Summary of the Day:
The Russian government has announced plans to allocate 41% of its 2025 budget, amounting to 17 trillion rubles ($183 billion), to national security and defense. This significant increase in defense spending may impact the effectiveness and sustainability of various social programs, including the Kremlin’s pronatalist initiatives. The focus on military expenditure reflects Russia’s ongoing commitment to its war efforts in Ukraine and preparations for potential future conflicts.
In a move to consolidate power and prepare for generational transition, Russian President Vladimir Putin has promoted his close ally and presidential aide Alexei Dyumin to the Russian Security Council, along with three other officials. This appointment, coupled with recent efforts to co-opt previously critical milbloggers through state and regional awards, demonstrates the Kremlin’s continued attempts to control the information space and maintain domestic support for its policies.
On the diplomatic front, Russian Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin arrived in Tehran on September 30 to meet with Iranian officials and discuss economic cooperation. This visit underscores Russia’s efforts to strengthen ties with allies in the face of ongoing international sanctions and isolation.
Russian forces have made recent advancements in several key areas, including near Svatove, Chasiv Yar, Toretsk, Pokrovsk, and Donetsk City. Additionally, both Russian and Ukrainian forces have made progress within the Ukrainian salient in Kursk Oblast. These developments indicate ongoing intense fighting along multiple fronts of the conflict.
Lastly, Putin has signed a decree for Russia’s semi-annual fall conscription, calling for 133,000 new draftees. This regular mobilization effort continues to replenish Russian forces engaged in the protracted conflict in Ukraine.
Picture of the Day:
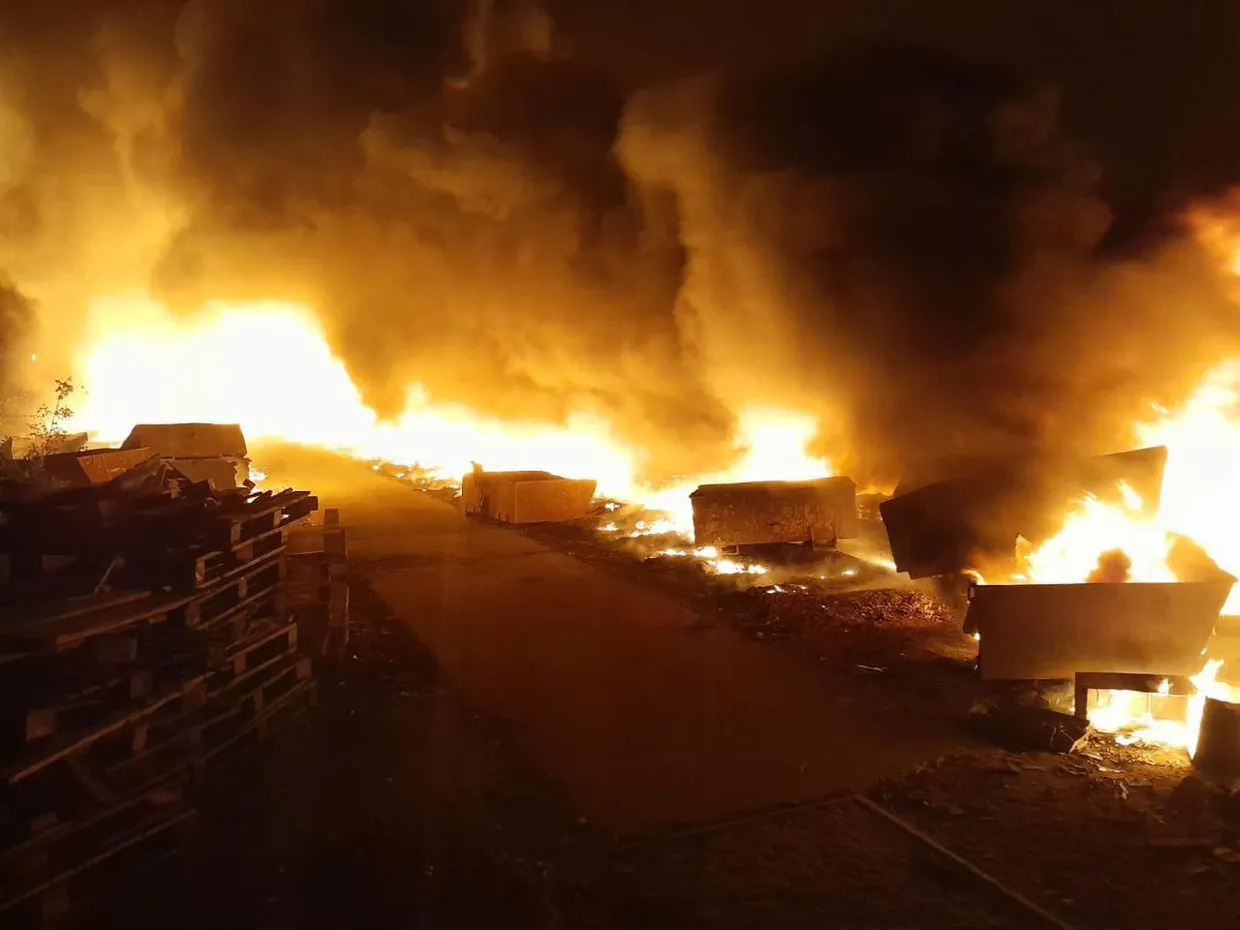 The aftermath of a Russian attack on Donetsk Oblast. (Vadym Filashkin/Telegram)
The aftermath of a Russian attack on Donetsk Oblast. (Vadym Filashkin/Telegram)
| Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War |
An investigation by the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project revealed that likely Russian-linked actors are using Telegram to recruit saboteurs for attacks in NATO countries. The report found an anonymous account offering rewards for crimes in Estonia, including spying on NATO bases and arson attacks. Estonian officials suggest Russian intelligence services may be behind these recruitment efforts, indicating a potential escalation in sabotage operations against NATO.
Turkey’s purchase of Russia’s S-400 missile system in 2019 led to significant consequences. The US removed Turkey from the F-35 fighter program and imposed sanctions. Recently, the US offered to readmit Turkey if it disposed of the S-400s. However, Turkish President Erdogan faces challenges in doing so due to his close ties with Russian President Putin. Options being considered include transferring the missiles to Ukraine, selling them to other countries, or placing them under US control in Turkey. Russia has warned that any transfer requires their consent. The situation highlights ongoing tensions between Turkey, the US, and Russia, with potential implications for regional military balance and NATO relations.
Austria’s far-right Freedom Party (FPO) won 29% of the vote in recent elections, marking a significant victory for Ukraine-skeptic parties in Central Europe. Led by Herbert Kickl, the FPO opposes sanctions against Russia and military aid to Ukraine. The party’s success follows similar gains by far-right groups in Germany and Slovakia. While the FPO now holds 56 seats in the 183-seat parliament, it will need to form a coalition to govern. However, mainstream parties have signaled their unwillingness to work with the FPO, potentially leading to a coalition that excludes them. The election results reflect growing support for anti-immigration and Russia-friendly policies in Austria, where neutrality remains a key political issue.
Lithuania has asked the International Criminal Court (ICC) to investigate crimes against humanity committed by Belarusian leader Alexander Lukashenko’s regime since May 2020. The request focuses on the deportation of citizens and persecution of political opponents, which Lithuania argues is a systematic attack on dissent. Despite Belarus not being a party to the Rome Statute, the ICC has jurisdiction due to crimes committed in participating nations. The appeal follows unrest in Belarus after contested 2020 elections, where Lukashenko claimed victory over opposition candidate Sviatlana Tsikhanouskaya. Since then, over 1,000 political prisoners have received long sentences, and 1,500 others have been jailed for protesting against the war in Ukraine.
The Path to Peace
On the two-year anniversary of Russia’s annexation of four Ukrainian regions, President Putin gave a speech, while Russian ultranationalist bloggers called for the complete dismantling of Ukraine. This suggests that many Russians may not accept any outcome short of Ukraine’s total defeat.
Senator Marco Rubio, vice chair of the US Senate Intelligence Committee, defended former President Donald Trump’s stance on ending the Ukraine war through negotiations. In an NBC interview, Rubio stated that the conflict will likely conclude with a negotiated settlement, emphasizing the need for Ukraine to have leverage in such talks. Trump, after meeting with President Zelensky, maintained his position that the US cannot pursue outright victory in Ukraine. Rubio suggested that Republicans aim to strengthen Ukraine’s negotiating position but criticized President Biden for not defining what victory would look like. The senator’s comments reflect ongoing debates in US politics about the approach to the Ukraine conflict and its potential resolution.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Ukrainian forces made minor advances near Korenevo on the western edge of their salient in Kursk Oblast. Geolocated footage shows Russian airborne troops engaging Ukrainian forces southeast of Korenevo, indicating recent Ukrainian progress. Russian sources, including the Ministry of Defense, claim to have repelled Ukrainian attacks near Lyubimovka, Olgovka, Kremyanoye, Kamyshevka, and Plekhovo in the Korenevo and Sudzha areas. These reports suggest ongoing Ukrainian offensive operations in the region.
Russian forces advanced southeast of Veseloye in Glushkovsky Raion, Kursk Oblast, as shown by geolocated footage from September 24. This progress occurred amid ongoing Ukrainian offensive operations in the area. The Russian Ministry of Defense reported repelling Ukrainian attacks near Novy Put, while Russian milbloggers claimed Ukrainian forces attacked near Veseloye and Medvezhye.
Russian forces have made confirmed advances near Plekhovo in Kursk Oblast, Ukraine. Geolocated footage shows Ukrainian forces repelling a Russian mechanized assault south of Plekhovo. Russian sources claim to have seized Obukhovka and advanced near Uspenovka, though this is unconfirmed. The Russian Ministry of Defense reports that naval infantry elements have captured fortified positions in an unspecified part of Kursk Oblast.
Ukraine launched a large drone attack on a Russian ammunition depot in Kotluban, Volgograd region, on September 29. The Ukrainian military claimed success, stating they hit a facility that had recently received Iranian missiles. However, satellite images from Radio Svoboda suggest the main arsenal remained intact, with damage limited to areas outside the weapons storage. Russia reported that 125 Ukrainian drones targeted several regions, including Yeysk, Rostov, and Voronezh. The conflicting reports highlight the ongoing drone warfare between Ukraine and Russia, with each side presenting different accounts of the attack’s effectiveness.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces have made slight advances northeast of Kharkiv City, particularly focusing on Vovchansk’s Aggregate Plant, which was recently recaptured by Ukraine’s military intelligence special forces on September 24. Russian troops are conducting attacks near Buhruvatka, Starytsya, and Vovchansk, while maintaining defensive positions along the Lyptsi-Hlyboke-Krasne line. They are intensively targeting the Vovchansk plant with heavy artillery, guided aerial bombs, and “Solntsepek” rocket launchers, using long-range weapons and rotating troops. Reports suggest Russian forces may be constructing tunnels in Vovchansk’s urban areas. The situation in the Kharkiv sector remains difficult, with ongoing Russian assaults, although fighting in northern Kharkiv Oblast has decreased in intensity compared to other eastern sectors. Ukraine claims to have captured Russian soldiers and inflicted casualties during the plant’s recapture, but these reports are unverified. The loss of the facility has reportedly dealt a blow to Russian morale.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces have advanced near Svatove, with confirmed progress in southern Makiivka. They’ve conducted offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, including attacks near Synkivka, Kucherivka, Novoosynove, Hlushkivka, Kruhlyakivka, Stelmakhivka, Vyshneve, Zarichne, Hrekivka, Nevske, Dibrova, Serebryanka, and Hryhorivka.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces launched unsuccessful ground attacks near Siversk, Ukraine. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that these attacks occurred northeast of Siversk near Bilohorivka and east of Siversk near Verkhnokamyanske. The attempts were unsuccessful, with Russian forces failing to gain ground in these areas.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces advanced northeast of Chasiv Yar, progressing along the E40 highway near Zaliznyanske. Fighting continued on Chasiv Yar’s eastern outskirts and near Bila Hora to the south.
Toretsk
Russian forces advanced near Toretsk, making gains in western Druzhba. They claimed to capture Nelipivka, though unconfirmed. Fighting continues around Toretsk, including towards Zabalka Microraion and near Shcherbynivka. Ukrainian reports indicate Russian attacks near Toretsk, Zalizne, Nelipivka, and towards Shcherbynivka.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces are advancing north and south of Selydove, attempting to bypass the town. They made progress along the M04 highway north of Selydove and towards the rail line to its south. Fighting is reported in numerous settlements around Pokrovsk and Selydove, including Vozdvyzhenka, Mykolaivka, and Krutyi Yar.
West of Donetsk City
Russian forces continued attacks west of Donetsk City with fighting reported near Heorhiivka, Hostre, and Oleksandropil. No confirmed Russian advances were made. Russian sources claimed a missile strike damaged a bridge over the Kurakhivske Reservoir.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces advanced northeast of Vuhledar, progressing south of Maksymilyanivka and Katerynivka. They continued attacks near Katerynivka, Yelyzavetivka, and Vodyane.
Russian forces advanced on Vuhledar’s western outskirts, with the 403rd Motorized Rifle Regiment planting a flag there. They also progressed north of Pavlivka. Russian attacks on Vuhledar continue from three directions: Pavlivka, Prechystivka, and Vodyane. The situation in Vuhledar is described as difficult, with Russian forces attempting to surround it. Various Russian units, including special forces and tank brigades, are operating in the area.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
There were no reports of fighting in the border region between Donetsk and Zaporizhia Oblasts, according to both Russian and Ukrainian sources. This area had not seen any significant combat activity that day.
Zaporizhia Line
Russian forces attacked near Novodanylivka, north of Robotyne, in western Zaporizhia Oblast. No frontline changes were confirmed.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Neither Ukrainian nor Russian sources reported fighting in the Kherson area. A Russian military blogger complained about a lack of drones for Russian forces on islands in the Dnipro River Delta.
Ukraine News
Russia launched a significant aerial attack on Ukraine, involving 76 aerial objects including various missiles and 73 Shahed drones, originating from several Russian regions such as Kursk, Yeisk, Oryol, and occupied Crimea. Ukrainian air defenses successfully intercepted 67 drones and one missile across multiple regions. Kyiv was the primary target, with an air raid alarm lasting over five hours and debris from a downed drone falling near a residential area in the Obolon district. Mayor Vitalii Klitschko reported no damage or casualties in Kyiv. The attacks caused a forest fire in Kharkiv Oblast, fires in Kyiv Oblast, and damage to a critical infrastructure facility in Mykolaiv Oblast. These drone attacks on Kyiv have increased in frequency throughout September.
President Volodymyr Zelensky of Ukraine is preparing to unveil a five-point “victory plan” to the public, with some parts remaining classified for security reasons. Andriy Yermak, head of the President’s Office, emphasized the importance of keeping certain details confidential to prevent information leaks to Russia. The plan reportedly includes military and diplomatic components, such as requests for security guarantees, modern weapons, financial aid, and Ukraine’s potential NATO membership. Zelensky presented this plan to U.S. officials during his recent visit, where he met with key political figures and received assurances of continued support. While conflicting reports exist about the plan’s reception, with some suggesting the White House was unimpressed, presidential spokesperson Serhii Nykyforov stated that Washington received it “constructively.”
Ukraine’s new Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha met with Hungarian counterpart Peter Szijjarto in Budapest. They discussed bilateral relations, minority rights, and Ukraine’s EU and NATO accession. Hungary has opposed Ukraine’s Western integration and maintained close ties with Russia. Recently, Ukraine sanctioned Russian oil transits through its territory, affecting supplies to Hungary. This visit is part of Sybiha’s regional tour, following trips to Romania and Slovakia. Despite previous high-level meetings, tensions remain, with Hungary’s Prime Minister Viktor Orban suggesting a ceasefire during his July visit to Kyiv, which President Zelensky rejected.
Ukrainian singer Jamala’s documentary “Songs of Freedom” won the Gold Dolphin at the Cannes Corporate Media & TV Awards in the Human Concerns and Social Issues category. The film highlights her work and support for Ukraine during Russia’s full-scale invasion. Jamala, who won the 2016 Eurovision Song Contest with her song “1944” about the deportation of Crimean Tatars, comes from a family that was deported to Central Asia in 1944 by Soviet authorities. The documentary was selected out of nearly 800 applications from 46 countries, reflecting the ongoing struggles and fight for freedom in Ukraine.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 3 INJURIES: 45
Russian forces conducted attacks across multiple regions in Ukraine. In Zaporizhzhia, an air strike injured 16 people, including two boys. The villages of Lysivka and Shevchenko in Donetsk Oblast saw two fatalities. Sumy Oblast reported 10 injuries from guided bomb and drone attacks. In Kharkiv Oblast, attacks on Bohuslavka and Odnorobivka injured four people. Kherson Oblast faced widespread attacks, with one person killed and 12 injured across 17 settlements, including Kherson city.
Ukraine’s Allies
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky’s recent visit to the United States was described as challenging but successful by Andriy Yermak, head of the President’s Office. Zelensky’s ‘Victory Plan’ was well-received by Congress, President Biden, and presidential candidates. The visit resulted in strong ongoing support for Ukraine, with plans for future meetings to discuss next steps. Zelensky expressed confidence about the potential easing of restrictions on using US-donated weapons for strikes within Russia. The trip included meetings with various US leaders and highlighted continued efforts to gain support from neutral countries.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
A Russian company, Donskoy Ugol Trading House, plans to export coal from occupied Donbas through Mariupol’s port starting October, according to Russian state media. The company reportedly leased 10 coal mines in Luhansk Oblast, some previously owned by Ukrainian company Metinvest. Negotiations are underway with potential buyers in China, India, Iran, Uzbekistan, and Malaysia. The coal may be exported through occupied Mariupol, Russian cities, and by rail through Azerbaijan and Iran. Mariupol, in Donetsk Oblast, was devastated during Russia’s 2022 siege, with an estimated 25,000 casualties.
Russia News
The Russian government plans to allocate 41% of its 2025 budget, totaling 17 trillion rubles ($183 billion), to national security and defense. This includes 13.5 trillion rubles for defense and 3.5 trillion rubles for security. The budget also includes funds for a military mobilization reserve, veteran support, and technological development in areas like unmanned aircraft and microelectronics. However, increased spending may not directly translate to improved military capabilities, as a significant portion is earmarked for benefits to soldiers, veterans, and their families.
The 2025 Russian budget allocates 6.4 trillion rubles ($69 billion) to social policies, including 4 trillion rubles for child-related payments and 1.7 trillion rubles for the maternity capital program through 2030. Education receives 1.57 trillion rubles, while healthcare gets 1.86 trillion rubles. The government has also set aside funds for pensions and their increases. However, the continued focus on defense spending may impact the effectiveness and sustainability of these social programs, potentially affecting the Kremlin’s efforts to address Russia’s demographic crisis and maintain domestic support.
Russian President Vladimir Putin marked the second anniversary of Russia’s claimed annexation of four Ukrainian regions – Donetsk, Luhansk, Zaporizhzhia, and Kherson. In a video message, Putin vowed to achieve all intended goals in Ukraine, despite not fully controlling these territories. He accused Western allies of turning Ukraine into a “military base aimed at Russia.” Putin’s initial invasion goals, including the capture of Kyiv and removal of Ukraine’s government, have not been realized. Russia now focuses on fully occupying the Donbas region, which includes Donetsk and Luhansk Oblasts.
Russian President Vladimir Putin has updated the membership of the Russian Security Council, a key advisory body on national security issues. Putin added four new members: presidential aide Alexei Dyumin, First Deputy Prime Minister Denis Manturov, Head of the Federal Medical-Biological Agency Veronika Skvortsova, and Head of the Kremlin’s Main Directorate for Special Programs Alexander Linets. Notably, Dyumin, at 52, becomes the youngest member of the council. These appointments, particularly of younger officials like Dyumin and Manturov, suggest Putin may be preparing a new generation of leadership while maintaining control over key national security decisions.
Russian opposition leader Alexei Navalny died at age 47 in a prison in Russia’s Far North on February 16, 2024. Investigators from The Insider obtained documents suggesting his death may have been due to poisoning, contrary to official reports of natural causes. The documents mention symptoms like severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and seizures, which were omitted from final reports. Medical experts consulted by The Insider stated these symptoms are consistent with poisoning, possibly by an organophosphate compound. However, Ukraine’s intelligence chief Kyrylo Budanov claimed Navalny died from a blood clot. Navalny, known for his anti-corruption work, had previously survived a Novichok poisoning in 2020 before being imprisoned in 2021.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1370 654430 |
Tanks +9 8883 |
Artillery +33 18855 |
Arm. VEH +44 17547 |
Aircraft 369 |
Heli 328 |
Ships 28 |
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian President Vladimir Putin ordered the fall conscription of 133,000 men from October 1 to December 31. This is fewer than the 150,000 conscripted in spring 2024. While Defense Minister Andrei Belousov says there are no plans for general mobilization, authorities may pressure these draftees to sign contracts allowing deployment to Ukraine.
Russia’s new RS-28 Sarmat ICBM, known as “Satan II,” has faced setbacks in its development. Despite claims by Russian officials that the missile was operational, a recent explosion at the Yubileynaya silo launch site suggests otherwise. This marks the fourth failed Sarmat launch. The missile, intended to replace older ICBMs, can reportedly carry up to 15 nuclear warheads and cover nearly 18,000 kilometers. However, experts question Russia’s ability to produce these missiles due to potential parts shortages and Western sanctions. The Sarmat’s failures come amid ongoing tensions between Russia and Ukraine, with Russian officials continuing to make nuclear threats. Despite these challenges, Russia remains eager to upgrade its aging missile fleet.
The Russian government has backed a bill to develop domestic replacements for imported aircraft parts. This legislation would allow the Federal Air Transport Agency to approve the production and use of non-original components in aviation equipment.
Russia’s Allies
Russian Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin visited Tehran on September 30 to meet with Iranian officials, including President Masoud Pezeshkian and First Vice President Mohammad Reza Aref. Discussions focused on expanding economic cooperation and Russian investment in Iran. Mishustin expects Russia and Iran to sign a comprehensive strategic cooperation agreement at the upcoming BRICS summit in Kazan from October 22 to 24. This visit, which included a meeting with Iranian Oil Minister Mohsen Paknejad, underscores both countries’ efforts to strengthen their economic and financial ties as part of their growing bilateral relationship.
Belarus has announced a new stage of military inspections, focusing on air force and air defense units. The exercises will involve multiple brigades, regiments, and air bases across all training areas. Belarus is also calling up reservists for these drills. While Belarus hosts Russian troops and equipment, it has not directly participated in the invasion of Ukraine. However, tensions remain high, with Belarus reportedly moving a third of its army to the Ukrainian border earlier this summer. Ukraine has warned of a significant build-up of Belarusian forces and former Wagner Group mercenaries near its border, stating it will take necessary measures to defend itself if its border is violated.
Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko met with Aisen Nikolaev, the leader of Russia’s Yakutia region. They discussed trade relations and cooperation between Belarus and Yakutia.
Controlling the Narrative and Russian Propaganda
Russian President Vladimir Putin awarded milblogger and state TV correspondent Yevgeny Poddubny the Hero of Russia award for “demonstrating heroism” while on duty, following a personal call after Poddubny’s injury in Kursk Oblast. Simultaneously, authorities awarded milblogger Roman Alekhin the “Defender of Kursk Oblast” medal, despite his previous criticisms of local government. Alekhin was also appointed as a volunteer advisor by Kursk Oblast Governor Alexey Smirnov. These actions, along with similar efforts involving milbloggers Alexander Kots and Mikhail Zvinchuk, are part of the Kremlin’s broader strategy to control the information space by co-opting previously critical voices, particularly among ultranationalists. This approach has been increasingly employed since late 2022, with Poddubny, who supported Putin’s presidential campaigns in 2018 and 2024, being used to spread official narratives.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
