Summary of the Day:
Russian forces are successfully building on their capture of Vuhledar, making significant tactical advances south of Kurakhove in western Donetsk Oblast, with confirmed progress near Antonivka and Katerynivka. Additional advances continue in central Novoselydivka, north of Kurakhove, with Russian sources claiming advances into eastern Kurakhove along Stantsiyna and Kozatska streets.
Their forces continue pushing into the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border area, particularly around Velyka Novosilka, though their advance remains at a moderate pace – covering about 10 kilometers from the Vuhledar-Prechystivka line in five weeks. This pace likely won’t allow for rapid encirclement of Ukrainian positions, giving Ukrainian forces sufficient time for organized withdrawals.
Damage to the Kurakhivske Reservoir’s Ternivska Dam has caused limited flooding in the Velykonovosilkivska Hromada area, with water levels rising by 1.2 meters. Both sides dispute responsibility for the damage, though reports indicate Russian forces previously struck the dam in September 2024. The dam damage may be part of a Russian strategy to create a water barrier between Ukrainian forces and disrupt supply routes, particularly along the H-15 highway.
Additional Russian advances have been reported in Kursk Oblast and near Kreminna, while Russian regional governments are allocating substantial social budget funds to veteran payments to encourage military service. Meanwhile, Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov denied reports of a recent phone conversation between Russian President Vladimir Putin and US President-elect Donald Trump, contradicting a Washington Post report claiming such a call occurred on November 7.
Picture of the Day:
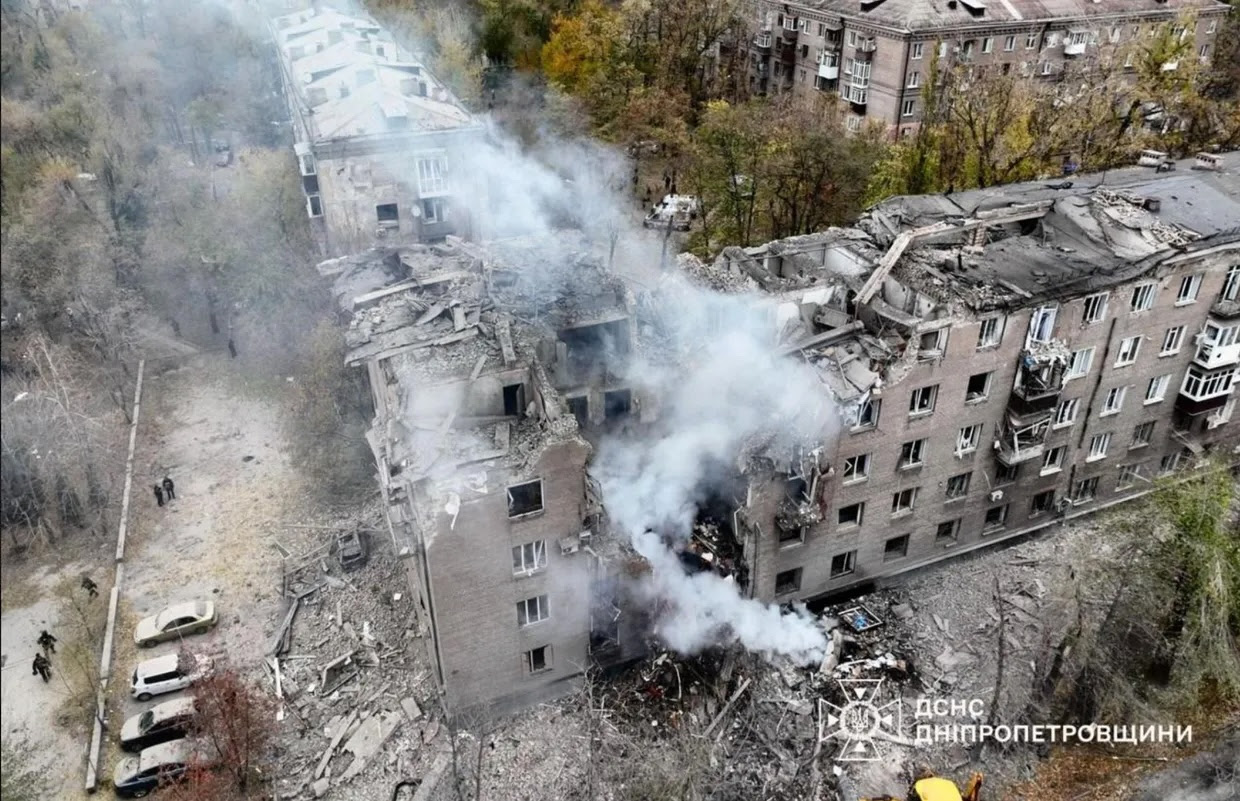 Three children and a woman were killed when a high-rise residential building in Kryvyi Rih was hit by a Russian missile. (X / President Zelensky)
Three children and a woman were killed when a high-rise residential building in Kryvyi Rih was hit by a Russian missile. (X / President Zelensky)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Belarus’s entry into BRICS as a partner country raises geopolitical concerns, as this closer alignment with Russia, China, and other BRICS nations could further shift global power dynamics and potentially increase tensions with Western nations. This partnership allows Belarus, already a close Russian ally, to strengthen its ties with other major non-Western powers through permanent participation in BRICS summits and ministerial meetings.
The formalization of a mutual defense treaty between North Korea and Russia marks a significant shift in global power dynamics, raising serious international security concerns. The alliance combines Russia’s nuclear capabilities with North Korea’s military support, which already includes 10,000 troops deployed to the Ukraine conflict and weapons supplies. This partnership, condemned by G7 nations, potentially violates UN Security Council resolutions and threatens to escalate global tensions beyond the current Ukraine conflict. The treaty’s requirement for immediate military assistance between the two nuclear-armed nations creates a dangerous new dynamic in international relations, particularly as Ukrainian forces report their first direct clashes with North Korean troops in Russia’s Kursk region. This development could potentially draw more nations into the conflict and further destabilize world peace.
Georgia’s contested parliamentary elections in October 2024 signal a concerning shift in the balance of power between Russia and the West in the strategic Caucasus region. The victory of the pro-Russian Georgian Dream party, amid widespread allegations of election fraud, threatens to create another potential foothold for Russian influence alongside its ongoing war in Ukraine.
International security experts, including Laura Thornton of the McCain Institute, warn that Georgia’s apparent pivot away from its EU and NATO aspirations could significantly weaken the democratic alliance in Eastern Europe. The ruling party’s campaign deliberately exploited fears of war by linking Georgia’s pro-Western opposition to the conflict in Ukraine, suggesting that closer ties with Europe could lead to Russian aggression like what Ukraine is experiencing.
This development represents a potential strategic victory for the Kremlin, as it could gain another allied state on NATO’s periphery. With Georgia potentially aligning more closely with Moscow, the international community faces a new challenge in containing Russian influence in a region crucial for European security and energy interests. The situation mirrors broader patterns of democratic backsliding that have preceded increased Russian regional influence, raising concerns about further instability in the region.
The Path to Peace
Russian President Vladimir Putin has emerged decisively victorious in his first diplomatic confrontation with President-elect Donald Trump, skillfully maneuvering Trump into a position where he must either publicly admit to lying or face embarrassment over an alleged November 7 phone call. The situation stems from Trump supposedly warning Putin against escalating the Ukraine war and reminding him of America’s strong military presence in Europe, only to have Putin thumb his nose in response and launch a major escalation of the war within days. The Kremlin has given Trump a way out of the situation by claiming the phone call never happened, but that would mean that Trump’s camp lied about the phone call.
Putin’s dominant position has already influenced Trump’s camp to shift toward accommodation, with Trump’s senior advisor Bryan Lanza telling the BBC that the administration would prioritize peace over helping Ukraine recover Russian-occupied territories, boldly declaring “Crimea is gone.” This aligns with Trump’s undetailed promise to end the war “in 24 hours” through direct talks with Putin, a stance that has earned optimism from Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov despite initial skepticism about potential policy changes, marking a clear departure from the current administration’s position.
Trump now faces a constitutional crisis of his own making, as forcing Ukraine to accept territorial losses would violate the US Constitution. The Constitution requires honoring all treaties, including the 1994 Budapest Memorandum guaranteeing Ukraine’s territory in exchange for nuclear disarmament. This leaves Trump with limited options: either acquiesce to Putin’s demands and violate the Constitution, or abandon his campaign promises regarding peace in Ukraine.
The international community stands in opposition to this emerging Trump-Putin dynamic, with British Prime Minister Starmer and French President Macron not taking the cowardly and dishonorable approach advocated by Trump, but jointly pledging continued support for Ukraine, while Poland’s Prime Minister Tusk plans meetings with Starmer and NATO Secretary-General Rutte to maintain Ukraine’s support. France’s Foreign Minister Jean-Noel Barrot has cautioned against premature judgment of Trump’s Ukraine policy at the Paris Peace Forum, emphasizing Ukraine’s need for a stronger negotiating position. Meanwhile, Putin maintains his demand for Ukrainian troop withdrawal from eastern and southern territories before negotiations, despite President Zelensky’s warnings against such concessions.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Russian Defense Minister Andrei Belousov met with Colonel General Mikhail Teplinsky to discuss operations in the Kherson and Zaporizhia regions. Teplinsky reported effective use of Russian-made drones in their reconnaissance operations.
The Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) claims it foiled a Ukrainian plot to recruit a Russian Mi-8MTPR-1 electronic warfare helicopter pilot to defect. According to FSB video released November 11, Ukraine’s Main Intelligence Directorate (HUR) allegedly offered to relocate the pilot’s family to Moldova via Turkey in exchange for delivering the aircraft. The pilot was reportedly instructed to neutralize his crew and fly to a specified Ukrainian airfield. The pilot claims he informed his commanders instead, leading Russian forces to strike Ukrainian air defense positions identified during the plot.
Russian forces allegedly executed two unarmed Ukrainian prisoners of war in the Kursk region, as evidenced by recently surfaced social media video footage, prompting both an investigation by Ukraine’s Prosecutor General’s Office and a call for international action from Ukraine’s Human Rights Commissioner Dmytro Lubinets.
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Ukrainian and Russian forces are engaged in ongoing operations in Kursk Oblast, where Russia has concentrated approximately 50,000 troops, including 11,000 North Korean soldiers. Ukrainian forces have made small advances near Novoivanovka, while Russian forces have recaptured positions near Pogrebki and advanced in eastern Darino, recovering about half of the territory lost since Ukraine’s surprise offensive in August. Russian forces are conducting frequent attacks near several settlements including Leonidove, Nikolayevo-Darino, Kruglenkoye, and Novoivanovka, with Ukrainian Colonel Vadym Mysnyk reporting attacks every 10-15 minutes and noting increased strike intensity in Kursk Oblast compared to neighboring regions.
According to British defense intelligence, Russia is planning to reclaim the remaining lost territory in the Kursk region before Donald Trump’s inauguration on January 20, with elite Russian units attempting to push Ukrainian forces out and potentially expand into Ukraine’s Sumy Oblast. Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi reports that Russian forces have suffered significant casualties, including over 7,900 soldiers killed and 12,200 injured. In a recent development, Ukraine’s Special Operations Forces reported a successful mission in the region, resulting in 14 Russian servicemen killed and three captured, with video footage showing Ukrainian forces using advanced equipment including night vision and drone reconnaissance.
Ukraine’s military intelligence (HUR) reports that a Russian Mi-24 attack helicopter was destroyed at the Klin-5 airbase in Moscow Oblast. The helicopter, belonging to Russia’s 92nd squadron of the 344th center, was reportedly set on fire, though the method of attack wasn’t disclosed.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces continued attacks near Vovchansk and Starytsya, northeast of Kharkiv City, though no confirmed advances were made.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces claim to have captured Kolisnykivka near Kupyansk, with reported advances near Petropavlivka and Berestove. Fighting continues near several settlements including Kindrashivka, Zahryzove, Zeleny Hai, and Hrekivka. Ukrainian officials report that Russian forces, composed of mixed units with varying experience levels, are now relying on small infantry groups rather than heavy equipment. Ukrainian authorities have ordered mandatory evacuations for 10 settlements in the Borivska Hromada area, including Borova.
Russian forces made advances near Kreminna, specifically in central Terny. Operations continued near Torske and Serebryanka. Ukrainian drone and artillery strikes have reportedly slowed Russian progress near Terny. Russian forces in the Lyman direction include approximately 35,000 personnel, 540 tanks, and nearly 1,000 armored vehicles, according to Ukrainian military observer Kostyantyn Mashovets.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces launched attacks near Siversk focusing on Verkhnokamyanske and Vyimka, though no frontline changes were confirmed. According to Ukrainian military observer Kostyantyn Mashovets, Russian forces advanced about 3 kilometers near Zolotarivka and Verkhnokamyanske during Summer-Autumn 2024. Russian attempts to advance from Rozdolivka toward Pereizne and from Zaliznyanske toward Privillya were unsuccessful, with forces withdrawing from some forward positions.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued attacks near Chasiv Yar and Stupochky with no confirmed advances. While Russian sources claimed to have entered Stupochky, they remain approximately 2.5 kilometers from the settlement.
Toretsk
Russian forces attacked near Toretsk, including operations near Shcherbynivka and Nelipivka, but made no confirmed advances. Russian special forces units are reportedly operating near Niu York and in Toretsk.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces attacked multiple settlements near Pokrovsk, including Promin, Myrolyubivka, Lysivka, Sukhyi Yar, Selydove, Hryhorivka, Petrivka, and Novooleksiivka. While Russian sources claimed advances near Selydove, Hryhorivka, and Novooleksiivka, no visual confirmation exists for these claims.
West and Southwest of Donetsk City
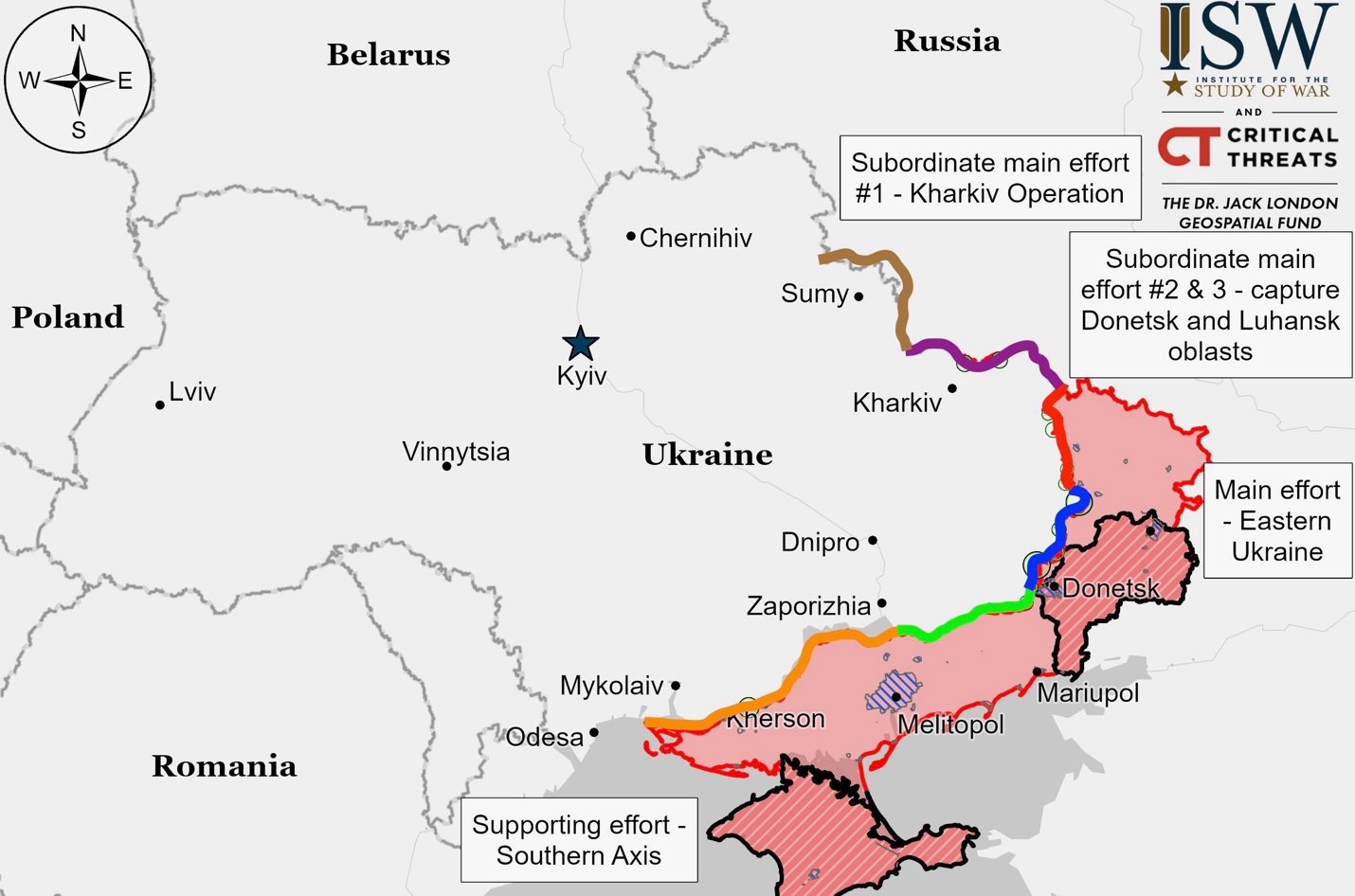
Russian forces are making significant advances in western Donetsk Oblast following their October 1 capture of Vuhledar, moving north and northwest with confirmed advances near Antonivka, Katerynivka, and positions near Dalne, south of Kurakhove. Their strategy appears aimed at enveloping Kurakhove and leveling the frontline between Sontsivka and Shakhtarske, potentially bypassing the defensive line of Romanivka-Uspenivka-Sukhyi Yar. Russian forces have pushed into central Novoselydivka and reportedly advanced into eastern Kurakhove along Stantsiyna and Kozatska streets, as well as near Novooleksiivka and Sontsivka. They are conducting assaults in multiple directions: northeast of Kurakhove near Novodmytrivka; north near Voznesenka, Illinka, and Berestky; south near Dalne; and around Vuhledar including Maksymilyanivka, Antonivka, Katerynivka, and Bohoyavlenka.
The pace of Russian advances is moderate, covering approximately 10 kilometers from the Vuhledar-Prechystivka line in five weeks. At this speed, Ukrainian forces likely have sufficient time to conduct organized withdrawals without risking encirclement, and even if Russians eliminate the Kurakhove salient, this doesn’t suggest a broader frontline collapse as Ukrainians can establish new defensive positions in settlements further west. The pace and cost of these advances in terms of personnel and equipment may limit Russian forces’ ability to exploit any gains.
Russian forces have damaged the Kurakhove Reservoir’s Ternivska Dam near Stari Terny, causing limited flooding in the Velykonovosilkivska Hromada area with water levels rising by 1.2 meters. While Ukrainian authorities cannot inspect the dam due to Russian shelling, they report no houses have been flooded as of 1600 local time, though flooding may affect settlements along the Vovcha River in Donetsk and Dnipropetrovsk oblasts. While roads near the dam remain usable, dirt roads cannot support armored vehicles. This follows earlier attacks on the dam in September 2024, when strikes on September 18 damaged the lock control system but didn’t cause flooding. The dam attack may be part of a larger Russian strategy to split Ukrainian forces around Kurakhove, potentially creating a water barrier between Ukrainian force groupings and possibly disrupting the H-15 highway, a key Ukrainian supply route. This incident is the latest in a series of dam attacks, following the destruction of the Kakhovka dam in June 2023 and damage to dams in Kyiv and Zaporizhzhia.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces have resumed offensive operations in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border area since mid-October, with confirmed control of Shakhtarske. They are now advancing toward Velyka Novosilka from multiple directions. Russian sources claim advances in southern Makarivka, with reports of Russian forces conducting attacks near Novodarivka and Rivnopil. To reach Velyka Novosilka, Russian forces would need to capture Blahodatne, Neskuchne, and Vremivka. They appear to be using their positions in Shakhtarske to pressure Ukrainian defenses in the area.
Zaporizhia Line
Russian forces attacked near Mala Tokmachka and Novoandriivka in western Zaporizhia Oblast with no confirmed frontline changes, while Ukrainian spokesperson Colonel Vladyslav Voloshyn warned of possible increased Russian assaults in the region, noting a 30-40 percent rise in reconnaissance operations and air strikes over recent weeks and stating that attacks could begin “any day,” with Russia deploying trained assault groups and planning to use armored vehicles, light vehicles, and drones; Russian forces are specifically massing near Orikhiv and Mala Tokmachka, areas that were part of Ukraine’s southern counteroffensive in 2023 which liberated Robotyne, and have already increased attacks in the region, including targeting civilian infrastructure with guided aerial bombs.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Fighting continued along the Dnipro River in eastern Kherson Oblast with no changes to the frontline reported.
Ukraine News
Russia launched a major aerial attack against Ukraine including 74 drones and two cruise missiles. Ukrainian forces intercepted 39 drones across multiple regions, while 30 were disrupted by electronic warfare. Russian strikes hit civilian areas in Kryvyi Rih, Kramatorsk, Mykolaiv City, Zaporizhzhia City, and Prymorsk City, causing casualties and damage. Ukraine’s Military Intelligence reported that Russia used over 2,000 drones in October 2024, with about half being decoys meant to overwhelm air defenses, including two that landed in Moldova.
Ukraine went on high alert when eight Russian Tu-95 bombers took off from Olenya airfield, triggering air raid sirens across the country, including Kyiv. The situation prompted emergency blackouts and sent people to shelters, including EU diplomat Josep Borrell. However, what appeared to be an imminent attack turned out to be a Russian aviation training exercise. Ukrainian officials, including Andrii Kovalenko of the Centre for Countering Disinformation, warn that Russia has accumulated enough missiles for massive strikes and may be preparing for unprecedented attacks on Ukraine’s electricity infrastructure as winter approaches.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 4 INJURIES: 14+
A Russian missile struck a high-rise residential building in Kryvyi Rih, President Zelensky’s hometown, hitting between the first and fifth floors and killing four people, including three children – one under a year old – and injuring at least 14 people, including a 10-year-old girl and an 11-year-old boy, with rescue workers continuing operations overnight searching for four more people, including three children, who may be trapped under the rubble.
Ukraine’s Allies
Estonia’s Defense Minister Hanno Pevkur visited Kyiv, signing a new military aid package that includes clothing and small arms. Estonia has committed 0.25% of its GDP to Ukraine’s military support and recently signed a 10-year security agreement worth over 100 million euros. During the visit, Pevkur and President Zelensky discussed financing long-range drone production and Estonia’s support for Ukraine’s EU and NATO membership aspirations, reinforcing Estonia’s position as one of Ukraine’s strongest allies since Russia’s invasion.
In 2024, the EU delivered 980,000 of the promised one million artillery shells to Ukraine, with production limitations causing a slight shortfall, according to EU diplomat Josep Borrell. However, total EU ammunition supplies are expected to exceed 1.5 million shells by year’s end, boosted by a Czech-led initiative that aims to provide 800,000 additional shells. The initiative, supported by Canada, Germany, and the Netherlands, has already delivered 50,000 shells. Looking ahead, Ukraine and Czechia plan to begin domestic ammunition production in 2025, while Slovakia’s citizens contributed over 4 million euros despite their government’s non-participation.
British Prime Minister Starmer and French President Macron met in Paris to urge President Biden to allow Ukraine to use Western weapons for strikes inside Russia before a potential administration change, with Ukraine’s President Zelensky seeking permission to use US-made ATACMs and UK’s Storm Shadows for deep strikes, particularly targeting Russian airbases and camps where North Korean troops are gathering, while former US special representative Kurt Volker suggested that the Biden administration should quietly drop its objections to Ukraine using these weapons, arguing there’s no justification for preventing Ukraine from striking back at Russia; simultaneously, Poland’s Prime Minister Donald Tusk is seeking to form an alliance with the UK to maintain support for Ukraine after 2025, planning meetings with British Prime Minister Starmer, French President Macron, and NATO Secretary-General Rutte to discuss this initiative, emphasizing that decisions about Ukraine’s future must include Ukrainian input, particularly given speculation about possible Russia-US agreements under a new administration.
President-elect Trump’s selection of Rep. Mike Waltz as national security adviser and Senator Marco Rubio as secretary of state signals a potential major shift in U.S. support for Ukraine, as both officials view the war as having reached a stalemate requiring negotiation rather than continued U.S. military support, with Waltz advocating reducing U.S. military aid to Ukraine in favor of increased European responsibility, aligning with Trump’s campaign promise for a swift end to the conflict; the nomination of Rep. Elise Stefanik as UN Ambassador further reinforces this shift, as despite her earlier backing of Ukraine and authorship of Russian sanctions legislation, her recent opposition to the $61 billion Ukraine aid package reflects a growing reluctance to continue U.S. military support, prioritizing domestic issues instead, while the Biden administration is racing to deliver the remaining $6 billion in allocated aid before the January 20 transition, suggesting concerns about future U.S. support for Ukraine under the new administration.
Life in Ukrainian Occupied Russia
Russian refugees from Sudzha protested in Kursk’s Red Square demanding the Kremlin officially recognize the conflict in their region as a war. The displaced residents are protesting poor temporary living conditions and lack of housing assistance after fleeing Ukrainian military advances in the Kursk region. When local official Anatoly Drogan termed the gathering illegal and demanded dispersal, protesters refused and criticized local leadership’s silence following Ukraine’s August 6 offensive into Sudzha. While officials promised a meeting with leadership, protesters were told they would meet with the district head instead of the governor. The Russian social network Vkontakte has blocked posts about the protest.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
Russia suffered record-high daily losses of 1,950 casualties, bringing total Russian casualties to 712,610. UK Defense Staff Chief Admiral Anthony Radakin confirmed high Russian losses, averaging 1,500 casualties daily in October. Despite these losses, Russian forces are making significant territorial gains in eastern Ukraine, particularly in Donetsk Oblast near Toretsk and Chasiv Yar, as well as near Kupiansk and in Kursk Oblast. Ukraine has lost 1,146 square kilometers since August, with Commander-in-Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi describing the current Russian offensive as “one of the most powerful” since the war began. The high casualty rate may have influenced Russia’s decision to deploy North Korean troops to supplement their forces.
| Troops +1950
712610 |
Tanks +23
9276 |
Artillery +38
20352 |
Arm. VEH +81
18847 |
Aircraft
369 |
Heli
329 |
Ships
28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian regions are heavily prioritizing military service incentives, with Stavropol Krai allocating 83% of its social budget to veteran payments. On average, Russian regions spend 13% of their budgets on one-time payments to contract soldiers. In over one-third of Russian regions, payments to veterans and families of deceased servicemembers now consume at least 25% of their entire regional budgets.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
