Summary of the Day:
Russia faces deepening economic and military challenges as it enters 2025. Putin has significantly reduced compensation for wounded soldiers, with severe injuries now receiving 4 million rubles ($40,136) while minor injuries get just 100,000 rubles ($1,015). The policy shift reveals mounting pressure from war costs and sanctions. Meanwhile, Russia’s defense industry cannot match battlefield losses, producing only 20 tank and artillery barrels monthly while losing about 320.
Russian forces advanced in several areas, conducting a mechanized assault on Kupyansk, though Ukrainian officials maintain control of the city. Additional Russian advances were reported in Kursk Oblast, Chasiv Yar direction, and along the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border area. Evidence suggests North Korea may be supporting Russia’s artillery shortages, with Russian military bloggers sharing images of North Korean M1989 “Koksan” self-propelled artillery systems being transported through Krasnoyarsk.
The Kremlin faces serious demographic challenges, with labor shortages reaching 4.8 million people and population expected to decline by over 600,000 annually until 2032. Despite these issues, a state poll indicates 83% of Russians feel unaffected by the war, concerning officials about public indifference as the conflict continues.
Picture of the Day:
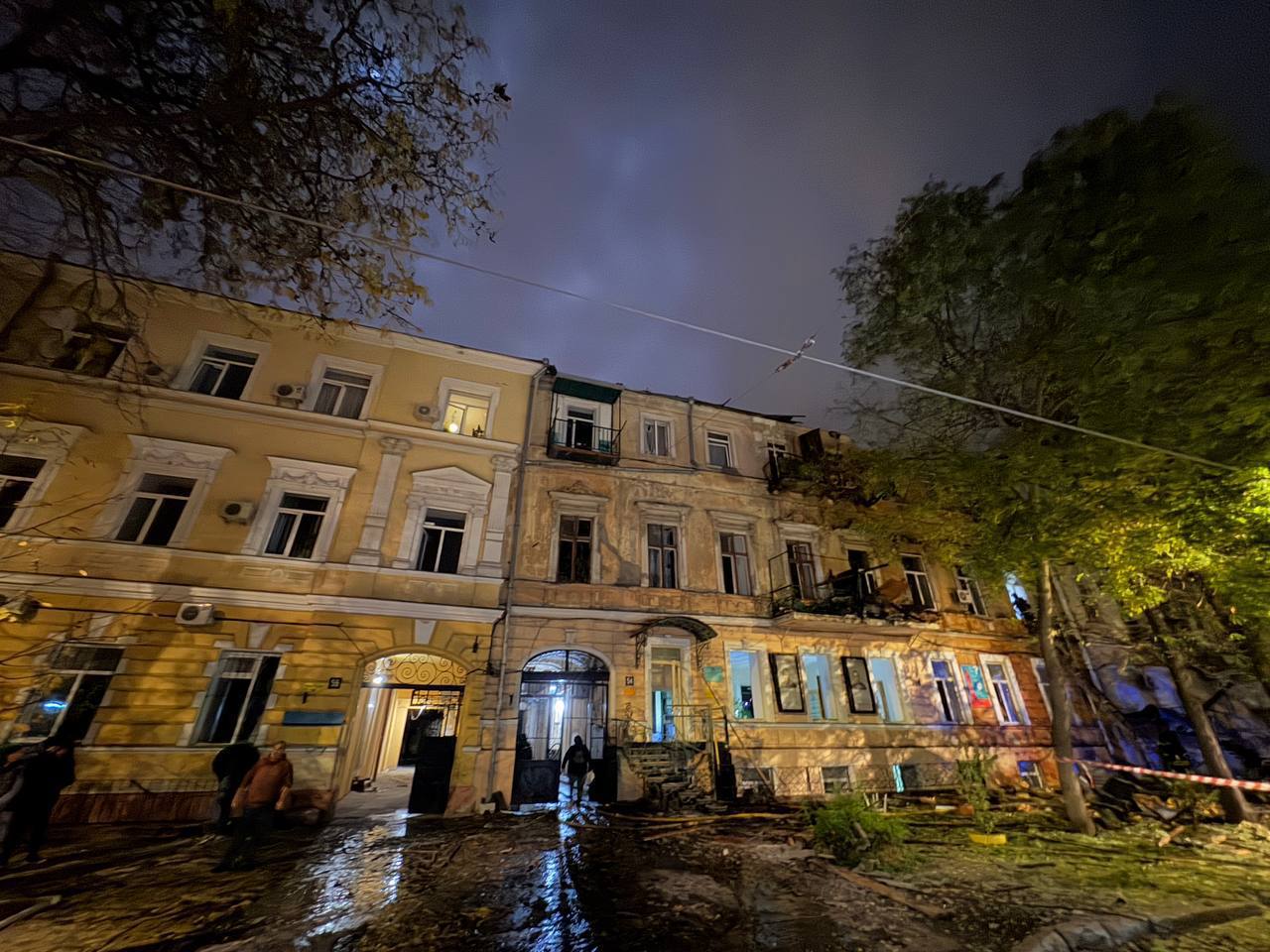 A residential building in Odesa damaged by a mass Russian drone strike. (Hennadiy Trukhanov / Telegram)
A residential building in Odesa damaged by a mass Russian drone strike. (Hennadiy Trukhanov / Telegram)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Russia’s UN Ambassador in Geneva says Donald Trump’s potential return to the White House may not significantly change US-Russia relations but could open doors for dialogue. While suggesting possible diplomatic opportunities, Ambassador Gatilov remains skeptical about major policy shifts, noting that Washington’s approach of containing Moscow typically persists across administrations. The ambassador dismissed Trump’s claims about quickly resolving the Ukrainian crisis, though welcomed potential talks if they acknowledge current realities. This comes amid concerns from Ukraine and European allies about Trump’s historically friendly stance toward Putin, whom Trump has previously called a “genius.” The situation highlights ongoing tensions in global diplomacy and their potential impact on international peace, particularly regarding the Ukraine conflict that began with Russia’s 2022 invasion.
Russia and Belarus have deepened their integration by signing an agreement to unify their border controls and export systems. This closer alliance between Belarus, which has supported Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, and Russia itself signals growing military cooperation between the two nations, potentially heightening tensions with NATO countries and Ukraine’s other western allies. The planned permanent electronic passport system, set for late 2024, suggests a long-term strategic partnership that could further destabilize Eastern Europe.
A significant shift in global oil dynamics is emerging as Chinese refinery Landbridge Petrochemical Co. moves away from Russian and Iranian oil imports, choosing West African oil instead. This change comes amid Ukraine’s efforts to disrupt Russian oil production, a key funding source for Moscow’s war effort. The shift is particularly notable as Chinese independent refineries typically rely on sanctioned Russian and Iranian oil. The timing coincides with market uncertainty following Trump’s election, with expectations of potentially stricter U.S. sanctions policies. This development suggests a possible weakening of Russia’s oil market position and could impact its strategic relationships with China, traditionally a reliable buyer of sanctioned oil supplies.
Germany’s Economy Ministry has ordered its state-operated gas terminal to reject incoming Russian liquefied natural gas (LNG) deliveries, reinforcing Europe’s move away from Russian energy dependence. This decision follows Germany’s shift from being Europe’s largest Russian gas importer after Putin cut pipeline supplies following the 2022 invasion of Ukraine. While Germany has ended direct Russian LNG imports, some Russian gas still reaches the country through France via a contract between German company SEFE and Russia’s Yamal facility. European Commission President von der Leyen has discussed replacing Russian LNG with American supplies in recent talks with President-elect Trump, noting that U.S. LNG could provide a cheaper alternative.
The Path to Peace
Donald Trump’s potential administration signals a significant shift in U.S. policy toward the Russia-Ukraine war. His national security advisor pick, Mike Waltz, indicates Trump wants to bring both sides to negotiations, aiming to end the conflict “within 24 hours.” The approach may involve freezing the conflict, suspending Ukraine’s NATO bid, and creating an eastern demilitarized zone. Cabinet nominations, including Ukraine-skeptic Tulsi Gabbard and Pete Hegseth, have raised concerns in Ukraine. With Russia currently holding battlefield advantage and Ukraine rejecting territorial concessions, peace prospects remain uncertain. This policy shift could significantly impact Ukraine’s position and the war’s outcome, as direct talks between Russia and Ukraine have been stalled since early 2022.
Western officials are privately considering a potential peace deal that could involve Ukraine ceding some territory in exchange for security guarantees, according to a Washington Post report based on interviews with 10 officials. This shift comes amid Ukraine’s battlefield challenges and uncertainty about future U.S. support under Donald Trump. While Russia occupies about one-fifth of Ukraine’s territory, Ukrainian President Zelensky maintains that full territorial integrity must be restored. However, with Russia advancing in Donetsk Oblast and showing little interest in compromise, some Ukrainian officials acknowledge that diplomatic solutions may be needed as resources dwindle. Putin has stated that any peace deal must favor Moscow, while potential proposals include delaying Ukraine’s NATO entry by at least 20 years in exchange for military support.
Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov stated that President Putin is personally handling Ukraine matters and doesn’t need special envoys. This statement appears to be a response to reports that Donald Trump plans to appoint a “Ukrainian peace envoy” to negotiate an end to the war.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Russian military bloggers are criticizing the Defense Ministry’s failure to properly distribute medical supplies to troops in Ukraine, despite having adequate stocks in storage. The situation came to a head in Novosibirsk City, where soldiers from the 35th Management Brigade reportedly rioted after being denied medical care. Despite nearly three years of war, bloggers claim the military still lacks effective medical supply networks at various unit levels, forcing volunteer organizations to inadequately fill the gaps.
A road bridge on the Dzhankoy-Maslove highway in occupied Crimea collapsed falling onto railway tracks and temporarily disrupting transport between Crimea and southern Ukraine. Russian officials blame an oversized truck and claim railway service has resumed, though road repairs may take 3-4 months. The incident raised concerns about Russian military supply routes to occupied Kherson Oblast.
Due to poor weather, Russian Black Sea Fleet ships have halted operations in the Black Sea and switched to using aircraft instead.
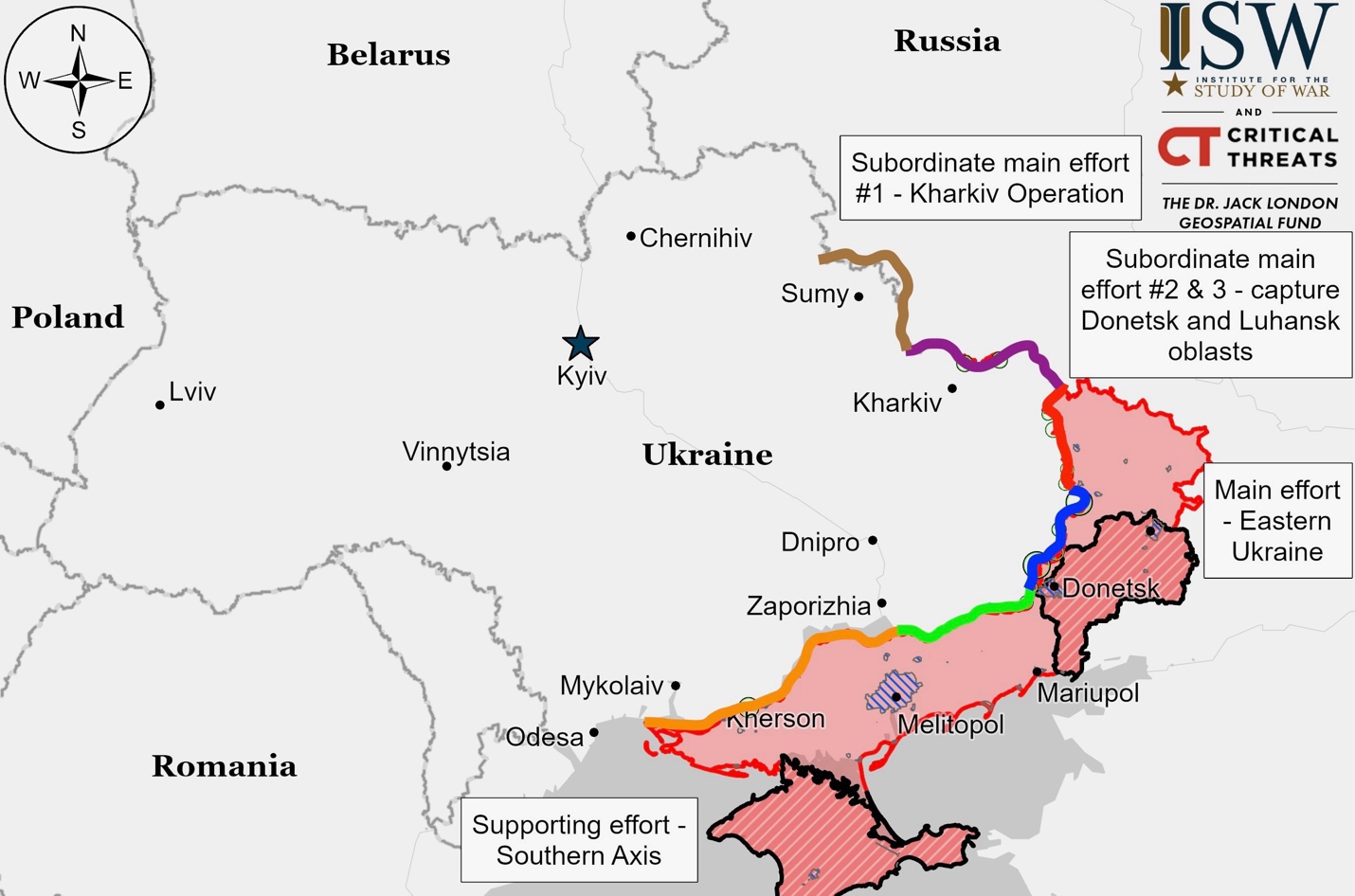
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Russian forces have made advances in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast region. Video evidence confirms Russian military movements near several settlements, including Zeleniy Shlyakh, Maryevka, Pogrebki, Orlovka, and Novaya Sorochina. Russian forces have reached southern Novaya Sorochina, though their advance has reportedly slowed. Fighting continues around Korenevo and Sudzha areas, with operations being conducted by Russian naval infantry, airborne units, and special forces. Russian forces have made a small advance near Novy Put, east of Glushkovo, in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast region.
A Russian military blogger reports that commanders are overstating their advances in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast, leading to increased casualties. The 810th Naval Infantry Brigade is reportedly suffering heavy losses in daily unprepared attacks near Orlovka, Pogrebki, and the Sorochina settlements, with one unit reportedly being destroyed. These exaggerated reports appear to be a response to Kremlin pressure to push back Ukrainian forces, while some Russian residents in the Kursk border area have begun protesting the situation.
Ukrainian forces reportedly hit a Russian military storage facility in Belgorod City damaging military trucks and injuring several Russian soldiers.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces continued attacks in northern Kharkiv Oblast near Hlyboke and Vovchansk, with raids reported near Vysoka Yaruha. Poor weather is limiting both sides’ ability to use drones, which Russian forces are using as an opportunity to resupply their positions.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces have made a limited advance into Kupyansk with a mechanized assault using two armored columns, including an attack where forces wearing Ukrainian uniforms launched four waves with 15 armored vehicles but were driven back by Ukrainian defenders who destroyed the vehicles and inflicted significant casualties. While footage shows Russian vehicles moving along a railway line and operations continue around Holubivka, Petropavlivka, Kolisnykivka, Hlushkivka, Kruhlyakivka, Lozova, Zahryzove, and Kucherivka, Ukrainian officials maintain they control Kupyansk, though Russian forces remain 2-3 kilometers from the city’s industrial outskirts as they attempt to reach the Oskil River that divides the city. While this represents increased Russian activity in the area over the past two months around this strategic railway and logistics hub in Kharkiv Oblast, as acknowledged by President Zelensky, it’s unclear if these tactical gains will lead to significant strategic advances. The eastern bank of Kupiansk currently lacks basic utilities due to constant shelling.
Russian forces attacked along the Svatove-Kreminna line targeting multiple settlements including Pershotravneve, Zeleniy Hai, Pishchane, Cherneshchyna, Novoyehorivka, and several others near Kreminna. However, no confirmed advances were reported.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces attacked areas near Siversk focusing on Verkhnokamyanske but failed to make advances. While a Russian military blogger claimed advances near Rozdolivka, south of Siversk, this remains unconfirmed. A failed Russian mechanized assault was reported near Spirne.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces advanced near Chasiv Yar with confirmed progress east of Bila Hora. While claims of additional advances near Stupochky remain unverified, Russian airborne and motorized rifle units are actively operating in the area.
Toretsk
Russian forces attacked several areas around Toretsk, including Krymske, Dyliivka, Shcherbynivka, and Nelipivka, but made no confirmed advances in the region.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces attacked multiple settlements near Pokrovsk, including Promin, Myrolyubivka, Lysivka, Krutyi Yar, and several other villages in the area, but failed to make any confirmed advances.
Kurakhove
Russian forces continued attacks around Kurakhove but made no confirmed advances. While Russian forces likely occupy Illinka, with footage showing their flag raised in the town center, full control remains contested. Russian claims of capturing Voznesenka and advancing in eastern Kurakhove lack visual confirmation. Russian forces are attacking multiple settlements including Zorya, Sontsivka, Novoselydivka, and Maksymilyanivka, using various military vehicles. Reports indicate Russia has concentrated approximately 70,000 troops in the Kurakhove area.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces attacked multiple areas near Vuhledar, including Dalne, Antonivka, Katerynivka, Yantarne, and Trudove, but made no confirmed advances. While Russian sources claim to have captured Dalne and advanced near Antonivka and Maksymivka, these claims remain unverified.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces are preparing for imminent ground assaults in Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia region, according to Ukrainian military officials. The attacks are expected “any day” near Hulyaipole, Orikhiv, and Kamyanske, with Russian forces already making advances near Levadne and Novodarivka. While Russia has concentrated significant troops and equipment in the area, military experts believe these are likely tactical moves rather than preparation for capturing the city of Zaporizhzhia itself, which would require far more resources than Russia currently has available. The timing appears linked to creating leverage before Donald Trump’s potential return to the White House. Ukrainian forces report a 30-40% increase in Russian airstrikes in the region, indicating preparation for the offensive.
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces made advances near the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border area. Video evidence shows Russian troops moving south of Rivnopil and north of Levadne, both located southwest of Velyka Novosilka. Reports claim Russian forces took Novodarivka, though this remains unconfirmed. Russian attacks continued around Makarivka, Novodarivka, Rivnopil, and Novopil.
Zaporizhia Line
Russian sources claim their forces advanced near Hulyaipole in eastern Zaporizhia Oblast, specifically near Marfopil and Dorozhnyanka. However, Ukrainian officials report no Russian offensive operations in this area. Russian snipers are reportedly active in the Polohy area.
Russian forces reportedly advanced north of Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast, though this remains unconfirmed. Russian attacks occurred near Novodanylivka and Novoandriivka. Artillery units from Russia’s “Viking” Detachment are operating in the area, though reports suggest no major Russian troop movements to this region from other fronts.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Fighting continues along the Dnipro River in eastern Kherson Oblast with Russian reserve units active in the area. No changes to the front line have been confirmed.
Ukraine News
Russia launched 59 Shahed drones from Kursk Oblast against Ukraine. Ukrainian forces shot down 21 drones over Sumy, Kharkiv, Poltava, and Kyiv regions, with 11 downed in Sumy Oblast alone. Another 38 drones were reportedly disrupted by electronic warfare.
President Zelensky announced that Ukraine will present a 10-point “internal resilience plan” next week, focusing on strengthening the country’s domestic capabilities. The plan, developed with input from civil society and businesses, will address the front line, military production, economy, and regional development. This initiative is separate from Ukraine’s previous five-step victory plan presented to Western allies. The new plan includes measures for energy security, weapons production, and cultural sovereignty. This development comes as Ukraine faces Russian military pressure and uncertainty about Western support.
Ukraine’s sovereign bonds have risen 12% following Trump’s election victory, as investors anticipate a quick end to the war under his presidency. The price increase began in mid-October when markets started predicting Trump’s win. The bond rally follows Ukraine’s September agreement with creditors to restructure over $20 billion in international debt, reducing state debt by $9 billion. However, some investors remain cautious about Ukraine’s recovery prospects, given uncertainties about potential peace terms and the country’s future.
Despite Russia’s increased use of Shahed drones against Ukraine, Ukrainian forces are successfully countering about 90% of these attacks through multiple defense strategies. Ukraine employs mobile fire groups with machine guns, electronic warfare systems that disrupt drone navigation, and traditional anti-aircraft weapons. The electronic warfare is particularly effective, causing drones to lose direction, sometimes even turning back toward Russia, as recently happened in Belgorod. However, experts warn that Russia is working to upgrade the Shaheds with satellite communication capabilities, including Starlink systems, which would make them operator-guided rather than following preset paths. Military experts suggest that targeting the drone production facility in Yelabuga, Russia, and implementing stricter sanctions on component suppliers from China, Taiwan, and the US could help reduce Russia’s drone attack capabilities.
Ukraine is expanding its nuclear power capacity with new construction projects amid ongoing energy security concerns. The South Ukraine Nuclear Power Plant near Pivdennoukrainsk is preparing to add two new power units using American Westinghouse AR1000 technology, while plans are also underway to resume construction of the previously abandoned Chyhyryn plant in Cherkasy Oblast. These developments are crucial as nuclear power provides more than half of Ukraine’s energy needs, especially important given Russian attacks on energy infrastructure. Meanwhile, the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant, Europe’s largest nuclear facility, remains under Russian occupation since March 2022, raising significant safety concerns as Russian forces reportedly use the site for military purposes and ammunition storage.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 4 INJURIES: 38+
Russian forces launched a major aerial attack on Odesa killing one woman and injuring at least 10 people, including a 9-year-old boy. The attack damaged residential buildings in the city center, a church, and educational facilities. A critical heating pipeline was also hit, disrupting heat supply to 220 apartment buildings, seven kindergartens, four schools, and a maternity hospital housing 22 babies and 28 expectant mothers. Emergency repairs are underway, with the maternity hospital temporarily relying on generator power for heating.
Russian forces attacked multiple locations in Donetsk Oblast, resulting in two deaths and eight injuries. The attacks struck the villages of Novotroitske (one killed, two wounded) and Shevchenko (one killed, one injured), as well as the city of Kostiantynivka (four injured) and Predtechyne (one injured). Russian soldiers killed an unarmed civilian woman in pink clothing who was walking through the front-line village of Terny in Donetsk Oblast on November 10. The Donetsk Oblast Prosecutor’s Office has launched a war crimes investigation into the incident, which adds to numerous documented cases of Russian forces targeting civilians since the 2022 invasion began.
A Russian drone attack on Kharkiv injured two people when it hit an apartment building. In a separate incident in Kupiansk, a 67-year-old medical facility driver was wounded.
Russian forces attacked Kherson Oblast, injuring 15 people and damaging a utility company, a fire station, and residential buildings.
Russian forces attacked the Myropillia community in Sumy Oblast, resulting in two civilian injuries.
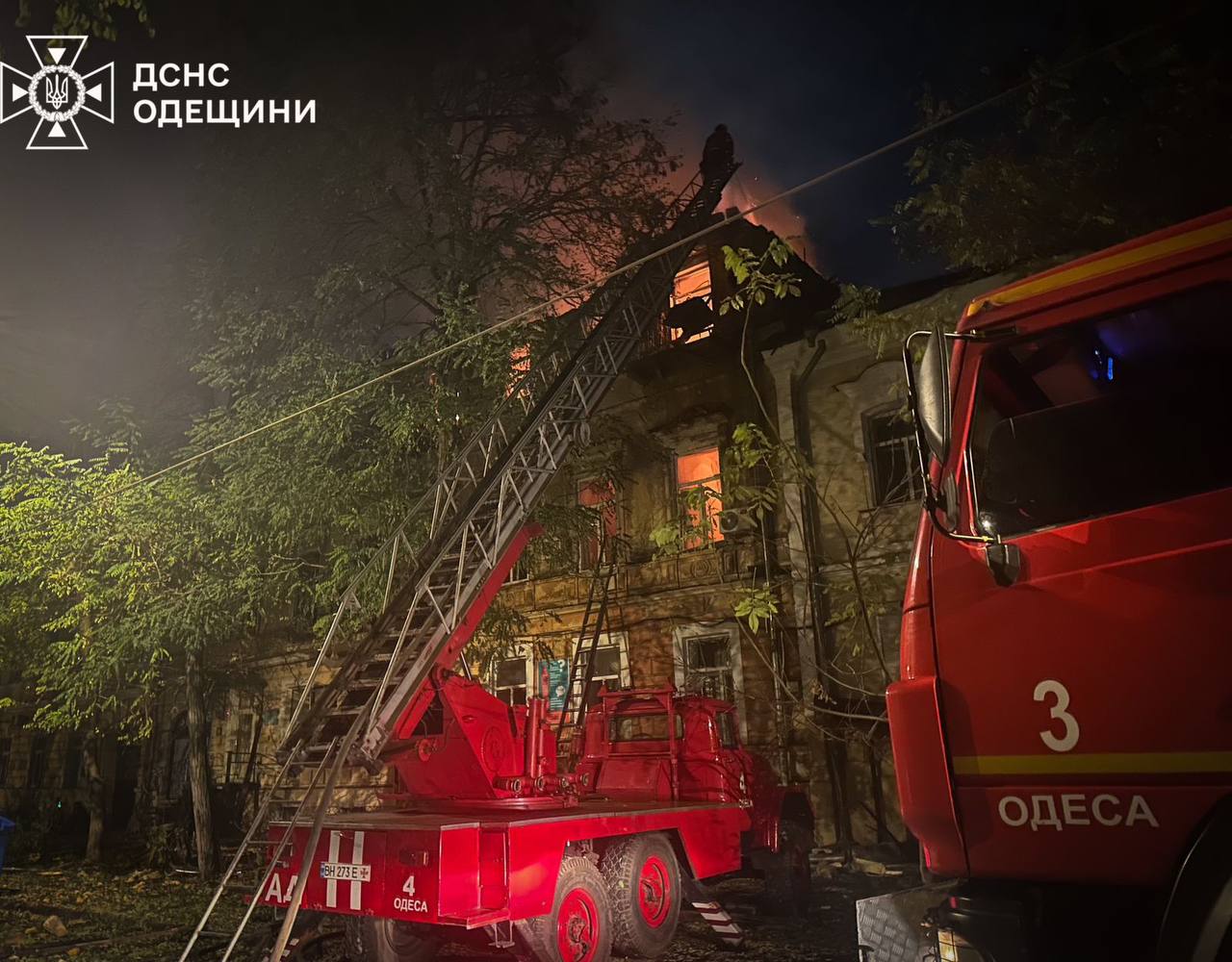 The aftermath of a Russian combined aerial attack on Odesa, Ukraine, where apartment buildings were destroyed and damaged. (Ukraine’s State Emergency Service/Telegram)
The aftermath of a Russian combined aerial attack on Odesa, Ukraine, where apartment buildings were destroyed and damaged. (Ukraine’s State Emergency Service/Telegram)
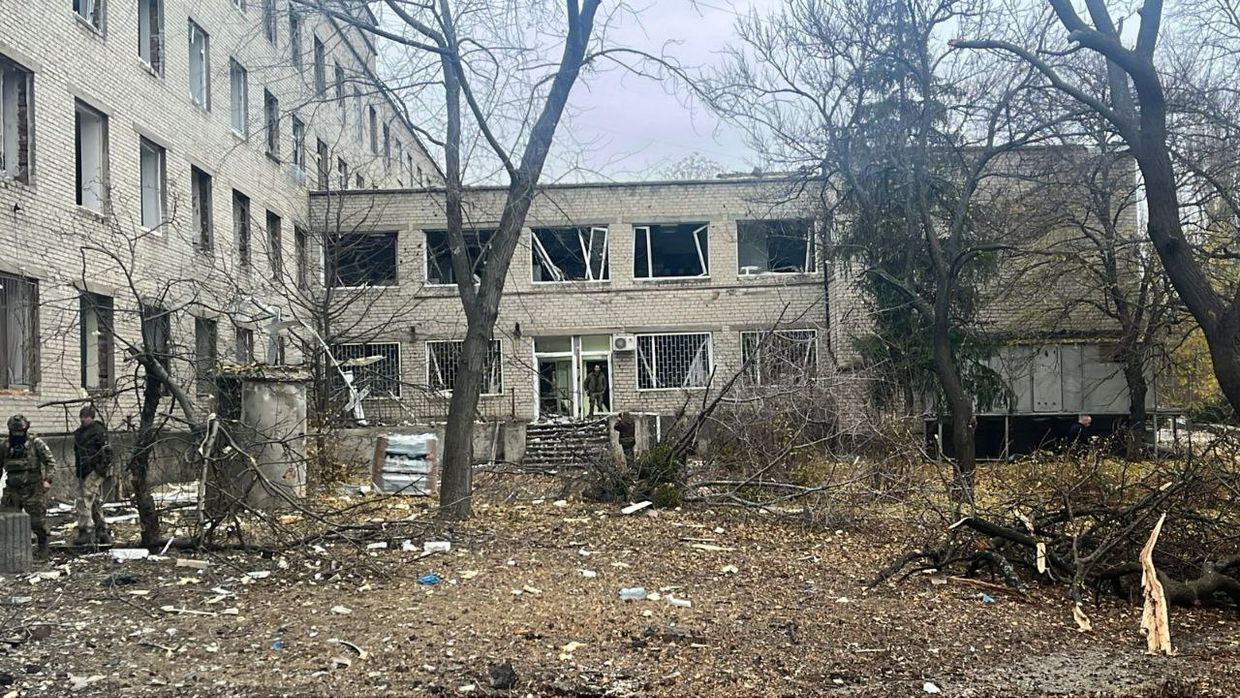 The aftermath of Russian attacks in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. (Governor Vadym Filashkin/Telegram)
The aftermath of Russian attacks in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. (Governor Vadym Filashkin/Telegram)
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine’s Defense Ministry is developing new legislation by December 18, 2024, to establish clear procedures for discharging military personnel during martial law. Currently, Ukrainian soldiers, many serving continuously since Russia’s February 2022 invasion, cannot be demobilized except for injuries or family care obligations. This development follows parliament’s April adoption of an updated mobilization law, which removed previous provisions allowing discharge after 36 months of service. The new framework aims to address the ongoing challenge of managing military service terms while maintaining Ukraine’s defense capabilities during wartime. The specific conditions for discharge are yet to be determined by the Defense Ministry.
Ukraine’s Allies
European leaders are urgently seeking additional U.S. support for Ukraine before President-elect Trump takes office in January 2025. They’re requesting more weapons, artillery, and permission for long-range strikes on Russia. While the Biden administration has promised to deliver the remaining $6 billion in aid, it maintains restrictions on Ukraine’s use of long-range American weapons against targets within Russia. Secretary of State Blinken confirmed efforts to secure additional assistance during the transition, as Europe becomes Ukraine’s primary defense partner amid uncertainty about future U.S. support.
Polish President Andrzej Duda expressed confidence that President-elect Trump would continue supporting Ukraine against Russia, citing significant U.S. taxpayer investments and Trump’s competitive nature. Poland is working to secure continued support for Ukraine by building an alliance with the UK, with Polish Prime Minister Tusk planning discussions with British, French, and NATO leaders.
The European Union is developing new sanctions targeting Russia’s “shadow fleet” – older vessels used to circumvent international oil sanctions imposed in 2022. The package, expected to be approved by year’s end, aims to penalize individuals involved in this trade and may include stronger measures against Russian liquefied natural gas. Russia has invested $10 billion in its shadow fleet since 2022 to evade the West’s $60-per-barrel price cap. The EU hopes to implement these new sanctions by February 24, 2025, marking the third anniversary of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, pending unanimous approval from all 27 EU members.
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) is intensifying efforts to support Ukraine’s damaged energy infrastructure following two years of Russian attacks. Under new leader Arvid Tuerkner, the bank has invested 5 billion euros ($5.3 billion) in Ukraine, with nearly a quarter going to energy companies. Russian attacks have destroyed half of Ukraine’s power generation capacity by late 2024, leading to concerns about severe power shortages this winter. The EBRD is supporting quick solutions including gas turbines and solar panels to help prevent extended blackouts, which could last up to 20 hours daily in worst-case scenarios. The bank is working with both state-owned companies like Naftogaz and private sector initiatives, though wartime conditions and safety concerns continue to challenge investment efforts.
Senator John Thune of South Dakota has been elected as the new Republican Senate leader, potentially signaling continued support for Ukraine in Congress. Unlike Trump’s preferred candidates, Thune has consistently backed funding and arming Ukraine against Russia. In a March PBS interview, he emphasized that defending Ukraine serves U.S. national security interests and argued that providing weapons to Ukraine now could prevent having to send American troops later if Russia were to attack NATO countries. Despite aligning with Trump’s administration, Thune maintains that American leadership is crucial in global affairs and has advocated for giving Ukraine the resources needed for victory over Russia.
Donald Trump has nominated Senator Marco Rubio as Secretary of State, signaling potential shifts in U.S. support for Ukraine. Despite previously praising Ukrainian defenders, Rubio voted against the $61 billion Ukraine aid package in April 2024 and recently characterized the conflict as a “stalemate” that needs conclusion. As future top U.S. diplomat, Rubio would be central to any peace negotiations between Kyiv and Moscow, aligning with Trump’s promise to end the war within 24 hours. His recent statements suggest a pragmatic approach, acknowledging Ukrainian bravery while expressing concerns about the conflict’s sustainability and Ukraine’s long-term reconstruction challenges. This appointment indicates a possible shift from the current administration’s strong support for Ukraine toward a more nuanced position aligned with Trump’s stance.
President-elect Trump’s nomination of Fox News anchor Pete Hegseth as Defense Secretary has sparked alarm at the Pentagon, potentially impacting U.S. military support for Ukraine. Despite Hegseth’s military experience as an Army National Guard infantry captain, Pentagon officials express serious concerns about his lack of large-scale organizational management experience needed to lead 1.3 million troops and 750,000 civilians. This unprecedented appointment of a media personality to such a crucial defense position has worried foreign diplomats and could deter qualified candidates from filling other key Pentagon positions. The choice of Hegseth, known more for discussing “wokeness” than national security strategy, signals a potential shift in U.S. defense priorities and could significantly affect the Pentagon’s approach to supporting Ukraine and managing international military relationships.
Donald Trump has announced he will appoint Tulsi Gabbard, former Democratic congresswoman from Hawaii, as national director of intelligence. Gabbard has been a vocal critic of U.S. support for Ukraine and advocates for a peace deal from March 2022 that would give Russia control of a neutralized, demilitarized Ukraine. As director of national intelligence, Gabbard would oversee critical agencies like the CIA and NSA, which have been key in supporting Ukraine’s defense against Russia. Former National Security Council staffer Jamie Metz expressed concern that U.S. allies might become hesitant to share intelligence with the U.S. given Gabbard’s perceived sympathies toward Putin. The appointment could significantly impact U.S. intelligence sharing and support for Ukraine’s war effort.
Elise Stefanik, Trump’s nominee for U.N. envoy, has shifted her stance on Ukraine, avoiding questions about her previous support for Ukraine’s NATO membership and her description of Russia’s actions as “genocidal.” After initially backing Ukraine following Russia’s 2022 invasion, Stefanik voted against a $60 billion aid package in April 2024. Her office now states that she fully aligns with Trump’s positions, who has promised to end the war within “24 hours” after taking office, though details remain unclear. Trump recently appointed Stefanik to lead U.S. representation at the United Nations, praising her as an “America first fighter.”
Life in Russian Occupied Ukraine
Russia has reportedly shelved plans to create a “Novorossiya” Federal District encompassing occupied Kherson, Zaporizhia, Donetsk, and Luhansk regions. Originally announced by occupation governor Yevgeny Balitsky in June 2024, the project’s abandonment suggests Russia is struggling to establish unified control over occupied Ukrainian territories. Instead, the Kremlin is relying on Presidential Administration Deputy Head Sergei Kiriyenko to oversee occupation efforts, despite his other significant responsibilities in Russian domestic affairs.
Russia News
Russia faces growing economic strain heading into 2025, with Putin showing concern about long-term stability. The Kremlin has introduced new policies to reduce spending on wounded soldiers, fight inflation, and address falling birth rates and worker shortages. Despite Russian claims of resilience, these moves suggest Western sanctions and war costs are taking a toll. The policies indicate Russia may struggle to maintain its war effort while protecting its population from economic hardship. Continued Western support for Ukraine is likely to increase these pressures on Russia’s economy.
Russia’s Central Bank raised interest rates to 21 percent in October, triggering concerns about economic stability. The Kremlin’s own economic analysis center warns of potential stagflation – a combination of stagnation and high inflation. If high rates continue until mid-2025, experts predict a recession. Dynamic rate loans have increased from 44% to 53%, raising risks of production decline, bankruptcies, and corporate defaults. While not yet directly affecting military support, these policies are reportedly hampering defense industry expansion and economic mobilization efforts.
Russia has unveiled a new Strategy of Action through 2036 to address declining population and labor shortages that threaten its defense industry, with population expected to decline by over 600,000 annually until 2032 and current labor shortages reaching 4.8 million people in 2023, exacerbated by 800,000 to 900,000 skilled workers having fled since February 2022. The plan aims to boost birthrates through increased family support, improved housing access, better work-life balance, enhanced women’s healthcare, and pro-family media messaging as part of broader government efforts to grow Russia’s population through both policy and promotion of traditional values. While Putin acknowledges reliance on migrant workers, racism, deportations, anti-migrant policies, and recent measures like revoking migrants’ citizenship for avoiding military service undermine this solution, while the defense industry’s priority access to workers has depleted other sectors, threatening both Russia’s civilian economy and defense industry long-term.
A recent state-affiliated Russian poll shows 83% of Russians claim the war in Ukraine has little to no impact on their daily lives. This apparent indifference concerns Russian officials, including Russian Orthodox Church leader Patriarch Kirill, who criticized citizens for ignoring frontline realities and border region hardships. This disconnect between those directly affected by the war and those insulated from it suggests potential challenges for war support and future military recruitment.
A Russian soldier, Roman Ivanyshyn, faces the first-ever criminal trial in Moscow for voluntarily surrendering to Ukrainian forces. Ivanyshyn, a former miner from Sakhalin who was mobilized into the 39th Separate Guards Motorized Rifle Brigade, surrendered near Stepove in Ukraine’s Donetsk region in June 2023. After being exchanged in January 2024, he was arrested upon return to Russia. He faces up to 20 years for surrender charges and an additional 15 years for desertion. In a video interview before his return, Ivanyshyn opposed the war and claimed his fellow soldiers were fleeing their positions. This case highlights the risks Russian soldiers face upon returning home, with some POWs previously expressing fears of execution for surrendering.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
Russia’s defense industry can’t keep pace with battlefield losses. Reports indicate Russia loses about 320 tank and artillery barrels monthly but produces only 20, suggesting they may exhaust supplies by 2025. Similarly, Russian forces are losing approximately 155 infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) monthly while producing just 17.
| Troops +1520
717590 |
Tanks +11
9330 |
Artillery +20
20492 |
Arm. VEH +21
18968 |
Aircraft
369 |
Heli
329 |
Ships
28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian military compensation for combat injuries in Ukraine has been drastically reduced from the original 3 million rubles ($30,124) promised to all wounded soldiers. The new tiered system offers 4 million rubles ($40,136) for severe disabilities, but only 1 million rubles ($10,152) for light wounds and 100,000 rubles ($1,015) for minor injuries. Military medical boards are reportedly becoming stricter in classifying injuries, effectively reducing payouts. This policy change has angered Russian military bloggers, as many soldiers enlisted primarily for financial benefits, and indicates Russia’s growing struggle with war-related costs.
Russia’s Allies
Russian military bloggers report spotting what appears to be North Korean M1989 “Koksan” artillery systems on a train in Krasnoyarsk. These 170mm self-propelled weapons, mounted on Russian tank chassis, have a range of 40-60 kilometers and can fire every 2-5 minutes. Pro-Kremlin sources suggest this could help replace Russia’s lost 2S7 Pion artillery systems, though these claims cannot be independently verified.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
