Summary of the Day:
Russian forces are intensifying mechanized assaults in Ukraine, aiming to make significant tactical gains before muddy fall conditions hamper movement. Recent Russian advancements have been reported near Kreminna, Siversk, Toretsk, Pokrovsk, and Robotyne. The Russian military command is likely pushing for a high tempo of operations to consolidate positions before weather deteriorates, potentially complicating both mechanized and infantry maneuvers in fall 2024 and early winter 2024-2025.
U.S. European Command Commander and NATO Supreme Allied Commander Europe, General Christopher Cavoli, reportedly stated that the United States is withholding several weapon systems and military communications networks from Ukraine that could support its war effort. Meanwhile, South Korean Defense Minister Kim Yong-hyun reported that a limited number of North Korean military personnel are likely operating near occupied Donetsk City.
Concerns have been raised about Russia’s continued use of chemical weapons in Ukraine, violating the Chemical Weapons Convention. Additionally, Russia has banned the partially-encrypted communications platform Discord, potentially disrupting some frontline Russian forces’ communications. In a separate development, Russian arms dealer Viktor Bout reportedly brokered a $10 million arms deal between Russia and Yemen’s Houthi rebels in August 2024, amid deepening Russo-Iranian cooperation.
Picture of the Day:
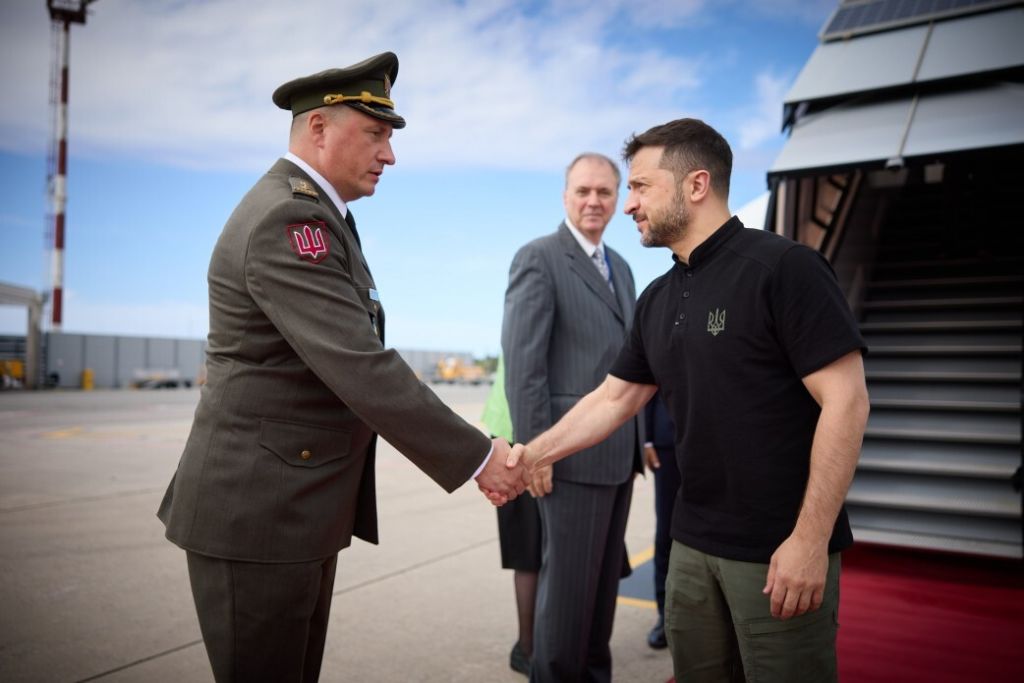 President Volodymyr Zelensky (L) attends the Ukraine-Southeast Europe Summit in Dubrovnik, Croatia. Zelenskyy held separate meetings with the Prime Minister of Albania, Edi Rama, the Prime Minister of North Macedonia, Hristijan Mickoski, the Prime Minister of Greece, Kyriakos Mitsotakis and the President of Slovenia, Natasa Pirc Musar. (Ukrainian Presidency / Handout/Anadolu via Getty Images)
President Volodymyr Zelensky (L) attends the Ukraine-Southeast Europe Summit in Dubrovnik, Croatia. Zelenskyy held separate meetings with the Prime Minister of Albania, Edi Rama, the Prime Minister of North Macedonia, Hristijan Mickoski, the Prime Minister of Greece, Kyriakos Mitsotakis and the President of Slovenia, Natasa Pirc Musar. (Ukrainian Presidency / Handout/Anadolu via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Malian forces, likely aided by Russian Wagner mercenaries, reportedly killed seven civilians and injured three in a drone strike on October 5-6 in northern Mali. The attack targeted areas controlled by Tuareg separatists fighting for the independence of Azawad. The strike hit a convoy of gold mine workers near Tinzaouatene, destroying two vehicles. This incident follows July clashes where Tuareg rebels killed dozens of Wagner troops. The rebels, known as CSP-DPA, also claimed a successful ambush against Wagner mercenaries on October 2. Local residents have condemned the violence and demand an end to what they see as aggression and occupation. The situation highlights ongoing tensions in the region, with Russian mercenaries accused of aiding the Malian government in controlling natural resources.
In August 2024, Viktor Bout, a Russian arms dealer and Ulyanovsk Oblast parliamentarian, reportedly helped negotiate a $10 million arms deal between Russia and Yemen’s Houthi rebels. According to the Wall Street Journal, the deal primarily involves AK-74 rifles, with potential for Kornet antitank missiles and anti-air weapons. Deliveries could begin in October 2024 through Hodeidah Port, disguised as food supplies. This development comes amid reports of Russia’s involvement in talks to transfer Yakhont anti-ship missiles to the Houthis, possibly aiming to use Iranian proxies to indirectly confront the West and influence decisions regarding support for Ukraine.
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), led by Russia, met in Moscow. They adopted plans for a “Eurasian security architecture” and a “deradicalization” system. At the meetings, Russian President Putin and Belarusian President Lukashenko praised the Soviet Union’s role in World War II and accused Western countries of supporting Nazism by aiding Ukraine.
The Russian Defense Ministry reported that Russian and Chinese naval forces conducted joint patrols and anti-submarine drills in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. These activities followed the conclusion of the “Beibu/Interaction-2024” military exercises involving both countries.
Lithuania has fortified a bridge linking it to Russia’s Kaliningrad exclave, deploying obstacles and reinforcing it with iron beams. Defense Minister Laurynas Kasciunas stated that other bridges to Kaliningrad will also be fortified, with some possibly mined. This action comes amid heightened tensions between NATO and Russia following the invasion of Ukraine. Lithuania, bordering both Belarus and Kaliningrad, is particularly vulnerable in a potential conflict. The country has been a strong supporter of Ukraine, providing military aid and recently repurposing seized Russian military supplies for Ukraine’s benefit. Tensions were further highlighted by recent incidents involving pro-Russian symbols on trains traveling through Lithuania.
NATO is evolving into its “3.0” version, returning to its original role as a deterrent against threats, primarily from Russia, according to Finnish President Alexander Stubb. Finland, which joined NATO in early 2023 after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, emphasizes the importance of collective defense and deterrence.
The Path to Peace
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky visited Croatia or the third “Ukraine – South East Europe” summit and a meeting with Croatian Prime Minister Andrey Plenkovich. The summit includes leaders from several Balkan and Eastern European countries, with discussions focusing on peace, Ukraine’s NATO and EU aspirations, and reconstruction efforts. Zelensky and Plenkovich are also set to address defense cooperation and the rehabilitation of wounded Ukrainian soldiers. During his visit, Zelensky emphasized the need for decisive action to end Russia’s war against Ukraine by 2025, highlighting the opportunity for peace in the coming months despite challenges on the front line, particularly in Donetsk Oblast. He mentioned Ukraine’s recent withdrawal from Vuhledar, while Russia concentrates on Pokrovsk and Toretsk. Zelensky also discussed Ukraine’s ongoing work on a peace formula and a five-point victory plan, which was presented to U.S. President Joe Biden in September, stating that its full implementation would prevent Russia from threatening Europe further.
Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban expressed strong support for Donald Trump in the upcoming U.S. presidential election during a news conference in Strasbourg. Orban, known for his pro-Russian stance and opposition to aid for Ukraine, claimed Trump would immediately work to end the war in Ukraine if elected, without waiting for inauguration. Orban has previously met with Russian President Putin, Chinese leader Xi Jinping, and Trump on a “peace tour.” Trump has repeatedly claimed he could end the Russia-Ukraine war quickly but has not provided specific plans. Orban urged European leaders to prepare for swift action in response to a potential Trump victory.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Russian forces are intensifying mechanized assaults in Ukraine, aiming to make significant advances before fall 2024’s muddy conditions limit movement. Ukrainian National Guard Spokesperson Ruslan Muzychuk reported increased use of armored vehicles in the Kharkiv and Pokrovsk areas, with large-scale attacks occurring in western Donetsk Oblast and along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line since late July 2024. The goal is to capture key settlements like Kurakhove and Pokrovsk for further operations. As fall approaches, loss of foliage will reduce infantry cover, making them more vulnerable to Ukrainian drones and tactical strikes, especially in the Pokrovsk area.
Despite these challenges, Russian forces are likely to continue offensive operations through the mud season and unfavorable weather. This strategy, directed by President Putin, aims to maintain pressure on Ukrainian forces across the frontline, preventing them from regrouping. While Russian forces have depleted many reserves during their Summer 2024 Donetsk offensive and are expected to reach culmination in the coming months, they may continue fighting beyond this point based on past patterns.
South Korean Defense Minister Kim Yong-hyun reported on October 8 that a small number of North Korean military personnel are likely operating near occupied Donetsk City in Ukraine. This statement follows a report of Ukrainian missile strikes killing several North Korean officials in the area on October 3. Ukrainian official Lt. Andriy Kovalenko added that these personnel, mainly engineers, are working in occupied Donetsk Oblast to improve the quality of ammunition that North Korea supplied to the Russian military.
The Ukrainian Support Forces Command reported that Russian forces continue to use chemical weapons in Ukraine, violating the Chemical Weapons Convention. In September 2024 alone, there were 250 cases of Russian forces using munitions containing unknown chemical agents. Since February 2023, Ukraine has recorded 4,228 instances of Russian chemical weapons use. Russia employs K-51 and RG-VO grenade launchers to deploy riot control agents, which are prohibited in combat by the Convention. This systematic use of chemical substances in combat by Russian forces has been increasingly reported.
Ukrainian resistance group Atesh reported conducting surveillance on a Russian naval arsenal in Sevastopol, Crimea. The 17th arsenal, which supplies ammunition and equipment to Russia’s Black Sea Fleet, was observed to have heightened security measures. Atesh also monitored missile deliveries to S-300 air defense systems near the Kerch Bridge and tracked fuel distribution from a logistics hub in Crimea.
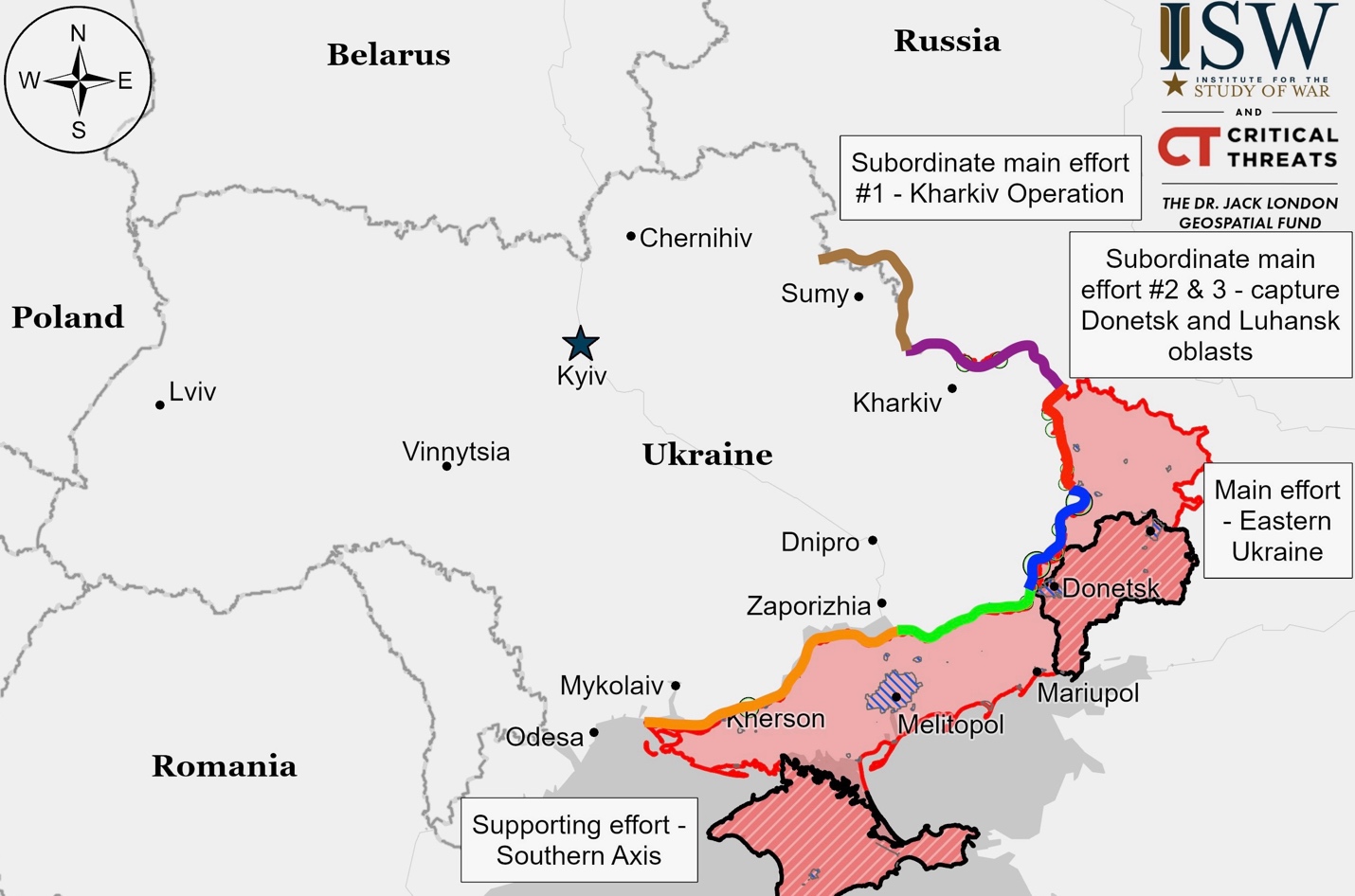
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Ukrainian forces continued their offensive in the Kursk Oblast. Russian sources reported ongoing Ukrainian ground attacks in several areas: east of Korenevo near Olgovka; southeast of Korenevo near Lyubimovka and Plekhovo; and northeast of Sudzha near Russkoye Porechnoye, Cherkasskoye Porechnoye, and Martynovka. These attacks represent a sustained effort by Ukrainian forces to advance in the main Ukrainian salient in this region of Russia.
Ukrainian and Russian forces clashed in Glushkovsky Raion, west of Ukraine’s main position in Kursk Oblast. Neither side made confirmed progress. Reports suggest Ukrainian attacks near Veseloye, while Russian sources claim their own offensive near Novy Put. Russian airborne units are reportedly active in the area. No significant territorial changes were reported.
Russian forces reportedly made advances in Ukraine’s main salient in Kursk Oblast. The Russian Ministry of Defense claims to have captured Novaya Sorochina and Pokrovsky. Russian sources also report taking part of Lyubimovka, though these claims lack visual confirmation. Attacks were reported near Daryino, Lyubimovka, and Plekhovo. The situation remains fluid with ongoing combat in the area.
Ukraine’s intelligence agency (GUR) reported damaging a Russian minesweeper, the Alexander Obukhov, in Baltiysk, Kaliningrad Oblast. The operation allegedly created a hole in the ship’s gas pipe, causing water to enter the engine. The vessel was docked at the time and is now undergoing repairs by the Russian military.
Ukrainian forces reportedly conducted multiple strikes on Russian military facilities. One attack targeted the 67th Arsenal of Russia’s Main Missile and Artillery Directorate, an ammunition storage facility near Karachev in Bryansk Oblast. This depot allegedly housed various weapons, including North Korean and Iranian-supplied ammunition, missiles, and guided aerial bombs. Local residents reported air raid sirens and multiple explosions, with video evidence showing a fire and explosions in the area. Another strike hit a storage facility for Iranian-made Shahed drones near Oktyabrsky village in Russia’s Krasnodar Krai, reportedly housing about 400 drones. This attack was conducted by Ukraine’s Navy and Security Service (SBU).
Russia claimed to have shot down 47 Ukrainian drones overnight, including 24 over Bryansk Oblast, but did not report any damage. These attacks follow a recent Ukrainian strike on another major Russian ammunition arsenal, highlighting Ukraine’s efforts to disrupt enemy logistics and reduce Russia’s ability to launch attacks on Ukrainian cities, despite facing a disadvantage in artillery shell quantities. The incidents also underscore Russia’s reliance on North Korean munitions supplies and extensive use of Shahed drones, with over 1,300 such attacks in September alone.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces advanced in Vovchansk, northern Kharkiv Oblast, likely recapturing the Vovchansk Aggregate Plant. Attacks continued near Vovchansk and Starytsya. Russians are reportedly building extensive trenches and underground routes in the area. Ukrainian officials noted increased use of glide bombs by Russian aviation.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces advanced northwest of Kreminna and continued operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line. They progressed southeast of Makiivka and attacked multiple settlements including Synkivka, Kucherivka, and Kruhlyakivka near Kupyansk; Vyshneve and Novovodyane near Svatove; and several locations around Kreminna. Russian drone units are reportedly active in the Kupyansk area.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces made advances near Siversk. They captured parts of Verkhnokamyanske and areas east of Hryhorivka. Russian sources claimed further gains in Hryhorivka, Serebryanka, and near Spirne, but these are unconfirmed. Ukrainian officials reported Russian forces using motorcycles and older Soviet vehicles in their attacks. Assaults continued near Ivano-Darivka and Spirne.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued their offensive near Chasiv Yar with no confirmed frontline changes. They attacked in and around Chasiv Yar, including near Minkivka, Kalynivka, Stupochky, Bila Hora, and towards Oleksandro-Shultyne. Russian sources claimed advances in Zhovtnevyi Microraion of Chasiv Yar, but this is unverified. Russian drone operators are reportedly active in the area.
Toretsk
Russian forces advanced in southern Toretsk, pushing along Heroiv Pratsi, Peremohy, and Konstytutsyi streets. They also entered eastern Toretsk, moving along Tsentralna Street towards the Tsentralna Mine. Russian troops are attacking in small groups, with special forces reportedly operating in the town. Assaults continue around Toretsk, including near Dyliivka, Shcherbynivka, Nelipivka, Niu York, and Sukha Balka. Russian sources claim further advances in central Toretsk, but these are unconfirmed.
Pokrovsk
Ukrainian forces advanced into northwestern Mykolaivka, east of Pokrovsk. Russian forces made gains north of Novohrodivka and in central Zhelanne Pershe, southeast of Pokrovsk. Russian claims of capturing Zoryane Pershe and other advances are unconfirmed. Russian reconnaissance groups are reportedly preparing for attacks near Selydove. Fighting continues in various settlements east and southeast of Pokrovsk, including Novotoretske, Myrolyubivka, Novohrodivka, and Hirnyk.
West of Donetsk City
Russian forces continued attacks west of Donetsk City targeting Maksymilyanivka, Heorhiivka, Hostre, Kurakhivka, and Kurakhove. Ukrainian forces reportedly repelled a large Russian mechanized assault in the Kurakhove area, damaging four armored vehicles. Russian special forces are said to be operating in the southern Donetsk region.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces continued attacks southwest of Donetsk City. They claimed to have captured Zolota Nyva and advanced near Vuhledar, but these claims are unconfirmed. Fighting persists around several settlements including Kostyantynivka, Vodyane, and Bohoyavlenka.
On October 8, the Russian Defense Ministry released footage showing Russian forces using D-74 122mm artillery guns near Vuhledar, Donetsk Oblast. These guns, first introduced in 1956, are rare in Russian service. A Russian military blogger suggested that Russia might seek to acquire more of these systems or related supplies from countries like North Korea, Vietnam, China, or Algeria, which still use them.
A Russian Su-57 fighter jet shot down its own S-70 Okhotnik drone near Kostyantynivka in Ukraine’s Donetsk region on October 5, 2024. The drone malfunctioned and was at risk of entering Ukrainian airspace. Ukrainian forces recovered the wreckage, revealing that the S-70’s advertised advanced features, including stealth technology and AI-powered systems, were largely exaggerated. Initial analysis suggests the drone was more basic than claimed, described by one expert as “more like a glider with basic flight capabilities.” The incident occurred during what appears to have been a combat test mission, as evidenced by a recovered 250 kg aerial glide bomb found among the wreckage.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
There were no reports of fighting in the border area between Donetsk and Zaporizhia Oblasts according to both Russian and Ukrainian sources.
Zaporizhia Line
Russian forces made a small advance in southwestern Kamyanske, south of Stepnohirsk, in western Zaporizhia Oblast. They claim to be pushing further into central Kamyanske. Russian attacks also occurred near Robotyne and towards Novodanylivka. Various Russian military units, including special forces and artillery, are reportedly active in the area.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces continued attacks in the Kherson direction from October 7-9, with no confirmed frontline changes. A Russian source claimed that Russian Airborne forces lack proper equipment and training for assaults on Dnipro River islands. A Russian reserve unit is reportedly active in the area.
Ukraine News
Russia launched missile and drone attacks against Ukraine on October 7-8. They fired ballistic missiles at Odesa Oblast and deployed 19 drones from Krasnodar Krai. Ukrainian forces intercepted 18 drones across several oblasts. A civilian ship in Odesa’s port was hit. Russian forces also struck Kostyantynivka with glide bombs, targeted Kharkiv Oblast and City with various weapons, and launched airstrikes on Kherson City. The Russian military claimed to have hit an ammunition depot in Sumy Oblast.
On October 8-9, Russia launched missile and drone strikes against Ukraine. They fired three ballistic missiles from Kursk Oblast and 22 drones from Krasnodar Krai and Crimea. Ukrainian forces shot down 21 drones over Odesa, Vinnytsia, and Kyiv oblasts. Kharkiv City was hit twice with glide bombs. In Odesa Oblast, drone strikes caused fires in apartment buildings in Chornomorsk and Odesa City.
The Belarusian monitoring group Hajun Project reported that an unidentified air target entered Ukraine from Belarus in the morning of October 8.
The Security Service of Ukraine (SBU) has arrested a 23-year-old man from Pokrovsk for allegedly spying on Ukrainian military positions. The suspect was reportedly recruited through a dating site by a woman claiming to be a Russian agent. He was tasked with scouting locations of Ukrainian forces in the Pokrovsk and Sumy regions and monitoring the results of Russian airstrikes. The SBU seized the phones used for this activity. If convicted, the man faces up to 12 years in prison. This incident highlights the ongoing use of dating platforms for intelligence gathering by both Russian and Ukrainian sides in the conflict.
Ukrainska Pravda (UP), a major Ukrainian news outlet, has reported “ongoing and systematic pressure” from President Volodymyr Zelensky’s office, claiming attempts to influence their editorial policy. UP alleges officials are being ordered not to communicate with their journalists, and businesses are pressured to stop advertising with them. The outlet vowed to make public any future attempts at pressure. This situation raises concerns about press freedom in Ukraine, with Reporters Without Borders noting a “worrying decline” in media autonomy. UP’s editor-in-chief, Sevgil Musayeva, emphasized the importance of maintaining freedom of speech in Ukraine’s democracy.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 48 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 6+ INJURIES: 11
Russian missiles struck Odesa Oblast in southern Ukraine killing at least six people and injuring 11 others, all Ukrainian citizens. The attack targeted a Panamanian container ship, Shui Spirit. Governor Oleh Kiper reported that seven victims are in serious condition. Officials emphasized the need to stop such attacks to maintain Ukraine’s role in global food security.
Ukraine’s Allies
The 25th Ukraine Defense Contact Group meeting in Ramstein, Germany, originally scheduled for October 12, 2024, has been postponed. The meeting was to coincide with US President Joe Biden’s visit to Germany, which was canceled due to Hurricane Milton. The gathering, involving leaders from over 50 nations, was expected to discuss Ukraine’s “Victory Plan” and potentially lift restrictions on using long-range weapons on Russian soil. A new date hasn’t been announced, but it may align with the NATO Defense Ministers meeting in Brussels on October 17-18. German Chancellor Olaf Scholz expressed disappointment at the postponement, which Ukrainian officials had extensively prepared for. The delay is not seen as diminishing Ukraine’s importance in US foreign policy.
US European Command Commander and NATO Supreme Allied Commander Europe General Christopher Cavoli reportedly informed Congress in September 2024 that several US weapon systems and military communication networks, which could aid Ukraine’s war effort, are being withheld. According to CNN, these include the air-launched Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile (JASSM) and the Link 16 data sharing network. The report doesn’t explain the reasons for withholding these systems, though an unnamed source suggested operational security concerns may be behind the decision not to provide the Link 16 system.
President Volodymyr Zelensky announced plans to meet leaders of the U.K., Germany, France, and Italy in the coming days. He will discuss Ukraine’s military strengthening and present a five-point victory plan, previously shared with U.S. President Biden. Zelensky’s schedule includes meetings with British Prime Minister Keir Starmer and NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte in London, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz and President Frank-Walter Steinmeier in Berlin, and Pope Francis. The Ramstein-format meeting in Germany was postponed due to Biden canceling his overseas travel.
France is training 2,300 Ukrainian soldiers of the Anne de Kyiv brigade in its Grand Est region, marking the first time a foreign country has trained a full Ukrainian brigade on its territory. The program, involving realistic combat simulations, includes training on French equipment such as AMX10 RC tanks, Milan missiles, and Caesar artillery systems. France has also trained Ukrainian pilots on Alpha Jets and plans to provide Mirage 2000-5 planes. Ukrainian Defense Minister Rustem Umerov and French officials, including President Emmanuel Macron, are set to meet with some of the 15,000 Ukrainian troops trained by France since Russia’s full-scale invasion. France has also supplied Ukraine with long-range SCALP missiles and is part of a coalition to provide medium- and long-range missiles and bombs to Kyiv.
EU countries have approved a €35 billion loan to support Ukraine’s economy, using Russia’s frozen Central Bank assets as collateral. This is part of a larger G7 plan to provide €45 billion in aid to Kyiv. The loan, expected to be distributed early next year, will be flexible in its use. Separately, Hungary announced it would block a key sanctions reform until after the U.S. presidential election. The proposed amendment aims to extend the renewal period for sanctions on Russia’s frozen assets from 6 to 36 months, addressing concerns about potential disruptions to the plan.
Germany has delivered two IRIS-T anti-aircraft systems to Ukraine, with two more expected by year-end, according to German Major General Christian Freuding. Chancellor Olaf Scholz announced an additional order of 17 IRIS-T systems, bringing the total to 24 systems to be delivered by 2026. This support comes as Ukraine seeks more air defense capabilities to counter Russian strikes on energy infrastructure. While Germany has become Ukraine’s second-largest military donor after the U.S., Chancellor Scholz remains hesitant to supply Taurus long-range missiles.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Seven Ukrainian children, aged 3 to 17, have been returned from Russian-occupied areas of Kherson, Zaporizhzhia, and Luhansk regions as part of the “Bring Kids Back UA” initiative. Andrii Yermak, Head of the President’s Office, reported that these children and their families endured difficult conditions in occupied territories. Adults faced repeated interrogations, while children were subjected to Russian propaganda through “patriotic education lessons” and other events. This successful repatriation highlights ongoing efforts to reunite Ukrainian families affected by the conflict.
Russia News
On October 8, Russian Deputy Defense Minister Anna Tsivileva visited a military hospital in Rostov-on-Don and met with leaders of the Donetsk and Luhansk People’s Republics. This visit appears to be part of the Russian Defense Ministry’s efforts to showcase improved medical care for soldiers injured in Ukraine.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1080
665200 |
Tanks +1
8945 |
Artillery +41
19263 |
Arm. VEH +14
17765 |
Aircraft +1
369 |
Heli
328 |
Ships
28 |
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
The Russian Africa Corps opened a recruitment center in St. Petersburg on October 9. They’re offering new recruits a significant bonus: a regional payment of 1.7 million rubles (about $17,494) for signing a contract, plus a federal payment of 400,000 rubles (about $4,116) upon joining a military unit.
Recent reports suggest Russian forces may have depleted their stockpile of aerial bombs for glide bomb attacks. Ukrainian spokesperson Vitaliy Sarantsev claims Russia is now using bombs produced just days ago, indicating a reliance on new production and logistics. This development follows Ukrainian strikes on Russian ammunition warehouses, potentially forcing Russia to reorganize its logistics systems to mitigate the impact of such attacks.
Russian state defense conglomerate Rostec announced on October 8 and 9 that its subsidiaries delivered new batches of unspecified quantities of Russian BMP-3 and BDM-4M infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) and Su-34 bomber jets to the Russian MoD.[98] Rostec reported that its subsidiary Kurganmashzavod increased production of the IFVs by 20 percent from January to September 2024 compared to January to September 2023.[99]
Russia’s Allies
Satellite images from October 3 show large numbers of tanks and armored vehicles, possibly in poor condition from combat use, at two Belarusian repair facilities: the 140th Repair Plant and 814th Maintenance Center. This unusual concentration suggests these centers may be repairing and restoring armored vehicles for the Russian military. Additionally, on October 9, a Russian MiG-31K interceptor capable of carrying Kinzhal hypersonic missiles landed at Belarus’ Machulishchy airfield, as reported by the Belaruski Hajun monitoring group. This is the first such landing in 18 months, with the last MiG-31Ks leaving Belarus in April 2023. While Belarus isn’t directly involved in the war, it allows Russia to use its territory for operations against Ukraine. The Kinzhal missile, with a 2,000-kilometer range, poses a significant threat to all of Ukraine. Ukrainian air defenses have reportedly intercepted 25 out of 63 Kinzhal missiles since the start of the full-scale invasion.
European Commission chief Ursula von der Leyen criticized Hungary’s stance on Russia’s war in Ukraine during a European Parliament session. She rebuked Hungary for blaming Ukraine rather than Russia for the conflict, drawing a parallel to Hungary’s 1956 uprising against Soviet rule. Von der Leyen also expressed concern over Hungary’s simplified visa process for Russian nationals. Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban rejected these criticisms, dismissing them as “political propaganda” and denying similarities between the current conflict and the 1956 uprising. Hungary has consistently blocked aid to Ukraine and pushed for negotiations, while refusing to supply weapons, despite condemning Russia’s invasion.
Controlling the Narrative and Russian Propaganda
Russia banned Discord, a partially-encrypted communications platform, potentially disrupting some frontline Russian forces’ communications. The ban follows Russian fines against Discord for non-compliance with censorship laws. Some Russian troops, including drone operators, use Discord to coordinate operations. This move, along with recent restrictions on personal electronic devices at the front, may hinder military communications. Russian military bloggers have criticized the lack of adequate alternative communication systems, with one Kremlin-affiliated blogger noting that the Russian Ministry of Defense has failed to address this issue for three years, though claiming troops have managed to use other services successfully.
Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov renewed vague threats of escalation. This appears to be part of Russia’s strategy to discourage Western countries from allowing Ukraine to use Western-supplied weapons against military targets inside Russia. The Kremlin aims to influence Western decision-making through these implicit warnings.
Russian officials, including the Investigative Committee, Foreign Ministry spokesperson Maria Zakharova, and the Russian Embassy in the UK, repeated claims that Ukraine is using chemical weapons in combat. These accusations likely aim to deflect attention from Russia’s own documented use of chemical weapons in Ukraine.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
