Summary of the day: US and German officials confirmed policy changes allowing Ukraine to use US- and German-provided weapons to strike Russian territory, albeit with some unspecified restrictions. Ukrainian forces launched drone and missile strikes against a Russian long-range radar system in Crimea and an oil depot in Krasnodar Krai. Concurrently, Russia reported recent advances near Vovchansk, Avdiivka, and Donetsk City. Additionally, Ukraine signed long-term bilateral security agreements with Sweden, Iceland, and Norway, and conducted a one-for-one POW exchange with Russia, the first since February 8.
These updates will be shorter until the end of July and will only use the Institute for the Study of War as a source while we are on holiday visiting family and friends. We will be back to our normal coverage again starting on July 22, 2024.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War
Russian Security Council Deputy Chairperson Dmitry Medvedev responded to the new Western policy allowing Ukraine to use Western weapons to strike inside Russia. Medvedev threatened escalation and suggested this could be a casus belli, framing the war in Ukraine as a broader conflict with the West. He also raised the specter of nuclear confrontation, continuing Russia’s pattern of nuclear threats.
Russia is trying to rally CSTO members against the West due to concerns about the organization’s future influence. Russian Defense Minister Andrei Belousov claimed that NATO’s military buildup threatens CSTO security and accused the West of destabilizing the region. He called for CSTO members to unite their foreign policies. Russia is particularly worried about Armenia’s decreased participation in the CSTO after losing Nagorno-Karabakh, fearing this could lead other members to question their involvement. Recent tensions with Tajikistan and Central Asian concerns about sanctions are also pushing Russia to strengthen CSTO unity.
Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan are skeptical of Russia’s claims of a geopolitical confrontation with the West, and Russia may need to offer more concrete promises to keep the CSTO aligned with its interests. Russian Defense Minister Andrei Belousov met with Tajikistani Defense Minister Sherali Mirzo to discuss addressing instability on the CSTO’s southern border, particularly from Afghanistan and terrorism threats. Russia is considering delisting the Taliban to cooperate against IS-Khorasan, which has targeted Central Asia. President Putin emphasized international counterterrorism cooperation, a point likely appealing to CSTO members seeking to combat regional terrorist threats.
The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs announced a conference titled “Baltic Fascism: Evidence for the Future Tribunal,” scheduled for June 3 in St. Petersburg. The event, organized by the Association for Baltic Studies, will focus on alleged violations against Russian-speaking populations in Baltic countries and will be supported by the St. Petersburg City Committee for External Relations. This effort is part of Russia’s ongoing campaign to justify potential future actions against Baltic states under the pretext of protecting “compatriots abroad.” The Kremlin has also added Baltic officials to Russia’s wanted list, asserting Russian legal jurisdiction over NATO member states.
Peace Talks
China announced it will not join the June 2024 Ukraine peace summit in Switzerland. Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Mao Ning stated that the summit does not meet China’s expectations and emphasized the need for both Russia and Ukraine to endorse the peace process. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has said Ukraine will negotiate with Russia only after creating a peace plan with allies. China and the US are seen as crucial for compelling Russia to engage in peace talks. Despite this, Russia has shown no genuine interest in negotiating to end the war.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
US and German officials confirmed policy changes allowing Ukraine to use US- and German-provided weapons to strike Russian territory with some restrictions. Secretary of State Antony Blinken stated that President Biden approved Ukraine’s use of these weapons to defend against Russian forces, especially those attacking from the border. The specific weapons allowed for use were not detailed. Blinken mentioned the US might adapt its policies as needed.
Germany confirmed that Ukraine can use German-provided weapons to defend itself against Russian attacks, particularly from positions near Kharkiv Oblast. German officials specified that these weapons could be used against attacks originating from the bordering Russian territory. Other Western countries, like the Netherlands, indicated fewer restrictions on the use of their provided weapons, including F-16s, for Ukraine’s self-defense against Russian targets.
On May 30, Luhansk People’s Republic Press Secretary Anna Romanova claimed that Ukrainian forces hit a gas pipeline in occupied Pervomaiske, west of Luhansk City, with HIMARS rockets.
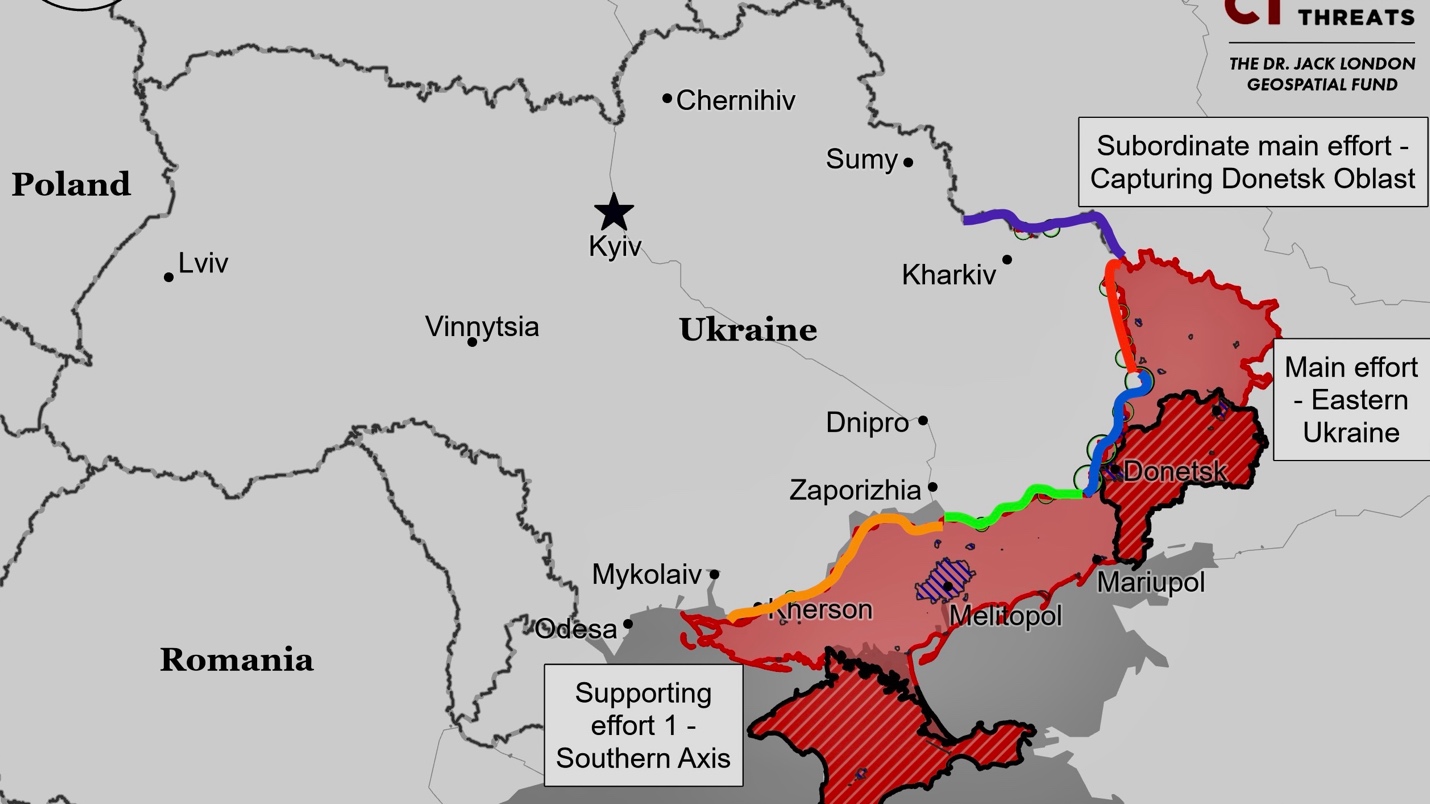
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Although Russian forces made some gains in northern Kharkiv Oblast in early May 2024, Defense Minister Andrei Belousov exaggerated their progress. Belousov claimed they had seized 880 square kilometers in 2024. However, the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) reports that Russian forces have actually seized about 752 square kilometers this year, with 516 square kilometers taken between January and April 29.
Russian forces made slight advances northeast of Kharkiv City today amid ongoing fighting. Footage shows marginal progress in Vovchansk’s eastern outskirts. Russian Defense Minister Andrei Belousov claimed Ukrainian forces retreated 8-9 kilometers in northern Kharkiv Oblast in May. Russian sources reported a 450-meter advance near Vovchansk and unsuccessful Ukrainian counterattacks in Vovchansk and Lyptsi. Russian forces continued assaults near Starytsya, with elements of various Russian brigades and special units operating in the area.
Ukrainian Air Force Spokesperson Major Ilya Yevlash reported that Russian forces are using groups of four to five Su-34/35 aircraft for glide bomb strikes in northern Kharkiv Oblast. He stated that the promised F-16 fighter jets will help deter Russian aircraft from the frontline.
The Conflict Intelligence Team (CIT) reported on May 30 that restrictions on Ukraine’s use of Western-provided weapons to strike Russian targets have enabled Russian forces to operate Lancet drones freely in Belgorod Oblast. This has led to an increase in successful Lancet strikes against Ukrainian forces, with at least 33 strikes in northern Kharkiv Oblast since May 10. A Russian source claimed 296 Lancet strikes in Ukraine in May, up from 178 in March. CIT attributed the increase to higher domestic production of Lancets and favorable conditions for strikes in northern Kharkiv. Russian forces have continuous surveillance over roads in the area, making it hard for Ukrainian vehicles to move undetected.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces continued their offensive along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line with no confirmed changes to the frontline. A Russian source claimed forces entered Myasozharivka, but this remains unconfirmed. Russian operations targeted areas near Kupyansk, Svatove, and Kreminna, with increased activity noted. A Ukrainian brigade spokesperson reported that Russian attempts to find weak spots in Ukrainian defenses have led to significant Russian losses in equipment and manpower. Russian forces are active near Novoyehorivka.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
The Ukrainian General Staff reported Russian offensives near Vyimka, Berestove, and Rozdolivka, southeast and south of Siversk.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued their offensive near Chasiv Yar, with no confirmed changes to the frontline. Ukrainian military observer Kostyantyn Mashovets reported Russian advances to the intersection of the Siversky-Donets Donbas canal and the T0504 highway, and to the eastern outskirts of Kalynivka. Fighting was ongoing northeast near Bohdanivka, north near Kalynivka, east near Ivanivske, and southeast near Andriivka and Klishchiivka.
Avdiivka
Russian forces advanced near Avdiivka amid ongoing offensives. Geolocated footage shows Russian forces moving southeast of Novooleksandrivka, northwest of Avdiivka near Kalynove, and west near Umanske and other areas. Claims of additional advances remain unconfirmed. A Russian source noted Ukrainian counterattacks near Sokil are slowing Russian progress. Ukrainian forces observed Russian troops using Soviet-era T-62 tanks, with typical attack groups of about six personnel. Fighting continued near multiple locations around Avdiivka, including Kalynove, Novooleksandrivka, Sokil, and Nevelske. Various Russian regiments and brigades are involved in these operations.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces advanced west of Donetsk City amid ongoing offensives. Geolocated footage from May 30 shows Russian troops reaching the city council building in central Krasnohorivka. A Russian source claimed advances over two square kilometers west of Solodke. Ukrainian FPV drones are reportedly hindering Russian vehicle support near Krasnohorivka. Fighting continued near Krasnohorivka, Heorhiivka, Novomykhailivka, Kostyantynivka, Paraskoviivka, and Vodyane.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Positional engagements continued near the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border, particularly around Staromayorske and Urozhaine, south of Velyka Novosilka.
Zaporizhia Line
Russian forces continued ground attacks in western Zaporizhia Oblast without confirmed changes to the frontline. A Russian source claimed advances of up to two kilometers near Mala Tokmachka and the seizure of windbreaks, though these claims are unverified. Another source reported intensified Russian offensives south of Shcherbaky. Assaults were conducted near Robotyne, Verbove, Mala Tokmachka, Mali Shcherbaky, and Novoandriivka.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Russian forces continued assaults in eastern Kherson Oblast near Krynky and the Dnipro River delta near Nestryha Island, with no confirmed changes to the frontline. A Russian source claimed that Russian forces are active in the Dnipro River delta and that Russian forces have recently gained the tactical initiative there.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched a limited missile and drone attack on Ukraine. They fired five S-300/S-400 missiles at Kharkiv from Belgorod, an Iskander-K missile at Kyiv from Kursk, and four Shahed drones from Krasnodar. Ukrainian forces destroyed the Iskander-K missile and all four drones over Kyiv, Zaporizhia, and Dnipropetrovsk. Kharkiv City was hit in the Novobavarskyi Raion by the S-300/S-400 missiles.
Ukraine and Russia conducted their first prisoner of war (POW) exchange since February 8, swapping 75 Ukrainian POWs for 75 Russian POWs. The Russian Ministry of Defense credited the United Arab Emirates with mediating the exchange. Russian authorities had previously blamed Ukrainian demands for the suspension of POW exchanges.
Ukraine’s Allies
Ukraine signed long-term security agreements with Sweden, Iceland, and Norway. Sweden will provide 6.5 billion euros in military aid over the next decade, including ASC 890 AEW&C aircraft and efforts to transfer JAS 39 Gripen jets. Iceland will offer $30 million annually from 2024 to 2028 for defense materials and industry development. Norway will provide 75 billion kroner in aid from 2023 to 2027, including air and missile defense systems like NASAMs and support for developing Ukraine’s aircraft capabilities with F-16 fighters.
Germany and Poland announced new military aid packages for Ukraine. On May 30, Germany’s Defense Minister revealed a 500-million-euro package including a Patriot air defense system, IRIS-T SLM and SLS missiles, drones, and spare parts. On May 31, Poland’s Foreign Minister announced a 4-billion-euro package to support Ukraine’s defense efforts.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Russian and occupation officials are working to strengthen logistics in occupied Ukraine and between these areas and Russia. Frontelligence Insight assessed on May 29 that Russia is close to launching an 80-kilometer rail line between Burne and Malovodne, Donetsk Oblast, providing a direct link between occupied southern Ukraine and Russia, bypassing the Kerch Strait Bridge. Satellite images show trains on this new line, though it’s unclear if they are test runs. Ukrainian officials previously noted that Russian forces stopped using the Kerch Strait Bridge for military and fuel transport. Kherson Oblast officials reported repairing 109.5 kilometers of roads for a 1,400-kilometer “land corridor” from Rostov Oblast to Crimea, nearly completing the Novotroitske-Chaplynka highway.
Russian authorities are indoctrinating Ukrainian children with military-patriotic education as part of a campaign to erase Ukrainian national and cultural identities. On May 29, the Kherson occupation administration reported sending 36 Ukrainian teenagers to a 21-day military camp in Volgograd, with previous groups sent to Vladivostok. On May 30, it was announced that 20 Ukrainian minors in Henichesk Raion will start a cadet class, with plans for more. The Ukrainian Resistance Center reported that Russia will introduce a mandatory course on security and defense for all high school students in occupied Ukraine, covering tactical medicine, military training, and the use of drones, grenades, and rifles.
Kremlin Commissioner on Children’s Rights Maria Lvova-Belova claimed that Russia has reunited 70 Ukrainian children with their relatives, likely to deflect from her and the Kremlin’s roles in forcibly deporting Ukrainian children to Russia. Lvova-Belova has repeatedly tried to distract from these illegal deportations. A recent investigation by opposition outlet Vazhnye Istorii implicated her and her sister in the forced deportation of Ukrainian adults with special needs to Russia.
Russia News
Ukrainian forces launched drone and missile strikes on a Russian long-range radar system in occupied Crimea and an oil depot in Krasnodar Krai. The strikes followed a May 30 attack on the Kerch Strait ferry crossing. Ukrainian media reported a successful strike on a $100 million radar system near Armyansk, Crimea. Additionally, Ukraine hit an oil depot near Kavkaz port with Neptune missiles, causing significant damage. Russian officials confirmed damage to petroleum tanks and reported repelling numerous Ukrainian drones.
Ukrainian forces successfully struck a ferry crossing in the Kerch Strait with ATACMS, damaging two ferries used by Russian forces to transport troops and equipment to occupied Crimea. This strike, occurring on the night of May 29-30, aims to disrupt Russian supply lines. Conflicting reports emerged, with Russian sources claiming various damages, including to pilot boats and a railway line. Ukrainian officials noted the continued reliance on the ferry crossing due to unfinished railway lines on the Kerch Strait Bridge.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
On May 30, Russian State Duma members Alexander Khinshtein and Vasily Piskarev announced a bill to eliminate toll fees for Russian military, Rosgvardia, and FSB vehicles. Russian milbloggers praised the bill, attributing it to months of public demand.
Russian forces are developing new missile and drone technologies for use in Ukraine. They have created the S-8OFP “armor piercing” variant of the S-8 unguided aerial rocket for targeting armored vehicles. Additionally, the Russian company Integrated Robotic Technologies (IRT) developed the “IRT-Scout,” a foam FPV drone with a top speed of 90 km/h, a range of 50 km, a flight time of 60 minutes, and a 200-gram payload. The “IRT-Scout” is resistant to electronic warfare and easily repairable.
Russia’s Allies
Russian President Vladimir Putin and Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko discussed their bilateral relationship and the upcoming Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) summit in July 2024. The Kremlin announced that SCO members are expected to grant member status to Belarus at the summit.
The Russian Ministry of Defense released footage of Russian and Belarusian pilots participating in joint tactical flight exercises in Belarus.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
