Summary of the Day:
US President Trump held separate phone conversations with Russian President Putin and Ukrainian President Zelensky. During his call with Putin, Trump discussed the war in Ukraine and reported they agreed to begin immediate negotiations. The Kremlin emphasized addressing what they call the “root causes” of the war, referring to NATO’s alleged eastward expansion. Meanwhile, Russian officials firmly rejected Ukrainian President Zelensky’s proposal to exchange occupied Ukrainian territory for land in Russia’s Kursk Oblast, indicating Putin remains committed to maximalist demands rather than compromise.
Ukrainian forces advanced in Kursk Oblast and near Toretsk, while Russian forces made gains near Borova, Siversk, Toretsk, Pokrovsk, and Kurakhove. Reports indicate Russia’s Shahed drone production rate may be declining, potentially impacting their aerial capabilities.
Denmark’s Defense Intelligence Service issued a concerning assessment that Russia could develop the capability to wage full-scale war against NATO within five years. The report indicates Russia is rebuilding its military with support from China, North Korea, and Iran, having spent $462 billion on defense last year compared to Europe’s $457 billion. In response to military pressures, Ukraine launched “Contract 18-24,” a new voluntary recruitment program targeting young adults aged 18-24, offering significant financial incentives including a $4,700 signing bonus and $19,120 during service.
Picture of the Day:
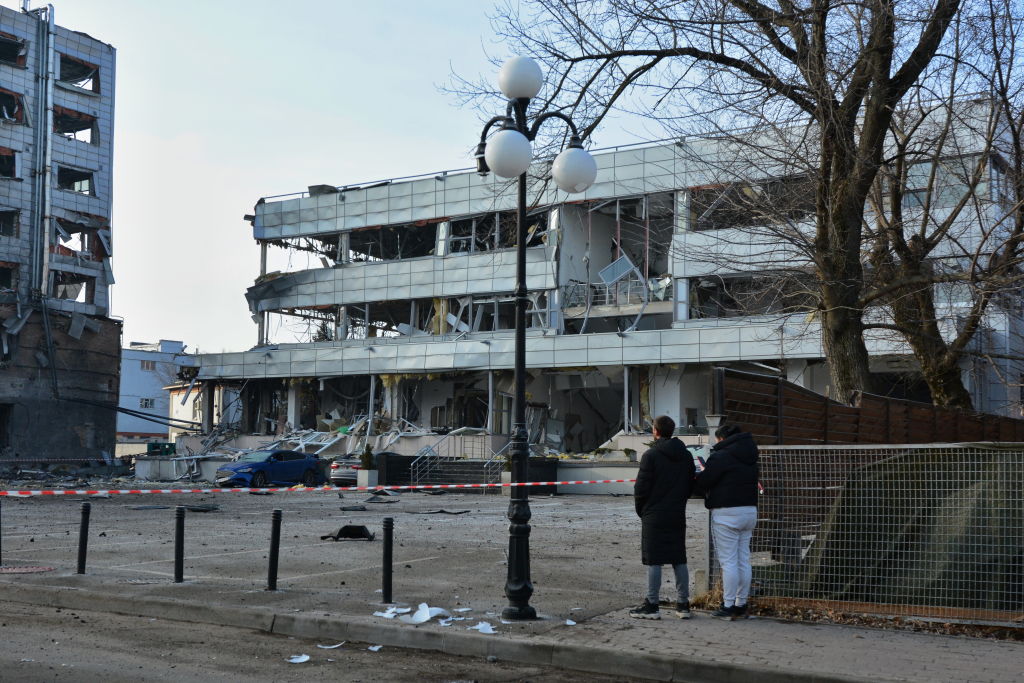 People stand near a damaged building in the Kurenivka neighborhood in Kyiv after a Russian missile attack. The Russian army attacked the capital and Kyiv Oblast with missiles and drones causing fires to break out in several districts. One person died and four others were injured. (Aleksandr Gusev/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images)
People stand near a damaged building in the Kurenivka neighborhood in Kyiv after a Russian missile attack. The Russian army attacked the capital and Kyiv Oblast with missiles and drones causing fires to break out in several districts. One person died and four others were injured. (Aleksandr Gusev/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
According to the Danish Defense Intelligence Service (DDIS), Russia could develop the capability to wage full-scale war against NATO within five years, supported by a military rebuilding effort backed by China, North Korea, and Iran, with Russia spending $462 billion on defense compared to Europe’s $457 billion. The DDIS assessment predicts a concerning timeline where Russia could attack a neighboring state within six months of any favorable Ukraine war conclusion, threaten Baltic NATO countries within two years, and be prepared for large-scale European conflict within five years if NATO fails to match Russia’s military buildup, with the risk particularly heightened if Russia perceives NATO as militarily or politically weakened or doubts US support for Europe. In response, NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte warned that NATO’s response to any Russian attack would be “devastating” and called for NATO allies to raise defense spending benchmarks from 2% to over 3% of GDP during a Brussels defense ministers’ meeting, while supporting U.S. President Trump’s position that Europe should increase support for Ukraine, noting that Ukraine’s battlefield strength would determine its negotiating power in any peace talks.
Russian President Putin held his first official call with Syrian Interim President Ahmed al Shara following the fall of former Russian-backed President Bashar al Assad. While Putin pledged support for Syria’s unity and promised continued economic aid, the call follows unsuccessful Russian attempts to secure military basing rights at Hmeimim Air Base and the Port of Tartus during recent negotiations in Damascus. Russia’s continued engagement with Syria’s interim government appears motivated by its desire to maintain its military presence in these strategic locations, which could affect regional stability and Russia’s military influence in the Middle East.
Armenia’s National Assembly took a significant step toward EU membership approving a draft law initiated by civic organizations that gathered over 50,000 signatures. While Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov acknowledged Armenia’s right to pursue EU membership, he questioned EU receptiveness and emphasized benefits of Armenia’s current membership in the Russian-led Eurasian Economic Union. This move reflects Armenia’s growing Western alignment amid deteriorating relations with Russia, whom they increasingly view as an unreliable security partner. This shift could significantly impact regional power dynamics and potentially reduce Russian influence in the Caucasus region.
Finland’s Parliament Speaker Jussi Halla-aho reports that Russian propaganda has largely failed to influence Finland, with most Russian-speaking residents well-integrated into Finnish society. Finland closed all border crossings with Russia in 2023 and has banned Russian vehicles and tourists, reflecting severely strained relations between the two nations. While some Finnish industries, particularly forestry, have experienced losses due to trade restrictions, Finland was not heavily dependent on Russian energy imports before the war. Halla-aho emphasizes that relations between Russia and Finland will likely remain distant for the foreseeable future, even after the Ukraine war ends, marking a significant shift in regional dynamics and contributing to ongoing tensions between Russia and Western Europe.
A significant prisoner exchange was announced where Russian cybercrime boss Alexander Vinnik, who was serving time in the U.S. for laundering $4 billion through cryptocurrency, will be released in exchange for American teacher Marc Fogel, who was imprisoned in Russia for possessing medical marijuana. The exchange, arranged by Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman and Russia’s Sovereign Wealth Fund Chief Kirill Dmitriev, coincided with Belarus releasing three additional prisoners, including a Radio Free Europe journalist. President Trump praised Putin for the deal, viewing it as a step toward peace negotiations in Ukraine. This exchange represents a notable diplomatic development that could influence U.S.-Russian relations during ongoing global tensions.
The Path to Peace
U.S. President Donald Trump held separate phone conversations with Russian President Putin (a 90-minute call) and Ukrainian President Zelensky to discuss ending the Ukraine war. During his call with Putin, they agreed to begin immediate negotiations and plan future meetings, including a proposed meeting in Saudi Arabia. In his call with Zelensky, they discussed peace opportunities, drone capabilities, and Ukraine’s upcoming February 14 meeting with U.S. Vice President JD Vance and Secretary of State Marco Rubio at the Munich Security Conference. While Zelensky expressed readiness to meet with Trump in Washington pending final arrangements, Trump suggested the meeting could occur this week, though Zelensky indicated no specific plans have been set. The Trump administration has appointed a negotiation team and set a 100-day goal to broker a peace deal, with Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent and peace envoy Keith Kellogg scheduled to visit Ukraine on February 20.
Russia’s position remains firm, with the Kremlin emphasizing addressing what they call the “root causes” of the war, referring to NATO’s alleged eastward expansion – a position indicating Russia’s continued stance on imposing its security interests on the US and Europe. Russian officials, including Kremlin Spokesperson Peskov and Security Council Deputy Chairperson Medvedev, firmly rejected Ukrainian President Zelensky’s proposal to exchange Ukrainian-held positions in Russia’s Kursk Oblast (where Ukrainian forces have maintained and recently advanced 2.5 kilometers since their August 2024 incursion) for Russian-occupied Ukrainian territories, which comprise about 20% of Ukraine, including the illegally annexed regions of Luhansk, Donetsk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia. Peskov threatened to forcefully remove Ukrainian forces from the region and stated Russia would never discuss exchanging its territory, with Medvedev dismissing the idea as “nonsense.”
U.S. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, speaking at the Ramstein summit in Brussels, declared it unrealistic for Ukraine to restore its pre-2014 borders or join NATO, stating these goals would only prolong the conflict. Trump echoed similar sentiments, suggesting Ukraine might not regain all its territory and that NATO membership was impractical. While the U.S. supports a sovereign Ukraine, Hegseth specified that any security guarantees must be backed by European and non-European troops, explicitly ruling out U.S. troop deployment. This position marks a significant shift in U.S. policy under Trump’s administration, with the UK now taking over leadership of the Ukraine Defense Contact Group. These statements drew criticism from multiple U.S. lawmakers, including Senators Blumenthal and Schiff, as well as European leaders, despite Trump’s proposal for U.S. support in exchange for Ukraine’s rare earth minerals, an offer Zelensky said he’s willing to discuss if “mutually beneficial.” This development comes even as NATO’s 2024 Washington Summit declared Ukraine’s path to membership “irreversible,” though several members, including the U.S., Germany, Hungary, and Slovakia, continue to oppose Ukraine’s membership.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
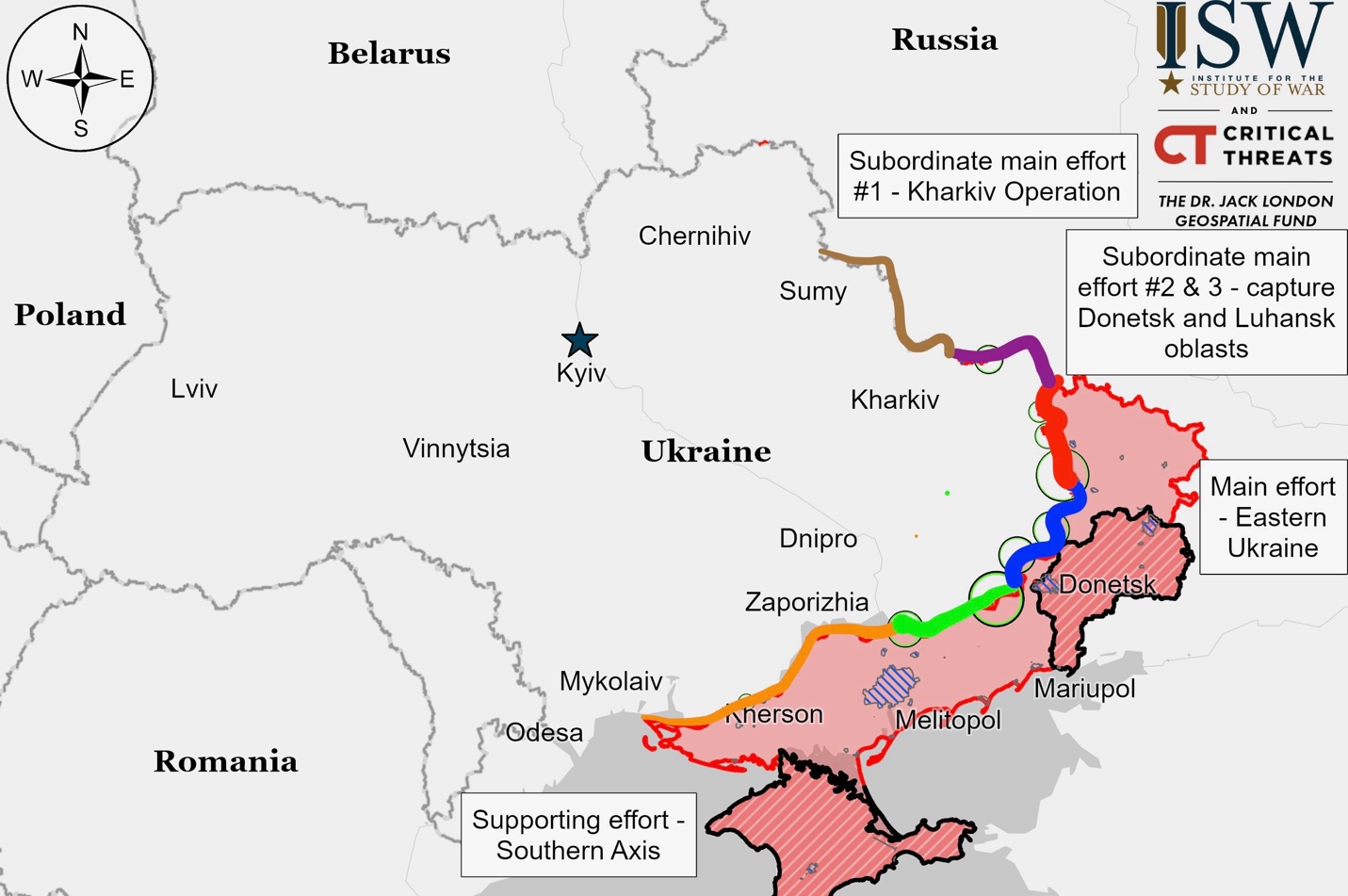
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative Russia
Recent fighting in Russia’s Kursk Oblast saw both sides make territorial gains. Ukrainian forces advanced near Fanaseyevka, while Russian forces moved into western Sverdlikovo. Combat occurred around several settlements including Nikolskiy, Russkaya Konopelka, and Cherkasskaya Konopelka. A Ukrainian commander reported that North Korean troops in the area have changed tactics, now attacking in smaller groups but continue to suffer heavy losses.
Russian air defenses shot down 12 Ukrainian drones that targeted several areas in Russia’s Kursk region, close to the Ukrainian border, according to Russia’s Defense Ministry. The ministry claimed it thwarted a series of drone attacks in Kursk city and two other unnamed settlements early Thursday. A 16-year-old civilian was reportedly injured, and several buildings were damaged in the attacks. The Kursk region, which borders Ukraine, has faced numerous drone attacks in recent months, highlighting the ongoing regional conflict and its impact on civilian areas.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian sources reported Ukrainian counterattacks near Lyptsi and Vovchansk in the Kharkiv region, though no Russian ground attacks were confirmed. A Ukrainian brigade spokesperson noted increased Russian drone activity in the area since mid-December, particularly the use of fiber-optic drones.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Kupyansk
Russian forces continued attacks near Kupyansk targeting the settlements of Kindrashivka and Petropavlivka but failed to make any advances.
Borova
Russian forces advanced near Borova, capturing positions in southern Makiivka. They launched attacks across multiple settlements including Zahryzove, Nova Kruhlyakivka, Zeleny Hai, Novoyehorivka, Kopanky, Novoserhiivka, and Novomykhailivka. A Ukrainian commander reported repelling a Russian mechanized assault in the area.
Lyman
Russian forces launched attacks near Lyman, targeting Nove, Novolyubivka, Kolodyazi, and Yampolivka, but failed to advance. While Russian sources claimed gains near the Zherebets River and Yampolivka, Ukrainian forces reported destroying two Russian armored vehicles while repelling a platoon-sized mechanized assault in the area.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces made gains northeast of Siversk, advancing along Tsentralna street on the western outskirts of Bilohorivka. Russian sources also claimed an advance north of Hryhorivka, though this remains unconfirmed.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces launched multiple attacks around Chasiv Yar but failed to make confirmed advances. The attacks targeted Vasyukivka and Hryhorivka to the northeast, Minkivka and Mayske to the north, and Stupochky to the south. While a Russian military blogger claimed advances in fields north of Chasiv Yar, these claims remain unverified.
Toretsk
Fighting intensified in Toretsk as both Russian and Ukrainian forces made confirmed advances in the area. Ukrainian forces gained ground near the Toretska Mine in northern Toretsk, while Russian forces advanced in the northwestern part of the city. Russian forces also conducted attacks near Shcherbynivka to the west and Dyliivka to the north.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces advanced in multiple areas near Pokrovsk, with confirmed gains southwest of Vodyane Druhe and in eastern Pishchane, while heavy fighting continued around Tarasivka, Yelyzavetivka, Promin, Lysivka, Zvirove, Kotlyne, Udachne, Molodetske, Nadiivka and Uspenivka, with video evidence showing Russian forces conducting a platoon-sized mechanized assault in the area; however, Ukrainian forces achieved significant tactical success in the Pokrovsk sector of Donetsk region, advancing more than a kilometer on an 8-kilometer wide front, recapturing the village of Pishchane (which had been under Russian control since January 7-9) and securing two adjacent villages – Dachenske and Vodyany Druhy – while also launching counterattacks near Pishchane, Zvirove, and Vodyane Druhe that reportedly pushed Russian forces back to Kotlyne’s outskirts, with military analyst Agil Rustamzade noting that the pace of Russian attacks has notably decreased in recent days, with only 30 out of 95 total engagements occurring in the Pokrovsk sector, down from over 150 daily assaults in January.
Andriivka
Russian forces advanced near Kurakhove, with confirmed gains southwest of Dachne. They continued attacks near Shevchenko, Andriivka, Kostiantynopil, Oleksiivka, and Bahatyr. Russian forces are operating in Dachne, while Russian military bloggers claimed an unverified one-kilometer advance north of Andriivka and movements toward Kostiantynopil.
Velyka Novosilka
Russian forces launched multiple attacks around Velyka Novosilka but made no confirmed advances. The offensive operations targeted Burlatske to the northwest, Novosilka to the west, and Rivnopil to the southwest. Russian military bloggers claimed unverified advances northwest of Vremivka.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces launched attacks near the settlements of Kamyanske and Charivne in western Zaporizhia Oblast focusing on areas around Robotyne. Despite these offensive operations, they failed to make any territorial advances.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
There were no reported military activities from either Russian or Ukrainian forces in the Kherson region.
Ukraine News
Russian forces launched a significant missile and drone strike against Ukraine, primarily targeting Kyiv City and Kryvyi Rih. The attack involved 7 ballistic missiles, and 123 drones launched from multiple Russian regions and occupied Crimea. Ukrainian forces successfully intercepted 6 missiles and 71 drones, while another 71 decoy drones were neutralized by electronic warfare. The strikes damaged buildings in four districts of Kyiv City and Boryspil, killing at least one person and causing civilian casualties. In Kryvyi Rih, Russian missiles struck the city center, damaging civilian infrastructure. Ukrainian officials emphasized their urgent need for US Patriot air defense systems to counter such ballistic missile attacks.
President Volodymyr Zelensky stated that if Ukraine is denied NATO membership, it must “build NATO on its territory” by doubling its military strength to match Russia’s capabilities. Zelensky acknowledged that NATO membership is unlikely due to opposition from the U.S., Germany, and Hungary, but suggested President Trump could influence this position. He expressed confidence that Trump could provide security guarantees without Russian consultation, while Europe could support Ukraine’s defense with missiles and Patriot air-defense systems. Despite NATO’s 2024 Washington summit declaring Ukraine’s path to membership “irreversible,” no formal invitation has been extended.
Ukraine’s Security Service (SBU) arrested Colonel Dmytro Koziura, head of its counter-terrorism department, for allegedly spying for Russia’s FSB, with SBU Chief Vasyl Malyuk documenting 14 illegal acts of transmitting sensitive information; the suspect, who was recruited in Vienna in 2018 and activated in December 2024, used a secret Kyiv apartment and special communication equipment to relay state secrets through a middleman to FSB handler Yuri Shatalov, though before the arrest, which involved extensive surveillance of the suspect’s electronic devices and is part of Ukraine’s broader effort to root out Russian infiltration of its security services during the ongoing war, the SBU used the mole to feed false information to Russia, with Koziura now facing life imprisonment if convicted of high treason.
Ukraine’s National Security and Defense Council has imposed sanctions against former President Petro Poroshenko, with President Zelensky announcing that an official decree will be published on February 13. Poroshenko, who served as president from 2014 to 2019, called the decision “unconstitutional” and “politically motivated,” warning it could damage Ukraine’s internal unity during wartime. The sanctions reportedly relate to allegations of “high treason,” though specific restrictions weren’t detailed. This development marks a significant escalation in domestic political tensions at a time when Ukraine faces both external threats and potential peace negotiations.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 1 INJURIES: 9
A Russian missile attack on Kyiv killed one person and injured four others, including a 9-year-old girl, in the Obolon district when a missile struck an office building. The attack, which reportedly involved four Iskander ballistic missiles, caused fires in multiple districts: a warehouse burned in Holosiivskyi district, and a residential building’s roof caught fire in Solomianskyi district. The offices of Freedom TV and Dim news channels were damaged, and in Kyiv Oblast, a warehouse storing animal shelter supplies was destroyed.
Russian forces launched multiple attacks across 13 communities in Sumy Oblast resulting in five civilian injuries. The assault, which caused 186 explosions, targeted the communities of Sumy, Bezdryk, Verkhnya Syrovatka, Yunakivka, Khotin, Krasnopillia, Bilopillia, Velyka Pysarivka, Krolevets, Esman, Druzhba, Seredyna-Buda, and Svesy. The most intense attacks occurred in Velyka Pysarivka near the Russian border, where 86 explosions were recorded. In Yunakivka, drone strikes injured three people and destroyed a civilian vehicle, while attacks in Verkhnya Syrovatka and Esman also resulted in injuries and damage to residential buildings, a school, and farm structures.
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine’s Ministry of Defense launched “Contract 18-24,” a new voluntary recruitment program targeting young adults aged 18-24, offering a one-year military contract with significant financial incentives: a signing bonus of $4,700-24,000, $19,120 during service, and a monthly salary of $2,870-3,000, along with benefits including subsidized mortgages, education, and medical care; the program, which Defense Minister Rustem Umerov frames as part of Ukraine’s strategy to develop a professional military force, provides three months of training before frontline deployment, exempts volunteers from mobilization for 12 months after completing their service, allows travel abroad, and aims to address troop shortages without lowering the draft age from 25, though it has sparked criticism from current soldiers like Alina Mykhailova and Masi Nayem, who question why existing troops receive fewer benefits.
Ukraine’s Allies
U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent visited Kyiv, becoming the first cabinet member from Trump’s new administration to meet with President Zelensky, delivering a draft minerals agreement that would give U.S. companies access to Ukraine’s rare earth minerals in exchange for continued American support, with Trump claiming Ukraine has “essentially agreed” to a $500 billion deal; Ukrainian officials, including Presidential Chief of Staff Andrii Yermak, confirmed Ukraine’s interest in developing its mineral resources with U.S. partners, though many deposits are currently in Russian-occupied territory, with the visit preceding the Munich Security Conference where other top U.S. officials will discuss potential peace frameworks with European allies, and presidential envoy Keith Kellogg expected to follow with a visit on February 20 after the conference.
The Netherlands announced that it will send 25 YPR armored vehicles to Ukraine for medical evacuations and wounded soldier transport. Dutch Defense Minister Ruben Brekelmans confirmed this latest aid package, which follows previous deliveries of over 200 YPRs and recently completed T-72 tank transfers.
Life in Russian Occupied Ukraine
Russian officials in occupied Sevastopol have launched the “Sevastopol – City of Heroes” program to train veterans of the Ukraine war for leadership roles in local government and state businesses. This initiative mirrors Russia’s existing “Time of Heroes” program, which places veterans in key positions across Russian government and business sectors.
Russia News
Russia’s military spending has surpassed all European nations combined, reaching 13.1 trillion rubles ($462 billion) in 2024, a 42% increase from the previous year. By comparison, European defense spending, including the UK and EU states, totaled $457 billion. The report highlights concerns about European security, especially as U.S. support may decrease under President Trump, who has called for European nations to increase their defense spending from 1.7% to 5% of GDP. While Russia’s military investment strains its economy, Russia can still sustain its war costs, with spending projected to grow another 13.7% in 2025.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1150 853030 |
Tanks +9 10023 |
Artillery +53 22976 |
Arm. Veh. +27 20871 |
Aircraft 370 |
Heli 331 |
Ships 28 |
Russia Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian military commanders are pressuring soldiers mobilized in 2022 to sign contracts with the Ministry of Defense, according to Russian opposition outlet Verstka. Those who refuse face threats of reassignment to high-casualty assault units. The push comes amid concerns about troop demoralization and fears that many soldiers will leave service without contractual obligations in place.
Russia’s Shahed drone production appears to be slowing down at its facility in the Alabuga Special Economic Zone in Tatarstan. According to Ukrainian military official Lieutenant Andriy Kovalenko, while the facility produced over 6,000 Shahed drones in 2024, production notably decreased in the final months of the year. This slowdown may be due to material shortages, continued reliance on Iranian components, or difficulties circumventing Western sanctions. Russia may also be shifting focus to producing less expensive decoy drones to overwhelm Ukrainian air defenses.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
