sprayed tear gas, and assaulted him with a hammer. Volkov’s current condition is being addressed by the police and ambulance. The identity and motive of the attacker remain unknown, but the incident echoes previous targeting of Russian political dissenters abroad, including Navalny’s poisoning in 2020, linked to Russian intelligence services.
The Kremlin is contemplating tax increases, potentially to bolster federal budget revenues for funding the war in Ukraine. Bloomberg reported that discussions involve raising personal income tax from 15% to 20% for those earning over five million rubles annually, and from 13% to 15% for lower earners. Corporate tax rates may also increase from 20% to 25%. Decision-making is anticipated in the summer of 2024, coinciding with the start of new presidential terms, deemed opportune for implementing unpopular reforms domestically.
The Kremlin made personnel changes in the Russian Ministry of Defense, Rosgvardia, and military command. Lieutenant General Andrei Bulyga was appointed Deputy Defense Minister for Logistics, while Colonel General Kuzmenkov returned to Rosgvardia. Additionally, Lieutenant General Alexander Peryazev, Igor Seritsky, and Esedulla Abechev were appointed deputy commanders in various military districts.
Russian military personnel changes and the search for a new naval commander to enhance naval activity were reported. Russian sources suggest Admiral Alexander Moiseev replaced Admiral Nikolai Yevmenov as Commander-in-Chief of the Russian Navy. Humenyuk also noted limitations in Russian missile carriers’ Black Sea operations due to maintenance facilities being in occupied Crimea, raising fears of Ukrainian strikes.
Russia’s Foreign Ministry summoned Swiss Ambassador Krystyna Marty Lang over Switzerland’s parliamentary move to develop a mechanism for seizing frozen Russian assets for Ukraine’s reconstruction. The Swiss parliament approved measures on March 7 allowing future confiscation of Russian state assets in Switzerland. Russia warned of retaliatory measures if Switzerland proceeds. Western countries froze around $300 billion of Russian Central Bank assets since the 2022 invasion, with Switzerland holding $8.8 billion. Ukrainian authorities may receive up to 3 billion euros ($3.3 billion) in EU-frozen Russian assets by July.
Armenian President Nikol Pashinyan announced on March 12 that Armenia might exit the Russia-led Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) if certain expectations regarding defense are not met. Pashinyan emphasized the need for the CSTO to clarify its responsibilities in Armenia and defend against foreign aggression. He also mentioned the withdrawal of Russian border guards from Zvartnots International Airport by August 1, 2024, following Armenia’s request.
Russia’s Allies
The US Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) 2024 Threat Assessment revealed that China is aiding Russia’s defense industry by supplying dual-use materials and components for weapons. Trade between China and Russia has surged since February 2022, with China’s exports of potentially military-use goods more than tripling since then.
The Belarusian Ministry of Defense announced that Belarusian officials are participating in the Collective Security Treaty Organization’s (CSTO) command and staff training on March 12 and 13.
Russian Special Presidential Representative for the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) Bakhtiyor Khakimov stated that Russia expects Belarus to join the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) on July 4 and that Belarus’ accession to the SCO will be one of the “key results” of the upcoming summit.
Hungary hosted Russian Rosatom’s Alexey Likhachev, coinciding with Budapest’s 25th NATO accession anniversary. Likhachev faces sanctions and is linked to Ukraine nuclear facility occupation. The visit highlights progress on Hungary’s Paks II Nuclear Power Plant, constructed by Rosatom. Szijjarto praised the project’s pace and continuous work. This follows Szijjarto’s frequent visits to Russia, including attendance at the Russian Energy Week forum in October 2023.
Russian Narratives and Propaganda
The Kremlin asserts its right to enforce Russian law on officials of NATO members and former Soviet states, despite lacking jurisdiction. Estonian Minister of Internal Affairs Lauri Laanemets was placed on Russia’s wanted list for alleged monument destruction. Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs banned 347 Baltic citizens, citing “hostile” policies. These actions are viewed as part of Russia’s efforts to justify potential escalations against NATO states.
The Security Service of Ukraine (SBU) dismantled a pro-Russian disinformation group in Kyiv, including a detained priest from the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the Moscow Patriarchate. The group, tied to Russia’s Federal Security Service (FSB), aimed to spread pro-Kremlin narratives and incite religious discord. The SBU called it one of the largest FSB networks operating in Ukraine since the invasion began. The detained priest, allegedly an intelligence operative, led the group. The suspects included heads of public organizations and UOC-MP’s media department employees. They spread pro-Kremlin content via social media and church websites, aiming to distort information about UOC-MP communities transitioning to the Orthodox Church of Ukraine. The group sought to destabilize Ukraine and discredit it internationally. Charges may include treason, collaboration, inciting religious hatred, and justifying Russian aggression.
Russian officials, including Children’s Rights Commissioner Maria Lvova-Belova and Kherson Oblast governor Vladimir Saldo, denied Ukraine’s independence and culture, and claimed that Ukrainian children prefer Russia. Lvova-Belova stated that there are “no foreign children in Russia,” while Saldo claimed Ukrainian children want to live in Russia due to Ukraine’s dependency. In response, the US joined the International Coalition for the Return of Ukrainian Children on March 7 to ensure the safe return of those illegally deported by Russia.
Kremlin officials are attempting to legitimize Russia’s annexation of Ukrainian territory through legal maneuvers. State Duma members introduced a bill to invalidate Crimea’s transfer to Ukraine in 1954. Putin previously voided a 2004 treaty concerning the Sea of Azov, claiming Crimea’s annexation changed Ukraine’s status. These efforts lack real legal legitimacy and contradict Russia’s 1994 pledge to respect Ukraine’s territorial integrity in exchange for nuclear disarmament.
Sumy Oblast Military Administration Head Volodymyr Artyuk debunked rumors of a Russian attack in Sumy Oblast, labeling them as part of Russian attempts to sow panic and destabilize the region. Ukrainian authorities have not detected any Russian strike groups near Sumy’s borders, and assessments suggest no significant Russian military buildup in the area.
Russian officials are intensifying their rhetoric to dissuade Western support for Ukraine. The German Bundestag believes a leaked conversation about providing missiles to Ukraine was part of a Russian hacking operation. Russian State Duma Chair Vyacheslav Volodin warned that discussing potential Ukrainian strikes on Crimea could lead to a “full-scale third world war.” However, such claims are seen as attempts to deter Western aid to Ukraine, according to ISW.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
