Summary of the Day:
Russian forces are showing significant activity across multiple fronts, advancing in Kursk and Kharkiv oblasts, as well as in the Svatove, Toretsk, Pokrovsk, Kurakhove, Vuhledar, and Velyka Novosilka directions. Ukrainian forces have achieved gains in the Vuhledar direction, demonstrating continued resistance against Russian advances.
Following Assad’s fall, Russian forces maintain a cautious posture in Syria, with naval vessels including the Admiral Golovko and Admiral Grigorovich frigates holding positions 8-15km offshore from Tartus. Russian troops are actively dismantling equipment at both the Tartus naval facility and Hmeimim Air Base, though some military assets remain in place.
Russia is strengthening its military alliance with North Korea through a significant deal to supply MiG-29 and Su-27 fighter jets in exchange for North Korean troops supporting Russia’s war in Ukraine. North Korean pilots are already training in Vladivostok, with troops positioned in Russia’s Kursk Oblast. Simultaneously, Russia maintains defense relationships with India, though India has reduced its Russian military purchases in favor of Western suppliers.
The Russian government is working to formalize irregular military units and veterans from the Donetsk and Luhansk People’s Republics under the Russian Ministry of Defense, indicating efforts to consolidate control over these forces. Reports suggest President Putin has promoted Deputy Defense Minister Pavel Fradkov to Major General, potentially signaling changes in military leadership structure.
Despite Western sanctions, Russia continues to utilize Western-produced high-tech components in its weapons systems, demonstrating ongoing ability to circumvent international restrictions on military technology.
Picture of the Day:
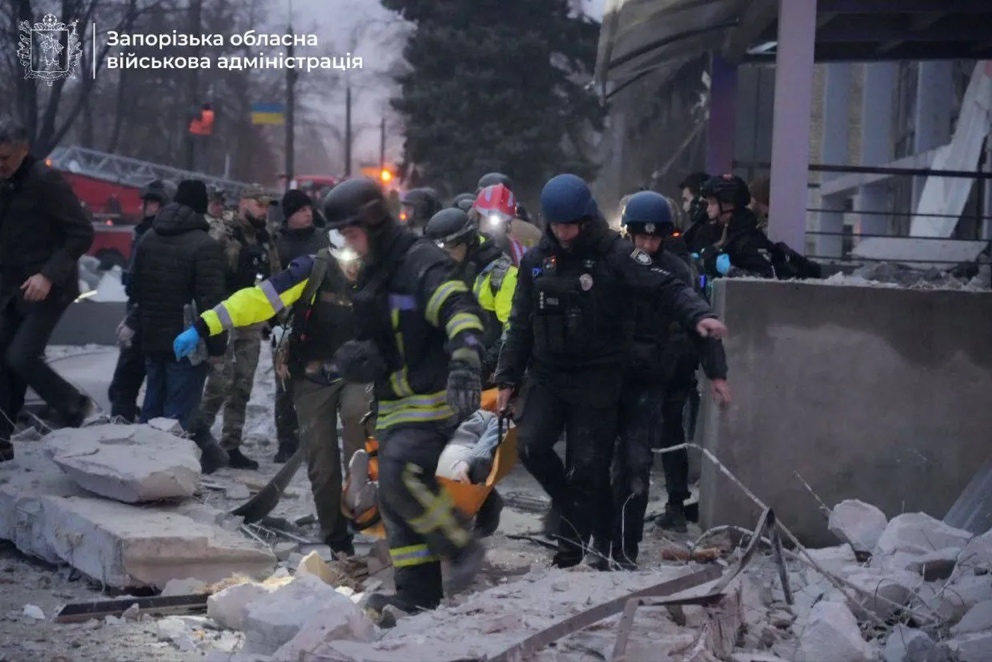 The aftermath of the Russian strike against the regional center of Zaporizhzhia in Zaporizhzhia Oblast. (Zaporizhzhia Oblast Military Administration / Telegram)
The aftermath of the Russian strike against the regional center of Zaporizhzhia in Zaporizhzhia Oblast. (Zaporizhzhia Oblast Military Administration / Telegram)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Syrian President Bashar al-Assad was ousted on Sunday, December 8, creating uncertainty about Russia’s military presence in the country. Russia, which had maintained a significant military presence in Syria since 2015, operates two strategic bases there – the Khmeimim Air Base in Lakatia and the Tartus Naval Base on the Mediterranean coast, with the latter being Russia’s only naval facility on the Mediterranean Sea. While Syrian rebel groups have gained control of regions hosting both bases, the Kremlin claims it has received guarantees from opposition forces that Russian military installations will be protected. Satellite imagery shows Russian naval forces, including the Admiral Golovko and Admiral Grigorovich frigates, maintaining an unusual distance of 8-15km offshore from their traditional base at Syria’s Port of Tartus, while Russian forces actively dismantle equipment at both facilities.
Russia has launched a major military withdrawal from Syria, evacuating troops and equipment via the Khmeimim Airbase using both military aircraft and naval vessels, with special forces deployed to secure the withdrawal process. The BBC reports that 543 Russian military personnel and mercenaries died in Syria between 2015-2024, including 346 Wagner Group members. This development, coupled with Russia’s ongoing war in Ukraine, signals a weakening of Russian influence in the Middle East, particularly as Russia had been using Syria as a base for recruiting mercenaries for its Ukraine operations. Turkey appears to be emerging as a key mediator in discussions about Russia’s continued military presence in Syria.
Following Assad’s fall, Israel has launched a massive air campaign against Syria, striking over 250 military installations across multiple provinces including Hama, Homs, and Latakia. The strikes targeted critical infrastructure including air bases, missile systems, and military warehouses, with significant damage reported by the Syrian Human Rights Monitoring Center. Israel has withdrawn from the 1974 disengagement agreement with Syria and deployed troops along the border, potentially preparing for a ground operation. While the IDF states it is not intervening in Syria’s internal affairs, Israel seeks to pressure the new Syrian opposition leadership into a non-aggression agreement, though rebel leader Abu Muhammad al-Julani has not yet engaged in direct talks with Israeli authorities.
A significant military alliance is forming between Russia and North Korea, marked by Russia’s agreement to provide North Korea with MiG-29 and Su-27 fighter jets in exchange for North Korean troops supporting Russia’s war in Ukraine, according to US Admiral Samuel Paparo. The deal, formalized by a strategic treaty in June 2024, may also include transfers of advanced military technology such as ballistic missile systems and air defense capabilities, while North Korean pilots are already training in Vladivostok, and 10,000-12,000 North Korean troops are positioned in Russia’s Kursk Oblast. This collaboration between two internationally sanctioned nations not only strengthens North Korea’s aging air force and circumvents international sanctions but also represents a concerning development that could alter the balance of power in East Asia, challenge international security norms, and escalate global tensions by strengthening North Korea’s military capabilities while supporting Russia’s aggressive actions in Ukraine, particularly given North Korea’s nuclear-armed status.
India’s delicate balancing act between Russia and Western allies is highlighting global diplomatic tensions. Russian President Putin met with Indian Defense Minister Rajnath Singh in Moscow, as India moves forward with acquiring Russian military technology, including a new frigate and potentially a long-range radar system. However, India has significantly reduced its Russian defense orders in favor of Western suppliers. This diplomatic tightrope walk by India, one of the world’s largest military powers, reflects the complex challenges facing international security cooperation in an increasingly divided world. The situation underscores how major powers’ relationships with Russia continue to shape global military alliances and peace prospects.
In a concerning escalation of nuclear threats, Belarusian President Lukashenko claimed that Belarus has secretly received numerous tactical nuclear warheads from Russia and threatened to strike Western countries if they cross Belarusian borders. This aggressive rhetoric appears to be part of Russia’s strategy to intimidate Western nations into reducing their military support for Ukraine, posing a significant risk to global stability.
A significant meeting between Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban, U.S. President-elect Donald Trump, and Elon Musk at Mar-a-Lago on December 9 signals potential dramatic shifts in global peace efforts. Trump’s promise to end the Russia-Ukraine war within 24 hours and hints at reducing U.S. aid to Ukraine, combined with Orban’s pro-Moscow stance and resistance to EU sanctions, suggests a major realignment in Western support for Ukraine. This partnership, following Orban’s recent visits to Moscow, Kyiv, and Beijing, could reshape the current international approach to resolving the conflict. Their strategy of forcing Ukraine to negotiate while reducing military support represents a fundamental departure from current Western policy, potentially altering the balance of power in Eastern Europe and global security dynamics.
A significant shift in global military dynamics is emerging as Chinese manufacturers begin restricting drone component sales to U.S. and European customers. This development could severely impact the Ukraine-Russia conflict, where drones play a crucial role. Russia aims to produce 1.4 million drones by 2024 using Chinese parts, while Ukraine plans 30,000 long-range drones by 2025. The restrictions, seen as China’s response to U.S. semiconductor sanctions, come amid evidence of China’s support for Russia’s military efforts despite claims of neutrality. With President-elect Trump’s expected tough stance on China, this technological trade war could reshape military alliances and battlefield capabilities, potentially destabilizing current peace efforts and military balances worldwide.
Politico has released its influential Europeans list for the coming year, highlighting key figures in the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Ukrainian President Zelensky’s chief of staff Andriy Yermak, nicknamed “The Fixer,” is listed in the “dreamers” category for his shift from wartime strategy to peace efforts. Russian President Vladimir Putin, labeled “The Imperialist,” appears in the “doers” category, with Politico noting his apparent success in dividing Western unity despite Russia’s economic challenges. The list also reflects Eastern Europe’s growing influence, featuring four Polish representatives and prominent right-wing figures like Hungary’s Viktor Orban and France’s Marine Le Pen.
The Path to Peace
Polish Prime Minister Donald Tusk announced that peace negotiations for the Ukraine war could begin this winter, with Poland planning to take an active role when it assumes the EU Council presidency in January. French President Macron will visit Warsaw this week to discuss his recent talks with U.S. President-elect Trump and Ukrainian President Zelensky, while Ukraine is forming a coalition of allies to coordinate battlefield and diplomatic strategies. Tusk emphasized Poland’s commitment to shaping decisions that will secure peace while protecting Polish interests.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian military spokesperson Colonel Nazar Voloshyn reported that Russian forces currently maintain a 3:1 artillery advantage over Ukrainian forces, down from a 5:1 advantage at the start of the invasion. Russian forces have deployed approximately 150,000 troops across three main areas: 70,000 near Pokrovsk, 36,000 near Kurakhove, and 40,000 in the Vremivka direction.
Russian forces reportedly advanced near the Ukrainian border village of Oleksandriya in Sumy Oblast, occupying 2 square kilometers according to DeepState Map analysts, though local authorities, including Military Administration head Volodymyr Artyukh and Ukrainian border services, deny any border breach and some Russian sources dismiss these claims as false. Sumy Oblast, which borders Russia’s Bryansk, Kursk, and Belgorod regions, faces frequent attacks on its border communities.
Recent satellite images show that Russia has reduced the number of protective barges in the Kerch Strait from 34 to 18, weakening defenses for the Crimean Bridge against Ukrainian attacks. The 19-kilometer bridge, built after Russia’s 2014 occupation of Crimea, has been hit multiple times, suffering major damage in October 2022 and July 2023. Some protective barriers were previously lost during storms, with debris washing up on Kerch beaches. The bridge remains a crucial supply route for Russian forces and is the subject of ongoing legal disputes between Ukraine and Russia.
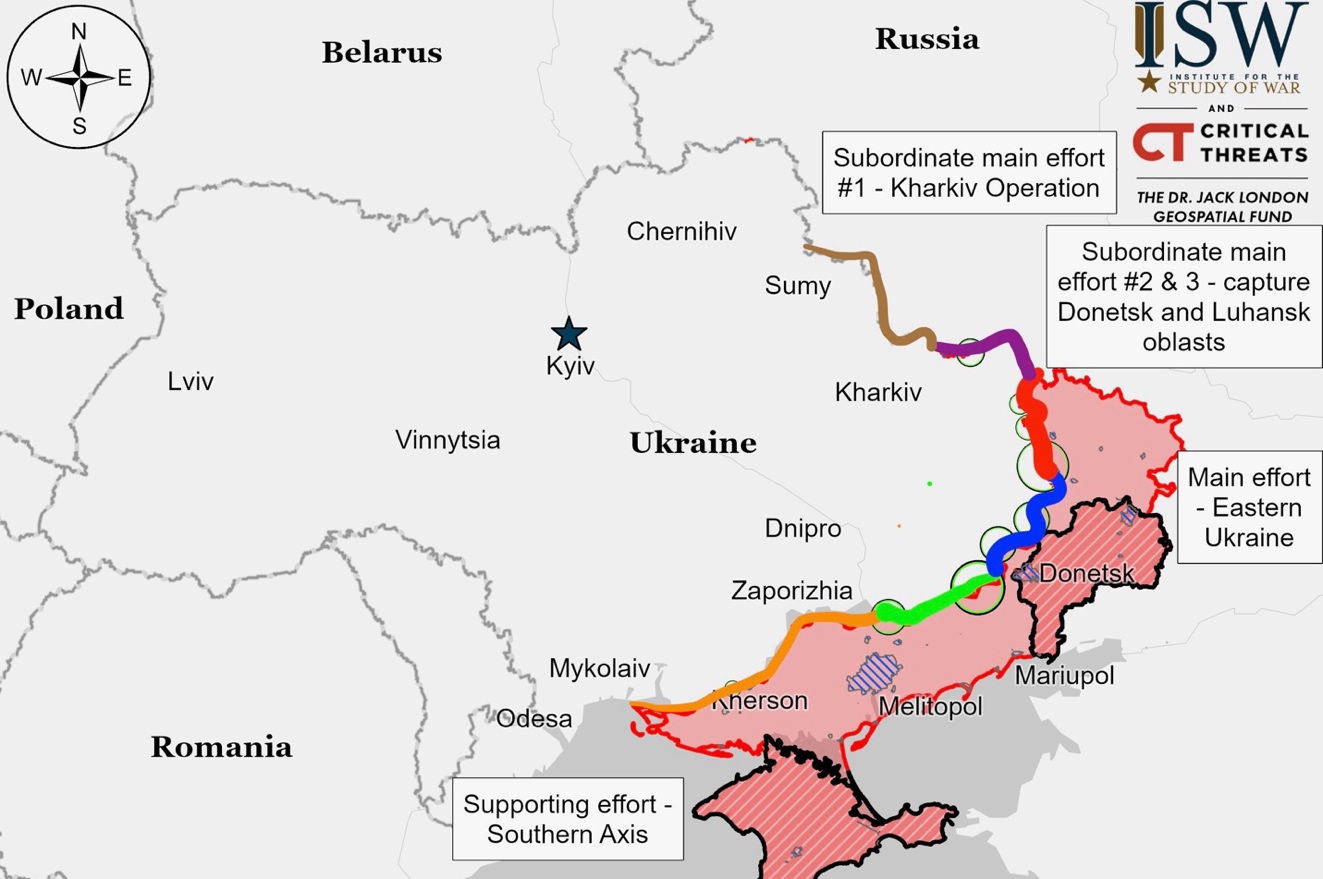
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative Russia
Russian forces made advances in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast, particularly in southern Darino. Fighting was reported in several settlements including Plekhovo, Novoivanovka, Malaya Loknya, Kamyshevka, Guyevo, Pogrebki, and Nikolayevo-Darino. Russian forces are using both modern and Soviet-era equipment, including T-90 tanks, with various military units including airborne divisions and motorized rifle regiments participating in the operations.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces continued attacks north and northeast of Kharkiv City near Hlyboke, Vovchansk, and Starytsya. While Russian sources claim to have captured positions in southern Vovchansk, these claims remain unverified. Ukrainian officials report that Russian forces are attempting to cross the Vovcha River near Vovchansk, using inexperienced infantry for initial attacks followed by more experienced units. Russian forces are reportedly not using armored vehicles in these assaults due to limited supplies.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces advanced west of Svatove, capturing Vyshneve and Pershotravneve, and are attempting to establish a position to cross the Oskil River, though they remain 15km away from it. Russian forces also claim advances near Lozova, Zeleny Hai, Novoyehorivka, and Hrekivka, though these are unconfirmed. Fighting continues across multiple locations including Dvorichna, Petropavlivka, Kolisnykivka, Zahryzove, Kopanky, Makiivka, Cherneshchyna, Druzhelyubivka, Terny, Torske, and Yampolivka. Russian forces are using light vehicles and small infantry teams in their attacks.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Fighting continues near Siversk, with clashes reported at Bilohorivka and Verkhnokamyanske. Ukrainian forces are reportedly using drone swarms to slow Russian advances toward Siversk by blocking their movements in combat zones.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued attacks around Chasiv Yar, including near Orikhovo-Vasylivka and Bila Hora, but made no confirmed advances. Cold weather is hampering drone operations in the area, while Russian forces are using drones to plant mines along Ukrainian supply routes.
Toretsk
Russian forces advanced in central Toretsk along Frunze Street and in southeastern Shcherbynivka. Fighting continues in and around Toretsk, Shcherbynivka, and Nelipivka. Ukrainian forces reported a successful counterattack near the Siverskyi-Donets Donbas Canal northeast of Toretsk, where Russian forces have increased drone and artillery strikes.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces advanced in northern Novotroitske along Myru Street and claimed to have captured Zhovte, southwest of Pokrovsk. While Russian sources also claim to have taken Shevchenko, this remains unconfirmed. Fighting continues near several settlements including Promin, Myrolyubivka, Lysivka, Dachenske, Zelene, Chumatske, and Novyi Trud. Ukrainian sources note that Russian forces have a significant drone advantage in this area, helping them make rapid tactical advances.
Kurakhove
Russian forces advanced in central Kurakhove, capturing the grain elevator, while claiming additional gains near Pushkina and Lermontova streets, the City Council building, and the Yuzhnyi Microraion district. Russian sources also claim advances between Sontsivka and Stari Terny, and movements toward Dachne and the H-15 highway, though these claims remain unconfirmed. Fighting continues near several settlements including Zorya and Dalne. Russian forces claim to control key supply routes into Kurakhove and are attempting to straighten their front-line north of the Kurakhivske Reservoir.
Andriivka
Ukrainian forces recaptured positions in western Romanivka, while Russian forces advanced in southeastern Kostiantynopolske and eastern Uspenivka near Vuhledar. Fighting continues near several settlements including Veselyi Hai, Hannivka, Sukhi Yaly, and Rozlyv. Russian forces are reportedly operating near the Sukhi Yaly River north of Vuhledar.
Velyka Novosilka
Russian forces advanced near Velyka Novosilka capturing Blahodatne. Fighting continues around several settlements including Rozdolne, Makarivka, Storozheve, Novodarivka, Rivnopil, and Zelene Pole.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces advanced north of Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast, moving along the Tokmak-Orikhiv highway. Several Russian military units are involved in the operation. Reports suggest that Russian forces, typically stationed near Pokrovsk, may have been redeployed to the area, potentially indicating a shift in Russian military priorities toward western Zaporizhia Oblast. However, according to Russian military bloggers, the main Russian forces have not yet been deployed to this region.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces attacked areas along the eastern bank of the Dnipro River and nearby islands in Kherson Oblast. According to Ukrainian military officials, Russian forces are focusing their efforts on advancing toward islands near where the Dnipro River meets the sea, though they have not made any confirmed progress in these areas.
Russian forces are reportedly struggling with internal sabotage as soldiers damage their own boats and equipment to avoid crossing the Dnipro River in Kherson Oblast, according to Ukrainian resistance group Atesh. Russia has gathered about 300 boats near the river, which separates Ukrainian-controlled territory from Russian-occupied areas. From the east bank, Russian forces continue to shell Kherson city and nearby villages. Some soldiers are allegedly sharing locations of boat bases and fuel supplies with Ukrainian forces, though these claims cannot be independently verified.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched missile strikes against Kharkiv and Zaporizhia regions. In Kharkiv Oblast, three ballistic missiles hit Zlatopil, damaging government and residential buildings. In Zaporizhzhia City, a missile struck a clinic and surrounding buildings.
In a recent meeting in Paris, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky met with Donald Trump and French President Emmanuel Macron to discuss Russia’s invasion. Zelensky later revealed that he told Trump that Russian President Vladimir Putin “fears only him and China.” While Zelensky seeks U.S. support for “a just and lasting peace,” Trump has indicated Ukraine would receive reduced assistance under his potential future administration. Trump claimed Zelensky is ready “to make a deal,” but Zelensky cautioned that peace requires more than signatures, warning that Putin has previously broken ceasefires.
A new survey by the Kyiv-based New Europe Center shows 70.3% of Ukrainians support joining NATO through a model like West Germany’s 1955 accession, where NATO protection would initially cover only unoccupied territories. The poll reveals that 64.1% of Ukrainians oppose talks with Russia without Western security guarantees, though support for a hardline stance has decreased from last year. President Zelensky recently suggested that NATO’s Article 5 protection might not apply to areas under active combat, indicating a shift toward accepting diplomatic solutions for some occupied territories, including Crimea.
A new survey by the New Europe Center reveals that 44.6% of Ukrainians trust U.S. President-elect Donald Trump, compared to 55.2% for President Biden, marking a significant shift from 2023 when only 10% preferred Trump. The relatively high trust in Trump comes despite his criticism of U.S. military aid to Ukraine and his stated intention to force peace negotiations. Trust in Western leaders has generally declined, with Biden’s approval dropping from 82% to 55.2%, and German Chancellor Scholz falling from 61.4% to 36.9%. Only French President Macron saw an increase in trust, rising to 58.4%, while European Commission President von der Leyen and Polish President Duda maintain 65% trust levels among Ukrainians.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 6 INJURIES: 41
Russian forces launched attacks on two Ukrainian cities. In Zaporizhzhia, a missile strike destroyed a private clinic, killing three people and injuring 16, with rescuers searching for survivors in the rubble. In Zlatopil, Kharkiv Oblast, another Russian strike injured 11 people and damaged buildings and vehicles near a bank.
Russian forces struck multiple settlements in Donetsk Oblast, resulting in two deaths and seven injuries. The attacks hit Mykolaivka and Stara Mykolaivka, each reporting one death and two injuries, while Kostiantynivka saw two people injured and Novoeconomichne had one injury.
Russian attacks in Kherson Oblast killed one person and injured seven others.
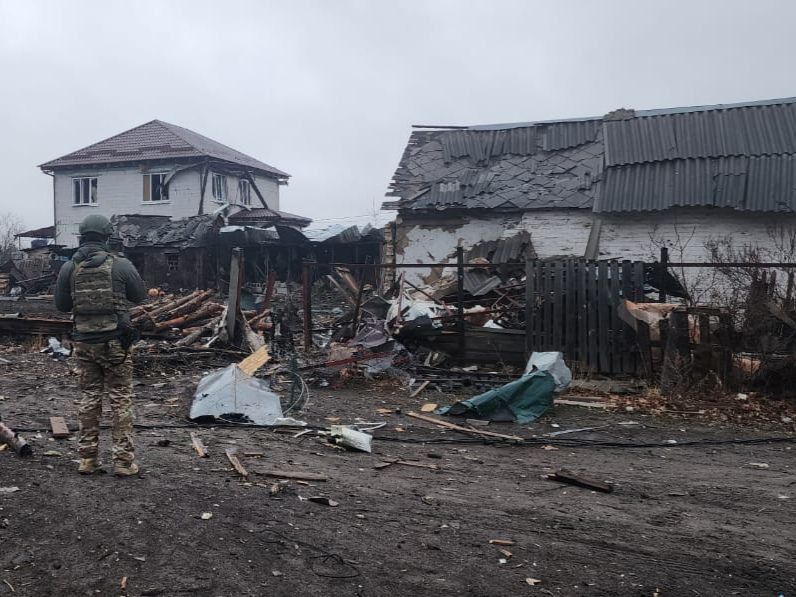 The aftermath of Russian attacks against Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. (Governor Vadym Filashkin/Telegram)
The aftermath of Russian attacks against Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. (Governor Vadym Filashkin/Telegram)
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine has successfully tested a new missile called Ruta (Rue). The country has also begun mass production of Palianytsia, a lightweight missile-drone hybrid, while another hybrid weapon called Peklo (Hell) is already in combat use. These developments, along with Ukraine’s first domestically produced ballistic missile tested in August, showcase the country’s growing missile program since Russia’s 2022 invasion.
Ukraine’s Allies
The U.S. State Department has approved a $266 million support package for Ukraine’s F-16 fighter jets, including maintenance services, parts, and training equipment. This follows Denmark’s recent transfer of a second batch of F-16s to Ukraine and complements Ukraine’s ongoing pilot training programs with Western allies. The package aims to strengthen Ukraine’s air defense capabilities. Additionally, the U.S. announced a separate $988 million military aid package on December 7, which includes HIMARS ammunition and drone deliveries. The aid comes as the Biden administration works to secure support for Ukraine ahead of the upcoming presidential transition.
German Chancellor candidate Friedrich Merz expressed support for delivering Taurus long-range missiles to Ukraine during his visit to Kyiv, but emphasized this would require coordination with U.S. and European partners. Speaking with Bild on December 9, Merz noted that training Ukrainian forces on the missiles would take at least four months, extending beyond U.S. President-elect Trump’s inauguration. While supporting strikes on Russian military targets, Merz stressed the need to avoid civilian casualties and prevent Germany from becoming a direct party to the conflict. Currently, Ukraine operates similar long-range missiles from the U.S., France, and the UK, which have recently permitted strikes within Russian territory.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
Russian occupation authorities announced evacuations in the city of Yenakiieve, Donetsk Oblast, on December 10 following reported explosions. Local Telegram channels shared footage of multiple explosions in the city, though Russian authorities claim the situation is “under control” without providing details. Yenakiieve, a mining and metallurgy center occupied by Russia since 2014, has been subject to Ukrainian strikes on Russian military facilities since the 2022 invasion.
A Russian drone attacked an International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) service vehicle heading to the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant for staff rotation, President Zelensky reported. IAEA Director Rafael Grossi condemned the attack as “unacceptable.” The plant, Europe’s largest nuclear facility occupied by Russia since March 2022, is currently connected to Ukraine’s power grid by just one transmission line and has faced multiple power disruptions from Russian shelling since November.
Russia News
A Russian insider source reported on December 9 that President Putin promoted Deputy Defense Minister Pavel Fradkov to Major General, with expectations of further promotion to lieutenant general within six months. Russian officials reportedly view Fradkov as a promising future leader with a track record of solving complex problems.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1400 757340 |
Tanks +2 9526 |
Artillery +3 21067 |
Arm. VEH +20 19616 |
Aircraft 369 |
Heli 329 |
Ships 28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russia’s parliament passed legislation granting combat veteran status to volunteer fighters who served in occupied Ukrainian territories, including Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson, and Zaporizhia. The law also extends to civilian workers in occupation administrations who served for more than six months. This appears to be part of Russia’s broader strategy to formalize irregular military units under its Ministry of Defense’s control.
Russia continues to obtain Western high-tech components for its weapons systems, including “Molniya” and “Phoenix” drones, despite international sanctions. A Bloomberg report from December 9 revealed that Russian defense companies are accessing semiconductors through third-country intermediaries, while Ukraine’s Military Intelligence confirmed the presence of American, Swiss, and Dutch components in Russian drones.
The People’s Front, a Russian organization, announced that it has developed a new unmanned ground vehicle called “Venom-Totem” to transport supplies and evacuate wounded soldiers from the frontline. The group plans to deliver 50 of these vehicles to Russian forces.
Russia’s Allies
Belarusian President Lukashenko announced that Belarus will begin manufacturing launchers for Russian “Oreshnik” ballistic missiles by late 2025. The state-owned Minsk Wheeled Tractor Plant will produce the launchers in exchange for missiles from Russia, with plans to deploy them at 30 locations across Belarus. This move further integrates Russian and Belarusian defense industries.
China’s trade with Russia saw a significant decline in November, with yuan-based exports to Russia falling 10.5% and imports dropping 7.4%, marking the first decrease since July. This shift follows increased Western sanctions on Russian financial institutions and growing scrutiny of Chinese companies helping Russia evade restrictions. While China-Russia trade initially surged after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, Chinese institutions are increasingly avoiding transactions with Russia due to fears of secondary sanctions. This trend suggests Western sanctions are beginning to impact the economic partnership between Moscow and Beijing, potentially affecting Russia’s ability to sustain its war effort.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
