Summary of the Day:
Russian forces launched multiple missile and drone attacks on Ukraine with a significant strike on Kyiv’s diplomatic quarter. Five ballistic missiles targeted the capital, and while Ukrainian forces intercepted them, falling debris damaged several embassy buildings, including those of Albania, Argentina, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Palestine, and Portugal. The overnight attacks, which included 65 drones and additional missiles, also caused damage to civilian infrastructure in the Dnipropetrovsk, Kharkiv, Kyiv, and Sumy regions.
Ukrainian forces marked a significant milestone in military technology by conducting their first attack using only unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) and drones near Lyptsi, north of Kharkiv City. The operation successfully targeted Russian positions using machine gun-equipped UGVs for both combat and mine-related tasks. Additionally, Ukraine has made progress in drone development, testing EW-resistant fiber optic cable drones and producing their first entirely Ukrainian-made FPV drone.
Russian President Vladimir Putin announced plans to designate 2025 as the “Year of the Defender of the Fatherland” to honor veterans of the Ukraine war and other Russian conflicts. This initiative follows the Kremlin’s recent efforts to integrate veterans into government positions through programs like “Time of Heroes,” aiming to both satisfy the growing veteran population and embed military values throughout Russia’s governance structure.
The Kremlin has arrested two Kursk Oblast Development Corporation officials – General Director Vladimir Lukin and former Deputy Director Igor Grabin – for allegedly embezzling 173.2 million rubles meant for border fortifications. Despite Russian President Vladimir Putin announcing major reconstruction plans for occupied Ukrainian territories during his annual televised conference, newly appointed Kursk Oblast Governor Alexander Khinshtein stated that the Russian government won’t fully fund repairs to war-damaged facilities in Kursk Oblast, citing budget constraints and ongoing war expenses.
Russian opposition outlet Mediazona has confirmed at least 20,364 Russian soldiers have been killed in action in Ukraine since January 2024, while Russian forces made territorial advances near Kupyansk, within Toretsk, and in the Vuhledar direction.
Picture of the Day:
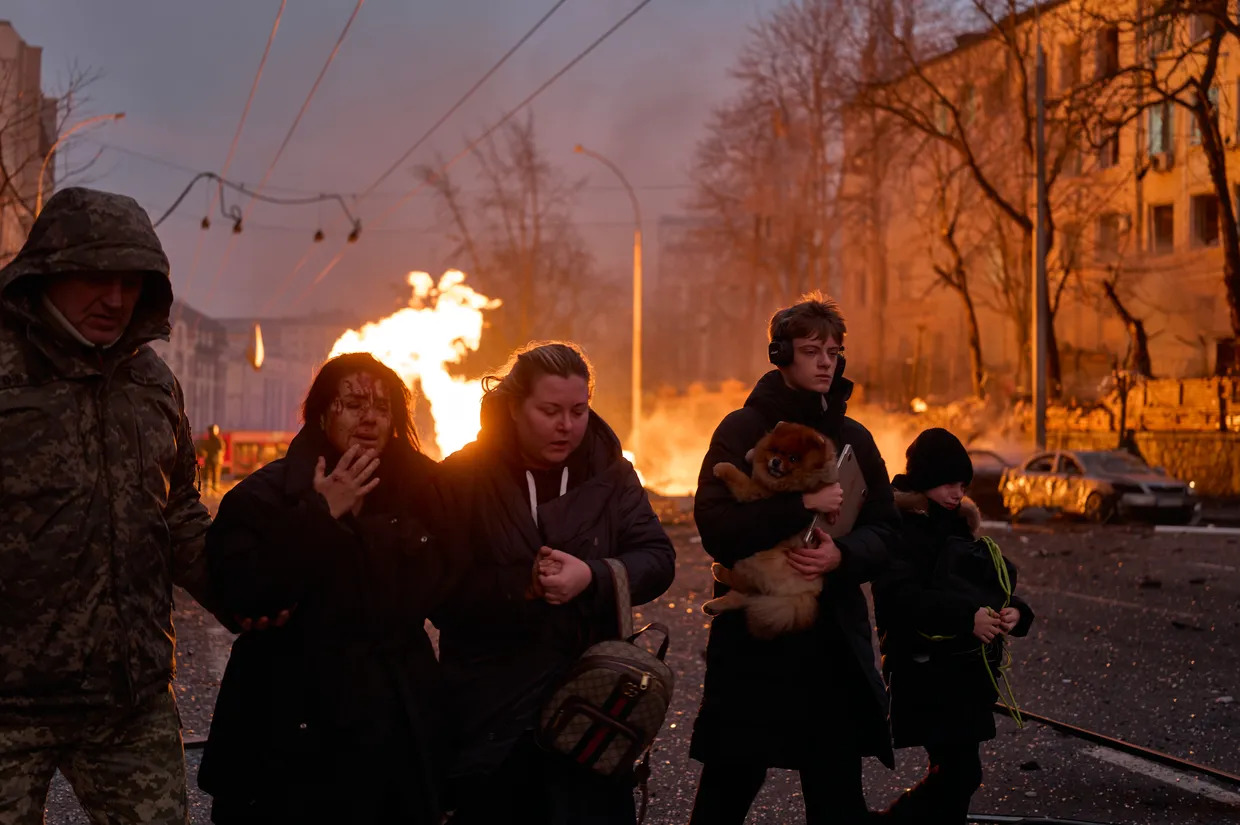 Civilians leave the site after a Russian ballistic missile hits the city center in Kyiv. (Vlada Liberova/Libkos/Getty Images)
Civilians leave the site after a Russian ballistic missile hits the city center in Kyiv. (Vlada Liberova/Libkos/Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
The OSCE’s final report on Georgia’s October parliamentary elections highlight growing concerns for regional stability and democratic values in the Caucasus. The report criticized the elections won by the pro-Russian Georgian Dream party, citing voter intimidation, unequal resources, and legislative backsliding. This political shift, marked by Georgia’s move toward Moscow and away from EU integration, has sparked mass protests in Tbilisi. The situation threatens to further destabilize the region, as Georgia’s democratic regression and closer alignment with Russia could impact the delicate balance between Western and Russian influences in the area. The contested election results and subsequent dismissal of opposition lawsuits underscore growing tensions that could affect broader European security interests.
The shutdown of Russia’s Druzhba pipeline, a major oil artery to Europe, has significant implications for regional energy security and international relations. Since December 19, technical issues at Russia’s Unecha pumping station have halted oil deliveries to Hungary, Slovakia, Czechia, and Germany, disrupting the flow of both Russian and Kazakh oil. While these EU countries received exemptions from Russian oil sanctions following Moscow’s invasion of Ukraine, the pipeline’s 300,000 barrels per day capacity interruption highlights the ongoing tensions between energy dependency and geopolitical stability. Though some shipments could be rerouted through Russian ports, the disruption underscores Europe’s complex transition away from Russian energy resources amid broader international security concerns.
The Path to Peace
In a December 19 phone call, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz and US President-elect Donald Trump agreed that the war in Ukraine has continued too long and needs a swift, just peace settlement. Both leaders confirmed they would restrict Ukraine from using long-range missiles against Russia. While Scholz pledged continued support for Ukraine, he maintained his position against providing Taurus cruise missiles. This comes as Scholz faces a no-confidence vote, while opposition leader Friedrich Merz has indicated potential support for enhancing Ukraine’s long-range capabilities if coordinated with the US.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
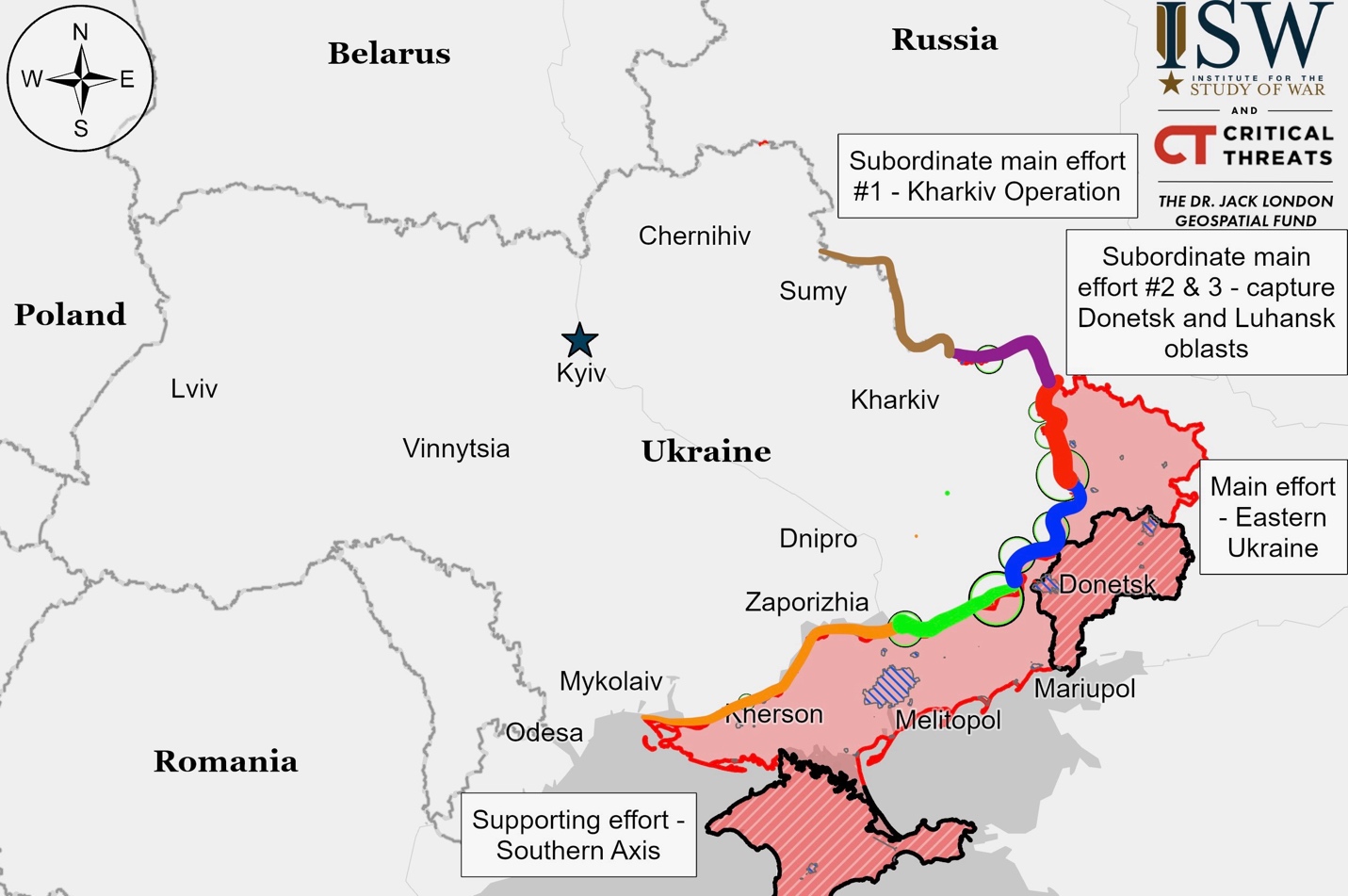
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative Russia
Russian forces advanced near Malaya Loknya in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast. Video evidence from December 18 showed Ukrainian forces striking suspected North Korean positions under Russian command in this area. Russian sources claim advances near Cherkasskaya Konopelka, while Ukrainian forces reportedly launched counterattacks near Novoivanovka and Darino.
The Pentagon estimates “several hundred” North Korean military personnel have been killed or wounded in Ukraine’s Kursk Oblast, according to spokesperson Major General Patrick Ryder. Ukraine’s military intelligence reports North Korean forces are operating near the settlements of Plekhovo, Russkaya Konopelka, and Ulanok in the Sudzha area, where they are reportedly experiencing shortages of rocket-propelled grenade ammunition.
Ukrainian forces reportedly struck Rylsk in Russia’s Kursk Oblast with Russian sources claiming the attack used ATACMS missiles. However, Kursk’s acting Governor Alexander Khinshtein countered this claim, stating that Russian forces intercepted several HIMARS rockets near Rylsk.
Ukraine’s Main Military Intelligence Directorate (HUR) reported that on December 12, a Russian An-72 military transport aircraft worth approximately $4.5 million exploded at Ostafyevo airfield near Moscow Oblast, over 1,000 kilometers from Ukraine’s border. While HUR shared footage of the explosion and noted the aircraft belonged to Russia’s naval fleet, they didn’t explicitly claim responsibility for the incident, which follows other Ukrainian operations targeting Russian aircraft, including attacks on helicopters at Moscow’s National Center of Helicopter Construction and Samara Kryazh military airfield, as well as the destruction of a $50 million Su-30SM fighter jet in September and a Tu-134 transport plane in October.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Neither Russian nor Ukrainian forces reported ground combat in northern Kharkiv Oblast. A Ukrainian commander in the area said Russian forces continue infantry attacks, but rainy weather is preventing both sides from using mechanized vehicles or reconnaissance drones.
Ukrainian forces marked a significant milestone in military technology by conducting their first attack using only unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) and drones near Lyptsi, north of Kharkiv City. The operation successfully targeted Russian positions using machine gun-equipped UGVs for both combat and mine-related tasks. Additionally, Ukraine has made progress in drone development, testing EW-resistant fiber optic cable drones and producing their first entirely Ukrainian-made FPV drone.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces advanced into northern Zahryzove, southeast of Kupyansk. The Kharkiv Oblast Military Administration reported that Russian forces are trying to bypass Dvorichna from the north and may hold positions in forests west of the Oskil River. Russian forces continued attacks across multiple settlements: near Dvorichna, Synkivka, Lyman Pershyi, Petropavlivka, Zahryzove, Lozova, Kolisynkivka, Hlushkivka, Zeleny Hai, Kopanky, Tverdokhlibove, Ivanivka, Terny, Yampolivka, Torske, and in the Serebryanske forest area.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces attacked near Bilohorivka, Hryhorivka, and Verkhnokamyanske in the Siversk area but failed to make any confirmed advances.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces attacked Chasiv Yar targeting the city’s eastern Novyi Microraion district and the central Refractory Plant but failed to make any confirmed advances in their offensive operations.
Toretsk
Russian forces made small advances in Toretsk reaching Ukrainska Street in the north and Haharina Street in the southeast. They reportedly gained up to 500 meters in the southeastern Zabalka Microraion. Fighting continued throughout Toretsk and nearby areas including Shcherbynivka and Leonidivka, while Ukrainian forces launched counterattacks near the Tsentralna Mine waste heap in central Toretsk.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces continued attacks near Pokrovsk with claimed advances near Solone, Novoolenivka, and Ukrainka, though these gains remain unconfirmed. Fighting occurred across multiple settlements including Myrolyubivka, Promin, Lysivka, Zelene, Dachenske, Novyi Trud, Novovasylivka, Novooleksiivka, Vovkove, Pishchane, Sukha Balka, and Ukrainka. It was confirmed that Russian forces captured Novopustynka on December 5.
Kurakhove
Russian forces continued attacking Kurakhove focusing on the western high-rise area while Ukrainian forces held the town’s western outskirts. Operations included assaults from Stari Terny toward Shevchenko, likely aiming to cut off the H-15 Kurakhove-Pokrovske road near Dachne. Russian forces deployed small squad tactics (2-5 soldiers) using FPV drones and light vehicles. Fighting occurred across multiple areas including Sontsivka, Andriivka, Dachne, and Dalne.
Andriivka
Russian forces made advances northwest of Vuhledar in late November, capturing Yasna Polyana and securing positions in the Uspenivka-Kostiantynopolske area after Ukrainian forces executed a planned withdrawal ordered by Commander-in-Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi to prevent encirclement, with the Khortytsia group of forces confirming the withdrawal from Uspenivka and Trudove settlements in Donetsk Oblast, approximately 8 kilometers south of Kurakhove, while Russian forces reportedly advanced toward Hihant and Yantarne, with claimed but unconfirmed operations near Ulakly, as fighting continued near Bahatyr, Rozlyv, Uspenivka, and Kostiantynopolske, and Russia is now reportedly regrouping in the captured territory and directing attacks toward the Shevchenko-Andriivka section, with a focus on Andriivka.
Velyka Novosilka
Russian forces continued attacks near the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border with claimed advances toward Storozheve from Blahodatne and Makarivka, though these gains remain unconfirmed. Fighting occurred across multiple locations including Velyka Novosilka, Neskuchne, Novopil, Novodarivka, and Novosilka.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian military bloggers report that Ukrainian forces have regained positions in western Zaporizhia Oblast advancing from Kamyanske toward Luhkove, while Russian forces continue their attacks near Robotyne, specifically around Mala Tokmachka and Novodanylivka.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched multiple attacks near Kherson City, including Kozatskyi Island and the Antonivsky Bridge area, with aerial strikes killing one person and injuring nine others, while Ukrainian officials successfully prevented a Russian reconnaissance group from crossing the Dnipro River, noting that such crossing attempts have continued throughout the past week as Governor Oleksandr Prokudin warned that Russia has assembled 300 boats for potential river crossings.
Ukraine News
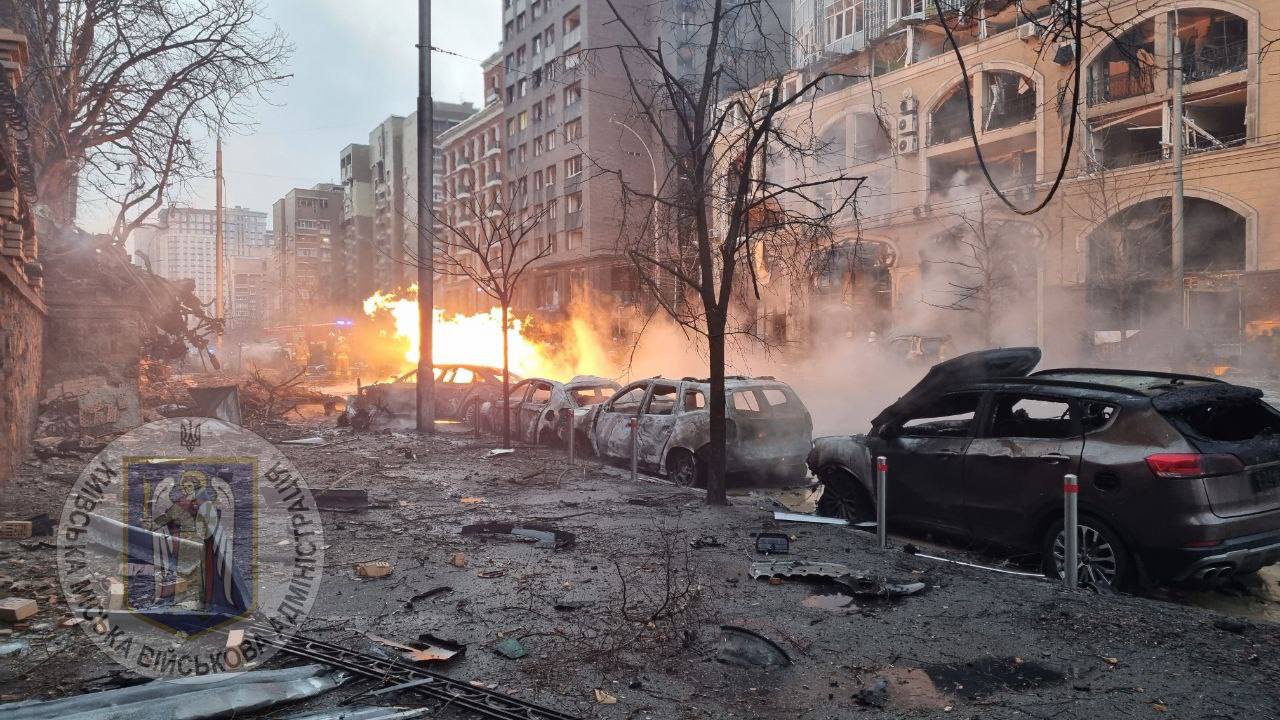
Russian forces launched multiple missile and drone attacks on Ukraine, with a significant strike on Kyiv’s diplomatic quarter where five ballistic missiles were intercepted by Ukrainian Air Force, though falling debris damaged several embassy buildings including those of Albania, Argentina, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Palestine, and Portugal, as well as the Czech Center, causing damage to windows, doors, and ceilings but no injuries to diplomatic staff, while Portugal’s Foreign Minister Paulo Rangel called the targeting of diplomatic facilities “absolutely unacceptable” and summoned Russia’s charge d’affaires to present a formal protest. The broader assault, which Russia claimed was retaliation for Ukrainian strikes on a Russian chemical plant, included 65 drones, multiple types of missiles including North Korean-made weapons, and caused damage across four Kyiv districts – Holosiivskyi, Solomianskyi, Shevchenkivskyi, and Dniprovskyi – resulting in fires, infrastructure damage, and two casualties in the Holosiivskyi district with one person requiring hospitalization, while the overnight attacks also impacted civilian infrastructure in the Dnipropetrovsk, Kharkiv, Kyiv, and Sumy regions.
Ukraine’s Security Service (SBU) has reported that Russian military intelligence (GRU) orchestrated a major cyberattack on December 19 that disabled approximately 60 Ukrainian government registers under the Ministry of Justice, with Acting SBU cybersecurity chief Volodymyr Karasteliov stating that while all ministry data was saved, the possibility of a data leak cannot be ruled out, as Deputy Prime Minister Olha Stefanishyna confirmed no data was lost and dismissed Russian propaganda claims about military recruitment databases being affected, noting that recovery efforts are underway with an estimated two-week restoration period, prioritizing notary and property rights registers, while this incident follows a series of Russian cyberattacks against Ukraine, including a significant attack on Monobank in August.
President Zelensky announced over 30 new Ukrainian ambassadorial appointments including Nariman Dzhelyal to Turkey, Alyona Getmanchuk as NATO representative, and Andrii Melnyk as UN representative. These appointments follow earlier diplomatic changes, including Andrii Sybiha replacing Dmytro Kuleba as foreign minister in September.
Ukraine repatriated 503 fallen soldiers’ bodies with most recovered from Donetsk Oblast (403), followed by Zaporizhzhia (57), Luhansk (12), and Russian morgues (31). The operation involved multiple Ukrainian agencies and support from the International Committee of the Red Cross. According to President Zelensky, approximately 43,000 Ukrainian soldiers have died since Russia’s full-scale invasion began.
Bulgaria’s bilateral security agreement with Ukraine has stalled after the country’s largest party, led by former Prime Minister Boyko Borissov, withdrew its support. Caretaker Prime Minister Dimitar Glavchev canceled the planned signing with President Zelensky in Brussels, citing need for parliamentary approval. Bulgaria joins Hungary, Austria, Slovakia, Malta, and Cyprus as the only EU countries yet to sign such agreements with Ukraine, despite having provided various aid since Russia’s invasion. The shift comes amid growing discussion of potential peace talks and reflects both international developments and Bulgaria’s internal political dynamics, including significant pro-Russian sentiment within the country.
Innocent Victims Of War
The United Nations reported over 12,340 civilian deaths and 27,836 wounded in Ukraine since Russia’s February 2022 invasion, according to UN Under-Secretary-General Izumi Nakamitsu. In 2024, aerial bombs killed 341 civilians and injured 1,803, marking a dramatic increase from 2023. Russian attacks intensified in late 2024, with increased drone strikes and approximately 100 guided bombs dropped daily in November, particularly targeting Kharkiv, Odesa, and Sumy. Putin has threatened further escalation, including Oreshnik missile strikes against Kyiv, as Russia’s long-range weapons now account for 42% of civilian casualties.
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 7+ INJURIES: 46+
A Russian missile attack on Kyiv involved five ballistic missiles (either Iskander-M or North Korean KN-23 models) that were all intercepted by Ukrainian air defenses, though falling debris caused significant damage across multiple districts including Holosiivskyi, Shevchenkivskyi, and Solomianskyi, resulting in one death and twelve injuries, with the Holosiivskyi district suffering the most damage as 16 medical facilities, 17 schools, 13 kindergartens, and 630 residential buildings lost heat, while the attack also damaged office buildings, homes, a gas pipe, vehicles, and the historic St. Nicholas Roman Catholic Cathedral’s stained glass windows in the Pechersk district, with fires breaking out in multiple locations and a separate large fire occurring in a warehouse in the Boryspil district of Kyiv Oblast.
Russian forces attacked Kharkiv striking an apartment building in the Saltivskyi district with a drone, injuring six people including a 12-year-old child. Emergency teams rescued three people from the rubble. A second drone attack the same evening caused minor damage to homes in the city’s Kyivskyi district.
Russian forces attacked the Kharkiv Oblast villages of Cheremushne and Dvorichna, injuring two women aged 46 and 54.
Russian forces struck Zaporizhzhia hitting a 9-story apartment building and injuring four people, including a 12-year-old boy and three women.
Russian forces launched a large-scale attack on Kherson killing at least two people and injuring ten others. The assault targeted residential areas and critical infrastructure facilities.
Russian forces struck a two-story house in Kryvyi Rih, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, injuring at least six people, including a 15-year-old girl.
Russian attacks killed four people in Donetsk Oblast across three settlements – Shevchenko, Katerynivka, and Siversk – while three others were injured.
Russian forces launched a missile strike near Kupiansk, injuring three people and damaging 12 houses and a Nova Poshta postal depot.
 The aftermath of a Russian missile attack in the Holosiivskyi district in Kyiv, Ukraine. (Kyiv City Military Administration/Telegram)
The aftermath of a Russian missile attack in the Holosiivskyi district in Kyiv, Ukraine. (Kyiv City Military Administration/Telegram)
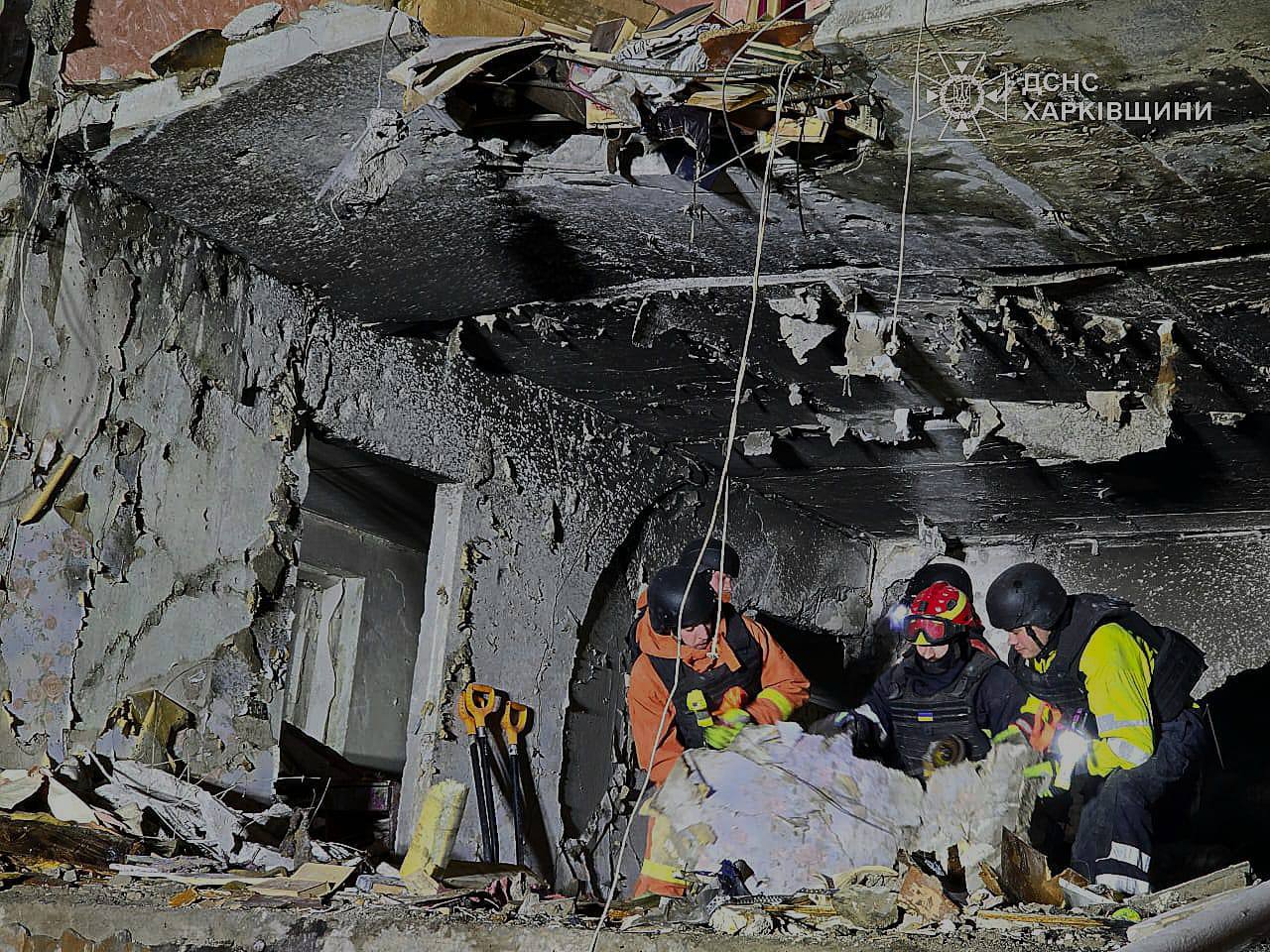 Rescue workers on the premises of an apartment building hit by a Russian in Kharkiv. (State Emergency Service / Telegram)
Rescue workers on the premises of an apartment building hit by a Russian in Kharkiv. (State Emergency Service / Telegram)
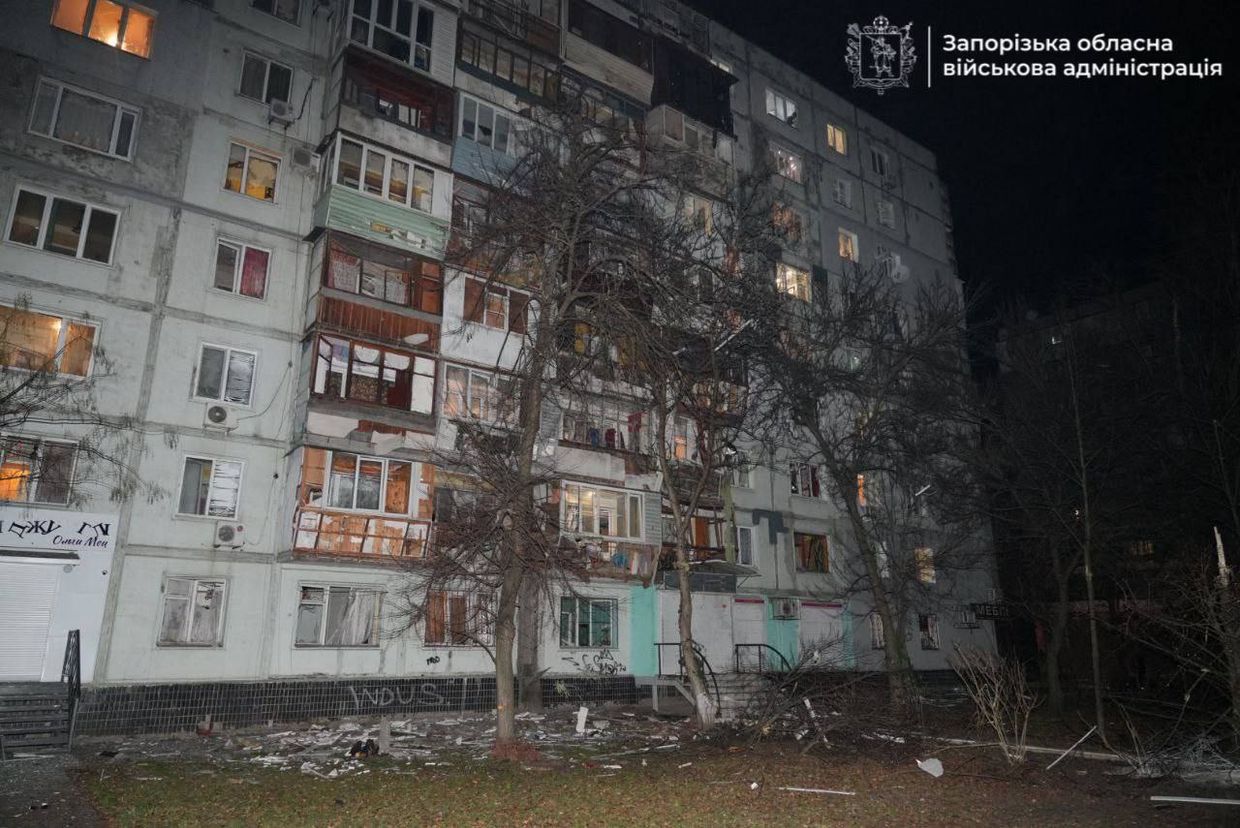 A residential building in Zaporizhzhia damaged in a Russian attack. (Ivan Fedorov / Telegram)
A residential building in Zaporizhzhia damaged in a Russian attack. (Ivan Fedorov / Telegram)
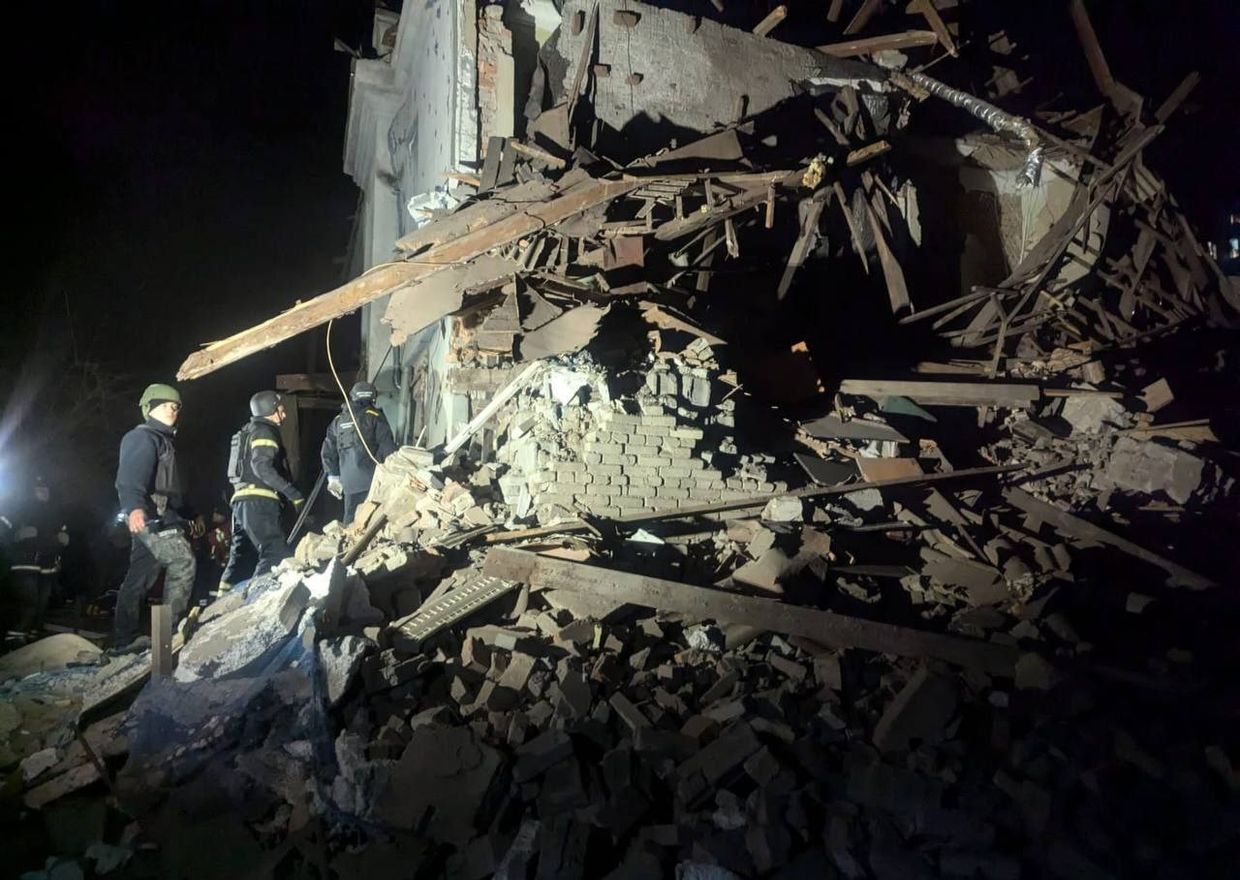 The aftermath of a Russian missile attack on the city of Kryvyi Rih, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. (Serhii Lysak/Telegram)
The aftermath of a Russian missile attack on the city of Kryvyi Rih, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast. (Serhii Lysak/Telegram)
Ukraine’s Allies
The Biden administration plans to announce its final $1.2 billion aid package to Ukraine under the Ukraine Security Assistance Initiative (USAI), which will include air defense interceptors and artillery ammunition. This comes as concerns grow about delivering the remaining $5.6 billion in military aid before a potential administration change.
Donald Trump plans to maintain U.S. military support for Ukraine if elected president in 2024, shifting from his previous campaign stance. While opposing Ukraine’s NATO membership and pushing for swift conflict resolution, Trump intends to continue providing military equipment to Ukraine. He also aims to pressure NATO allies to increase their defense spending from 2% to 5% of GDP. Though Trump has not invited Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky to his potential inauguration, he indicated Zelensky would be welcome to attend.
The European Council has condemned Russia’s deliberate targeting of Ukraine’s civilian and energy infrastructure as winter approaches and called for increased electricity exports to Ukraine. Following their December 19 meeting in Brussels, EU leaders urged member states, particularly Ukraine’s neighbors, to accelerate power supply support. The EU recently increased Ukraine’s electricity import capacity to 2.1 gigawatts starting December 1 and pledged to further integrate Ukraine and Moldova’s energy systems with the EU network.
The European Council called for urgent increased military support to Ukraine during meetings in Brussels with President Zelensky, emphasizing the need for air defense systems, ammunition, and missiles. The EC condemned Russia’s war and warned countries, particularly North Korea and Iran, to stop assisting Russia’s military efforts. Zelensky, meeting with EC President von der Leyen, stated Ukraine wants to end the war but opposes any ceasefire that would allow Russia to regroup and attack again.
Lithuania’s new Prime Minister Gintautas Paluckas and his entire cabinet visited Kyiv on December 20, demonstrating continued support for Ukraine despite a Russian missile attack on the capital that morning. During meetings with Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal, they discussed defense capabilities and Ukraine’s EU and NATO aspirations, with Lithuania pledging to invest in Ukraine’s Palianytsia missile-drone program.
The World Bank has approved $2.05 billion in grants to Ukraine as part of the broader G7 $50 billion loan package backed by frozen Russian assets. The funding, which represents part of the U.S.’s $20 billion commitment, will support Ukraine’s railway sector, banking, renewable energy, and domestic revenue generation. The EU plans to begin its contribution of 18.1 billion euros in January. Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal confirmed that Ukraine is already receiving U.S. funds under this framework.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has approved a $1.1 billion disbursement to Ukraine, bringing total IMF support under the Extended Fund Facility to $9.8 billion out of a planned $15.6 billion package. While noting Ukraine’s economic resilience despite the war, IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva emphasized the continuing toll of Russian attacks. The IMF predicts stronger economic growth in 2024 but expects a slowdown in 2025 due to infrastructure damage, labor market pressures, and rising inflation. Ukraine’s Finance Ministry indicates it will need an additional $12 billion in foreign aid for 2025, beyond the $42.5 billion received last year.
Russia News
Russian President Vladimir Putin announced plans to designate 2025 as the “Year of the Defender of the Fatherland” to honor veterans of the Ukraine war and other Russian conflicts. This initiative follows the Kremlin’s recent efforts to integrate veterans into government positions through programs like “Time of Heroes,” aiming to both satisfy the growing veteran population and embed military values throughout Russia’s governance structure.
The Kremlin has arrested two Kursk Oblast Development Corporation officials – General Director Vladimir Lukin and former Deputy Director Igor Grabin – for allegedly embezzling 173.2 million rubles meant for border fortifications. These arrests, along with the earlier dismissal of Governor Alexei Smirnov, appear to be part of a pattern of blaming local officials for Russia’s failure to prevent Ukrainian incursions into Kursk Oblast, rather than addressing military and security shortcomings.
Despite Russian President Vladimir Putin announcing major reconstruction plans for occupied Ukrainian territories during his annual televised conference, newly appointed Kursk Oblast Governor Alexander Khinshtein stated that the Russian government won’t fully fund repairs to war-damaged facilities in Kursk Oblast, citing budget constraints and ongoing war expenses.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
According to Russian opposition outlet Mediazona, at least 20,364 Russian soldiers have been killed in Ukraine in 2024, with most casualties being volunteer servicemembers. The Russian republics of Bashkortostan and Tatarstan experienced the highest losses. However, Ukrainian military officials suggest the actual number could be much higher, reporting over 120,000 Russian casualties (including both deaths and wounded) just between September and November 2024.
| Troops +1860 772280 |
Tanks +10 9594 |
Artillery +32 21252 |
Arm. Veh. +18 19841 |
Aircraft 369 |
Heli 329 |
Ships 28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russia is using substantial financial incentives to recruit soldiers for its military, with signing bonuses reaching up to 400,000 rubles ($3,850) from the federal government, plus additional regional bonuses. Some regions, like Khanty-Mansi and Belgorod, offer extra payments of over $20,000. These recruitment payments are straining regional welfare budgets, with some areas like Stavropol Krai and Karachay-Cherkessia allocating over 60% of their social welfare funds to war-related expenses. This leaves limited resources for traditional welfare recipients like children in state care and the unemployed. While these payments help struggling families and temporarily boost local economies, experts warn this strategy may harm Russia’s long-term economic stability and productivity, particularly as inflation reached 8.9% in November 2024.
Russia’s Allies
Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban has delayed voting on extending EU sanctions against Russia until after Donald Trump takes office on January 20, according to Bloomberg. This move follows Orban’s recent meeting with Trump in Florida and complicates the EU’s January deadline for renewing sanctions, which require unanimous approval. The decision comes amid broader concerns about future U.S. support for Ukraine under Trump’s presidency and follows the EU’s recent implementation of its 15th sanctions package against Russia’s defense industry and shadow fleet.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
