Summary of the day: Today’s developments saw significant geopolitical maneuvers and military actions. Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov met with Chinese officials in Beijing, emphasizing a joint effort to counteract Western containment strategies towards Russia and China. In a notable operation, the US CENTCOM transferred arms and ammunition seized from Iran to Ukraine, bolstering Ukrainian defense capabilities. Furthermore, Ukraine’s Main Military Intelligence Directorate conducted a drone strike on the Borisoglebsk Airbase in Russia, marking a tactical offensive move. On the ground, Russian forces made confirmed advancements in the conflict zones near Kreminna, west of Avdiivka, and around Donetsk City. Amidst these military actions, internal policies in Russia aim to reinforce Kremlin ideologies among the youth and tighten its grip on regions like Crimea and Armenia, highlighting a complex mix of international diplomacy, strategic military operations, and domestic policy shifts.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War
EU’s chief diplomat, Josep Borrell, warns of the increasing risk of a full-scale conflict in Europe, urging for more defense funds as the situation with Russia escalates. Borrell highlights the misuse of economic ties, cyber threats, and disinformation by adversaries, noting a conventional war in Europe is now a plausible scenario. He stresses the EU must become self-reliant in defense, hinting at the unpredictability of US support. Amid these concerns, US aid to Ukraine faces delays in Congress, with European leaders echoing the urgency of bolstering defense capabilities and supporting Ukraine to counteract Russian aggression. European Council President Charles Michel also underscores the necessity for the EU to assume responsibility for its security amidst this “existential crisis.”
The Kremlin is positioned to use a financial agreement between the pro-Russian leadership of Moldova’s Gagauzia region and a Russian state-owned bank to undermine Moldova’s democracy and EU aspirations. The deal involves opening bank accounts for thousands in Gagauzia, offering cards for a sanctioned Russian payment system. Despite legal and operational challenges, including Moldovan laws limiting such international agreements and the incompatibility of the Russian payment system in Moldova outside of Transnistria, the agreement aims to bolster pro-Russian sentiment in Gagauzia. This move is part of a broader strategy to portray Russia as a benefactor to Gagauzia, potentially influencing Moldovan politics and elections. The situation could escalate tensions within Moldova, as the legality and implementation of the deal are contested, possibly serving Kremlin objectives either way.
Russian military authorities detained a Russian citizen in Armenia for desertion, an action viewed as a challenge to Armenian sovereignty. This detention, carried out by military police at Russia’s 102nd Military Base in Gyumri, Armenia, marks another incident straining Armenian-Russian relations. The human rights group Helsinki Citizens’ Assembly reported the detention and criticized the legality of Russian law enforcement operating in Armenia, urging that such matters be handled by Armenian authorities. The Armenian Prosecutor General’s Office is looking into the report. This situation underscores ongoing tensions and the delicate balance of power between Russia and Armenia, with Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan previously stating Armenia will not tolerate illegal actions by foreign forces on its soil.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
The Russian Ministry of Defense reported that their air defense systems intercepted a Ukrainian Neptune anti-ship missile over the Black Sea near Crimea.
Ukraine is increasingly using first-person-view (FPV) drones to counter Russian tanks amid an ammunition shortage, destroying over two-thirds of them recently. These drones are inexpensive yet capable of taking down costlier military hardware. With a production spike to 50,000 units in December 2023, Ukraine plans further scale-up despite facing challenges like operational inefficiency in poor visibility and unreliable homemade explosives. Despite these drones’ less than 50% accuracy rate, their strategic use has pressured Russia’s armored vehicle reserves, contributing to significant Russian losses. Additionally, Ukraine employs innovative tactics like acoustic detection networks and rigged sensors to counter enemy drones, achieving notable success despite weapon limitations.
Russian troops in Ukraine are reportedly using Starlink internet terminals acquired through indirect channels, despite SpaceX’s policy against military use and the lack of official sales to Russia. While Elon Musk has denied enabling Starlink access in Russia, devices are being bought on online platforms and smuggled into Russian-controlled areas. Despite measures like geofencing, Russians are using roaming features to bypass restrictions. The U.S. is collaborating with Ukraine and SpaceX to halt Russian use of Starlink in the conflict. The terminals have also been found with a Sudanese group linked to the Russian Wagner Group. SpaceX provided terminals to Ukraine after the invasion, but Musk has resisted requests to activate the service in areas like Crimea to avoid escalation of the war.
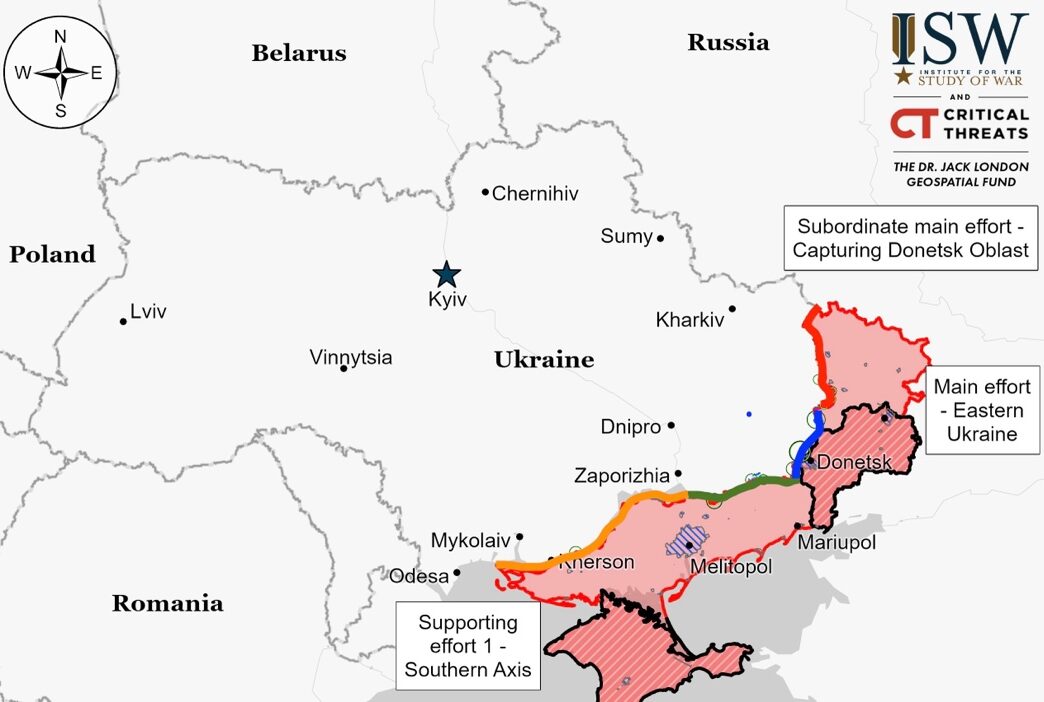
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces made slight advancements near Kreminna, securing marginal positions in the chalk quarry area south of Bilohorivka, according to recent geolocated footage and milblogger reports. Despite these gains, Russian troops faced setbacks near Terny due to Ukrainian counterattacks. Meanwhile, the Ukrainian General Staff noted Russia’s failed attempts to advance in other areas, including southeast of Kupyansk and west of Svatove.
The battlefront near Bakhmut saw ongoing positional fighting without clear shifts in control. Russian claims of capturing Bohdanivka and advancing toward Kalynivka are unverified, with reports of continued Ukrainian presence in the area. Additionally, Russian forces are said to have made advancements south and southeast of Chasiv Yar, but these claims lack visual proof. Ukrainian forces report heavy Russian infantry assaults in the region, with both sides deploying significant military resources, including airborne and motorized rifle divisions. The situation reflects intense, but largely static, combat dynamics around Bakhmut, with specific movements and territorial gains still subject to confirmation.
Russian forces are intensifying their use of heavy glide bomb strikes and missile attacks on Ukrainian defenses around Chasiv Yar, aiming to replicate their successful tactics from the capture of Avdiivka. Reports indicate that Russian Su-25 aircraft are employing FAB-250 guided glide bombs and S-8 and S-13 missiles to weaken Ukrainian fortifications and support ground assault operations by the 98th VDV Division. Videos of these airstrikes, showcasing both fixed-wing aircraft bombing runs close to Russian infantry and rotary-wing strikes near Bakhmut, have been widely shared, highlighting a significant escalation in aerial assaults in the region.
Russian forces, having advanced west of Avdiivka, seem to have taken control of Pervomaiske, southwest of Avdiivka, indicated by footage of Russian soldiers raising a flag, yet the full capture of the village remains in question. Reports of Russian advances also come from northeast of Netaylove and other strategic areas near Avdiivka. Ukrainian soldiers describe the enemy employing small-group infantry tactics complemented by heavy glide bomb strikes, suggesting a focused Russian military effort in the region, even in the absence of mechanized attacks in certain zones. These developments, including the possible capture of Pervomaiske, underscore Russia’s territorial ambitions in a crucial area of the conflict. Amidst these offensives, Ukrainian forces withstand severe strains from Russian artillery, drone operations, and infantry assaults, compounded by a critical ammunition shortage and delayed U.S. aid, representing the profound challenges Ukraine faces in sustaining its defensive stand against an aggressive Russian onslaught.
Russian forces made temporary gains west and southwest of Donetsk City, engaging in mechanized assaults. Despite an initial advance in Krasnohorivka, Ukrainian forces managed to counterattack successfully, regaining lost positions and destroying Russian military equipment. Further advances by Russian forces were reported in Novomykhailivka, where Ukrainian troops have also been effective, destroying a significant number of Russian vehicles, including tanks and combat vehicles. The situation remains dynamic, with ongoing engagements in areas around Donetsk City, demonstrating the fluid nature of frontlines in this region.
In the Donetsk–Zaporizhia Oblast border area, there were limited engagements without any shifts in the frontline. Ukrainian forces reported ongoing clashes near Urozhaine and Staromayorske, south of Velyka Novosilka. Russian forces carried out glide bomb strikes near Vuhledar. Additionally, Russian forces are active near Pryyutne, southwest of Velyka Novosilka, indicating continued military activity without significant territorial changes.
In western Donetsk Oblast, ongoing positional battles were reported with no changes to the frontline. The engagements occurred near Robotyne, Mala Tokmachka, and northwest of Verbove.
Ukrainian forces maintain control over the village of Robotyne in Zaporizhzhia Oblast, countering claims of a Russian breakthrough. Despite intensified fighting and attempts by Russian forces to establish a presence in Robotyne, located strategically near the front lines and key logistics routes to occupied areas, Ukrainian troops successfully repelled these attempts. The situation, while challenging due to increased hostilities and ammunition shortages, remains stable.
Ongoing positional battles took place on the east bank of Kherson Oblast, including areas near Krynky, with no changes reported in the frontline positions.
Ukrainian Victims Of War
The casualty toll from a Russian missile strike on Poltava Oblast on April 8 has increased to 16 injured, including four children, with one fatality previously reported. The attack damaged residential buildings, leading to hospitalizations, including one person in serious condition. Over 9,000 homes and 120 businesses experienced power outages, although electricity has been largely restored except in the damaged building.
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the death of at least 2 people and the injuries of at least 7 others:
- A civilian enterprise in downtown Kharkiv was hit by Russian guided aerial bombs injuring at least three workers, amid intensified attacks on Ukraine’s second-largest city. The strike caused significant damage and fires, with ongoing rescue efforts to locate potential survivors trapped in the rubble.
- Russian shelling on the outskirts of Sloviansk in Donetsk Oblast injured three individuals. The victims, aged 53, 64, and 66, received onsite medical aid and chose not to be hospitalized.
- A woman was killed in Semenivka, Chernihiv Oblast, due to a Russian artillery and rocket attack.
- In Kostiantynivka, Donetsk Oblast, a Russian air strike resulted in at least one civilian death and two injuries. The attack caused a house to collapse, potentially trapping a woman and child in the debris. Rescue efforts are currently suspended due to the risk of another strike. The assault also damaged numerous residential and infrastructure buildings.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched multiple missile and drone strikes across Ukraine on April 8 and 9, targeting industrial and energy facilities as well as civilian infrastructure. In Zaporizhzhia City, an industrial site was hit by a missile, which Russia claims was aimed at a drone workshop. Overnight, Ukraine intercepted 20 Shahed drones and four S-300 missiles from Russian launch sites, successfully downing them across several regions, though Russian drones still damaged critical infrastructure in the south. Additionally, missile attacks damaged civilian areas in Poltava, Donetsk, and Kharkiv oblasts, including strikes on Druzhkivka and Kostyantynivka, as well as civilian enterprises near Kharkiv. On April 9, a missile likely targeted Odesa Oblast’s coastal area.
The Ukrainian Prosecutor General’s Office is conducting 27 criminal investigations into the execution of at least 54 Ukrainian POWs by Russian forces, as stated by Yurii Belousov, head of the War Crimes Department. Recent incidents in Zaporizhzhia and Donetsk, including a video from Kherson showing Russian troops killing unarmed Ukrainian soldiers, have prompted these investigations. The involvement of Russian military and political leadership is also under scrutiny, with evidence of systematic policy rather than isolated events. Over 128,000 victims of war crimes have been documented in Ukraine to date.
Ukraine’s Allies
On April 4, the U.S. delivered to Ukraine a large shipment of arms and ammunition, including over 5,000 firearms such as AK-47s, and 500,000 rounds of ammunition, which were seized from Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) in December 2023 as part of a civil forfeiture by the Department of Justice. This assistance is in continuation of U.S. support, adding to over a million rounds already sent by October 2023. The cache, intercepted from 2021 to 2023 and originally destined for Yemen’s Houthis, now aids Ukraine’s defense against Russian aggression. CENTCOM’s action emphasizes the U.S. commitment to disrupting Iran’s destabilizing military support, while also indicating the strengthening military ties between Iran and Russia, particularly through Iran’s supply of drones and missiles for Russian use in Ukraine.
The U.S. State Department has sanctioned a $138 million military sales package for Ukraine to support essential repairs and acquire spare parts for Hawk missile systems. This action aims to boost Ukraine’s defense against Russian aerial attacks, safeguarding its populace and vital infrastructure. The Hawk missile, effective against low-to-medium-altitude threats, is a key component of Ukraine’s air defense. Amid Congressional delays on a larger aid package, this sale underscores ongoing U.S. efforts to assist Ukraine, with Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin highlighting the conflict’s significance for global security. The work on the Hawk systems will be carried out by RTX Corporation and PROJECTXYZ.
Germany has tasked Rheinmetall with supplying Ukraine with 20 more Marder armored vehicles, slated for delivery in 2024. This follows the company’s previous provision of over 100 such vehicles since the conflict’s escalation. Alongside Poland, Germany is initiating an “armored vehicles coalition” to bolster Ukraine’s military strength, with the U.K., Italy, and Sweden joining. Germany’s recent support package includes various armored vehicles, tank ammunition, artillery shells, and anti-tank weapons, marking it as one of Ukraine’s top military benefactors with contributions totaling around 17.7 billion euros.
On the 120th anniversary of the Entente Cordiale, U.K. Prime Minister Rishi Sunak and French President Emmanuel Macron discussed bolstering Ukraine’s defense against Russia. They agreed on escalating support through munitions, drones, and air defense systems. Both leaders plan to address Ukraine’s needs at the upcoming U.K.-hosted European Political Community meeting. Their conversation also covered cooperation on issues like AI, tackling illegal migration, organized crime, and reaffirming support for Moldova’s sovereignty. France’s recent military aid to Ukraine included Aster 30 missiles and armored vehicles, while the U.K. committed an additional £60 million for surveillance drones and air defense for Ukraine.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Ukraine has denied any involvement in attacks on the Russian-occupied Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP), labeling the accusations as Russian provocations, following Russia’s allegations of Ukrainian drone attacks on the facility. Energoatom, Ukraine’s nuclear operator, suggests these claims might be obscuring either a mishap by Russian staff or clandestine Russian intentions for the ZNPP. In the wake of these growing claims and counterclaims, Russia has called for a meeting of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Board of Governors on April 11 to deliberate on the issue, while also dispatching a high-ranking official to inspect the plant amid the dispute. Earlier in March, the IAEA had resolved that Russia should exit the plant, and Energoatom has urged compliance with this resolution to ensure the plant’s safety. Since March 2022, the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant has been under Russian control and subject to IAEA oversight since September 2022, experiencing multiple disruptions due to the ongoing conflict.
In occupied Crimea, Russian authorities are targeting the Orthodox Church of Ukraine (OCU), notably dismantling the dome of the OCU’s Cathedral in Simferopol on April 8. Since Russia’s initial occupation of Crimea in 2014, OCU presence has significantly declined, with the number of religious communities dropping from 49 to just seven. Russian forces have also forcibly mobilized OCU clergy for military service. This persecution aligns with Russia’s broader policy against religious minorities perceived as dissenting from the Kremlin-aligned Russian Orthodox Church.
Following the March 22 Moscow terror attack, Russian authorities in occupied Ukraine are intensifying actions against migrants, possibly exploiting the event to justify crackdowns. In Mariupol, 20 migrants were detained for not adhering to entry and work documentation rules, with plans to deport eight. Migrant workers, crucial for rebuilding infrastructure damaged by conflict, are now facing increased policing by Russian law enforcement, reflecting a broader strategy to target communities deemed susceptible to extremism.
Russian authorities in occupied Ukraine are intensifying Russification efforts, including replacing Ukrainian road signs with Russian ones and removing Ukrainian satellite dishes to limit access to Ukrainian news. In Kherson Oblast, plans are underway to replace 80 Ukrainian-language road signs by the end of 2024. In Luhansk Oblast, the removal of Ukrainian satellite dishes is part of a strategy to control the information space, with replacements likely to broadcast Russian propaganda. These actions are part of a broader effort to erase Ukrainian language and culture in occupied areas.
Save Ukraine, a Ukrainian NGO, recently rescued two children from Russian-occupied areas, including an orphan who had been living with his grandmother under harsh conditions. The ongoing conflict has resulted in approximately 1,800 children becoming orphans, with their safety and family connections severely compromised. The NGO has successfully returned 284 children to Ukraine-controlled territory since the invasion began, although the Children of War database reports that out of at least 19,500 children abducted by Russia, less than 400 have been returned.
Russia News
The Ukrainian intelligence (GUR) likely conducted a drone strike on the Borisoglebsk Airbase in Russia, damaging its facilities. This airbase is known for training Russian bomber and attack aviation crews. Two drones reportedly hit the base, with visual evidence supporting at least one strike. Russian sources confirm the attack but describe minimal external damage. The exact extent of the damage remains unconfirmed.
Ukraine’s drones targeted a Russian aviation training center in Voronezh, damaging a workshop. The attack, by Ukraine’s intelligence, involved two drones; Russia claims one was downed. Both struck the same building, causing significant damage.
The Russian missile ship Serpukhov sustained severe fire damage that will complicate repairs due to sanctions, according to Ukraine’s Navy. Communication and automation systems on board were notably destroyed. The attack, attributed to Ukrainian operatives, marked a first against Russian naval assets in the Baltic Sea. With the ship requiring extensive repairs, its redeployment to the Black Sea, potentially to offset Russian losses there, is uncertain. Meanwhile, Ukraine has been actively targeting Russian naval forces in Crimea. Separately, a Russian ice navigation vessel caught fire in Vladivostok, resulting in casualties and an ongoing investigation into the incident.
Russian ultranationalist bloggers have intensified their anti-migrant rhetoric, criticizing support for Uzbek cultural efforts in Leningrad Oblast and decrying a “migration catastrophe” allegedly brought on by Central Asian migrants. This xenophobic discourse highlights a broader inconsistency in their stance on “indigenous Russians,” often ignoring or discriminating against Russia’s own ethnic minority communities. For instance, ethnic groups such as the Tuvans face criticism for promoting their cultural identity, while regions with significant indigenous populations disproportionately contribute troops for the conflict in Ukraine, exacerbating ethnic tensions. The Kremlin, needing to maintain support among ultranationalists while also depending on migrants and ethnic minorities for military and economic needs, finds itself in a complex bind, reflecting the ongoing struggle within Russia to balance nationalist sentiments with practical dependencies on diverse ethnic groups.
Russia is planning to establish a new ministry focused on youth policy and patriotic education, aiming to strengthen pro-Kremlin ideology among young Russians. This initiative will reorganize existing structures, including transferring certain responsibilities from the Ministry of Education to the newly proposed ministry, which will evolve from the Russian Federal Agency of Youth Affairs. Additionally, there’s consideration to merge the Ministry of Science and Higher Education with the Ministry of Education to further align educational efforts with patriotic indoctrination. Funding for patriotic education has significantly increased, quadrupling in 2023 to support youth programs that promote militarized and pro-Russian sentiments. This move is seen as an effort to secure the allegiance of future generations to the Kremlin’s goals amidst ongoing tensions with the West and the prolonged conflict in Ukraine.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Kremlin officials are actively reassuring the public that there will not be another wave of partial mobilization in May 2024. Andrei Kartapolov, chair of the Russian State Duma Defense Committee, stated that the time for mobilization call-ups has passed and current recruitment methods are meeting needs, with ongoing schemes bringing in 20,000–30,000 troops monthly. This statement counters rumors of impending mobilization circulated by a Russian military blogger. Russia’s strategy seems to effectively compensate for manpower losses without resorting to formal mobilization.
Russian forces are adapting their tanks with large metal sheets to shield against Ukrainian drone attacks. Dubbed “turtle tanks,” these modified tanks were seen during a mechanized assault near Krasnohorivka, Donetsk Oblast. Initially identified as T-72 tanks, the adaptations include welding mine trawls to the body. However, this additional armor compromises the tank’s mobility and turret movement, potentially affecting its effectiveness in combat.
Moscow reportedly avoids acknowledging soldier deaths in Ukraine to dodge compensation payouts, revealed by a Russian serviceman’s intercepted call by Ukraine’s Military Intelligence. The Kremlin’s avoidance tactic includes listing soldiers as missing rather than deceased, complicating compensation claims. Despite Putin’s promise of substantial compensation for families of fallen soldiers, dissatisfaction grows within Russian ranks over unrealistic military expectations and the strain of extended service without leave. Some soldiers seek ways to avoid further frontline deployment, amid broader concerns of forced conscription among civilians.
International sanctions may be impacting Russia’s ability to produce the Kh-101 long-range cruise missile, suggests a U.K. Defense Ministry intelligence report. Russia has ramped up attacks on Ukrainian energy infrastructure using various missiles and drones, with the Kh-101 known for its 4,000-kilometer range. A recent malfunction in Saratov Oblast indicates production difficulties, potentially exacerbated by sanctions. Ukrainian intelligence predicts Russia might switch back to using Kalibr cruise missiles due to a dwindling Kh-101 stockpile. Meanwhile, Russian assaults continue to target and significantly damage Ukraine’s energy facilities.
Russia’s Allies
In Beijing, Russian and Chinese officials, including Minister Sergei Lavrov and President Xi Jinping, discussed reinforcing their alliance against Western containment strategies. They emphasized forming a broad front against Western dominance and creating a multipolar world order, including anti-terrorism efforts and future consultations, but avoided public mention of military support for Russia’s Ukraine operations. Discussions also covered the Ukraine conflict, criticizing the exclusion of Russia from international efforts and considering China’s peace proposal. Meanwhile, Lavrov’s visit to Beijing signaled a deepening Russia-China economic support amidst the war, despite Western apprehension. Both Lavrov and Wang Yi resisted “hegemonism” and supported a multipolar world, resisting bloc confrontations. Lavrov’s meeting with Xi endorsed the ongoing partnership between their nations. Reports suggest a forthcoming meeting in China between Putin and Xi in May.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
The Kremlin is falsely implicating Ukraine in terrorist activities to tarnish its government and military, aiming to weaken international support for Ukraine. Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov suggested Ukrainian “provocations” against the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP) as a pretext for allowing International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) inspections. Additionally, Alexei Polishchuk from the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs emphasized that Russia will not ignore alleged Ukrainian terror acts since 2022, demanding extradition of those supposedly involved. This stance continues Russia’s strategy of discrediting Ukraine on the international stage.
After failing to prevent the March 22 terrorist attack at Crocus City Hall, Russian officials are blaming senior US and NATO officials for allegedly funding terrorism, without specifying the incidents. This claim suggests a diversion from internal security lapses. Independent analysis supports that the Islamic State was behind the attack, with no evidence linking Western officials to such activities. Russian counterterrorism efforts in Dagestan and actions against Central Asian migrants in Russia indicate a focus on threats from within its own borders, particularly from Muslim minority communities, rather than external influences from Ukraine or the West.
Russian intelligence is falsely alleging that the US is recruiting Mexican and Colombian prisoners to fight for Ukraine, aiming to discredit US military support for Ukraine. This claim suggests a strategy to undermine the legitimacy of US assistance by portraying it as reliant on foreign mercenaries.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
