Summary of the day: Recent developments indicate a strong Ukrainian resistance to Russia’s demands for capitulation, with a poll showing widespread rejection among Ukrainians. Ukraine remains open to negotiations but insists on terms aligned with international law, contrasting Russia’s push for unconditional surrender. In Europe, EU officials are distancing their stance from Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban’s controversial views on the Ukraine war. Meanwhile, Russia has proposed broadening the criteria for labeling individuals as terrorists or extremists, a move seen as tightening control over dissent concerning the war. On the military front, Ukrainian forces have intensified their operations with successful drone strikes against Russian energy facilities and military assets in Crimea. Ukrainian troops have also recaptured positions near Toretsk, even as Russian forces make advances in the same area and near Avdiivka. Additionally, Russian President Vladimir Putin is focusing on integrating the metallurgical industry of occupied Ukraine into Russia’s defense sector. Elsewhere, Chechen leader Ramzan Kadyrov positions the North Caucasus as central to Russia’s diplomatic efforts in the Arab world, amidst internal challenges Russia faces with assimilating Central Asian migrants, highlighting tensions in its multicultural policy.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Peace Talks
A recent Ukrainian poll reveals widespread rejection of Russia’s demands for Ukraine’s capitulation, with 83% of respondents opposing the Kremlin’s requirement for Ukraine to relinquish control of parts of Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson, and Zaporizhia oblasts. Additionally, 58% reject altering Ukraine’s constitution to declare a neutral and non-nuclear status. These demands form part of Russia’s preconditions for peace talks, which also include recognition of Russian territorial claims and a pledge from Ukraine not to join NATO. Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov criticized NATO’s support for Ukraine’s membership prospects, asserting that such support negates the possibility of meaningful negotiations. This stance from Russia aims to discredit Ukraine’s internationally-backed negotiation positions and misrepresent Ukraine as the unreasonable party in the conflict.
Ukraine remains committed to negotiating peace with Russia on terms aligned with international law, contrasting Russia’s insistence on Ukrainian surrender. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky announced plans for a second peace summit by November 2024, with preparatory meetings to be held in Qatar, Turkey, and Canada on key issues like energy security, navigation freedom, and POW exchanges. However, the Kremlin has stated it will not participate in the summit, deeming the terms unacceptable due to their demands. Ukrainian officials assert that their calls for Russia to withdraw from Ukrainian territory are justified under international law, unlike Russia’s demands, which violate legal norms and facilitate ongoing ethnic cleansing in occupied Ukrainian regions. Ukraine’s stance aims for a full restoration of its territorial integrity to end the illegal occupation affecting over five million Ukrainians.
EU officials are actively distancing themselves from Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orban’s approach to the Ukraine conflict. Orban’s political director announced upcoming international discussions and detailed Orban’s communications with the European Council about his dialogues concerning Ukraine, Russia, China, and the US. In response, the EU has taken steps to isolate Orban’s diplomatic efforts; EU Commission Spokesperson Eric Mamer revealed that key EU leaders, including Commission President Ursula von der Leyen, will boycott informal meetings hosted by Hungary. Additionally, Politico reported that an alternative EU foreign affairs council meeting will coincide with Hungary’s own summit in Budapest, emphasizing EU disapproval of Hungary’s stance. Further highlighting this rift, Sweden’s Minister for EU Affairs stated that several Baltic and Nordic countries will limit their representation to civil servants at meetings related to Hungary’s EU Council presidency.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
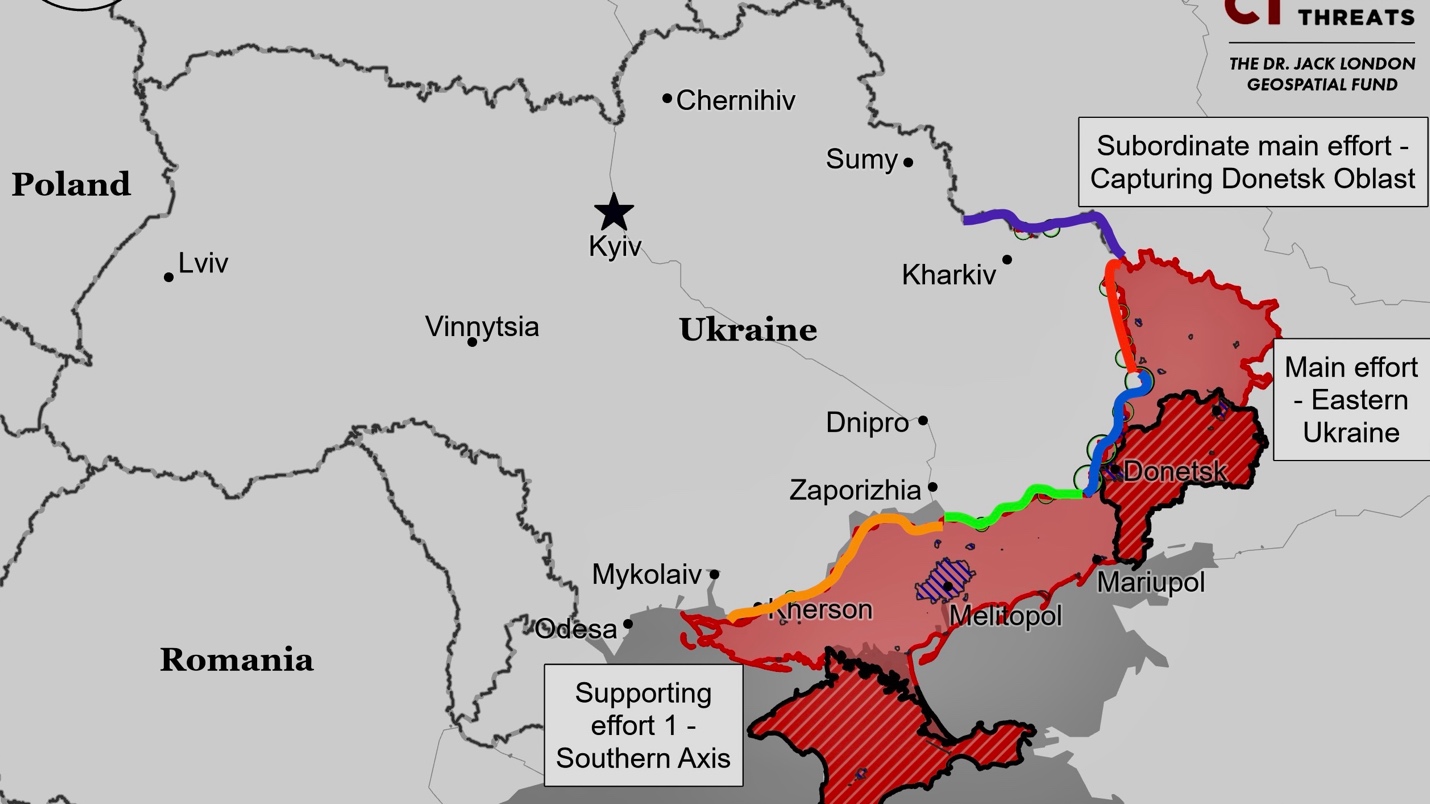
Kharkiv Front – Initiative None
Russian forces have not made significant progress in their offensive operations in northern Kharkiv Oblast, despite ongoing attacks. Colonel Yuriy Povkh of the Ukrainian forces noted that Russia is forming new assault groups for future operations in the area. There seems to be confusion about the specific units involved, with possible misidentification of the forces described by Povkh. Recent reports and social media suggest high casualties among Russian troops, particularly in the Vovchansk area where intense fighting is ongoing.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces engaged in offensive operations along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line but failed to make significant gains. Reports from a Russian military blogger suggested a minor advance near Makiivka, although this lacks visual confirmation. Attacks also occurred in areas northwest and west of Svatove and Kreminna.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces launched attacks around Siversk, targeting areas northeast, east, and southeast of the city, but did not achieve any confirmed territorial gains.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued to fight near Chasiv Yar on July 15 but made no confirmed territorial gains. Attacks occurred in the easternmost parts of Chasiv Yar, as well as to the north, east, and southeast of the city, particularly near Hryhorivka, Kalynivka, Ivanivske, and Andriivka.
Toretsk
In the Toretsk area, both Russian and Ukrainian forces made recent advances amid ongoing fighting. Ukrainian troops recaptured some positions in southern Niu York, south of Toretsk, while Russian forces marginally advanced in eastern Pivnichne, east of Toretsk. Russian attacks also continued near Zalizne, southeast of Toretsk, although claims of Russian advances there have not been confirmed.
Avdiivka
Russian forces made some advancements in the Avdiivka area amid ongoing fighting. Geolocated footage confirmed an advance in central Yevhenivka, northwest of Avdiivka. Although Russian military bloggers claimed further advances along a railway line east of Prohres and in fields southeast of Novoselivka Persha, these claims have not been verified. Russian troops also engaged in attacks near Novooleksandrivka, Vozdvyzhenka, Lozuvatske, and west near Yasnobrodivka.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces made slight advancements west of Donetsk City amid ongoing clashes. Geolocated footage confirmed a minor advance in western Krasnohorivka, with further unverified claims of progress in and south of the area. Additional attacks occurred southwest of Donetsk City near Paraskoviivka, Kostyantynivka, and Vodyane.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces did not secure any confirmed territorial gains despite ongoing combat in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area. Attacks continued south of Velyka Novosilka near Makarivka. Despite claims by Russian military bloggers that Russian forces captured Urozhaine on July 14, conflicting reports suggest that Ukrainian forces still hold positions in northern Urozhaine.
Zaporizhia Line
Positional battles continued in western Zaporizhia Oblast without any confirmed changes to the frontline. A Russian military blogger reported minor advances of up to 500 meters by Russian forces in the Orikhiv area, although specific locations were not detailed. Ukrainian forces successfully repelled Russian attacks near Robotyne in areas including Novoandriivka and Mala Tokmachka.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Ongoing positional battles were reported in the eastern Kherson Oblast, including the area near Krynky. Russian military bloggers also indicated continuous fighting on the Dnipro River Delta islands.
Ukraine News
Russian forces used two D-30SN glide bombs to strike a residential building and an educational institution in Myrhorod, Donetsk Oblast.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine’s defense industrial base continues to receive substantial support from Western partners. On July 10, the Danish Ministry of Defense announced that Denmark has funded the production of 18 Bohdana self-propelled howitzers in Ukraine, which are expected to be delivered to Ukrainian forces soon. Furthermore, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky engaged in discussions on July 11 with U.S. defense companies about potential joint ventures. On the same day, Ukraine’s Ukroboronprom and U.S. defense firm Northrop Grumman signed an agreement to establish a joint production line for NATO-standard medium-caliber artillery ammunition.
Ukraine’s Allies
Ukraine continues to receive significant support from Western partners in both military and financial forms. Recently, Germany delivered additional military aid, including ammunition for Leopard tanks, a Patriot air defense system with missiles, and 155mm artillery shells. Simultaneously, the European Union and Ukraine agreed on a financial aid package worth 5.27 billion euros to bolster Ukraine’s economy over the next four years. Portugal has committed to providing over 220 million euros annually in aid for 2024 and 2025. New Zealand has also stepped up, announcing a military aid package totaling six million NZD, which includes contributions to Ukraine’s military healthcare system, and an additional ten million NZD in humanitarian assistance. From North America, Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau announced a substantial military aid package of 500 million CAD. Norway’s commitment includes one billion kroner to enhance Ukraine’s air defenses. On the Eastern European front, Lithuania has contributed drone jamming equipment and ammunition, while Spain has started transferring 10 refurbished Leopard tanks to Ukraine, which will first be sent to Poland before reaching their final destination.
Starting in July 2024, a Czech-led coalition will begin delivering artillery shells to Ukraine, according to reports from Ceske Noviny. Czech President Petr Pavel indicated that Ukraine will receive 50,000 shells in July and August, with deliveries increasing to between 80,000 and 100,000 shells per month from September through the end of the year.
Ukraine’s Western partners are bolstering support for providing F-16 aircraft to Ukraine. Norway announced it will supply Ukraine with six F-16 jets sometime in 2024. Concurrently, the Netherlands committed an additional 300 million euros to purchase ammunition for these aircraft. Canada is also contributing, allocating 389 million CAD to fund the training of Ukrainian F-16 pilots through the Ukraine Defense Contact Air Force Capability Coalition.
Russia News
Ukrainian forces launched drone strikes targeting Russian energy infrastructure and military assets in occupied Crimea. Specific incidents include a Ukrainian drone hitting an electrical substation in Lipetsk Oblast and damaging an oil storage container in Oryol Oblast, despite Russian electronic warfare efforts. Additionally, there are unconfirmed reports of Ukrainian drones striking a Russian air defense system or an electronic intelligence unit in Crimea. The Russian Ministry of Defense reported intercepting six Ukrainian drones over Crimea and one in Lipetsk Oblast during the same night, plus another drone near western Crimea the following afternoon.
The Russian government has proposed a bill to expand the criteria under which individuals can be designated as terrorists or extremists, a move seen as an attempt to suppress criticism of its military actions in Ukraine. Introduced to the State Duma, the legislation would allow the Russian Federal Service for Financial Monitoring (Rosfinmonitoring) to include individuals convicted of disseminating “fakes” about the Russian military, driven by various forms of hatred, on the terrorist and extremist list. Additionally, the bill proposes that people accused of other, unspecified crimes motivated by similar hatred could also be added to the list, giving authorities broad discretion in labeling individuals as terrorists or extremists. This initiative is likely aimed at encouraging self-censorship among Russians and tightening control over public discourse, while ostensibly promoting political and religious freedom and societal harmony.
Russia’s new assimilation program for Central Asian migrants highlights ongoing tensions between the state’s need for labor and military support from these communities and the rising xenophobic sentiment among nationalist groups. The program, discussed in a 70-minute lecture developed by the Russian Federal Agency for Ethnic Affairs, is intended to integrate migrants by emphasizing the primacy of the Russian language, history, and culture. However, such policies may exacerbate frictions, as evidenced by recent proposals from the head of Rosnobrnadzor, Anzor Muzaev, that migrant children must know Russian to study in Russian schools, and even more extreme suggestions from ultranationalist commentators to restrict migrant families’ access to public education. This approach contradicts the Kremlin’s portrayal of Russia as a welcoming multicultural society and could further marginalize Central Asian migrants, isolating them from their cultural and religious practices.
Chechen leader Ramzan Kadyrov is positioning the North Caucasus as vital for Russia’s connections with the Arab world. During a meeting in Grozny with ambassadors from the UAE and Qatar at the Caucasus Investment Forum, Kadyrov highlighted the strong relationships between these countries and the Caucasus region. The Kremlin aims to leverage the Caucasus’ unique position to attract Arab investment and strengthen diplomatic ties, particularly as Qatar and the UAE play roles in mediating issues like POW exchanges and child repatriations.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian President Vladimir Putin highlighted the integration of Ukraine’s metallurgy industry in occupied regions into Russia’s defense industrial base. He stressed the strategic importance of the metallurgy sector to Russia’s defense and security, noting its growth despite Western sanctions. Putin reported a 30% increase in metal product production in the occupied Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts in 2023 compared to 2022.
The Russian Ministry of Defense announced the completion of its Spring 2024 conscription cycle, having conscripted 150,000 personnel. The Ministry reassured that these conscripts are not serving in the occupied regions of Luhansk, Donetsk, Zaporizhia, and Kherson and are not participating in combat in Ukraine. However, there are assessments suggesting that Russia might be pressuring conscripts to sign military contracts as part of broader mobilization efforts.
Russian opposition outlets have reported that pro-war Russian Telegram channels are using intimidation tactics against mobilized personnel and their families to deter complaints and demobilization efforts. Channels allegedly redubbed a video of Russian soldiers, originally discussing another topic, to falsely portray them as warning against “provocateurs” organizing demobilization rallies. This manipulation aims to silence dissent within the ranks and among relatives of those mobilized.
Rostec, a Russian state-owned defense conglomerate, announced on July 15 that it is developing improved modules to extend the range of unguided glide bombs. Rostec CEO Sergei Chemezov emphasized that producing unguided bombs with these modules is more cost-effective than producing guided ones. According to a source from the Russian defense industry, the FAB-3000 glide bombs equipped with these modules can reach up to 50-60 kilometers, and smaller FAB-250 to FAB-1500 bombs can achieve ranges of 60-70 kilometers.
The United Aircraft Corporation, a subsidiary of Rostec, delivered the first batch of repaired and modernized MiG-31 fighter jets for 2024 to the Russian Ministry of Defense.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
Russian military bloggers are using a report from the Ukrainian General Staff to foster unrest. The report disclosed that Ukrainian Commander-in-Chief Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi is investigating a Ukrainian brigade’s command following recent personnel losses, aiming to create discord and mistrust within the Ukrainian military command.
Russia is prosecuting Ukrainian officials for alleged crimes in absentia, asserting its legal influence beyond its jurisdiction. The Moscow City Basmanny District Court recently issued war crimes sentences against Valentyn Nalyvaichenko, former head of the Ukrainian State Security Service, and Oleksandr Lytvynenko, Secretary of the Ukrainian National Security and Defense Council, underscoring efforts to challenge Ukraine’s sovereignty.
NewsGuard, an outlet analyzing disinformation, reported on July 11 that it found 41 TikTok accounts using AI-generated English and French narration to spread disinformation, including pro-Kremlin narratives about the war in Ukraine. Of these, 17 accounts focus specifically on promoting Kremlin views, with 14 employing AI-generated French narration.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
