Summary of the day: Russian forces escalated their military actions against Ukraine with the largest combined drone and missile strikes on Ukrainian energy infrastructure since the invasion’s start on March 21-22. These strikes aim to weaken Ukraine’s defense by exploiting air defense shortages and pressuring the energy grid. Meanwhile, Russia is preparing for continued offensives into Spring and a larger effort in Summer 2024, despite facing logistical challenges in executing large-scale operations. The Ukrainian military is adapting by prioritizing frontline rotations and addressing manpower needs in anticipation of future engagements. Amidst these developments, the Islamic State claimed responsibility for an attack in Moscow, and Russian advancements were noted on several fronts, highlighting a period of intensified conflict and strategic positioning.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Russian Plans of Conquest Beyond Ukraine
Russian officials have intensified claims depicting their conflict with Ukraine as a confrontation with the West, spurred by Western military aid to Ukraine. Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov initially stated that Russia is “at war,” attributing the conflict’s start to the West’s support for Ukraine, but later clarified that the status of Russia’s “special military operation” remains unchanged, suggesting a “de facto” war situation. Additionally, Russia’s UN Representative Vitaly Nebenzya claimed Russia has nearly “demilitarized” Ukraine, pointing to Ukraine’s dependence on Western weaponry, a stance previously echoed by Peskov.
Ilan Shor, a US-sanctioned Moldovan politician with pro-Kremlin views, is reportedly in Moscow to discuss plans for Moldova-Russia cooperation and the overthrow of Moldova’s pro-Western government. This visit, his second in two months, is seen as part of Russia’s broader strategy to destabilize Moldova. Shor has criticized Western influence in Moldova and announced his participation in an upcoming economic forum in St. Petersburg. His meetings in Russia, including one with a Russian Duma official, have coincided with rising tensions in Moldova, involving requests for Russian “protection” from Transnistria and Gagauzia. Shor is considered a key figure in the Kremlin’s influence operations in Moldova.
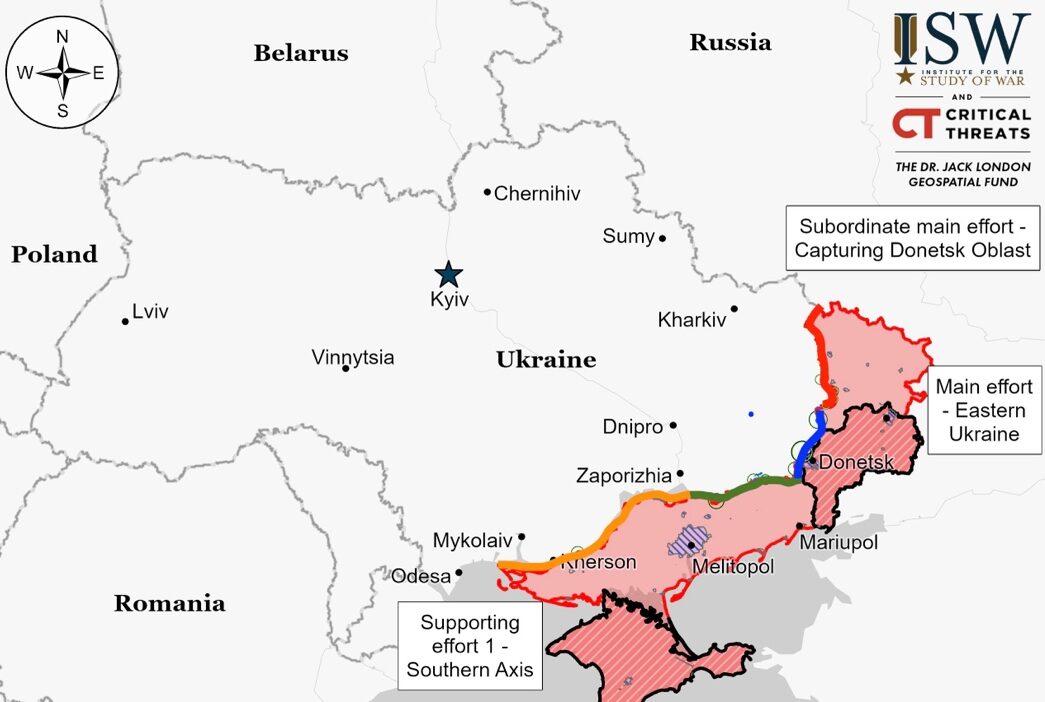
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
The General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces announced that Russian forces experienced 870 casualties in the past day.
Russian forces are expected to maintain their offensive in Ukraine through Spring and gear up for a larger effort in Summer 2024, despite facing challenges in staging wide-scale operations simultaneously across different fronts. Lieutenant General Oleksandr Pavlyuk noted Russia is currently focusing its efforts on Lyman, Bakhmut, and Avdiivka, employing significant troop numbers to keep the offensive momentum and disrupt Ukrainian defenses. Russia is gathering forces, with about 100,000 personnel along the Kharkiv-Luhansk axis and significant troop presences near Bakhmut, Avdiivka, and western Zaporizhia. These troops could replenish those losing combat strength, possibly assembling a large enough force for a single-direction offensive in the summer. However, Russia likely lacks the reserves for multiple, cohesive large-scale breakthroughs and has historically struggled with conducting simultaneous large-scale offensives.
Russian forces are capitalizing on Ukrainian equipment shortages, with an aim to deplete Ukraine’s incoming Western aid. Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister highlighted a current disadvantage in artillery, citing a seven-to-one Russian lead in ammunition, which is hampering Ukraine’s efforts to hold the front line. Delays in Western assistance is forcing Ukrainian tactical withdrawals. Despite challenging conditions, Russia plans to keep up its offensive to exploit these shortages before more Western support arrives. Anticipated Western security aid could alleviate immediate Ukrainian shortages, yet Russian strategies seem designed to continually drain Ukrainian resources, potentially undermining the effectiveness of Ukraine’s defense and future counteroffensives. The provision of consistent Western military support, especially in artillery ammunition, is crucial for Ukraine as it faces the expected Russian summer offensive and beyond.
The Ukrainian military is actively rotating frontline units to boost efficiency and manage personnel better. This reorganization includes regrouping and resting certain brigades to replenish their combat capabilities, a move suggesting some frontline stabilization. Ukraine aims to gain the upper hand in the conflict, but this requires a slowdown in Russia’s offensive. Russia currently sets the conflict’s pace, exploiting Ukrainian equipment shortages. Ukraine’s ability to contest this dynamic depends on resolving its manpower issues and the timely receipt of U.S. military assistance. Addressing these challenges is crucial for Ukraine to shift the strategic momentum in its favor.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces have made advances near Kreminna, with ongoing battles along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line. Confirmed movements show Russian gains east of Terny, with fighting reported in several areas, including near Kupyansk and Bilohorivka. The Russian 123rd Motorized Rifle Brigade is active near Bilohorivka. Despite the dynamic situation and daily assaults, especially in the Lyman direction, Ukrainian officials note that Russia has not been seen amassing extra troops beyond replacing losses.
Russian officials have indicated a desire to increase military personnel to enable an offensive to encircle Kharkiv City, avoiding a protracted siege like Mariupol. To support this, newly conscripted soldiers and reservists may be assigned to Russia’s southern border, releasing veteran troops for the operation. However, the ambition to encircle Kharkiv presents significant tactical challenges, as it requires extensive maneuvers over open terrain that Russian forces have not executed since the invasion’s onset. The plan involves redirecting combat-effective forces from other prioritized fronts, potentially weakening Russian positions there. Current intelligence does not suggest that Russian forces are actively preparing for such an encirclement.
Ukraine’s military intelligence spokesperson, Andrii Yusov, stated that actions by anti-Kremlin Russian militias inside Russia have disrupted Moscow’s potential attack plans in Ukraine’s north. These units, comprising Russian citizens, engaged in combat in Russia’s Belgorod and Kursk oblasts, leading to a reallocation of Russian troops. This incursion, which involved sabotaging Russian military equipment and capturing a U.S.-made Bradley Fighting Vehicle, has also reduced the pressure on Ukrainian forces in certain areas. Despite intensified Russian activity in the Kupiansk sector, Ukrainian intelligence suggests that Russia may lack the resources for a new large-scale offensive in the region.
Fighting persisted near Bakhmut with no frontline shifts reported. Claims of Russian force advances near Ivanivske have yet to be verified. Battles occurred in several directions around Bakhmut, including near Spirne, Bilohorivka, and other nearby locations.
Russian troops have recently made progress west of Avdiivka, as confirmed by geolocated footage showing advances within Tonenke. Ongoing battles have been reported around Avdiivka, including its northwest and southwest areas. A Ukrainian soldier noted the presence and tactics of Russian forces indicate a continued focus on offensive operations in the Avdiivka direction.
Russian troops made advancements southwest of Donetsk City, with recent footage showing progress in Novomykhailivka. Ongoing clashes were reported in areas west and southwest of Donetsk City, including near Krasnohorivka and Vodyane. Russian forces are active near Pobieda, indicating continued military actions in these regions.
Russian forces have made advancements in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, with movements detected west of Staromayorske. Ongoing engagements were reported southeast and south of Velyka Novosilka.
In western Zaporizhia Oblast, ongoing battles were reported without any confirmed shifts in the frontline. Claims of Russian advancements near Robotyne and Verbove were made, with continued fighting around these areas.
A Russian military blogger reported that Ukrainian forces continue to hold positions on the east bank of Kherson Oblast, specifically near Krynky and the Antonivsky bridge area.
Ukrainian Victims Of War
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the death of 4 people and injuries to at least 32 others:
- Search and rescue operations in Zaporizhzhia following a Russian missile attack have concluded. The attack resulted in three fatalities, including a child, and injured at least 29 people, with two children among the wounded. Among the deceased were a 35-year-old man and his eight-year-old daughter, victims of a strike on a residential area.
- A Russian drone strike targeted a bus in the Novhorod-Siverskyi district of Chernihiv Oblast injuring at least three people.
- Russian forces attacked the village of Zmiivka in Kherson Oblast’s Beryslav district, resulting in the death of a 57-year-old man.
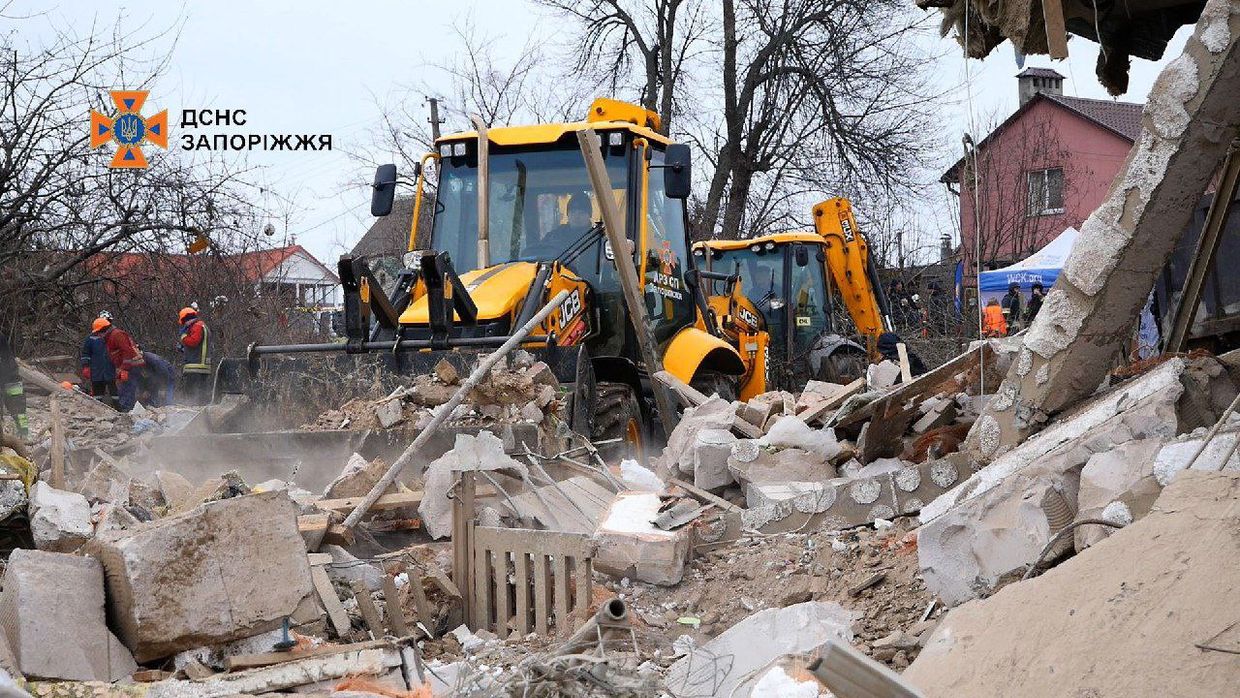 The aftermath of Russian attack against Zaporizhzhia
The aftermath of Russian attack against Zaporizhzhia
Ukraine News
Russian forces conducted their largest offensive against Ukraine’s energy infrastructure since the invasion began on March 21-22, targeting 136 facilities and causing significant damage. The coordinated attack with 151 drones and missiles, from which Ukraine shot down 92, was aimed at degrading Ukraine’s defense capacity and exploiting air defense shortages, particularly amid delayed Western security assistance. Despite the temporary outages in power and water supply, services were rapidly restored in many areas.
The eastern regions, especially Kharkiv, were heavily affected, leaving 700,000 residents without electricity, and outages were also substantial in Dnipropetrovsk, Odesa, and Poltava. Some areas remained powerless into the afternoon, and the Dnipro Hydroelectric Power Plant in Zaporizhzhia sustained critical damage, taking it offline with expected long-term repair needs. This large-scale campaign aims to not only cause physical damage but also erode confidence in the Ukrainian government, as indicated by misinformation campaigns about power shortages.
President Volodymyr Zelensky highlighted the urgency of international support for Ukraine’s air defense in response to the attacks, which resulted in casualties and extensive infrastructure damage. The attack included direct strikes on the Dnipro Hydroelectric Power Plant’s HPS-2 station, causing severe damage without immediate risk of a dam breach. The overall impact on Ukraine’s energy sector was significant, with one fatality reported, and it is part of an ongoing effort by Russia to destabilize Ukraine’s energy grid and undermine its resistance.
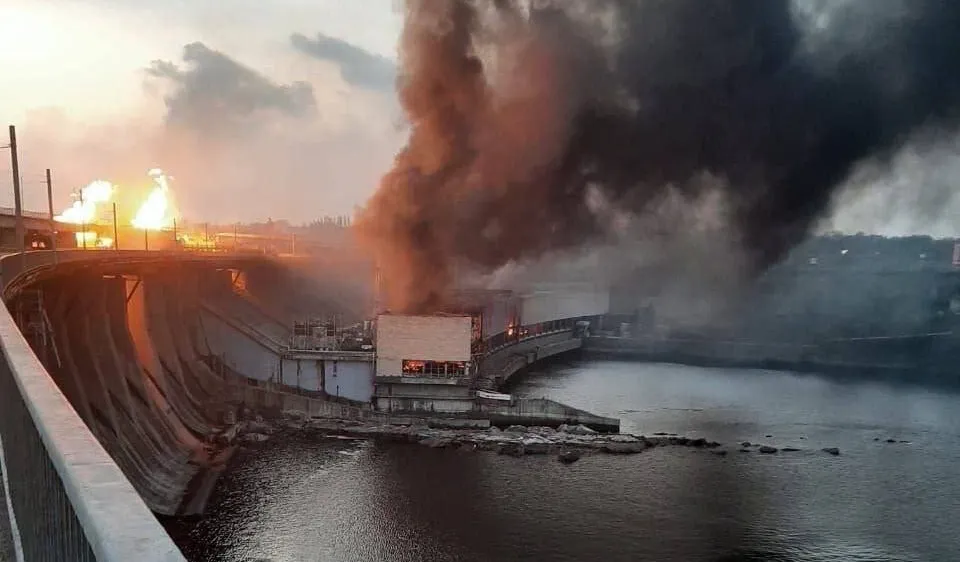 The aftermath of a Russian strike on the Dnipro Dam in Zaporizhzhia
The aftermath of a Russian strike on the Dnipro Dam in Zaporizhzhia
Ukraine’s Deputy Prime Minister Olha Stefanishyna, speaking at the Kyiv Security Forum, declared that strikes on Russian oil refineries, which Ukraine has been conducting, are militarily legitimate targets. This comes amid reports from the Financial Times about U.S. concerns regarding the attacks. The U.S. is allegedly wary of the strikes elevating global oil prices and provoking Russian retaliation, though the White House’s stance is not officially confirmed. The recent Ukrainian strikes on Russian oil facilities, which are deemed successful by Stefanishyna, align with NATO standards for engaging enemy infrastructure used for attacks. These actions are aimed at undermining Russia’s oil revenue, crucial for financing its invasion despite sanctions. The U.S. has expressed concerns about potential repercussions on the global oil market and political implications for President Biden’s re-election. Meanwhile, Ukraine continues to face Russian missile attacks and awaits a substantial U.S. aid package stalled in Congress. The situation presents a delicate balance for Kyiv between adhering to ally requests and ensuring national security.
Ukraine’s Allies
NATO’s focus has shifted back to collective security due to Russian aggression, as stated by Admiral Rob Bauer. Since Russia’s annexation of Crimea, NATO has been alert to the threat, moving away from crisis response to preparing for potential conflict. Bauer emphasized that in warfare, adversaries dictate the timing and duration of conflicts. He also pointed out that Russia’s actions against Ukraine were not driven by actual security threats from Ukraine or NATO but by broader aims against the alliance. Furthermore, Bauer praised Ukraine’s innovative use of naval drones against the Russian Black Sea Fleet and pondered the potential application of such drones in other maritime contexts, noting their increasing significance in modern warfare.
The White House strongly denounced Russia’s extensive overnight attacks on Ukrainian civilian areas, which resulted in at least five deaths and power outages affecting 1.5 million people. The U.S. National Security Council underscored the urgency of delivering more air defenses to Ukraine, pressing House Republicans to approve the security aid supplement without delay. Amidst the largest onslaught on Ukraine’s energy grid, the stalled $60 billion aid bill in Congress has heightened Ukraine’s need for air defense systems. Ukrainian Air Force data indicated a low interception rate for the missiles launched in the latest attacks. The strikes damaged the Dnipro Hydroelectric Power Plant, causing a fire, with officials confirming no risk of dam breach. Amid these developments, President Zelensky has called on the EU to utilize frozen Russian assets for Ukraine’s reconstruction and armament needs. The European Commission suggested using these assets to fund weapons for Kyiv, but consensus among EU leaders remains uncertain due to opposition from countries like Hungary.
The U.K. Defense Ministry announced that the first group of 10 Ukrainian pilots has graduated from flight school with training from Royal Air Force instructors. These pilots are part of Ukraine’s efforts to strengthen its Air Force with modern fighter jets, including the expected arrival of F-16s this summer from Denmark, the Netherlands, Norway, and Belgium. The training encompassed a range of flying skills and English language proficiency to enhance NATO interoperability. The U.K. Defense Secretary underscored the success of Ukraine’s Air Force and pledged continued allied support. The next phase will see the pilots advance to training on F-16 jets, with the first Ukrainian pilots set to complete a U.S.-led F-16 program by summer. Delivery of the jets from Denmark is subject to Ukrainian readiness.
The European Council has called for the EU to quickly begin accession talks with Ukraine and Moldova, following the European Commission’s recommendation to start negotiations with Kyiv. A draft framework for membership discussions was proposed on March 12. The Council praised both countries for their reform efforts towards EU integration and reiterated its commitment to supporting Ukraine across various sectors, urging other allies to do the same. Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal anticipates that accession negotiations could start in early 2024. European Council President Charles Michel expects the negotiating framework for Ukraine to be approved by the end of Belgium’s EU presidency on June 30.
The European Commission proposed implementing high tariffs on grain and oilseed imports from Russia and Belarus to shield the EU market and diminish Moscow’s revenue amid the conflict with Ukraine. The proposal, presented by Commission President Ursula von der Leyen during a Brussels summit, suggests a 95 euros ($103) per ton tariff on corn and wheat, and a 50% duty on oilseeds and related products. This move aims to reduce Russia’s financial gains from the EU, protect European farmers, and counteract the sale of Ukrainian grain misrepresented as Russian. The sanctions, which also target Belarus for its support of Russia, could take immediate effect upon approval by the EU Council.
The U.K. has pledged an additional 60 million pounds ($75.5 million) in military aid to Ukraine, focusing on new surveillance drones and air defense systems. This funding is part of the International Fund for Ukraine, aiming to enhance Ukraine’s defense capabilities.
Berlin has committed 300 million euros ($325 million) to a Czech-led initiative aimed at supplying Ukraine with hundreds of thousands of artillery shells, as reported by Bloomberg. This funding decision, detailed by Czech President Petr Pavel, is intended to address Ukraine’s urgent need for artillery shells amid ongoing conflicts and critical ammunition shortages.
The Netherlands will soon dispatch a significant amount of ammunition to Ukraine as part of a Czech-led effort aimed at providing Kyiv with hundreds of thousands of artillery shells, announced Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte
Czechia has completed its delivery of Soviet Mi-24 attack helicopters to Ukraine, with the final donation bringing the total supplied to eight, as reported by Czech media and confirmed by Defense Minister Jana Cernochova. This move is part of Czechia’s support for Ukraine amidst its conflict and comes as Czech military transitions to newer U.S. helicopter models. The specifics of the remaining helicopters, out of the original 17 operated by Czechia, were not disclosed. This gesture marks the end of Czech military equipment donations to Ukraine, as stated by Cernochova, citing depletion of surplus stock.
The European Council has imposed sanctions on 33 individuals and two entities related to the death of former Russian opposition leader Alexei Navalny. EU’s top diplomat Josep Borrell emphasized the sanctions as a response to Navalny’s “slow killing” by the Kremlin, highlighting the EU’s commitment to human rights accountability in Russia. The sanctions target key figures and facilities involved in Navalny’s detention, including the heads of the penal colonies where he was held and suffered abuses, and members of the Russian judiciary responsible for rulings against him. These measures reflect the EU’s support for Russian civil society and condemnation of political repression. The cause of Navalny’s death, whether due to harsh prison conditions or deliberate action, remains uncertain.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Ukraine successfully repatriated nine children from occupied territories and Russia, including four from Crimea, with assistance from Qatari mediation. This effort highlights ongoing attempts to bring back citizens to Ukrainian-controlled areas.
The UN reported on March 19 about ongoing Russian human rights violations in Ukraine from February 2022 to December 2023, based on over 2,300 interviews. The findings highlight forced Russification efforts, including language changes and legal system overhauls, while suppressing Ukrainian identity. The UN High Commissioner for Human Rights called for international support for Ukraine’s future reparations and accountability measures post-occupation.
Russia is advancing infrastructure projects to further integrate occupied Ukrainian territories and improve military supply routes. Deputy Prime Minister Marat Khusnullin announced plans for a new expressway linking Krasnodar, Temryuk, and the Kerch Strait Bridge, and the “Azov Ring” road connecting Crimea with Rostov Oblast and Krasnodar Krai in 2024. President Vladimir Putin highlighted the restoration of the railway from Rostov-on-Don to Donetsk City, Mariupol, and Berdyansk, and plans for a new rail link to Sevastopol, offering an alternate route to the Kerch Strait Bridge. These developments are expected to be complete by the end of 2024.
Russia News
A fire erupted at the Kiubyshev oil refinery in Samara Oblast, Russia, with local reports and Russian media suggesting a drone strike might be the cause. This incident aligns with recent Ukrainian attacks on Russian oil facilities. While Russian officials have not yet issued statements on this latest incident, Ukraine has acknowledged targeting such sites.
Russian officials reported that Ukrainian forces launched rockets at Belgorod city and its vicinity, resulting in one fatality and two injuries. The claims, made by Russia’s Defense Ministry and Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov, have not been verified and Ukraine typically does not respond to allegations of attacks on Russian territory. The incident in Belgorod, which lies adjacent to several Ukrainian oblasts, coincides with frequent reports of rocket or drone strikes in the area and recent anti-Kremlin militia activities. Russia also conducted a widespread assault on Ukraine that day, targeting its infrastructure and other sites.
Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov, in a notable departure from official terminology, referred to Russia’s actions in Ukraine as being in a “state of war” during an interview with a Russian state media outlet. He maintained that the aim was to protect residents in annexed Ukrainian territories and labeled Ukraine an “occupying force.” Peskov later qualified his statement, differentiating between the legal status of a “military operation” and the factual situation of war. Russia persistently calls its actions a “special military operation,” a narrative enforced by strict domestic laws that penalize referring to the conflict as a war or invasion. Peskov also reiterated Russia’s stance against a Ukraine that claims Crimea, which is recognized internationally as Ukrainian territory.
The Islamic State claimed responsibility for a mass shooting and bombing at a Moscow concert venue, which left at least 60 dead and more than 140 injured. Attackers in camouflage with automatic weapons and explosives targeted the crowded Crocus City Hall, causing a fire and structural collapse. Russian forces and emergency services responded to the incident, detaining one person, with the investigation ongoing. US officials have corroborated the IS claim, noting previous warnings of potential terrorist activities. In response, Russia heightened security nationwide and condemned the attacks, with unfounded speculation by Russian figures implicating Ukraine. However, Ukrainian officials and the US National Security Council have categorically denied any Ukrainian involvement.
India has reduced its imports of Russian crude oil, aligning with US sanctions and the G7 oil price cap, affecting Russia’s ability to bypass these restrictions. Indian oil refineries are rejecting Russian oil delivered by Sovcomflot tankers, which are under US sanctions and represent a significant portion of Russia’s oil exports to India. Additionally, scrutiny on tanker origins has increased, with some tankers carrying Russian oil remaining idle off India’s coast. India’s distancing from Russian oil, influenced by the conflict in Ukraine, supports international efforts to limit Russia’s oil revenue.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russia, facing a significant decline in voluntary military enlistments, is looking to bolster its forces by potentially adding 300,000 personnel, focusing on reservists and considering extended service periods for conscripts. This push for increased manpower comes as Moscow sees a drastic drop in daily recruitment numbers and may consider alternatives, including drafting convicts and migrants, to sustain its offensive operations in Ukraine. Concerns rise about the possibility of another large-scale mobilization, which strategists fear could lead to domestic unrest and negatively impact morale within the ranks.
Simultaneously, Ukraine’s military leadership, under Commander Oleksandr Pavlyuk, has identified Russian efforts to amass a large military force, which could indicate plans for an early summer offensive. Ukrainian forces, contending with ammunition shortages and delays in receiving U.S. aid, have withdrawn from strategic positions in Donetsk and continue to face intense battles in Kherson, Kharkiv, and Zaporizhzhia. Despite these challenges, Ukraine remains resolute in defending its sovereignty and civilian infrastructure against ongoing Russian aggression.
The Moscow military registration and enlistment office has started issuing electronic summonses for the Spring 2024 conscription cycle via SMS, marking a move towards digitizing the conscription process. This initiative, confirmed by Russian opposition sources and a movement of conscientious objectors, aims to streamline and modernize the handling of conscripts’ personnel files. Russian officials have acknowledged this new approach as part of a test phase during the upcoming conscription period.
Russia’s Allies
Belarus is suspected of building a storage site for Russian tactical nuclear weapons, indicated by satellite images showing upgrades to a military depot near Asipovichy. These enhancements, observed between February 2023 and January 2024, include a quadruple-fence perimeter and secured access, similar to Russian nuclear storage protections.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
