Summary of the day: Ten years after Russia’s annexation of Crimea, President Putin continues to justify the oppression of Ukrainians in the region and militarize Crimea to further his territorial ambitions against Ukraine. Amid claims of high voter turnout for his presidency, Putin is setting the stage for a prolonged conflict in Ukraine, responding to Western proposals with defiance and reiterating calls for the absorption of Ukraine into the Russian Federation. Recent developments include a marginal advance by Russian forces in western Zaporizhia Oblast and accusations against Ukraine for a drone strike in Transnistria, signaling a continuous escalation in the region.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Situation On The Ground And Air
Russia is outpacing Ukraine in artillery shell consumption by a ratio of seven to one in 2024, exacerbating Ukraine’s urgent need for ammunition amidst a shortage. The lag in U.S. military aid, amid Congressional disputes, has had tangible negative effects, with the loss of Avdiivka being a stark example. European allies are rallying to provide Ukraine with 800,000 artillery shells through a Czech-led initiative. Ukraine’s ammunition supplies are critically low, worsened by North Korea supplying Russia with over a million shells, missiles, and other arms. These North Korean weapons have been used extensively against Ukrainian territories. Ukraine’s air defense challenges, expected to be mitigated by F-16 jets, remain as Russia has significantly increased its aerial bombing campaigns. President Zelensky has been briefed on the dire ammunition situation, while Russia reportedly produces nearly triple the artillery munitions compared to what the U.S. and Europe are able to supply Ukraine, according to recent NATO intelligence and reports.
Ukraine’s military chief, Oleksandr Syrskyi, has emphasized the pivotal role of unmanned systems and electronic warfare in gaining an edge over Russian forces. Together with his deputy, Vadym Sukharevskyi, Syrskyi is pushing for rapid implementation of “innovative solutions” to enhance the capabilities of Ukraine’s defense. The focus is on saving soldiers’ lives through technology and training specialists in key areas like electronic and automated warfare. Syrskyi stresses the importance of adapting military needs based on combat experience and seeking asymmetric strategies to counter a numerically superior adversary. This approach follows the vision of former Commander-in-Chief Valerii Zaluzhnyi, who highlighted electronic warfare as crucial to succeeding in modern combat scenarios.
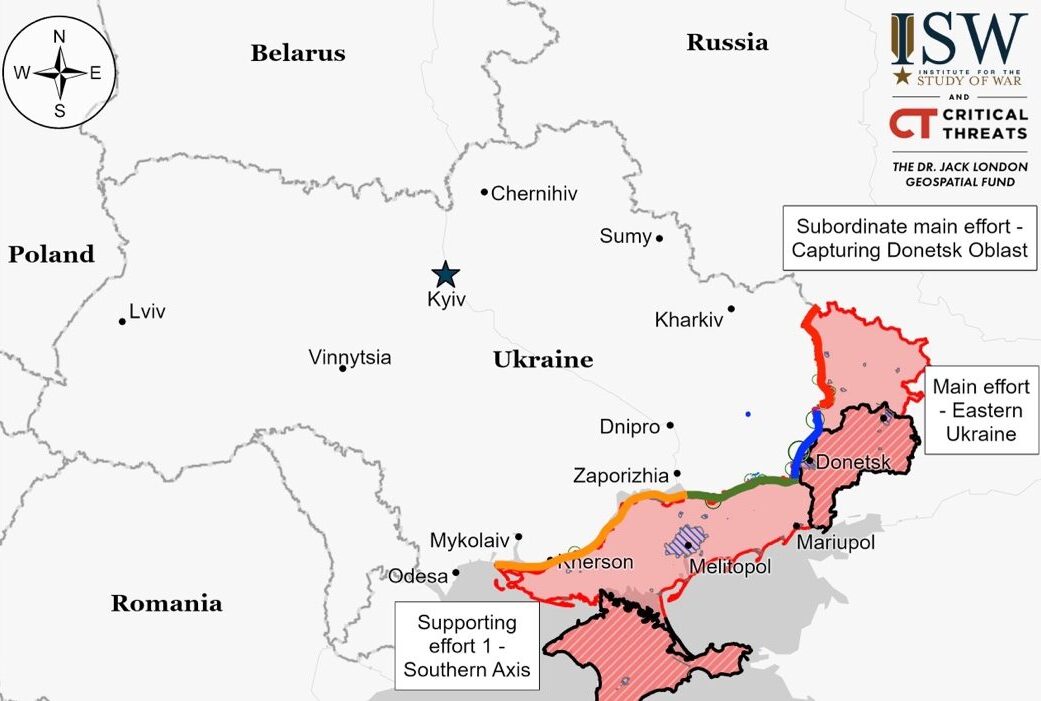
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces attempted but failed to advance along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, facing resistance from Ukrainian forces near Kupyansk and Kreminna. Ukrainian military successfully defended positions, repelling attacks in the areas surrounding these locations.
Russian forces failed in their attack attempts in the Siversk area, northeast of Bakhmut, with Ukrainian forces successfully defending near Rozdolivka. Despite ongoing clashes around Bakhmut, including areas to the west and southwest, the front lines remained unchanged.
Russian forces made claims of advancing near Avdiivka, specifically northwest and southwest of the city, but no frontline changes were confirmed. Despite ongoing engagements around Bakhmut and Avdiivka, visual proof of territorial gains remains unseen. Ukrainian and Russian forces continue to clash in several key areas around these locations. Additionally, the Russian Central Grouping of Forces, comprising various military units, is active in the Toretsk and Pokrovsk directions, focusing on offensive operations. This force includes a significant number of regiments, battalions, and specialized units, indicating a strategic emphasis on these areas without a clear shift in battlefield positions.
Fighting continued west and southwest of Donetsk City without any confirmed changes in frontline positions. Clashes took place near Krasnohorivka, Heorhiivka, Novomykhailivka, and Pobieda.
Fighting persisted in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area with no shifts in frontlines reported. Battles occurred near Urozhaine, Staromayorske, and Vodyane, south and southeast of Velyka Novosilka.
Russian forces achieved a slight advance in western Zaporizhia Oblast, with some progress east of Luhivske and claims of capturing half of Robotyne. Fighting persisted near Robotyne and surrounding areas. Russian military units are engaged in this region as part of the “Dnepr” Grouping of Forces. This grouping involves a variety of units, including motorized rifle brigades and regiments, indicating significant military activity in the Zaporizhia direction.
In Kherson Oblast’s east bank, ongoing clashes were reported near Krynky. A Russian military blogger also noted that Ukrainian forces hold some positions near the Antonivsky bridge.
Human Cost Of War
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the death of 4 people and injuries to 9 others:
- In Kherson Oblast, three villagers from Lvove were killed on March 18 due to the explosion of a munition from a kamikaze drone they were trying to dismantle. The victims, aged 45, 55, and 67, suffered serious injuries from the blast and died enroute to the hospital.
- On March 17, a Russian missile strike on Mykolaiv, a city in southern Ukraine, resulted in one death and nine injuries, including two children. The attack, involving two Iskander-M type ballistic missiles, targeted an infrastructure facility. The strike caused significant damage to over 10 apartment buildings, 50 private homes, numerous vehicles, the city’s outdoor lighting system, and tram tracks. The injured are currently receiving medical care.
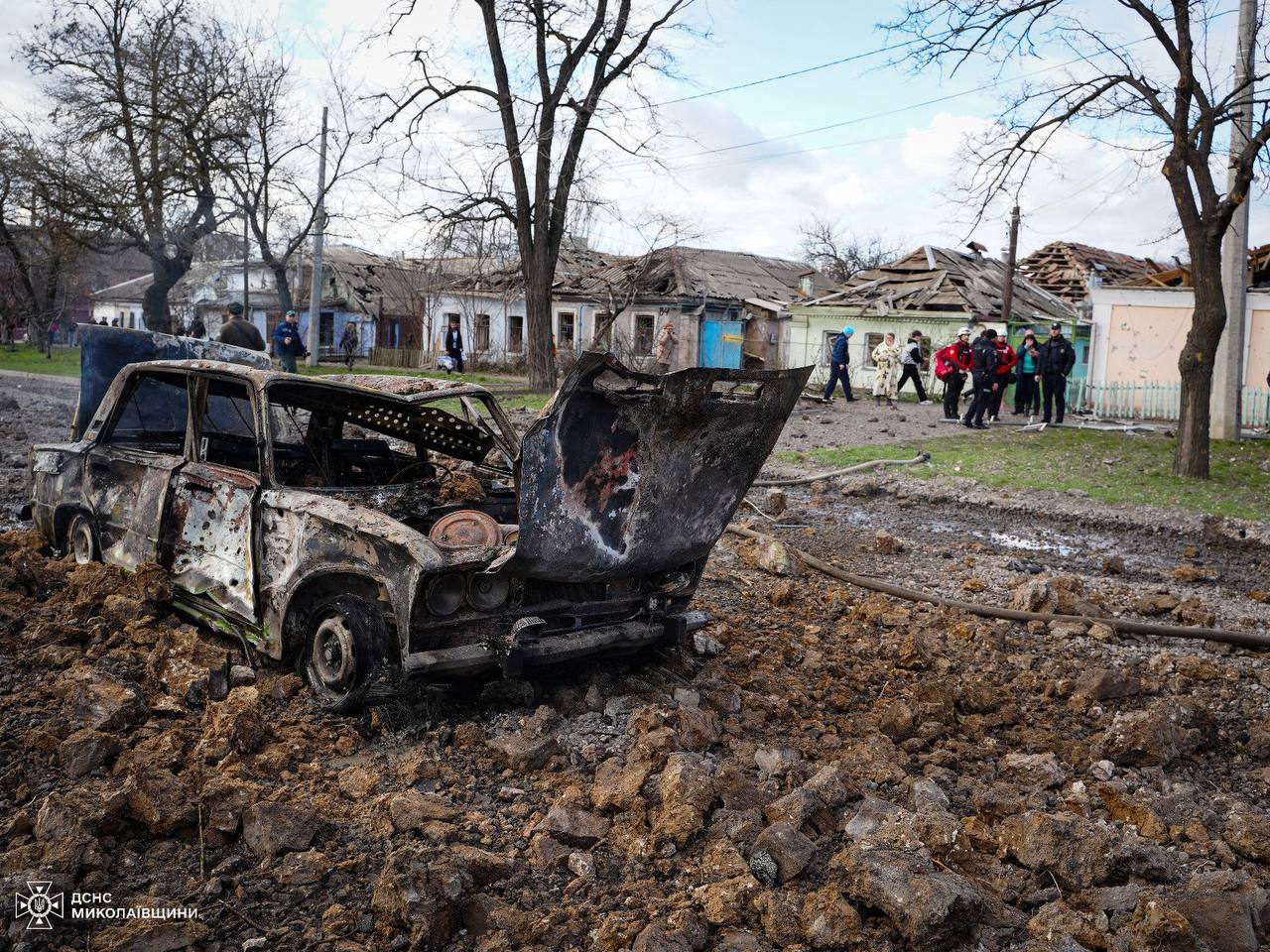 The aftermath of Russian missile attack against Mykolaiv
The aftermath of Russian missile attack against Mykolaiv
Ukraine News
Russian forces conducted missile and drone strikes across Ukraine, targeting multiple regions overnight on March 17 and 18. The attacks included missile launches against Kharkiv and Sumy oblasts, and drone strikes, notably with Shahed drones, across several oblasts including Kyiv and Dnipropetrovsk, with Ukrainian forces shooting down many of these drones. Despite these efforts, some drones caused damage to civilian infrastructure. Additionally, Ukraine identified a new Russian tactic targeting emergency responders at strike sites, with deliberate pauses between missile attacks to target those providing aid. In 2024, Russia has significantly increased its use of aerial bombs in Ukraine, dropping more than 3,500 bombs in just the first months, surpassing the total for all of 2023.
Ukraine’s Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal announced the country’s commitment to a series of reforms enabling EU support of up to €50 billion over the next four years. The reforms, part of the “Ukraine Facility” initiative, span areas including anti-corruption measures, public administration, and sectoral changes across energy to agriculture, also incorporating environmental and digital transitions. Performance will be tracked by over 100 quarterly indicators. The EU has dedicated €33 billion in loans and €17 billion in grants to this facility, with specific allocations for migration, defense, and emergency aid. Shmyhal expressed gratitude to the EU, noting that Ukraine anticipates receiving around €16 billion in 2024 through these reform efforts.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine is investing an additional $128 million to enhance its drone capabilities, a key component in its defense strategy against Russia. President Zelensky prioritizes drone operations and has established a new branch of the military specifically for drones, focusing on unit creation, production, training, and innovation. The funds for drones are sourced from the state budget’s reserve. Agreements with drone manufacturers have reached about $769 million, with more contracts on the way. Ukraine plans to continue funding drone procurement, with the potential to produce up to two million drones by year’s end. Over 200 Ukrainian companies are developing drones, with nearly 60 already receiving government orders.
Ukraine’s Allies
European Council President Charles Michel emphasized the need for Europe to enhance defense capabilities in response to the Russian threat, urging a shift to a “war economy” mode. He highlighted the importance of EU support for Ukraine’s defense efforts.
EU foreign ministers agreed to provide an additional €5 billion ($5.5 billion) in defense aid for Ukraine in 2024 through the European Peace Facility (EPF), aiding Ukraine’s defense efforts against Russia. Despite previous disagreements among member states, the decision marks renewed support. The funds will be channeled through the Ukraine Assistance Fund. Hungary, typically resistant to such aid, did not oppose the decision this time. The move comes as U.S. aid to Ukraine remains stalled due to domestic political issues, emphasizing the importance of European support.
Ukraine is receiving continued military support from international partners. Bulgaria is contributing 100 armored personnel carriers from the 1960s and 1970s, with the first 30 already delivered. Germany’s Rheinmetall plans to establish four factories in Ukraine. Portugal pledged 100 million euros to support the Czech artillery ammunition initiative. Greece is in talks with the Czech Republic to sell and directly send various munitions to Ukraine, including rockets and howitzers. Additionally, leaders from Germany, France, and Poland have discussed increasing artillery ammunition supplies and providing long-range rocket systems to Ukraine.
U.S. Senator Lindsey Graham, in Kyiv, urged the Biden Administration to list Russia as a state sponsor of terrorism and called for enhanced military aid to Ukraine. He suggested reshaping aid as loans and linking it to U.S. domestic issues, like border security. Graham supported Ukraine’s NATO bid and hinted at advanced arms support, with President Zelensky stressing an urgent need for more military aid due to shortages. Despite opposing a large aid bill stalled in Congress, Graham’s fifth visit underscores his support for Ukraine’s defense and his denouncement of Putin as a war criminal.
Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal anticipates that EU accession talks could begin in the first half of 2024, following a European Commission draft framework. The European Council has agreed to start talks, considering 2030 as a target year for enlargement, though Ukraine hopes for an earlier entry post-victory. Shmyhal stresses Ukraine’s commitment to rapid reform implementation and expects formal steps towards accession talks to be approved by EU member states soon. He argues that Ukraine’s contributions to the EU in various sectors will outweigh the estimated financial costs of its accession, suggesting that the mutual benefits far exceed the expenses.
The Czech Republic is leading an initiative, which intriguingly involves allies of Russia, to supply Ukraine with much-needed artillery shells. The Czechs have found potential sources for these shells outside the EU, engaging nations in the Global South with surplus Soviet-era arms. So far, the initiative has secured purchases and commitments for half a million shells. Unlike similar Western efforts, the Czech approach has been successful due to discreet negotiations, with logistics arranged to keep suppliers’ identities hidden from Moscow. Confidential dealings are prioritized, with the first deliveries to Ukraine expected by June. This ammunition is vital for Ukraine, especially given the delays in U.S. military aid that have affected combat outcomes like the loss of Avdiivka.
U.S. National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan criticized the legitimacy of Vladimir Putin’s recent electoral win as president of Russia, declaring it neither free nor fair due to political suppression and the silencing of opposition. Putin, having won 87% of the vote, faced no serious competition, as potential rivals were barred or imprisoned, such as the deceased Alexei Navalny. Despite the flawed electoral process, Sullivan acknowledges Putin’s role as Russia’s leader, a reality the U.S. continues to engage with amidst ongoing conflicts. He made these remarks against the backdrop of Putin celebrating his win in Moscow, flanked by nominal competitors who supported him.
Josep Borrell, the EU’s high representative for foreign affairs, declared the election results from Russian-occupied Ukrainian territories invalid and warned of consequences for the organizers. The elections, extending Putin’s rule, were conducted in parts of Ukraine in defiance of international law, a move the EU, U.S., and Canada have condemned. The EU criticized the lack of genuine electoral choice and the oppressive context, highlighting the death of opposition figure Alexei Navalny as indicative of Russia’s repression. The absence of OSCE observers undermined the election’s credibility. The EU reaffirmed its support for Russian civil society, human rights activists, and independent media.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Since Russia’s illegal annexation of Crimea, the region has faced oppression, militarization, and efforts to change its ethnic makeup by resettling Russians and undermining Ukrainian and Crimean Tatar identities. These actions aim to integrate Crimea into Russia and assert control. Reports highlight systematic attempts to erase local languages, restrict freedoms, and suppress cultural rights. The occupation strategy used in Crimea is being replicated in other Ukrainian territories, indicating Putin’s broader goal of full Russian control over Ukraine. The ongoing occupation and aggression suggest a future of oppression and ethnic cleansing to maintain Russian dominance.
Russia News
Vladimir Putin celebrated an election victory and the decade-long annexation of Crimea with a Red Square rally, flanked by supportive “opponent” lawmakers. The election, ending March 17 with Putin receiving 87.28% of the vote, was internationally criticized as neither free nor fair. During the event, Putin extolled Crimea as a Russian pride, and his unchallenged “rivals” echoed this sentiment. He also mentioned the link of a railroad from Rostov-on-Don to occupied Berdiansk in Ukraine. The election, involving coerced participation in occupied Ukrainian territories, concluded with Putin reasserting his war aims and making veiled threats to the West, receiving acknowledgment from only a few authoritarian figures.
Putin acknowledged that Russian citizens, whom he labeled as “traitors,” are part of pro-Ukrainian volunteer forces engaging in raids into Russia’s Belgorod Oblast. He claimed these groups, likely including the Russian Volunteer Corps and others, have seen 800 of their estimated 2,500 members destroyed by Russian forces. These admissions come amidst ongoing cross-border conflicts, with Putin and Russian military bloggers advocating for harsh actions against these individuals. This situation has led the Russian Ministry of Defense to closely monitor and report on activities in the Belgorod direction, indicating a significant concern over the persistence and scale of these raids compared to previous, more limited incursions.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukrainian military intelligence spokesperson Andrii Yusov stated on national TV that with President Vladimir Putin’s re-election, Russia can now more visibly proceed with mobilization, a process that has been ongoing even during the electoral period. Previously, it was speculated that further mobilization would be delayed until post-election to avoid public unrest, similar to the discontent and emigration seen during the large-scale mobilization in fall 2022. Despite official claims of mobilization’s end in October 2022, reports indicate it has continued. Russia has been encouraging voluntary service and offering citizenship to foreign recruits. With the election hurdle cleared, Russia is expected to ramp up its mobilization efforts, potentially recruiting around 30,000 individuals monthly.
President Putin announced the formation of a veteran-led “Administrative Corps” under the “Time of Heroes” initiative, aiming to integrate Russian veterans into the workforce. In a post-election interview, he highlighted plans to offer higher education to veterans, preparing them for careers in sectors like medicine, defense, security, and government. This initiative appears to be a strategy to encourage military enlistment by offering compensation and benefits in return.
The Russian State Duma passed a bill’s second reading that would clear individuals of criminal charges if they agree to military service. This move, expected to be approved, aims to broaden recruitment by including civilians alongside the existing schemes targeting prisoners.
Russian company Kaysant has created a drone jamming system to protect armored vehicles from first-person vision drones. This lightweight, dome-type jammer, designed for vehicle installation, disrupts drone signals at 800 and 900 megahertz. Kaysant is expanding the technology to cover more frequencies and has started production, receiving orders from the Moscow government. Discussions are underway for mass deployment to the frontlines.
Russia’s Allies
South Korea’s Defense Minister Shin Won-sik disclosed that North Korea sent around 7,000 containers of ammunition and military equipment to Russia in 2023. In return, North Korea likely received over 9,000 containers of aid from Russia, including food, economic assistance, and help with military upgrades. This exchange indicates a significant military and economic partnership between the two nations.
China is set to receive a record amount of Russian oil in March, according to Bloomberg. Russia has become China’s top oil supplier, surpassing Saudi Arabia. However, payment issues have delayed oil trade with India due to Western sanctions. While some countries have banned Russian seaborne oil imports, China’s intake is unaffected. The U.S. has tightened restrictions on financial backers of Russia’s war, prompting caution among foreign banks.
Russian Narratives and Propaganda
Ten years after Russia’s illegal annexation of Crimea, initiated by covert military action and an illegitimate referendum, President Vladimir Putin continues to justify his aggressive stance towards Ukraine. Claiming to protect Crimeans and denying Ukraine’s statehood, Putin sets the stage for ongoing conflict, asserting cultural unity among Russians, Ukrainians, and Belarusians. On the 10th anniversary of the annexation, he defends his occupation of Ukrainian territories and aims for a prolonged war.
Russian President Putin is leveraging claims of high voter turnout and support in the recent presidential election to justify ongoing conflict and occupation in Ukraine. Official reports claim Putin won with 87.28% of the vote amidst a record turnout of 77.44%, with especially high support claimed in occupied Ukrainian territories. Critics argue these figures are likely inflated and the result of coercion, particularly in occupied areas where Russian military presence is strong. Putin asserts the election results reflect national unity and support for his actions in Ukraine, suggesting a mandate for continued military engagement and control over occupied regions, framing it as protection for these areas.
Putin countered French President Emmanuel Macron’s idea of sending Western troops to Ukraine by asserting NATO forces are already there, suggesting their presence in roles that include French and English speakers. He used this claim to reiterate warnings of potential full-scale conflict with NATO and to argue that Western support for Ukraine could lead to negotiations undermining Ukrainian sovereignty. Despite warnings of nuclear conflict for sending NATO troops, reports indicate France is considering forming a coalition for military support in Ukraine. This move, according to Putin, crosses a “red line,” although history shows Russia’s “red lines” have been crossed before without significant reaction, suggesting these threats may be more about deterring Western support than actual limits.
Putin floated the concept of a “sanitary zone” in Ukraine, aligning with Dmitry Medvedev’s calls for erasing Ukrainian statehood for Russian security. This zone, suggested in response to border incidents, would demilitarize areas to buffer against Ukrainian and Western arms. While avoiding specifics, Putin indicated such a zone would prevent Ukrainian military reach, effectively extending Russian control. This strategy subtly mirrors Medvedev’s harsher rhetoric, both rooted in the Kremlin’s broader objectives of undermining Ukrainian sovereignty under the guise of “peace” initiatives.
The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs accused Ukraine of a drone strike in Transnistria, Moldova, claims seen as part of Russia’s efforts to destabilize the region. Despite Moldova denying Ukraine’s involvement, Russia insists the attack aimed to create panic. Meanwhile, Moldovan and Ukrainian officials suggest the strike might be a Russian information operation to spread fear and justify hybrid activities in Moldova. The actual perpetrator remains unclear, but the nature and target of the strike suggest it aligns more with Russian interests in undermining Moldova’s stability.
Kremlin criticized Western leaders for not recognizing Putin’s election win, calling it rigged, and highlighted support from allies. The Russian Foreign Ministry labeled Germany’s dismissal of the election, especially in occupied Ukraine, as Russophobic. Russian military bloggers mocked Germany’s stance. Meanwhile, leaders from former Soviet states and authoritarian regimes friendly to Russia offered their congratulations to Putin, as reported by TASS.
Russian Ambassador to the US, Anatoly Antonov, restated Kremlin claims aiming to weaken Western backing for Ukraine, suggesting the US has lifted limits on arms supplies to Ukraine and is directly involved in the conflict. This narrative seeks to deter further military support for Ukraine.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
