Summary of the Day:
Russian forces advanced along multiple fronts near Siversk, Pokrovsk, and Kurakhove, though they faced a significant setback near Bilohorivka. The failed assault by the 123rd Motorized Rifle Brigade led to heavy losses and sparked outrage among Russian military bloggers, who criticized commanders for inflating battlefield successes to secure promotions.
In notable Russian losses, Major General Pavel Klimenko, commander of the 5th Motorized Rifle Brigade, was killed near Kurakhove, along with sniper commander Pavel “Joker” Apalkov near Chasiv Yar. Ukrainian authorities have documented a sharp increase in Russian executions of POWs in 2024, with 124 cases under investigation, primarily in Donetsk Oblast.
On the diplomatic front, President Putin addressed the Valdai Discussion Club, seeking improved relations with US President-elect Trump while demanding an end to sanctions and Ukraine support. Meanwhile, Ukrainian strikes have successfully disrupted three major Russian oil refineries – Volgograd, Ilsky, and Yaisky – exposing Russia’s vulnerability to Western sanctions and equipment shortages. Russian authorities are reportedly attempting to strengthen their hold on occupied territories by creating artificial volunteer battalions merged with existing Cossack organizations.
Picture of the Day:
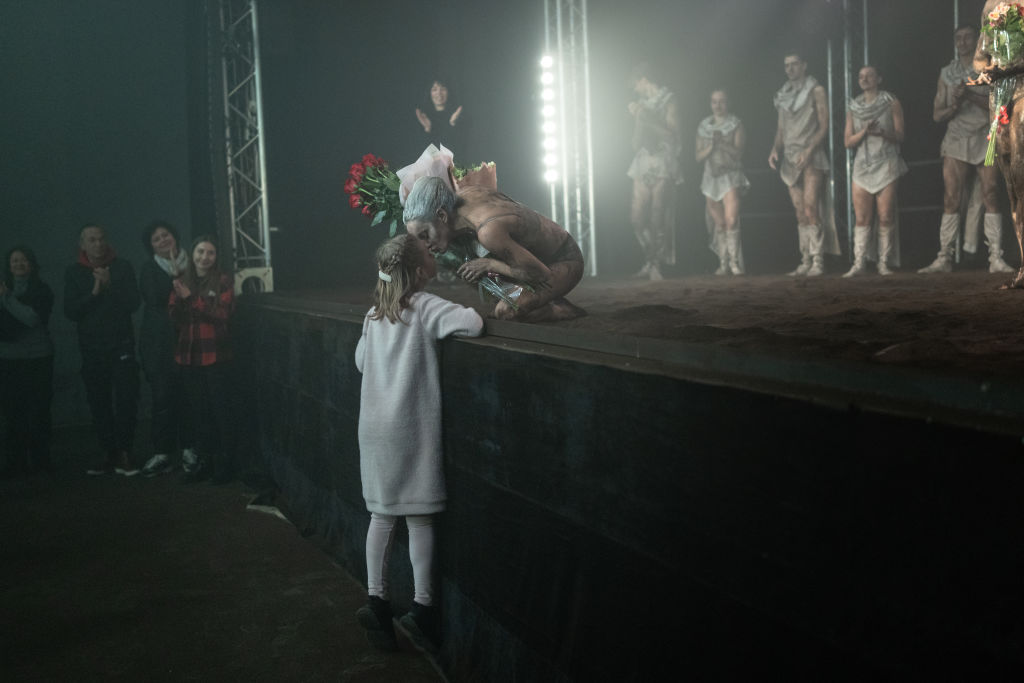 Dancer Antonina Radievska kisses her daughter at the end of the show “Drakony” created by the Ukrainian composer Maksym Kolomiets at the Kharkiv National Opera and Ballet in Kharkiv. The theater resumed operating earlier this year in a basement below the main auditorium. Kharkiv is only 40 km from the Russian border and is a regular target of Russian attacks. (Diego Fedele/Getty Images)
Dancer Antonina Radievska kisses her daughter at the end of the show “Drakony” created by the Ukrainian composer Maksym Kolomiets at the Kharkiv National Opera and Ballet in Kharkiv. The theater resumed operating earlier this year in a basement below the main auditorium. Kharkiv is only 40 km from the Russian border and is a regular target of Russian attacks. (Diego Fedele/Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
A disturbing escalation in international tensions has emerged with Lithuania’s revelation of an alleged Russian military intelligence plot targeting civilian cargo aircraft. This dangerous development threatens not just aviation safety but marks a potential expansion of conflict beyond the Ukraine war into civilian infrastructure of NATO countries. The discovery of incendiary devices in Germany, Poland, and the UK represents a concerning shift from military confrontation to targeting civilian transportation systems, risking a broader international crisis. Lithuania’s President has demanded NATO action, highlighting the serious implications for global stability. The targeting of civilian aircraft – a tactic historically associated with terrorism – signals a potentially dangerous new phase in East-West relations that could undermine peace efforts and international cooperation. U.S. officials, while maintaining there’s no immediate threat to flights, acknowledge the need for heightened vigilance, underscoring the growing challenges to maintaining global peace and security.
The escalating repression in Belarus under Alexander Lukashenko represents a growing threat to regional stability and international peace. His intensifying crackdown – including mass arrests, doubled treason convictions, and systematic destruction of civil society – creates dangerous tensions along NATO’s eastern border. As a key Russian ally and staging ground for Moscow’s military activities, Belarus’s increasing authoritarianism and suppression of democratic voices heightens the risk of broader regional conflict. The imprisonment of over 1,300 political opponents and shutdown of 1,700 non-profit organizations eliminates crucial channels for peaceful dialogue and conflict resolution. Opposition leader Tsikhanouskaya’s exile and the targeting of social media groups further isolates Belarus from international democratic norms, potentially destabilizing the delicate balance between East and West. This democratic backsliding in a strategically located nation poses significant risks to European security and global peace efforts.
The Path to Peace
At the Valdai Discussion Club in Sochi, Russian President Vladimir Putin extended an olive branch following Donald Trump’s victory in the 2024 U.S. presidential election, suggesting renewed diplomatic relations and expressing readiness for discussions about the “Ukrainian crisis.” According to Russian news outlet Verstka, Putin initially sent informal congratulations through intermediaries rather than making an official call, though Kremlin spokesperson Peskov denied this report as “unreliable.” While advocating for improved international cooperation, Putin emphasized the need for lifting U.S. sanctions and reducing support for Ukraine as prerequisites. His vision of international harmony, which includes promoting BRICS as a peaceful alternative to NATO, contrasts with Russia’s strengthening ties to Iran, North Korea, and China.
Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal expressed cautious optimism about continued U.S. support, citing bipartisan Congressional backing and a positive phone call between Trump and President Zelensky. Ukrainian officials drew parallels to Ronald Reagan’s firm stance toward Moscow, hoping for a “peace through strength” approach under the new administration. The Wall Street Journal reported on November 6 that President-elect Trump’s team was considering a proposal to end the war that would include delaying Ukraine’s NATO membership for at least 20 years while maintaining arms supplies, freezing the conflict along current front lines where Russia occupies roughly 20% of Ukrainian territory, and establishing an 800-mile demilitarized zone in the east, potentially monitored by European troops. Two advisors, retired General Keith Kellogg and Fred Fleitz, suggested conditioning military aid to Ukraine on peace negotiations with Russia.
Russian Security Council Secretary Sergei Shoigu called for the West to acknowledge Russia’s advantage in the war and begin negotiations as Russian forces advance in Donetsk Oblast. Both Kyiv and Moscow have dismissed Trump’s claim of ending the war within 24 hours, with Ukraine refusing to recognize Russian occupation while maintaining some territories may require diplomatic resolution. Trump, who has previously praised Putin and called Russia’s invasion “genius,” reportedly had multiple undisclosed conversations with Putin after leaving office. Other Russian officials, including Foreign Minister Lavrov and former President Medvedev, also sent informal congratulations, though some expect no fundamental changes in U.S. foreign policy. The Kremlin officially maintains its position that the U.S. is an “unfriendly country involved in a war against Russia,” while Russia, currently holding battlefield advantage, shows little interest in settlement.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Two Russian commanders have been reported killed in recent combat operations in Ukraine. Major General Pavel Klimenko, commander of the 5th Motorized Rifle Brigade, was killed near Kurakhove. Klimenko, who had served in occupied Crimea and was promoted to Major General in May 2024, was previously linked to the torture of conscientious objectors near Donetsk City. Additionally, Pavel “Joker” Apalkov, a sniper platoon commander from the 88th “Hispaniola” Volunteer Brigade, was killed near Chasiv Yar.
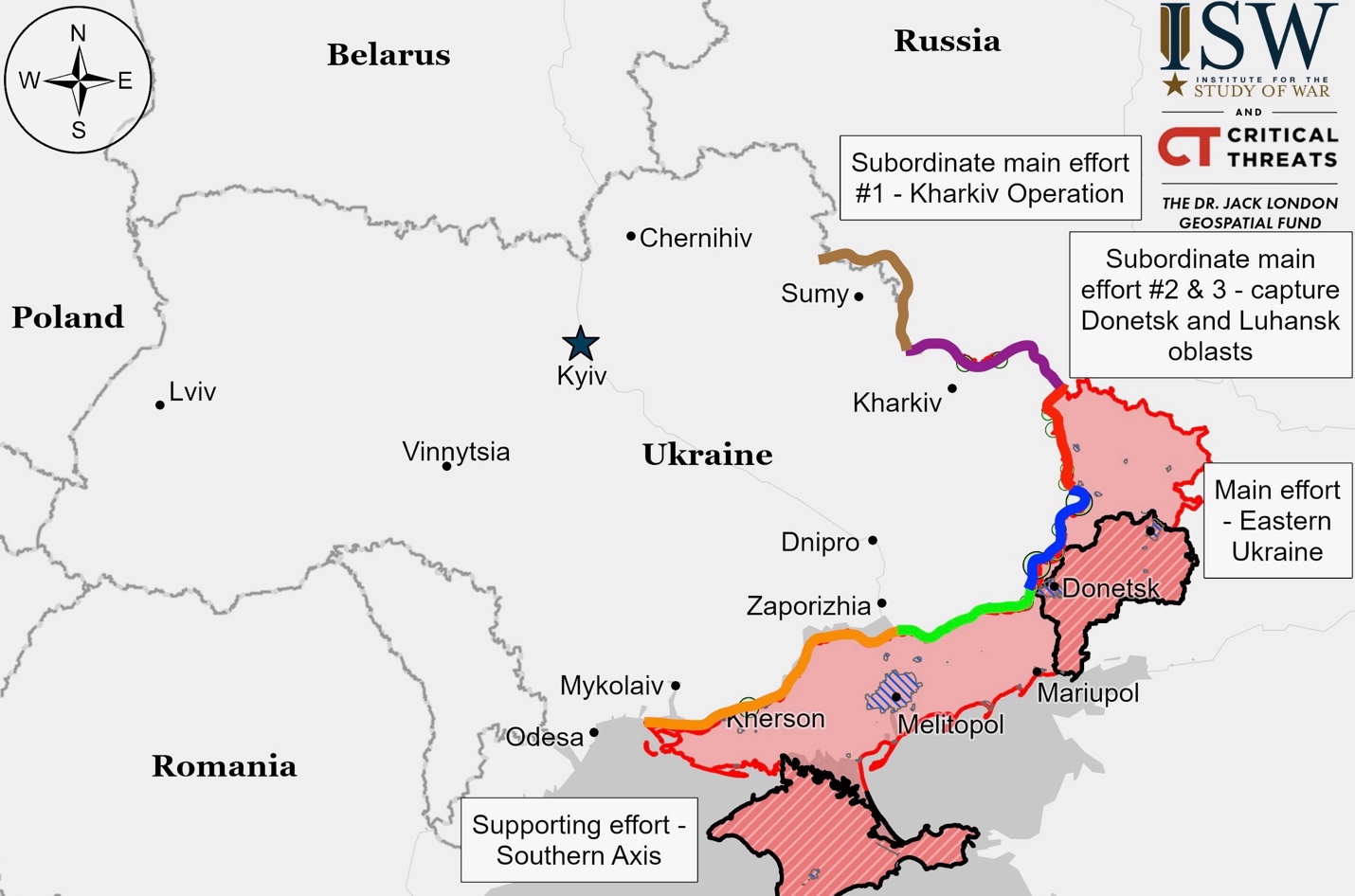
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Russian and Ukrainian forces clashed near Novoivanovka and Darino southeast of Korenevo, and near Plekhovo south of Sudzha in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast with no territorial changes reported. Russian forces reportedly struck a Ukrainian position near Cherkasskoye Porechnoye with a glide bomb. A Ukrainian commander noted that Russian forces in this area operate with fewer armored vehicles and less artillery compared to other fronts, particularly Donetsk Oblast. The Glushkovsky region remained quiet with no reported combat activity.
Ukraine reportedly conducted a drone attack on Kaspiysk, a Russian port city in Dagestan located about 1,000 kilometers from the front line. According to Ukrainian military intelligence sources, the strike damaged at least two Russian missile ships, the Tatarstan and Dagestan. The attack is significant as it targeted a route previously considered safe for Iranian weapons deliveries to Russia. The nearby Makhachkala airport suspended operations following the incident, which reportedly involved a Ukrainian A-22 Flying Fox drone.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched unsuccessful offensive operations near Vovchansk and Starytsya, northeast of Kharkiv City. A Ukrainian brigade spokesperson reported that Ukrainian forces had reclaimed approximately 400 hectares of territory and several strategic forest areas in northern Kharkiv Oblast during October 2024.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces conducted multiple offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line but failed to gain ground. The attacks focused on several locations: near Synkivka (northeast of Kupyansk); Petropavlivka and Kucherivka (east of Kupyansk); Kruhlyakivka, Kolisynkivka, and Lozova (southeast of Kupyansk); Druzhelyubivka and Hrekivka (southwest of Svatove); Makiivka and Katerynivka (northwest of Kreminna); and near Torske, Terny, Serebryanka, and Dibrova (west and southwest of Kreminna).
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces made advances near Siversk with confirmed movement south of Verkhnokamyanske. They also claimed advances northwest of Zolotarivka and near Ivano-Darivka, though these claims lack visual confirmation. Additional Russian operations continued around Bilohorivka, Hryhorivka, and Pereizne
Russian ultranationalist military bloggers are criticizing a failed Russian assault near Bilohorivka, northeast of Siversk. The 123rd Motorized Rifle Brigade reportedly launched an ill-conceived frontal attack on November 2, resulting in heavy losses of personnel, tanks, and infantry vehicles. The bloggers accused Russian commanders of routinely inflating battlefield successes in reports to senior leadership to secure promotions, citing the Russian Ministry of Defense’s false claim of capturing Serebryanka in late October. Bilohorivka has been a particularly contentious location since May 2022, when Russian forces suffered a devastating defeat during a failed river crossing attempt.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces attacked Chasiv Yar and nearby settlements of Stupochky, Bila Hora, and Klishchiivka though no confirmed advances were made despite claims of gaining 1.5 kilometers southeast of Chasiv Yar.
Toretsk
Russian forces attacked Toretsk and nearby areas of Dyliivka and Shcherbynivka but made no advances, partly due to poor weather. Russia has reportedly deployed about 21,000 troops, 50 tanks, and 240 armored vehicles in the Toretsk area, with limited reserve forces from the 132nd Separate Motorized Rifle Brigade.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces advanced south of Pokrovsk capturing Novooleksiivka with their 80th Tank Regiment. They also continued attacks near Myrolyubivka, Promin, Selydove, Krutyi Yar, Novohrodivka, Sukhyi Yar, and Lysivka, though claims of advances near Lysivka and Hryhorivka lack visual confirmation.
Kurakhove
Russian forces advanced north of Kurakhove with confirmed gains in northern Novoselydivka and Illinka. They also attacked Kurakhove itself and nearby settlements of Novodmytrivka, Kreminna Balka, Sontsivka, and Maksymilyanivka. While Russia claimed to have captured Kreminna Balka and made advances in Novodmytrivka, these claims remain unconfirmed.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces continued attacks near Vuhledar without new advances, though earlier footage from October 31 showed gains northwest of Vodyane. They claimed to have captured Antonivka and Maksymivka, while continuing operations near Katerynivka, Dalne, and Trudove.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces made a small advance in western Zaporizhia Oblast moving to a position northeast of Nesteryanka, near Robotyne. Ukrainian officials reported that Russian forces continued their attacks near Novoandriivka in the same area.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces attempted attacks along the Dnipro River in eastern Kherson Oblast, but Ukrainian officials reported they made no advances.
Ukraine News
In a major overnight attack lasting eight hours from midnight until morning, Russia launched 106 drones against Ukraine from multiple locations including Crimea and regions in southern Russia, marking a serious escalation in urban warfare that threatens civilian peace and international stability. Ukrainian forces intercepted 74 drones across eleven regions, while 25 others were disabled by electronic warfare, with Ukrainian officials revealing that up to half of Russian drones are decoys using 3D-printed balls wrapped in foil to confuse radar systems. The attacks caused minor damage in Kyiv and damaged infrastructure in Odesa, while deliberately targeting civilian infrastructure including a hospital, restaurant, and residential buildings, causing fires at a medical center, high-rise buildings, and industrial sites; in a separate incident, Russian forces struck Zaporizhzhia City with glide bombs, injuring 33 civilians.
Ukrainian prosecutors report a sharp increase in Russian executions of Ukrainian prisoners of war (POWs) in 2024. Denys Lysenko, head of Ukraine’s Department for Combating War Crimes, announced that authorities are investigating 49 cases involving 124 executed POWs. Most of these executions occurred in Donetsk Oblast, where 62 POWs were killed in 17 separate incidents, with additional cases in Zaporizhia and Kharkiv regions. These actions violate the Geneva Convention on POW treatment, and evidence suggests Russian commanders have enabled or failed to punish these war crimes.
Ukrainian military personnel have expressed mixed reactions to Donald Trump’s 2024 presidential victory. While some soldiers see potential opportunities in Trump’s unpredictable nature and desire to prove superiority over Putin, others worry about possible compromises with Russia. Servicemembers like Andriy and “Diego Rodriguez” acknowledge that Trump’s business-minded approach could either increase military support or lead to concerning compromises with Russia. Soldiers in the Donetsk region remain cautiously optimistic, hoping Trump will continue and potentially strengthen the military support established under Biden’s administration. Overall, Ukrainian forces emphasize that while they prefer stability, they must adapt to any changes in U.S. leadership, focusing on their primary goal of achieving victory rather than concessions to Russia.
Ukraine may resume commercial flights by late January 2025, according to Marsh McLennan Senior Partner Crispin Ellison. While Lviv Airport is considered safer for insurance purposes, President Zelensky prefers reopening Boryspil International Airport near Kyiv first. The resumption requires at least $750 million in insurance coverage per aircraft and depends on adequate air defense capabilities. Ukraine’s airspace has been closed since Russia’s invasion in February 2022, though earlier forecasts suggested restrictions might last until 2029.
The revelation that a top Ukrainian presidential aide, Oleh Tatarov, made multiple trips to Moscow between 2014-2019 raises serious security concerns during Russia’s ongoing invasion. Tatarov’s undisclosed visits to Moscow and Russian-occupied Crimea, combined with his previous role under pro-Kremlin President Yanukovych and a dismissed corruption case, could impact Ukraine’s wartime leadership credibility. Despite these concerns, President Zelensky has defended keeping Tatarov in his sensitive position, citing his counterintelligence work against Chechen operatives. The controversy emerges at a critical time when Ukraine relies heavily on Western support and trust in its war effort against Russian aggression.
The looming end of Ukraine’s gas transit agreement with Russia in December 2024 has significant implications for the war effort. The lack of a viable alternative deal, despite talks with Azerbaijan, potentially strengthens Russia’s leverage over key European nations, particularly Hungary, Slovakia, and Austria, which remain heavily dependent on Russian gas. This energy dependency could weaken European unity in supporting Ukraine, especially as Hungary already seeks to increase its Russian gas purchases. The situation is further complicated by suggestions that Azerbaijan’s proposed alternative might be rebranded Russian gas, potentially providing Moscow with continued economic benefits despite wartime sanctions. This energy dilemma highlights the ongoing challenge of reducing Europe’s reliance on Russian resources while maintaining unified support for Ukraine’s defense efforts.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 11 INJURIES: 80
Russian forces launched five guided aerial bomb strikes on Zaporizhzhia killing nine people, including a 1-year-old boy, and wounding 42 others. The attack damaged a cancer hospital and residential buildings. Among the injured were three children: a 4-month-old girl and two boys aged 5 and 15. Search and rescue operations continue.
A Russian aerial bomb struck a 12-story apartment building in Kharkiv’s Saltivskyi district injuring 25 people, with five requiring hospitalizations. The attack, launched from occupied Donetsk Oblast, caused a fire and extensive damage. Additional strikes hit the city center and a residential neighborhood, damaging buildings and infrastructure, though no casualties were reported in these incidents. Search and rescue operations continue.
Russian forces attacked 21 settlements across Kherson Oblast, including the city of Kherson, resulting in one death and eight injuries.
A Russian aerial bomb attack on the Yampil community in Sumy Oblast killed one person and injured another.
Russian forces launched a prolonged drone attack on Kyiv, with air defenses intercepting over 30 unmanned aerial vehicles. Falling debris damaged buildings across six districts, injuring at least two people. The air raid alert lasted eight hours.
A Russian drone strike on Odesa damaged multiple residential buildings, 14 cars, and a gas pipeline, with falling debris injuring a 30-year-old man who was treated at the scene.
A Russian attack in the village of Sukhi Yaly, Donetsk Oblast, resulted in one injury.
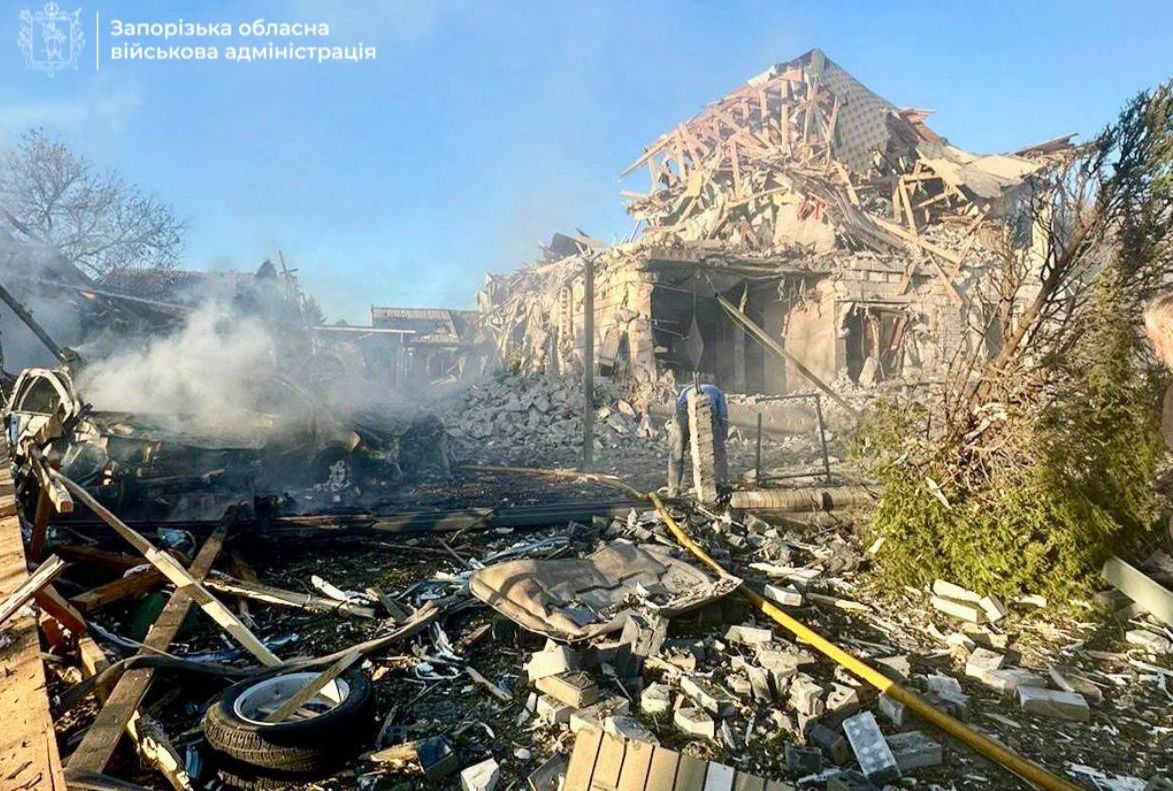 The aftermath of a Russian attack against Zaporizhzhia. (Governor Ivan Fedorov/Telegram)
The aftermath of a Russian attack against Zaporizhzhia. (Governor Ivan Fedorov/Telegram)
 The aftermath of a Russian attack on an apartment building in Kharkiv. (Oleh Syniehubov / Telegram)
The aftermath of a Russian attack on an apartment building in Kharkiv. (Oleh Syniehubov / Telegram)
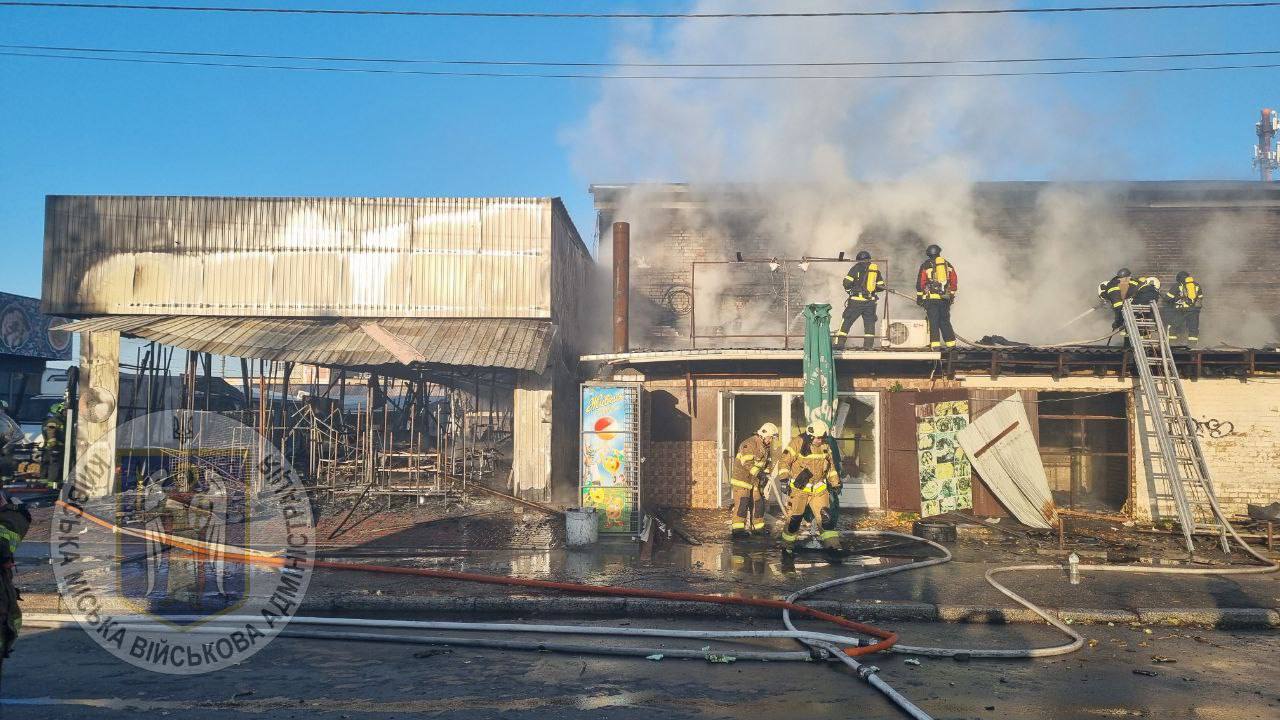 The aftermath of the Russian drone strike against Ukraine’s capital, Kyiv. (The Kyiv City Military Administration / Telegram)
The aftermath of the Russian drone strike against Ukraine’s capital, Kyiv. (The Kyiv City Military Administration / Telegram)
Ukraine’s Allies
At the European Political Community Summit in Budapest on November 7, President Zelensky addressed concerns about Donald Trump’s recent electoral victory and its implications for Ukraine’s support, emphasizing Europe must remain united against Russian aggression and stressing that peace cannot be achieved through weakness; while Zelensky acknowledged Trump’s desire to end the conflict quickly, he admitted he lacks details of any specific plan and expressed worry that a hasty resolution could harm Ukraine, despite having what he called an “excellent” phone conversation with Trump and stating “we hope that America will become stronger.” He specifically rejected suggestions of territorial concessions to Russia and criticized the West’s limited response to North Korea’s involvement in the conflict, which includes sending approximately 10,000-12,000 soldiers to support Russia, with North Korean troops now stationed in Russia’s Kursk region. The situation is particularly critical as Russian forces continue making their fastest advances in months in Donetsk Oblast, while questions arise about future Western support, especially given Trump’s claim that he could end the war within “24 hours” if returned to office, with reports suggesting his plan might include postponing Ukraine’s NATO membership and establishing a demilitarized zone in the east.
South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol announced his country may reconsider its position on providing weapons to Ukraine, prompted by North Korea’s reported deployment of 12,000 troops to Russia’s Kursk Oblast to support the war against Ukraine; while South Korea has previously only supplied humanitarian and non-lethal aid, this policy might change given its significant military capabilities, including large stockpiles of artillery ammunition – notably 3.4 million 105mm rounds that could be compatible with Ukrainian weapons, particularly significant as the current Ukrainian military requires approximately 75,000 shells monthly to maintain its defensive positions, while Russian forces reportedly receive about half their shell supply from North Korea. In a related development, Yoon Suk Yeol and Donald Trump held a 12-minute phone conversation discussing several key issues, including North Korea’s nuclear capabilities and missile tests, as well as trilateral relations between the U.S., South Korea, and Japan, and shipbuilding industry cooperation, with the two leaders agreeing to meet in person in the future.
The UK announced its largest sanctions package against Russia since May 2023, targeting 56 entities including the Africa Corps mercenary group, Wagner Group-linked companies, and military suppliers. The sanctions specifically target Russia’s defense industry network, including 28 companies in China, Central Asia, and Turkey that supply military components. The Africa Corps, which replaced Wagner Group after its 2023 rebellion and Prigozhin’s death, was sanctioned along with other mercenary groups for human rights violations in Libya, Mali, and the Central African Republic. The package also includes sanctions against Russian military intelligence officer Denis Sergeev, linked to the 2018 Salisbury poisoning.
According to German media outlet Berliner Zeitung, following Germany’s coalition government collapse, former Finance Minister Christian Lindner claims he was dismissed by Chancellor Olaf Scholz over disagreements about Ukraine aid, where Lindner opposed transferring 3 billion euros to Ukraine and instead proposed sending long-range Taurus cruise missiles, which Scholz has consistently refused to provide, while Scholz reportedly sought to increase Ukraine support to 15 billion euros by suspending debt brake rules; despite this political dispute that may trigger snap elections, sources from the budget committee indicate that most of the promised 4 billion euros ($4.3 billion) in aid to Ukraine can still be provided in 2025, even without formal budget approval, although Germany’s 2024 budget included 7.6 billion euros in military assistance while the 2025 draft reportedly halved this amount. The political instability raises concerns due to the rising influence of the Kremlin-friendly AfD party, which opposes Ukraine funding, though Germany has become the second-largest provider of military aid to Ukraine after the U.S. despite initial criticism for slow response.
The International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) announced plans to reduce arbitration costs for foreign investors involved in Ukraine’s reconstruction projects. Speaking at the Kyiv International Economic Forum, ICC Secretary General John Denton emphasized the importance of dispute settlement access for foreign investors. The ICC, which facilitated $17.5 trillion in economic activity last year, aims to help Ukrainian businesses expand into South American, African, and Asian markets. The organization will provide Ukrainian small and medium-sized businesses access to its One Click digital platform in Ukrainian and is working on developing a new Black Sea initiative following Russia’s withdrawal from the previous agreement in July 2023. While Ukraine’s economy shows some improvement from its 29.1% GDP drop in 2022, investment remains low due to war risks and corruption concerns.
Russia News
Ukrainian intelligence reports significant disruptions to Russia’s oil industry due to combined pressures from Ukrainian strikes and Western sanctions. Three major Russian refineries – Volgograd, Ilsky (Krasnodar), and Yaisky (Kemerovo) – partially suspended operations in October 2024 after failing to repair damage from Ukrainian attacks. Russia’s inability to obtain Western equipment due to sanctions has hampered repairs, with domestic manufacturers only able to supply 30-45% of needed components. Attempts to use Chinese replacements have faced compatibility issues, leading to increased costs and reduced refining capacity, which is affecting Russia’s fuel supply and export capabilities.
Vladimir Putin appointed Vladimir Uyba as the new Deputy Head of Medical Services at Russia’s Defense Ministry. Uyba had just stepped down from his previous role as leader of the Komi Republic two days earlier.
A Russian Kh-59MK cruise missile debris found in Ukraine revealed significant modifications, indicating potential supply chain issues. The missile was missing its active radar homing seeker, replaced with a metal block for weight balance, and used an older Ukrainian-made engine from Soviet-era stocks. These modifications suggest Russia is struggling with component shortages for complex missile parts and likely reduce the missile’s accuracy and range. This follows a pattern seen in previous instances where Russia has used modified missiles with substitute parts in attacks on Ukraine.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1580
705880 |
Tanks +9
9233 |
Artillery +32
20226 |
Arm. VEH +49
18661 |
Aircraft
369 |
Heli
329 |
Ships
28 |
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian authorities are forming paper-only volunteer battalions in occupied Ukraine, merging them with Cossack groups. According to the Ukrainian Resistance Center, these units are funded by Russia but largely exist just to create an illusion of local support. The Cossack organizations are being used to establish military reserves and police services using local residents.
Voronezh Oblast has increased recruitment referral bonuses from 50,000 ($510) to 75,000 ($765) rubles for residents who help recruit other locals into the Russian military, part of a broader pattern of Russian regions offering incentives for military recruitment.
Russia’s Defense Ministry reports that since launching a digital verification system on November 1, it has processed 52,000 veteran status certificates for Ukraine war veterans, with another 48,000 applications pending review.
Russia’s Defense Ministry is upgrading its combat drones to evade Ukrainian electronic warfare, according to former Ukrainian General Ihor Romanenko. The new drones reportedly use AI and fiber optic cables for control systems that resist jamming. Following Ukraine’s destruction of Russia’s A-50 radar aircraft, Russian forces are shifting to tactical drones with 100+ kilometer range for reconnaissance missions.
Russia is rapidly expanding its drone capabilities on multiple fronts: The new “Molot” anti-drone gun targets UAVs within 200 meters using heat-seeking munitions. The SuperCam reconnaissance drone has been upgraded with a precise laser scanner. According to a Ukrainian expert, Russia has tripled its long-range drone production from 17 to 50 daily, with plans to reach 90 per day. Meanwhile, Russian troops are reportedly manufacturing improvised drone munitions in field labs due to supply shortages.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
