Summary of the day: Ukrainian forces continued their mechanized offensive deeper into Russia’s Kursk Oblast, advancing as far as 35 kilometers from the border with Ukraine’s Sumy Oblast. This operation marks a significant push into Russian territory, challenging the Kremlin’s narrative of stability and security under President Vladimir Putin. Despite Ukrainian advances, they do not control the entire area claimed by Russian sources. In response, the Russian military is considering several courses of action to counter the Ukrainian push, including deploying various military and security forces to regain control of the lost territory. Options include using border guards, conscripts, and more seasoned units from other regions, as well as enhancing air and strike capabilities. Meanwhile, the lack of a cohesive Russian military response has allowed Ukrainian forces to achieve a degree of operational surprise. Official statements from Ukrainian leaders regarding the operation have not been made, but US officials have clarified that these actions do not breach any restrictions on Ukrainian military engagements within Russian borders.
Picture of the day:
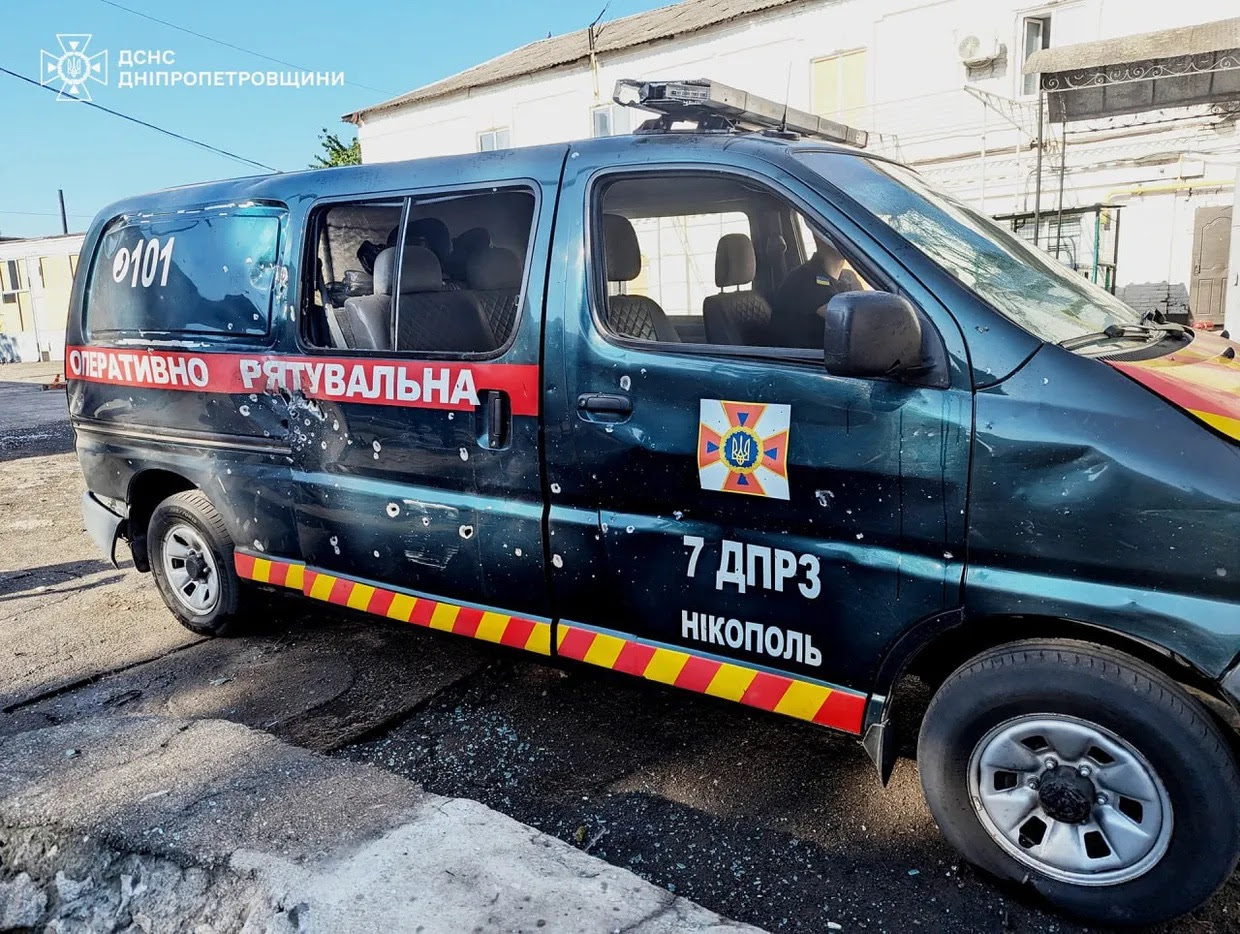 A State Emergency Service’s service vehicle damaged in a Russian drone attack against Nikopol, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Ukraine. (State Emergency Service/Telegram)
A State Emergency Service’s service vehicle damaged in a Russian drone attack against Nikopol, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Ukraine. (State Emergency Service/Telegram)
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Despite earlier announcements and ongoing developments suggesting otherwise, Russian-backed Abkhazian Foreign Minister Sergei Shamba stated that there are currently no plans to build a Russian naval base at the Ochamchire port in Abkhazia, Georgia. This statement comes after previous confirmations from January 2024 about designing a permanent naval base and an October 2023 agreement to construct it. However, recent observations noted the arrival of the Russian Project 22870 support ship at Ochamchire port, indicating some level of military activity. The rationale behind potentially halting the base construction is not clear, especially as Ukrainian strikes have compromised Russian naval operations in Crimea, pushing Russia to seek alternative basing in the eastern Black Sea.
The Road To Peace
Ukrainian presidential advisor Mykhailo Podolyak stated on August 7 that Ukrainian operations in Russian border regions like Kursk Oblast could psychologically impact Russian society and strengthen Kyiv’s position in future peace negotiations. While Podolyak did not confirm recent incursions, he suggested such actions would increase pressure on the Kremlin by escalating Russian losses and costs. He emphasized that Ukraine aims to negotiate from a position of strength and is planning to invite a Russian representative to an upcoming peace summit.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian military observer Yuriy Butusov reported that Ukrainian forces used a HIMARS strike on August 5 to target a Russian command post near Bohdanivka in occupied Luhansk Oblast. This attack reportedly resulted in the death of the commander of the Russian 2nd Battalion, 51st Airborne Regiment, and several officers. This claim has not been independently verified.
The Russian Ministry of Defense reported that their air defense systems intercepted a Ukrainian drone over occupied Crimea.
Kursk Front – Initiative Ukraine
Since August 6, Ukrainian forces have launched a mechanized offensive into Russia’s Kursk Oblast, advancing up to 35 kilometers from the Sumy Oblast border. Despite their significant penetration, Ukrainian forces have not established full control over the territories they’ve entered, leading to a complex and dynamic situation on the ground. Reports indicate that small Ukrainian armored groups are engaging in rapid and targeted advances, attacking Russian positions and then swiftly withdrawing. This strategy has led to inconsistent reports due to the fleeting presence of Ukrainian forces and has exploited the sparse Russian military presence to push deeper into enemy lines.
Ukraine’s state project “Khochu nayti” reported on August 7 that many Russian soldiers, including conscripts and contract soldiers, were captured in Russia’s Kursk Oblast following an incursion by Ukrainian forces on August 6. The project, which aids relatives of captured Russian military personnel, also noted uncollected casualties among the Russian troops. Drone footage purportedly showing 32 captured soldiers was released, with claims of more not shown in the frame. The validity of these claims has not been independently verified.
Russian military bloggers have noted that Ukrainian forces are employing innovative tactics and technologies, details of which have been withheld to maintain operational security. On the Russian side, there is a determination to reclaim lost territories, as these advances pose a direct challenge to President Vladimir Putin’s portrayal of stability and security. During a virtual meeting with Kursk’s Acting Head Alexey Smirnov, discussions centered on civilian safety and compensation, but the specifics of military responses were not addressed.
The Russian military is contemplating several strategic responses to counter the Ukrainian advances:
Local Forces Response: Utilizing conscripts, FSB border guards, Rosgvardia, and other irregular forces already stationed in Kursk Oblast.
Northern Grouping of Forces: Potentially deploying up to 75,000 personnel for defensive operations, although this force has suffered casualties and may not be at full strength.
Redeploying Reserves: Shifting better-equipped and more experienced units from other fronts to Kursk Oblast.
Enhancing Air and Strike Capabilities: Increasing aviation and strike operations, though Ukrainian air defenses may pose challenges.
The unexpected Ukrainian military activity in Kursk Oblast caught Russian forces off guard, achieving operational surprise—a significant feat in a modern, sensor-rich battlefield environment. Bloomberg reported that this situation arose after Valery Gerasimov, Chief of the Russian General Staff, neglected prior intelligence warnings about Ukrainian troop movements near Kursk. This oversight led to the surprise assault on August 6, which Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky suggested was just retribution, stating Russia must “feel what it has done” by initiating the conflict. In the aftermath, Russian President Vladimir Putin, who was also uninformed about the buildup, convened a meeting with Gerasimov. Despite Russian Defense Ministry claims of halting Ukrainian advances, tensions are escalating within the Kremlin over Gerasimov’s management of the situation, reflecting the high stakes and ongoing tensions in Kursk Oblast.
President Vladimir Putin announced that residents displaced by the ongoing conflict in Russia’s Kursk Oblast will receive a one-time payment of 10,000 rubles ($115) each. The conflict is particularly intense around Sudzha, a village near the Ukrainian border, which has led to the evacuation of several thousand people. Due to the disturbances, Moscow Railway has temporarily closed stations in Sudzha, Korenovo, and Psel, affecting the local area significantly. While these stations are closed, train services in other parts of Kursk Oblast continue normally but with enhanced security measures. Additional train services to Moscow have been arranged to help accommodate the displaced residents.
A document, humorously suggesting that the Ukrainian city of Sudzha and its district should join the Sumy region of Ukraine, was circulated online. Despite appearing genuine, the Sumy District Council confirmed it was fake and beyond their authority. The document played on historical claims similar to those used by Russian President Vladimir Putin for annexing parts of Ukraine. It proposed that Sudzha, founded in the 17th century and historically linked to Ukraine, could hold a referendum to join Ukraine, ensuring rights like Ukrainian-language education and media, and cultural freedoms. The public reaction highlights local dissatisfaction with Russian governance, with sentiments on social media suggesting some in Sudzha might prefer Ukrainian rule.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces continued their offensive operations north and northeast of Kharkiv City, specifically near Hlyboke, Vovchansk, and Tykhe, without achieving any confirmed changes to the frontline. The Ukrainian Kharkiv Group of Forces noted that an unspecified Russian unit was moved from occupied Luhansk Oblast to the Vovchansk area. Additionally, it was reported that Russian forces did not deploy tactical aviation in the Kharkiv region on those days. A Russian military blogger also mentioned that Ukrainian forces are counterattacking near Hlyboke.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched multiple attacks along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, targeting areas northeast, east, and southeast of Kupyansk, as well as northwest, west, and southwest of Kreminna. Despite these efforts, there were no confirmed changes to the frontline positions. Specific locations of the attacks included Synkivka, Petropavlivka, Novoosynove, Kolisynkivka, Novoserhiivka, Nevske, Makiivka, Terny, and the Serebryanske forest area.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
The Ukrainian military’s ongoing offensive in Russia’s Kursk region is aimed at diverting Russian forces from the east, particularly as Russian troops have advanced near Toretsk in Donetsk, threatening a vital supply route. Despite heavy bombardment, Toretsk remains under Ukrainian control, but its fall could give Russia access to key roads and potentially the entire Donetsk region. Russian forces are also pressing west toward Pokrovsk, a significant logistical hub. In response to the escalating situation, Ukraine initiated an offensive in Kursk on August 6, targeting crucial infrastructure like a railway line vital for Russian supplies and potentially the Kursk Nuclear Power Plant. The operation is seen as a strategic move to alleviate pressure on the eastern front. Additionally, security at the Kursk plant has reportedly weakened, with many male guards mobilized and replaced by female staff.
Siversk
Russian forces conducted offensive operations near Siversk, targeting areas to the east, southeast, and south including Verkhnokamyanske, Ivano-Darivka, Spirne, Vyimka, and Pereizne.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces conducted offensive operations around Chasiv Yar, specifically to the north near Kalynivka and to the east near Ivanivske.
Toretsk
Russian forces conducted offensive operations near Toretsk, including to the east near Pivnichne and southeast near Zalizne, without confirmed changes to the frontline. Additional advances were reported within Niu York, south of Toretsk, where Ukrainian forces reportedly made an unsuccessful counterattack.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces continued their offensive operations around Pokrovsk, targeting areas to the northeast, east, and southeast including Vozdvyzhenka, Kalynove, Novooleksandrivka, Ivanivka, Lysychne, Zhelanne, Karlivka, and Yasnobrodivka. Although advances were reported, particularly east of Pokrovsk towards Hrodivka, Lysychne, and Ivanivka, and the seizure of Serhiivka southeast of Pokrovsk, these claims remain unconfirmed as there were no verified changes to the frontline.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces engaged in offensive operations west and southwest of Donetsk City, specifically near Krasnohorivka, Kostyantynivka, Paraskoviivka, Vodyane, Volodymyrivka, and Vuhledar. While there were reports of Russian advancements southwest of Donetsk, particularly southeast of Vodyane, these gains remain unconfirmed.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
Russian forces achieved minor territorial gains south of Velyka Novosilka, near the Zaporizhia-Donetsk Oblast border, with recent geolocated footage confirming marginal advances northeast of Urozhaine. However, there were no reports of active fighting in this area.
Zaporizhia Line
Russian forces conducted ground attacks near Robotyne and northeast of Robotyne near Mala Tokmachka in western Zaporizhia Oblast.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Ukrainian forces successfully repelled Russian attacks in the Dnipro direction within Kherson Oblast. Russian forces continue to operate on the islands of the Dnipro River Delta.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched a limited series of missile and drone strikes against Ukraine. According to Ukrainian Air Force Commander Lieutenant General Mykola Oleshchuk, the strikes included two Kh-59 cruise missiles from the Sea of Azov, two Iskander-M ballistic missiles from Belgorod Oblast, and four Shahed-136/131 drones from Yeysk in Krasnodar Krai. Ukrainian forces successfully intercepted two Kh-59 cruise missiles and all four Shahed drones over the regions of Odesa, Kherson, and Kirovohrad.
Ukraine’s Energy Minister Herman Halushchenko reported that nuclear power currently supplies up to 60% of the country’s electricity, helping avoid supply restrictions despite recent challenges. Following Russian attacks on Ukraine’s energy infrastructure, state-owned Ukrenergo implemented rolling blackouts, exacerbated by a heat wave in July. The Verkhovna Rada is expected to review legislation to expand the Khmelnytskyi Nuclear Power Station by 2.2 GW. Amid ongoing damage, DTEK, a major private energy provider, predicts severe electricity shortages this winter, with potential blackouts up to 20 hours per day if repairs and protective measures fail. The IMF has estimated Ukraine’s energy sector losses at $56.5 billion due to the conflict.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours:
DEATHS: 7 INJURIES: 28
- Russian attacks in Ukraine’s Nikopol district, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, injured two men and a 12-year-old boy. The assaults damaged residential buildings, houses, solar panels, and other civilian properties. Additionally, a Russian drone strike targeted the local State Emergency Service department, damaging a service vehicle and the fire station, though no casualties were reported from this specific attack.
- Russian artillery strikes on Nikopol, Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, resulted in the death of a 50-year-old man and caused damage to a hospital, garages, cars, and power lines. Despite efforts, doctors were unable to save the injured man.
- In Donetsk Oblast, recent Russian attacks resulted in two deaths in Mykhailivka and four injuries across Novohrodivka, Orlivka, Pleshchiivka, and Promin.
- A Russian glide bomb attack in Selydove, Donetsk Oblast, using a 500-kilogram FAB-500 bomb, resulted in the deaths of two men and injuries to 11 people, including a child born in 2019. The attack damaged 20 high-rise buildings, six administrative buildings, and three businesses.
- In Kherson Oblast, eight people were injured due to Russian attacks in the past day. The assaults damaged critical infrastructure, a school, nine high-rise buildings, 11 houses, and other structures.
- A Russian airstrike using KAB bombs targeted the village of Mohrytsia in Sumy Oblast, 6 kilometers from the Kursk border, killing a 22-year-old man and his 6-year-old sister in a school yard. Governor Volodymyr Artiukh reported that the family had chosen to stay in the village despite ongoing cross-border strikes, which have intensified since Ukraine’s recent incursion into Kursk Oblast. Two other individuals were injured in the attack.
- A Kernel oilseed processing plant in western Ukraine was damaged in a Russian drone attack.
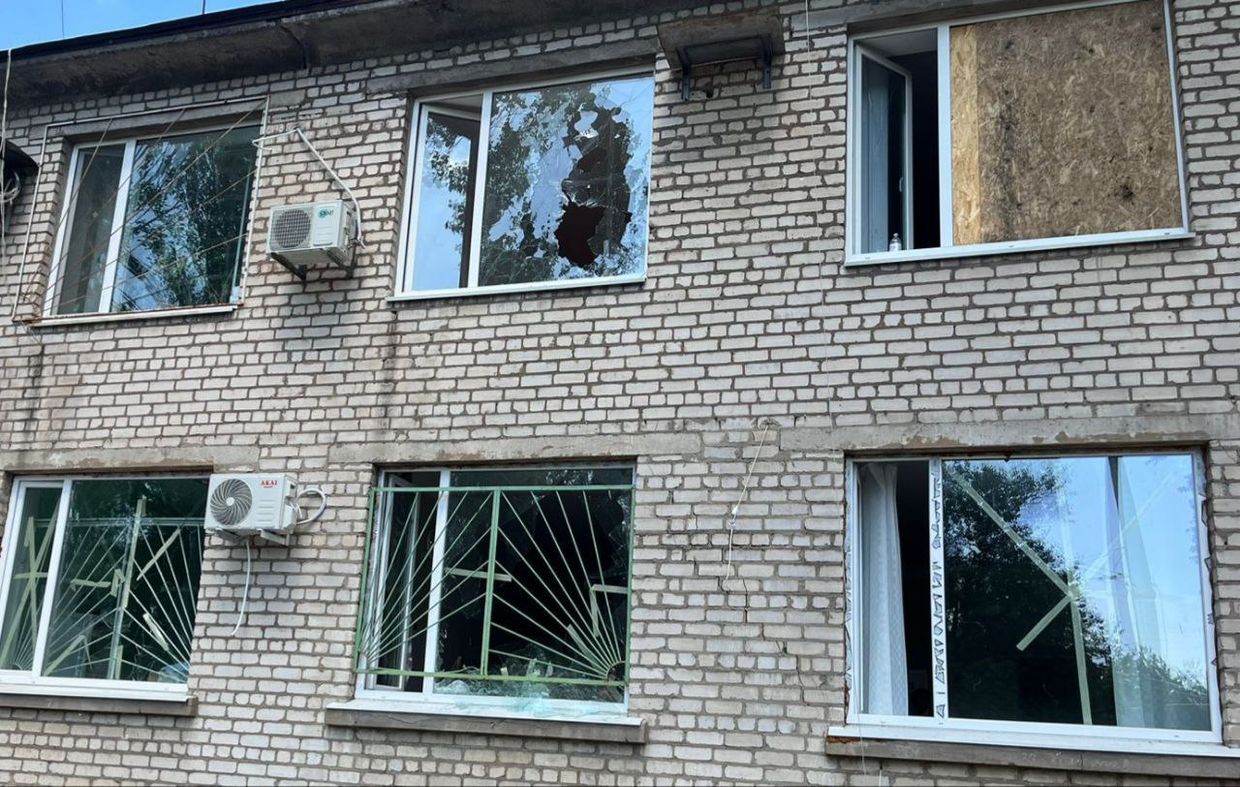 Russian forces attacked the city of Nikopol with artillery targeting a hospital. (Dnipropetrovsk Oblast Governor Serhii Lysak / Telegram)
Russian forces attacked the city of Nikopol with artillery targeting a hospital. (Dnipropetrovsk Oblast Governor Serhii Lysak / Telegram)
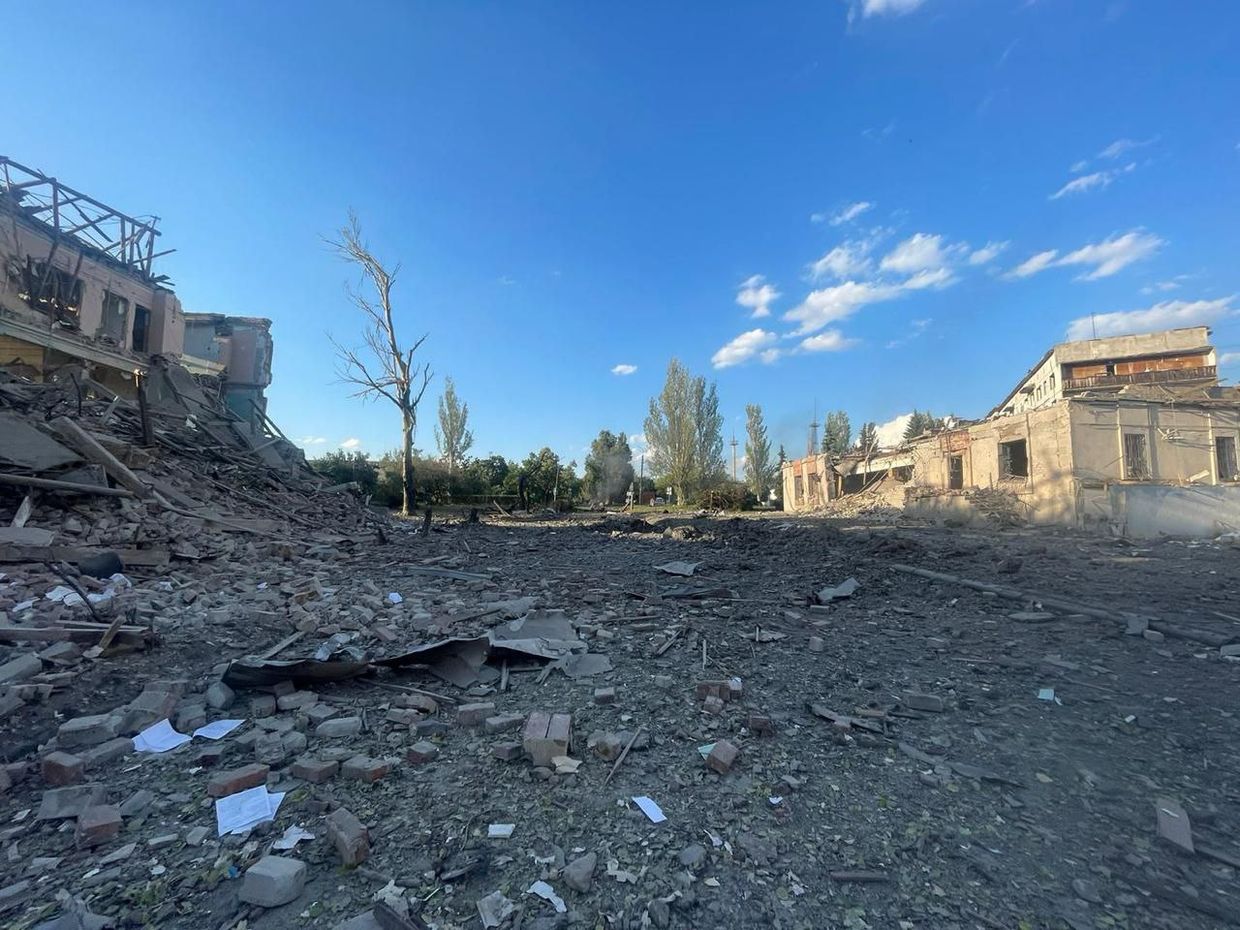 Aftermath of a Russian attack on Selydove in Donetsk Oblast. (Vadym Filashkin / Telegram)
Aftermath of a Russian attack on Selydove in Donetsk Oblast. (Vadym Filashkin / Telegram)
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine introduced the “Armiya (Army)+” app, announced by President Volodymyr Zelensky, designed to reduce paperwork and streamline operations for military personnel. This digital tool builds on the success of Ukraine’s “Diia” public services portal, allowing soldiers to electronically submit reports, access training programs, and manage medical records and salaries. The app also includes features for IT support and secure communications, with mechanisms to assess military supply situations and provide feedback. Defense Minister Rustem Umerov emphasized that “Armiya+” centralizes various military services into a single digital system, enhancing efficiency and focusing on operational needs. Future updates are expected to expand services for military families and ensure no data storage to prevent leaks. Currently, the app is available for download but is restricted to military users.
Ukraine’s state-owned defense company, Ukroboronprom, has entered the top 50 global defense companies for the first time, ranked by Defense News, according to Strategic Industries Minister Alexander Kamyshin. Moving up from 65th place last year, Ukroboronprom has seen the fastest growth among the world’s 100 largest defense firms, with a 72% revenue increase in 2023, reaching $2.2 billion. The company, which focuses on producing and modernizing military hardware and weapons, aims to bolster the Ukrainian Defense Forces effectively and rapidly. Amidst the ongoing war, Ukroboronprom has moved much of its production abroad and recently opened a representative office in Washington to enhance international defense partnerships. Kamyshin anticipates the defense sector becoming a key export sector post-victory over Russia.
Ukraine’s Allies
US officials have confirmed that Ukraine’s military operations in Kursk Oblast do not breach US-imposed limits on striking targets within Russia. During a press briefing on August 8, Pentagon Press Secretary Sabrina Singh stated the operation aligns with US policy, emphasizing America’s support for Ukraine’s self-defense. This stance was echoed by White House and State Department spokespeople, who labeled Ukraine’s actions as “common sense” and defensive. According to US and Ukrainian officials, the aim of these operations is to disrupt and weaken Russian military morale and to divert forces from key frontlines in eastern Ukraine.
Marcus Faber, Chair of the Bundestag’s Defense Committee, confirmed that German-supplied military equipment, including Leopard 2 tanks, could be used in Ukraine’s incursion into Russia’s Kursk Oblast. Faber argued that once delivered to Ukraine, these weapons are considered Ukrainian, and their use is governed by international law. He described Ukraine’s actions as legitimate and strategically necessary to force Russian troop redeployments and demonstrate Ukraine’s resilience. Amidst these developments, Berlin remains Ukraine’s second-largest military donor after the U.S.
At the NATO summit in Washington in July, a new Alliance-led body, the NATO Security Assistance and Training for Ukraine (NSATU), was established to assist and train Ukrainian soldiers and coordinate military support from member states. In response, Bulgarian lawmakers recently voted to allow their forces to participate, a move the Bulgarian government highlighted as a commitment to Euro-Atlantic values and international peace, underlining the conflict’s significance to Europe’s security. Additionally, Bulgaria independently contributed 50 soldiers to the EU Military Assistance Mission in support of Ukraine (EUMAM Ukraine). This initiative aims to integrate Ukraine’s forces with NATO standards, marking Bulgaria’s ongoing support for Ukraine and emphasizing transparency in its military contributions, particularly since the tenure of Prime Minister Nikolai Denkov began in June 2023.
Estonia has intensified border checks with Russia to enforce sanctions more effectively, aiming to block the entry of sanctioned goods into Russia.
Despite a $60 per barrel price cap on Russian oil by Western allies, five Western insurance companies continue to cover Russian oil tankers, some possibly above the cap. The cap, set in December 2022, aimed to cut Moscow’s fossil fuel revenue, but enforcement challenges persist. Insurers are required to collect trader attestations without verifying compliance, leading to potential breaches. Some insurers might end contracts if violations are confirmed.
Russia News
Gazprom reported a decrease in gas transit through Ukraine’s Sudzha station in Kursk, with volumes dropping to 37.3 million cubic meters from 39.4 million cubic meters the previous day. This 12% reduction occurs amid Ukraine’s military advance into Kursk, though it’s not confirmed if the offensive directly caused the decrease. Despite ongoing EU sanctions on Russia’s energy sector following Moscow’s 2022 invasion of Ukraine, Europe continues to import Russian gas, with imports dropping from 40% of its gas supply in 2021 to about 8% in 2023.
Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a law that broadens the scope of “undesirable” organizations to include those funded by foreign states, subjecting them to potential bans. This extension of the 2015 law aims to counter various threats including sanctions and foreign interference in Russian elections. Organizations labeled as undesirable cannot operate in Russia, and their leaders face up to six years in prison, with members facing up to four years. The law could impact foreign media such as the BBC or Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty, classifying them as undesirable.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a law that prohibits Russian military personnel from using personal electronic devices in the combat zone in Ukraine for non-official purposes, punishable by up to 10 days of arrest. The law allows the use of such devices for official duties and also penalizes military personnel for distributing information about Russian military operations, unit locations, or servicemembers’ families online or to the media. This legislation, part of efforts to tighten operational security, was adjusted to permit device use for official tasks after criticism from Russian military bloggers about its impact on logistics and operations.
A Kremlin-affiliated Russian military blogger shared footage reportedly showing the Russian 242nd Motorized Rifle Regiment using unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) for ammunition delivery and evacuating wounded personnel in eastern Ukraine’s frontline areas. The blogger mentioned that acting Moscow Oblast Governor Andrei Vorobyov backed the production of these UGVs, and the Russian Ministry of Defense is currently testing several models.
Russia’s Allies
Russia and China are discussing initiating a barter trade system, with the first agriculture deal expected this autumn, amidst financial transaction difficulties due to increased U.S. scrutiny. The discussions, reported by Reuters on August 8, follow President Putin’s visit to China in May to address payment issues. This move comes as both countries develop barter trading regulations, potentially marking their first such trade in nearly 30 years.
Belarusian and Russian officials advanced their collaboration through the Union State framework. Union State Secretary Dmitry Mezentsev and Belarusian Security Council State Secretary Alexander Volfovich met in Minsk to discuss the final draft of the Union State’s Security Concept, set for upcoming review by the Council of Ministers and the Supreme State Council. They also talked about enhancing the infrastructure and rear facilities of Belarusian and Russian forces. Additionally, Belarusian Foreign Minister Maxim Ryzhenkov and Russian Ambassador Boris Gryzlov discussed preparations for signing the Security Concept. On August 7, the National Bank of Belarus and the Central Bank of Russia signed a cooperation agreement to enhance information exchange and oversight of the financial market, further implementing the Treaty of the Establishment of the Union State.
The independent Belarusian monitoring group, The Belarusian Hajun project, reported that from July 11 to 31, at least nine Russian Shahed-136/131 drones entered Belarusian airspace. According to the report, one drone fell in Belarus, seven continued into Ukrainian airspace, and the fate of one remains unknown. In response, Belarusian forces have enhanced their air defenses, deploying Su-30SM aircraft in southern Belarus during Russian air strikes and moving helicopters to Babruysk Airbase to intercept drones more effectively near the Ukrainian-Belarusian border.
Ukraine’s Foreign Ministry expressed regret over Niger’s decision to sever diplomatic ties, following a similar move by Mali. Mali accused Ukraine of supporting rebels causing losses to Russian Wagner Group mercenaries and Malian soldiers, which Ukraine vehemently denies. The Ministry refuted all accusations as baseless and untrue, including allegations of supporting international terrorism and violating international laws. Ukraine views these diplomatic breaks as aligned with nations showing solidarity with Russia, which has been at war with Ukraine for over two years. Despite these setbacks, Ukraine remains committed to fostering relations with all African nations, as emphasized during Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba’s ongoing African tour, which includes visits to Malawi, Zambia, and Mauritius. President Zelensky has highlighted the importance of strengthening ties with Africa as a key foreign policy goal for 2024.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
