Summary of the day: The International Criminal Court and European Court of Human Rights announced decisions confirming Russia’s long-term war crimes and human rights violations in Ukraine. Ukrainian forces conducted a drone strike on a Russian ammunition depot in Voronezh Oblast and struck Pantsir-S1 air defense systems in Belgorod Oblast. Russia imposed countersanctions against 81 EU-based news outlets following EU sanctions on Russian state-affiliated media. In troop movements, Ukrainian forces regained lost positions in Vovchansk, while Russian forces advanced near Siversk and Avdiivka. The Dagestan Republic Head ordered investigations into senior officials’ records following recent terrorist attacks, suggesting intensified efforts to address extremist threats in the North Caucasus.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War
On June 11, Russia and Venezuela signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to counter “coercive measures,” likely aimed at demonstrating Russian influence in the Western hemisphere. The MOU, signed by Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov and Venezuelan Foreign Minister Yvan Gil during the BRICS summit, intends to develop a joint strategy against “unilateral coercive measures” through informational and diplomatic means. Both countries provided limited details about the MOU, with Venezuela briefly announcing it on social media before deleting the post, and Russia delaying its announcement until June 25. This agreement follows recent Russian naval activities near Cuba and aligns with the Kremlin’s interest in expanding cooperation with Venezuela, potentially supporting Russian narratives about a new multipolar world order.
The European Union officially began accession negotiations for Ukraine and Moldova. Additionally, the EU Council approved a draft for a joint EU-Ukraine security agreement, as announced by Belgian Foreign Minister Hadja Lahbib.
Armenian Foreign Minister Ararat Mirzoyan met with Belarusian opposition leader Svitlana Tsikhanouskaya in Vilnius on June 20, amid worsening Armenian-Belarusian relations. They discussed cooperation between Belarus’ democratic forces and Armenia’s government. This public meeting indicates Armenian dissatisfaction with Belarus, following accusations that Belarus helped Azerbaijan prepare for the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War. Recent reports suggest Belarus provided Azerbaijan with military equipment used against Armenia between 2018 and 2022.
Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov met with Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko and other officials in Minsk to discuss Union State integration and cooperation. They have created 28 programs and identified 31 priority areas. Lavrov criticized the UN and OSCE, and announced that Belarus will become a full member of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization at the July 2024 summit.
Belarusian President Lukashenko met with a Chinese official in Minsk to discuss cooperation in education, technology, biotechnology, chemical industry, and drone manufacturing. They plan to establish a joint center for fundamental research.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Kharkiv Front – Initiative None
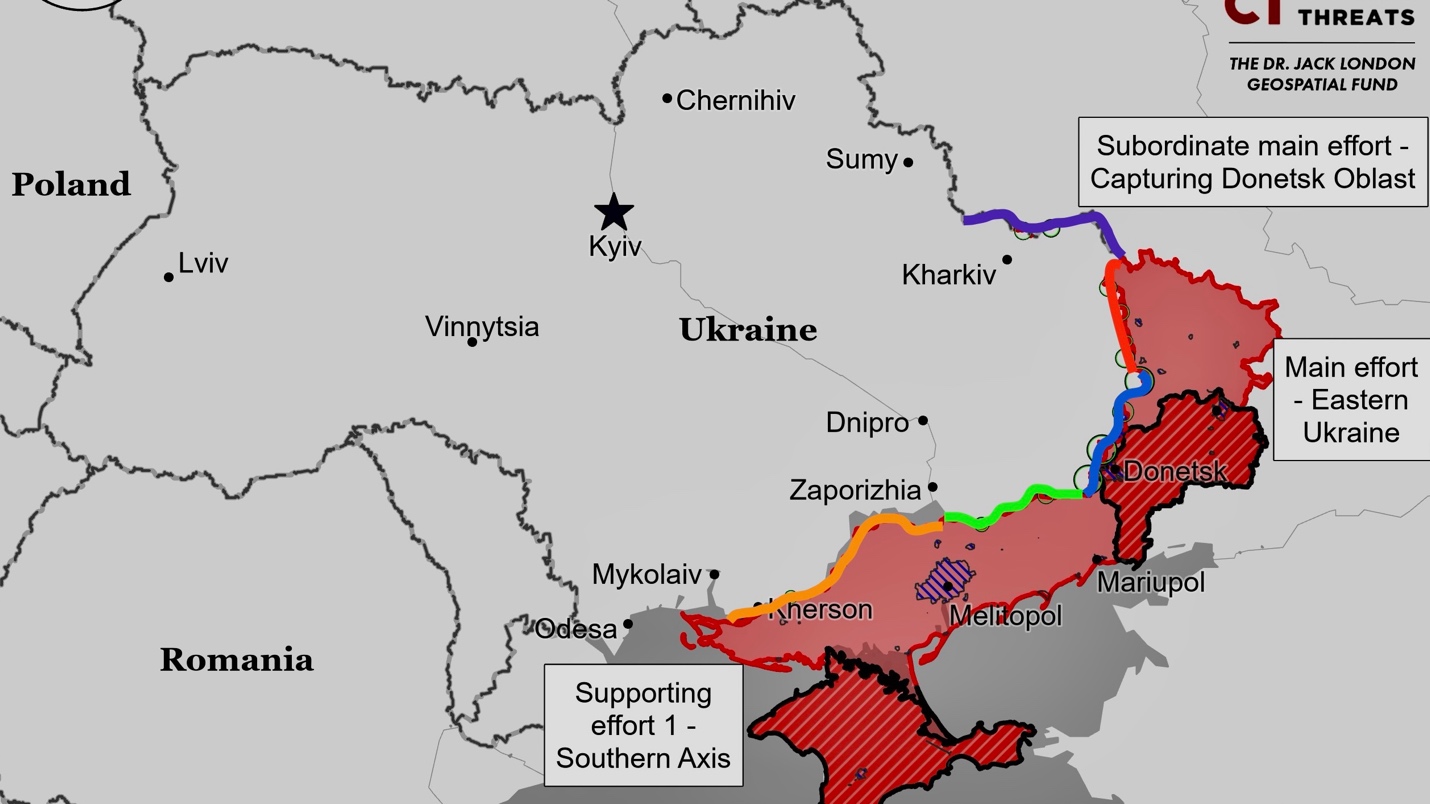
Ukrainian forces made a small advance along Soborna Street in central Vovchansk, northeast of Kharkiv City. Fighting continued near Lyptsi, Hlyboke, Vovchansk, and Tykhe in northern Kharkiv Oblast. A Russian milblogger claimed that Russian forces conducted a fifth strike using a FAB-3000 glide bomb against Ukrainian forces in Vovchansk, though this claim remains unconfirmed.
Ukrainian military spokespersons reported that Russia intends to transfer elements of the “9th Motorized Rifle Brigade of the 51st Army” and the 155th Naval Infantry Brigade to the Kharkiv direction. These units are reportedly being moved from Kherson Oblast and areas west and southwest of Donetsk City to compensate for Russian losses. The mention of a “51st Army” may indicate that Russia has formed a new combined arms army, possibly resurrecting a Second World War-era formation, as part of ongoing military reforms.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces reportedly conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, targeting multiple locations including Synkivka, Pishchane, Stepova Novoselivka, Stelmakhivka, Kopanky, Andriivka, Hrekivka, Makiivka, Nevske, Torske, Terny, and the Serebryanske forest area. A Russian milblogger claimed advances near Stelmakhivka, but this remains unconfirmed. There were no confirmed changes to the frontline in this area.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces made a small advance southeast of Siversk during a platoon-sized mechanized assault near Spirne. Geolocated footage shows Ukrainian forces repelling the attack, which involved four armored fighting vehicles. Russian milbloggers claim ongoing fighting in Rozdolivka, with confirmed Russian presence in the southeastern part of the settlement as of June 23. Russian forces continued ground attacks in multiple locations around Siversk, including near Bilohorivka, Verkhnokamyanske, Spirne, Vyimka, and Rozdolivka.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued offensive operations near Chasiv Yar but made no confirmed advances. Fighting was reported north of Chasiv Yar near Kalynivka, east near Ivanivske, and southeast near Andriivka and Klishchiivka.
Toretsk
Russian forces continued offensive operations in the Toretsk direction, with no confirmed advances. Russian milbloggers claimed that forces reached the outskirts of Pivnichne after capturing Shumy, but this remains unconfirmed. The Ukrainian General Staff reported Russian attacks near Pivnichne and Pivdenne, as well as 11 guided glide bomb strikes on Toretsk.
Avdiivka
Russian forces made small advances northwest of Avdiivka, with geolocated footage showing their presence north of Sokil and along the O0544 Ocheretyne-Pokrovsk road northwest of Ocheretyne. Russian milbloggers claimed advances near Yasnobrodivka and partial encirclement of Ukrainian forces. Fighting continued in multiple locations around Avdiivka, including Oleksandropil, Yevhenivka, Novooleksandrivka, Vozdvyzhenka, Sokil, Novoselivka Persha, Umanske, Yasnobrodivka, Karlivka, Nevelske, and near the Karlivske Reservoir.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces claimed advances west of Donetsk City, but visual confirmation is lacking. Fighting continued in Krasnohorivka, Heorhiivka, Kostayntynivka, and Paraskoviivka. Ukrainian forces reportedly repelled a Russian attack near Kurakhove, destroying several Russian vehicles.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Fighting continued near Urozhaine and Staromayorske in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border area. Russian forces claimed to be advancing in Urozhaine, but there is no visual confirmation of these claims.
Zaporizhia Line
Fighting continued in western Zaporizhia Oblast near Robotyne, Verbove, and Mala Tokmachka on June 25, with no changes to the frontline.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Fighting continued on the east bank of Kherson Oblast, including near Krynky. The frontline remained unchanged.
Ukraine News
Ukrainian forces have shot down nearly 86% of the 2,277 Shahed drones launched by Russia since January 1, 2024, according to the Ukrainian Air Force Commander. Mobile fire groups were largely responsible for this success.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Russian authorities continue to forcibly deport Ukrainian children to Russia or relocate them within occupied Ukraine. They have issued Russian passports to Ukrainian children in St. Petersburg, planned to send about 1,000 children from occupied regions to a camp in Berdyansk, deported disabled children and their parents from Kadiivka to Moscow, taken children from Krasnodon to Crimea with plans for more, deported children to Chechnya and Kabardino-Balkaria, and planned to deport over 12,000 children from Luhansk Oblast to Russia. Ukraine has only recovered about 800 of at least 20,000 deported children.
Russian authorities are forcing over 10,000 children in occupied Donetsk Oblast to join the “Young Republic” organization, which aims to indoctrinate them with Russian patriotic education, similar to the Soviet-era Komsomol.
The Kremlin is working to integrate occupied Ukraine into the Russian economy. Putin met with the Kherson Oblast occupation head to discuss priorities such as gas and energy supply, housing, and industry. The occupation administration is developing a program with Gazprom and a seized Ukrainian company to bring gas pipelines to occupied Kherson Oblast.
Russia News
Ukrainian forces conducted a drone strike on a Russian ammunition depot in Olkovatka, Voronezh Oblast. Ukraine’s Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) claimed responsibility for the attack, which reportedly targeted two warehouses containing over 3,000 shells. Satellite imagery showed at least two fires at the depot. Voronezh Oblast Governor Alexander Gusev acknowledged explosions in the area but claimed they occurred far from civilian buildings.
The Ukrainian National Guard reported striking two Russian Pantsir-S1 anti-aircraft systems near Belgorod City on unspecified dates. One system was hit near Dubovoe on June 22, while another was struck near Borisovka. The type of munitions used in these attacks remains unclear. A Ukrainian OSINT account had previously geolocated one of these Pantsir systems in January 2024, suggesting it hadn’t been moved in six months before being hit.
The International Criminal Court (ICC) issued arrest warrants for former Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu and Chief of the Russian General Staff Valery Gerasimov. They are accused of directing attacks on civilian objects in Ukraine, causing incidental harm to civilians, and committing inhumane acts. The ICC stated there is reasonable evidence to believe both men bear individual responsibility for these war crimes, which violate the Rome Statute. The court emphasized that even when targeting potential military objectives, the civilian harm was excessively disproportionate to the expected military advantage.
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) ruled that Russia has committed numerous human rights violations in Crimea since its illegal occupation in February 2014. These violations include infringements on the right to life, liberty, security, freedom of religion, expression, and assembly, among others. The ECHR found that the evidence provided by Ukraine demonstrates a “pattern or system of violations” by Russia in Crimea. This marks the first time an international legal body has recognized Russia’s widespread and systemic human rights abuses in occupied Crimea over the past decade.
Russia imposed countersanctions on 81 European Union-based news outlets on June 25, following EU sanctions against four Russian state-affiliated news outlets. The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs blocked access to major European media outlets including Der Spiegel, Die Welt, El Mundo, Le Monde, and Politico’s European service, among others. Russia stated these sanctions were in response to EU blocking of Russian news sites RIA Novosti, Rossiskaya Gazeta, and Izvestia, but did not mention EU sanctions against Voice of Europe.
Dagestan Republic Head Sergei Melikov ordered investigations into senior Dagestani officials’ personal records following the June 23 terrorist attacks. He dismissed Sergokalinsky district head Magomed Omarov after reports that two of Omarov’s sons were involved in the attacks. Russian security services detained Omarov, who may face charges of aiding terrorists. A Russian insider claimed the Kremlin is reconsidering its approach to preventing extremism in the North Caucasus. Russian milbloggers criticized local officials and youth policies for allegedly breeding extremism. This suggests the Kremlin may be intensifying efforts to address Islamist extremist threats while attempting to maintain an appearance of stability and unity.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
The Russian Volunteer Society for Assistance to the Army, Aviation, and Navy (DOSAAF) will begin training Russian military personnel and forming motorcycle units on October 1, 2024. DOSAAF has been involved in recruitment and will likely increase its role in military training. The Russian military has already created an experimental motorcycle platoon for combat, logistics, and medical evacuation.
The Russian military is offering large one-time payments, monthly salaries, and the suspension of debt, loan, and criminal proceedings to attract recruits. Laws passed in December 2022 and March 2024 protect mobilized servicemen and volunteers from legal proceedings and criminal liability.
A Ukrainian military observer provided details on Russian Airborne (VDV) assault companies, which typically consist of five specialized platoons of about 19-29 personnel each. These include assault, fire support, reconnaissance, and drone platoons. However, due to losses and challenging combat conditions, VDV forces often attack with only one or two platoons rather than the full company.
Rostec, a Russian state-owned defense company, delivered a new batch of Malva 152mm self-propelled guns to the Russian military. These artillery pieces are mounted on maneuverable and cost-effective wheeled chassis, have a capacity of at least 30 rounds, and can fire multiple shells on different trajectories simultaneously.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
Russian officials, including high-ranking diplomats, are blaming Ukraine and the US for civilian casualties from an ATACMS strike on Sevastopol, Crimea, on June 23. They claim it was a deliberate attack on civilians, despite the Russian Ministry of Defense stating that Russian air defenses deflected the missile, causing the casualties. Russia will likely use this incident to vilify Ukraine at the upcoming UN Security Council meeting.
The Russian Investigative Committee released results of its investigation into the January 2024 downing of a Russian Il-76 transport plane, likely to discredit Ukraine and the US. They claimed Ukraine used US-provided Patriot missiles to shoot down the plane, which allegedly carried Ukrainian POWs. However, Russia has not provided evidence of POWs on board, and Ukraine noted many listed POWs had been previously exchanged.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
