Summary of the day: In a day marked by strategic maneuvering, Russian forces consolidated their position northwest of Avdiivka, with potential advances prompting Ukrainian troops to consider retreating westward to stronger defensive lines. Concurrently, intensified Russian offensives near Avdiivka and Chasiv Yar could lead to operationally significant territory gains. Amid these developments, US officials expressed concerns that the latest US military aid might fall short in helping Ukraine reclaim all lost territories, emphasizing that Ukraine’s needs extend beyond foreign assistance as it tackles internal manpower challenges and seeks to bolster its defense industrial base. Meanwhile, Ukrainian forces achieved progress near Siversk, contrasting with Russian gains around Avdiivka and the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border. On the technological front, Russia is reportedly deploying drones designed to counter Ukrainian electronic warfare, a move possibly timed to anticipate the arrival of US security aid. In the broader geopolitical context, France’s President Macron called for European defense self-sufficiency, and the Kremlin furthered its international media influence by opening a “media school” in the Balkans, while President Putin defended the nationalization of Russian enterprises, including those in the defense sector.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War
Russia vetoed a UN Security Council resolution on April 24 to prevent a nuclear arms race in space, proposed by Japan and the U.S. Thirteen members voted in favor, with Russia against and China abstaining. Concerns arose after U.S. Congressman Mike Turner warned of a “serious national security threat,” allegedly linked to Russia’s desire to deploy a nuclear weapon in space. Sources suggest Russia may aim for a nuclear-powered device with electronic warfare capabilities. While not an active threat, it poses risks to satellite communications.
The European Parliament passed a resolution denouncing Russian President Vladimir Putin’s March election as illegitimate, Ukrinform reported on April 25. The election, held from March 15-17, resulted in Putin receiving 87.2% of the vote, but was widely criticized for lacking fairness and freedom. The resolution urges EU states and the international community not to recognize the election’s results due to its conduct in both Russia and occupied Ukrainian territories. It also calls for limiting relations with Putin to essential peace and humanitarian matters. Putin’s potential tenure could extend until 2036 following constitutional changes in 2021.
German Defense Minister Boris Pistorius, as reported by n-tv, stated that Russia is producing surplus arms and military equipment beyond its needs for the war in Ukraine, filling warehouses with weaponry. Despite Western attempts to curb Russian military output, Russia is investing heavily in arms production, devoting a record portion of its 2024 federal budget to military needs. Pistorius cautioned against assuming that Putin’s accumulation of weapons is merely precautionary, suggesting broader intentions. Russia’s significant arms production has given it a battlefield advantage, with Ukrainian forces struggling to match its output.
In a recent speech, French President Emmanuel Macron stressed the urgency for Europe to achieve autonomy in defense to safeguard its sovereignty. Highlighting the unbridled nature of the Russian threat, he urged a push for a credible European defense strategy, prioritizing European defense suppliers, and boosting cybersecurity. Macron also advocated for deeper defense collaboration with the UK and proposed a European academy for military training.
Russian Deputy Foreign Minister Sergei Ryabkov stated to state-controlled media that Russia might reduce diplomatic ties with the U.S. if frozen Russian assets are transferred to Ukraine. The U.S. recently passed the REPO Act, allowing the transfer of these assets to Ukraine, making it the first Western nation to do so. Ryabkov emphasized that Russia’s response would depend on further discussions. The EU holds the majority of frozen Russian assets, with the U.S. holding around $5 billion. While the U.S. seeks to direct these funds to Ukraine, European nations are cautious, exploring alternative uses for the assets’ profits, such as funding defense assistance for Ukraine.
Russia declared two Latvian diplomats persona non grata, retaliating against Latvia’s similar action against two Russian diplomats on March 27. The Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs cited this as a response to ongoing “hostile actions” from Latvia, warning of further “painful” measures if such actions continue. The delay in Russia’s response remains unexplained. Additionally, Kremlin officials have been actively portraying Latvia and other Baltic states as antagonistic towards Russia and Russian citizens residing there, with criticisms also targeting Latvia’s language policies in education.
Senior Belarusian officials have escalated their rhetoric against the West, echoing Russian narratives by making unfounded allegations of Western threats. Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko claimed that Belarusian opposition abroad, with NATO’s support, aims to seize parts of Belarus. Additionally, the head of the Belarusian KGB, Ivan Tretel, asserted that Belarusian security thwarted drone attacks from Lithuania on Minsk and accused Lithuania and Poland of developing combat drones for attacks and forming an extremist group for terrorist activities in Belarus. These claims have been dismissed by Lithuanian military spokesperson Major Gintautas Ciunis as “nonsense.”
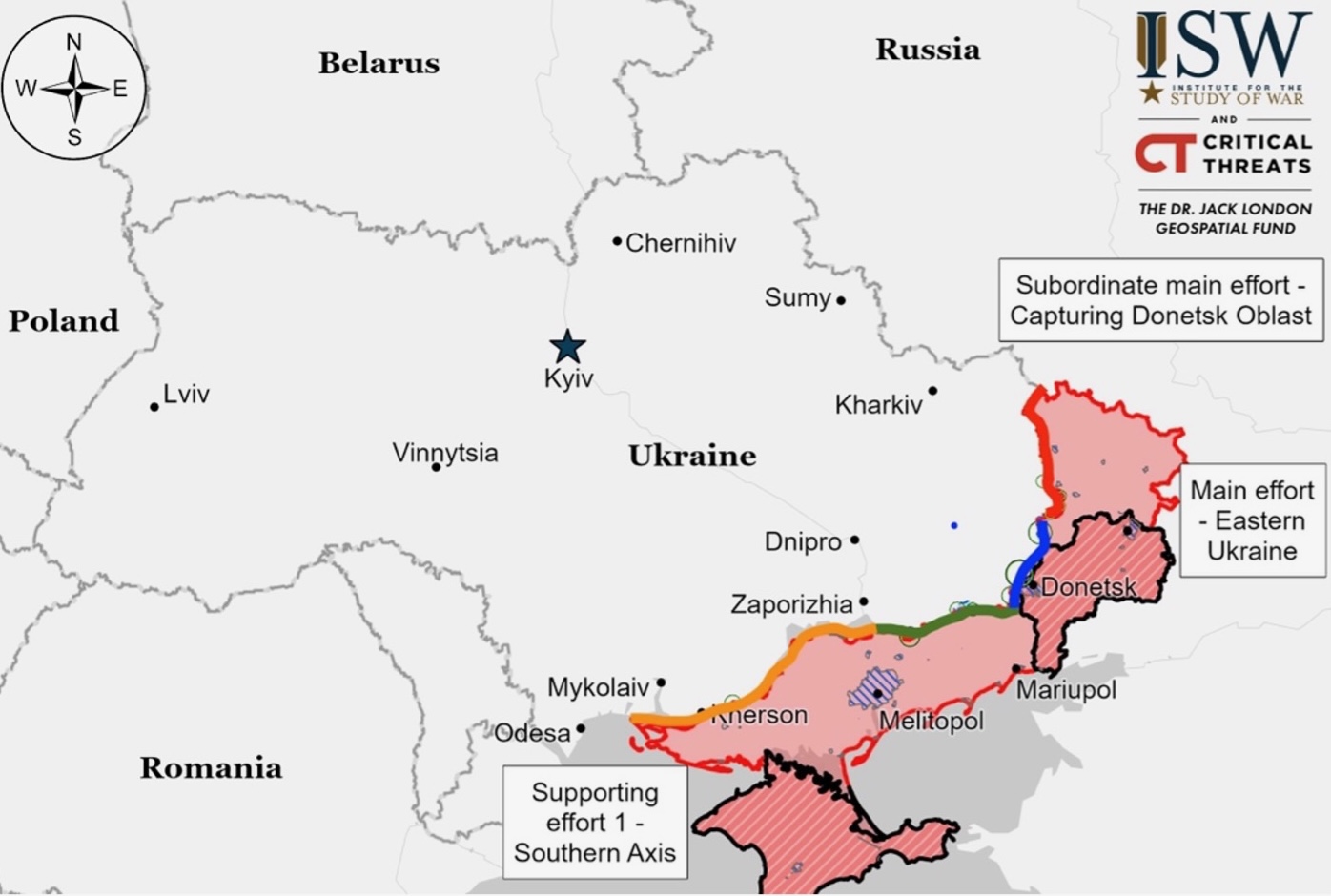
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
General Oleksander Syrskyi, an experienced artillery officer, assumed command of the Ukrainian Armed Forces on February 8, amidst a dire situation with severe ammunition shortages and Russian air superiority. Under his leadership, Ukraine’s military strategy has evolved from crisis management to more structured planning, emphasizing drone warfare as a primary tactic against Russian forces. Syrskyi’s approach includes utilizing drones extensively to inflict casualties and damage, significantly impacting Russian tank units and personnel, as highlighted by successful drone attacks near Avdiivka. Despite heavy losses and challenges, including a breakdown in relations between the military leadership and President Zelensky, Syrskyi has maintained discipline and effectiveness. His leadership saw the introduction of strategies that not only conserve manpower but also enhance operational capabilities, such as the strategic use of air defenses that downed several Russian aircraft. Syrskyi’s tenure marks a shift towards a more professional military structure, aiming to rejuvenate the armed forces by integrating new recruits and allowing veterans rest, reflecting a long-term vision to improve fighting efficiency and readiness. His actions and strategies indicate a focus on sustaining pressure on Russian forces, optimizing resources, and preparing for continued conflict, without explicitly claiming immediate victory.
Russian forces have significantly increased their drone deployments along the Russo-Ukrainian front line, aiming to exploit their technological advantage over Ukrainian electronic warfare systems. Recent reports indicate a doubling of drone activity in frontline hotspots, with these drones operating on frequency bands that challenge Ukrainian disruption efforts. This development underscores a temporary strategic advantage for Russia in the ongoing technology arms race within the conflict. In response, Ukraine is actively working to upgrade its electronic warfare systems to counter this emerging threat. This highlights the dynamic nature of modern warfare, where advancements in drone technology are reshaping military tactics and necessitating constant adaptation. Ukraine is also bolstering its defensive capabilities by acquiring jamming devices and enhancing its own attack drone capabilities to mitigate the impact of increased drone activity.
Ukrainian forces have withdrawn U.S.-supplied Abrams M1A1 tanks from the frontline due to heightened risk of detection by Russian drones, as confirmed by two U.S. military officials to the Associated Press (AP). The decision comes after the delivery of 31 tanks, announced in January 2023, with all vehicles received by October 2023. The officials cited increased drone surveillance, resulting in the loss of five Abrams tanks on the battlefield. As a response, the tanks have been temporarily removed from the frontline, with plans for the U.S. and Ukraine to adapt tactics. U.S. Joint Chiefs of Staff Chair Adm. Christopher Grady emphasized the need for new strategies to counter the evolving threat environment, including combined arms warfare tactics. Training on tank operation was provided in Germany in spring 2023, but Ukrainian utilization of the Abrams tanks and combined arms tactics has been limited since then. These updates were discussed ahead of the April 26 Ukraine Defense Contact Group meeting, marking the coalition’s two-year anniversary.
Ukrainian forces successfully thwarted a Russian reconnaissance group along the Sumy Oblast border.
The Ukrainian Special Operations Forces (SSO) destroyed a Russian Buk-M1 anti-aircraft missile complex, worth $100 million, before it launched any missiles. Discovered during reconnaissance, SSO relayed its coordinates to Ukrainian Defense Forces, promptly destroying it. Drone footage showed its destruction, although the weapon used was not specified. The Buk-M1 is designed to target aircraft and other aerial objects and has been previously used in conflicts. This adds to SSO’s recent destruction of Russian heavy equipment and soldiers.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Ukrainian forces engaged in positional battles along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line without any shift in the frontlines. Clashes occurred in areas northwest, southwest, west, and south of key locations such as Svatove, Kreminna, and the Serebryanske forest. Reports indicate Russian regiments from various divisions and army corps are actively involved in these engagements, deploying to different directions along the front.
Ukrainian forces were involved in ongoing positional fighting northeast of Bakhmut, in the Siversk area. Recent footage suggests that Ukraine has made advancements east of Verkhnokamyanske, although these are not new developments. The conflict also persists near Verkhnokamyanske and southeast of Siversk around Spirne and Vyimka.
Skirmishes around Chasiv Yar did not alter the frontlines significantly. Battles took place on the city’s eastern outskirts and the adjacent areas of Novyi Microraion and Ivanivske. While Russian forces reportedly made slight progress near Klishchiivka, this remains unverified. Russian airborne and motorized rifle units are engaged in the vicinity, with strategic caution from Russian command regarding further advances without securing positions on the southern flank near Ivanivske and Klishchiivka. Russian military preparations for potential assaults in these areas are underway.
Russian troops have bolstered their positions near Avdiivka, securing areas northwest of the city, including Novobakhmutivka and Solovyove. This has enabled them to establish a narrow salient, although it remains vulnerable to Ukrainian counterattacks. Since mid-April Russian forces have pushed forward up to five kilometers in certain sectors along the Avdiivka frontline. Despite these incremental territorial gains, the overall stability of Russian advancements is not guaranteed. Ukraine’s defenses have effectively slowed Russian progress since the fall of Avdiivka in February. The continuation of Russian offensive efforts, aiming to drive Ukrainian forces to more fortified lines, depends on a considerable investment of resources and could lead to a reconfiguration of Ukrainian defenses towards the west should Russian movements continue.
Russian forces are making tactical advances in areas west of Avdiivka and particularly targeting Chasiv Yar, aiming to consolidate gains before the anticipated U.S. aid bolsters Ukrainian defenses. There’s a pressing race against time as the U.S. expresses doubts that its support will enable Ukraine to recover all lost ground. This concern is heightened by the fact that Ukraine is not only grappling with equipment shortages but also faces a critical need for manpower. Despite this, Ukrainian defense strategies are evolving, with ongoing efforts to increase conscription and develop its defense industry, suggesting a focus on long-term military self-sufficiency. However, the urgency and potential effectiveness of Ukraine’s response may well depend on the swift integration of these new resources.
Russian forces are said to have progressed west of Donetsk City, with claims of a mechanized assault near Krasnohorivka. However, these reports lack visual confirmation. Attacks were also reported west and southwest of Donetsk City in areas like Krasnohorivka, Heorhiivka, Novomykhailivka, and Vodyane, with a Russian milblogger citing bomb strikes on Ukrainian positions. Ukrainian military commentary identifies the presence and operations of various Russian regiments and brigades along key tactical lines and within specific locations like Novomykhailivka.
Russian forces made progress southeast of Urozhaine, south of Velyka Novosilka, continuing their push in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border region. This advancement followed several days of intense air strikes and ground assaults. However, Ukrainian officials report that attacks near Staromayorske were repelled. Russian aerospace units are also involved, conducting bomb strikes in the area around Urozhaine.
Positional engagements persisted in western Zaporizhia Oblast, particularly near Robotyne and northwest of Verbove, with no shifts in the frontline reported. Russian forces are active near Hulyaipole, continuing their operations in the region.
Ongoing positional skirmishes were reported in east Kherson Oblast, particularly near Krynky. A Russian military blogger noted that Russian forces have ramped up drone activities and shelling in this area.
Ukrainian Civilian Victims Of War
The casualty count of Ukrainian civilians in the past 24 hours:
DEATHS: 0 INJURIES: 0
Ukraine News
Russian forces targeted Ukrainian transportation infrastructure with missile strikes, impacting railway and logistics hubs. Specific attacks included an Iskander-K missile strike on a connection point in Smila, Cherkasy Oblast, and another missile hit a railway station in Balaklia, Kharkiv Oblast, injuring civilians. Additionally, Ukrainian forces intercepted a cruise missile over Kryvyi Rih Raion, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, launched from an Su-57 over the Black Sea. This pattern of strikes appears aimed at disrupting Ukrainian logistics, potentially to hinder the distribution of incoming U.S. security assistance and affect Ukraine’s frontline resupply capabilities.
Kyiv has restored over 1,000 units of electrical equipment, fixing 70% of the damage caused by Russian attacks with drones and missiles.
Ukrainian journalist and soldier Alla Pushkarchuk, known as “Ruta,” was killed in action in Donetsk Oblast. Her former colleague, Dmytro Krapyvenko, confirmed her death. Pushkarchuk worked at the Weekly and Chytomo, focusing on cultural and political projects. With a background in theater studies, she aimed to become a theater critic.
Ukraine’s Allies
President Volodymyr Zelensky announced that Ukraine has intelligence indicating Russia plans to disrupt the upcoming Global Peace Summit scheduled for June 15-16 in Switzerland. According to Zelensky, Russia intends to reduce country participation and prolong the conflict, opposing the summit’s goal to formulate a global consensus on peace in Ukraine. The summit, to be held at the Burgenstock resort near Lucerne, expects participation from 80 to 100 countries. Despite not being invited, Russia will receive a peace plan summary through representatives. Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov dismissed the summit’s effectiveness without Russia’s involvement, while Zelensky emphasized he would not negotiate with Vladimir Putin, labeling him a murderer.
The United States plans to announce a $6 billion military aid contract for Ukraine, according to Politico’s April 25 report. President Joe Biden signed a $61 billion foreign aid bill on April 23, with the weapons package drawing from these funds. The contract includes Patriot air defense systems, artillery, drones, and more, expected to be finalized by April 26. However, due to the Ukraine Security Assistance Initiative (USAI), these weapons won’t reach Ukraine for several years. U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin is likely to announce this aid at the Ukraine Defense Contact Group meeting on April 26. Additionally, an immediate $1 billion package was announced on April 24, including air defense missiles and fighting vehicles. The New York Times revealed that over 100 Army Tactical Missile Systems were shipped to Ukraine secretly last week. Delays in military aid have worsened Ukraine’s battlefield challenges, with critical shortages in ammunition and air defense systems.
Zelensky expressed Ukraine’s intent to collaborate with the U.S., regardless of the outcome of the upcoming presidential election, in an interview with Fox News. He noted differences in views but emphasized working together based on common values. Zelensky extended invitations to Trump to visit Ukraine, which were declined. Ukraine remains committed to working with the U.S., its strategic partner and global leader, under any presidency chosen by the American people.
The Danish parliament approved an additional 4.4 billion Danish kroner ($633 million) for military support to Ukraine in 2024, announced by the Danish Foreign Ministry on April 25. This increases the total funding to 64.8 billion Danish kroner ($9.3 billion) for 2023-2028. Danish Defense Minister Troels Lund Poulsen emphasized Denmark’s continuous support for Ukraine during the ongoing conflict. The military aid will cover weapons, equipment, and training, including purchases from Danish and foreign defense industries.
Italy, Ukraine, and UNESCO will sign an agreement to rebuild Odesa and its damaged Transfiguration Cathedral, Italian Foreign Minister Antonio Tajani announced on April 24. Russian strikes in July 2023 partially destroyed the cathedral, causing casualties. Italy previously pledged 500,000 euros for roof repairs. Tajani stated the deal will be signed in Rome on May 15. UNESCO estimates Ukraine lost $19 billion in tourism revenue due to the war and needs $9 billion over 10 years for cultural and tourism sector recovery.
Greek Prime Minister Mitsotakis stated in an April 25 interview with Iefimerida that Greece will not supply Ukraine with Patriot air defense systems or S-300 missiles, citing the importance of these systems for Greek air security. Despite requests and Ukraine’s air defense shortage, Greece will not compromise its own deterrence capabilities.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian President Vladimir Putin defended the nationalization of Russian enterprises, including those in the defense industry, as necessary when owners’ actions damage national interests. This justification was given at the Congress of Russian Union of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs, amidst ongoing legal actions against company owners. Reports indicate that since the 2022 invasion of Ukraine, Russia has targeted over 180 companies for nationalization, impacting a range of industries from rare earths and defense to non-military sectors like car dealerships. These nationalizations are said to account for a substantial economic value, reflecting a significant shift in control to the state.
Russian defense industries are experiencing labor shortages, a situation President Putin acknowledged at an April 25 congress, noting that migrant labor won’t resolve the issue and new solutions are needed. Recent reports include a drone strike in St. Petersburg leading to staff departures at the Special Technology Center, which manufactures reconnaissance drones. The center is contemplating an “electronic warfare dome” to protect itself, though this poses further complications. Additionally, the Kingisepp Machine Building Plant, also in St. Petersburg, faces challenges with its largely Uzbek workforce, with frequent raids causing many to leave. In response, the plant is incentivizing employees with bonuses for recruitment and promotional activities.
Russia’s Allies
China is continuing to indirectly aid Russia’s military efforts in Ukraine by supplying dual-use goods that can be used for both civilian and military purposes. U.S. Ambassador to NATO, Julianne Smith, noted that these supplies include machine tools, microelectronics, drone technologies, and materials for gunpowder production, though there is no evidence of China providing lethal weaponry to Russia.
A North Korean cargo ship linked to arms smuggling for Russia has been stuck at a Chinese port for months. The ship, named Angara, has reportedly been transporting military cargo from North Korea to Russia. The U.S. State Department acknowledges the reports, indicating a possible violation of U.N. resolutions. The vessel, sanctioned by the U.S. in 2022, has made multiple trips between North Korea and Russia. Despite inquiries, Chinese and Russian authorities remain silent on the matter.
Russian Narratives and Propaganda
The Kremlin-backed Russian milblogger channel Rybar has launched a “media school” in the Balkans, aimed at extending Russia’s informational influence. They conducted training in Serbia and Republika Srpska, teaching participants to create and manage Telegram channels, curate content, and counteract misinformation. This move aligns with broader Russian objectives to strengthen its global media presence and follows high-level talks between Russian officials and Balkan leaders to deepen cooperation.
Kremlin officials have intensified their information campaigns in response to the U.S. secretly supplying Ukraine with long-range ATACMS missiles in April 2024. Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov stated that these weapons will not alter the war’s outcome in Ukraine’s favor, asserting that Russia will ultimately prevail. Russian Foreign Affairs spokesperson Maria Zakharova criticized the U.S. move as contrary to peace efforts and supportive of terrorism, while Russian Ambassador to the U.S., Anatoly Antonov, viewed it as escalating U.S.-Russia tensions. Confirmations of the missile supply were made by U.S. Ambassador to Ukraine, Bridget Brink, and Deputy Spokesperson of the U.S. Department of State, Vedant Patel.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
