Summary of the Day:
Russian forces have intensified their offensive near Vuhledar in western Donetsk Oblast, reaching the outskirts of the settlement. However, military analysts suggest that capturing Vuhledar may not provide Russia with a significant operational advantage for further offensives in the region. Meanwhile, Ukrainian forces have made advancements west of the Kursk Oblast salient, within Vovchansk, and in eastern Toretsk.
Ukraine has conducted strikes against Russian rear ammunition depots, exposing vulnerabilities in Russian military logistics. These strikes demonstrate how Western restrictions on Ukraine’s use of certain weapons against targets in Russia have allowed Russian forces to operate these facilities with less concern for protection.
Russia continues to strengthen its ties with China to support its war effort in Ukraine. This includes the alleged use of Chinese satellites for intelligence gathering and the acquisition of Chinese-made military equipment. Simultaneously, Russia faces internal criticism from ultranationalist military bloggers over the misuse of technical specialists in frontline operations, highlighting tensions between military leadership and specialized units.
Russian opposition sources report that the topic of mobilization remains sensitive among Kremlin officials, suggesting ongoing challenges in managing public perception and military manpower needs.
Picture of the Day:
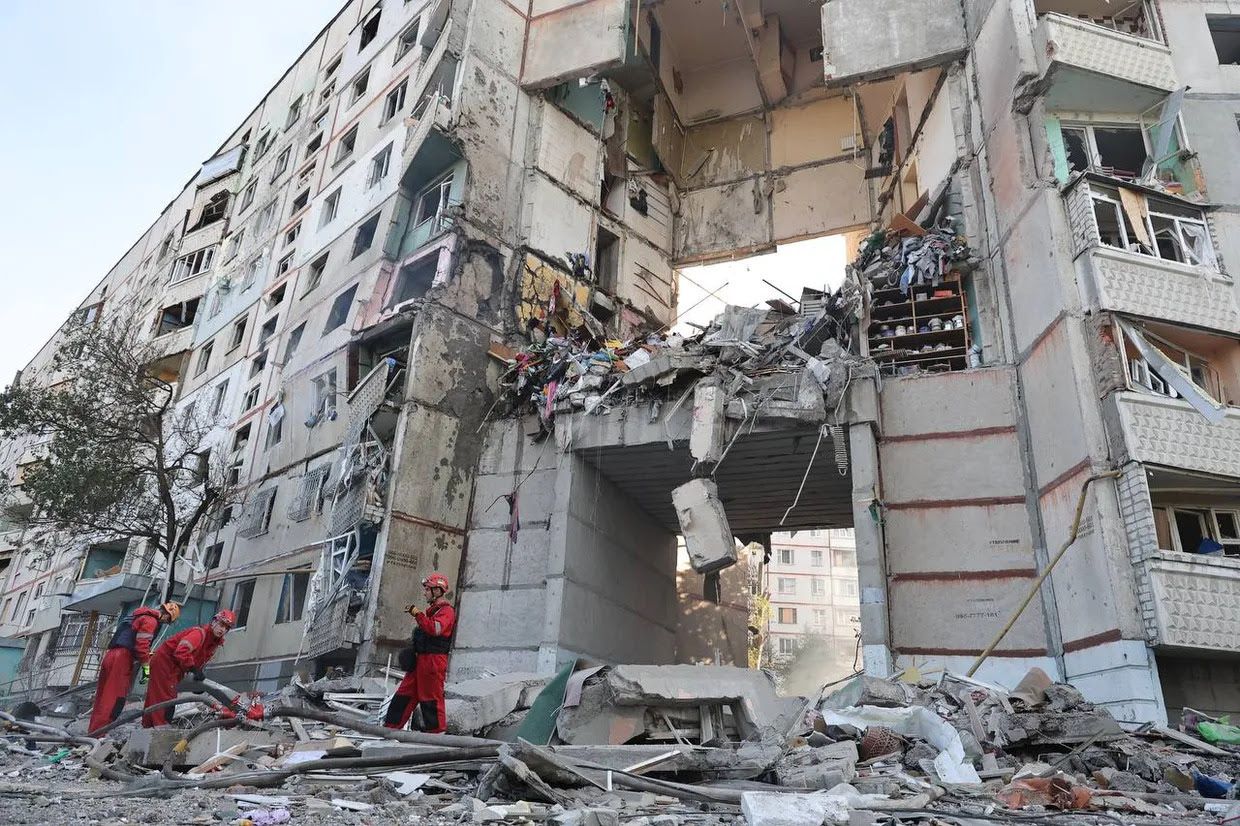 Russia attacked the city of Kharkiv in Kharkiv Oblast resulting in damages of several buildings and casualties among civilians. (Kharkiv Oblast Governor Oleh Syniehubov / Telegram)
Russia attacked the city of Kharkiv in Kharkiv Oblast resulting in damages of several buildings and casualties among civilians. (Kharkiv Oblast Governor Oleh Syniehubov / Telegram)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
Recent developments in Eastern Europe are contributing to an escalation of geopolitical tensions, with implications for regional stability and NATO-Russia relations. In the Republic of Karelia, Russian military bloggers are making unverified claims of NATO and Finnish involvement in anti-Russian activities. These allegations, centered on the actions of a Finnish Lutheran Church society, include accusations of supporting separatism and pro-Ukrainian sentiment. The situation has raised concerns about potential threats to Russian military infrastructure in the region. While unsubstantiated, these claims reflect growing paranoia within Russian nationalist circles and could be used to justify increased military presence along the Finnish border, further straining the already deteriorated Russia-Finland relations following Finland’s NATO accession.
Simultaneously, a coordinated disinformation campaign is targeting Moldova’s upcoming election. Russian-aligned sources are spreading baseless claims of Western control over the electoral process and circulating unfounded rumors about illegal migrants being used for military purposes. This narrative aims to undermine faith in Moldova’s democratic institutions and foment anti-Western sentiment. If successful, it could potentially destabilize Moldova’s pro-European trajectory and complicate its relationships with NATO and the EU.
In Belarus, President Lukashenko has announced the creation of a new military unit composed of former contract soldiers. While likely small in scale, this move signals Belarus’s continued militarization and alignment with Russian strategic interests. Though not a significant change in military capability, this development reinforces Belarus’s role as a potential staging ground for Russian operations and may increase anxiety among NATO’s eastern members.
These events collectively point to a hardening of divisions between Russia and the West in Eastern Europe. NATO may face increased pressure to bolster its presence in the region, particularly along its northeastern flank. The ongoing disinformation campaigns threaten to erode trust in democratic processes and institutions in countries caught between Russia and the West. Perhaps most concerning is the potential for miscalculation or unintended escalation, especially in contested border regions.
The Path to Peace
Czech President Petr Pavel suggests that Russia’s “temporary” occupation of some Ukrainian territories is the most likely outcome of the invasion. Currently, Russia controls about 27% of Ukraine, including parts of Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia oblasts, as well as Crimea. Pavel believes neither side will achieve total victory, and that Ukraine may need to be realistic about recapturing all occupied territories. However, Ukraine maintains its stance on full Russian withdrawal, with President Zelensky set to present a “victory plan” to President Biden during his U.S. visit. Zelensky emphasizes that freezing the conflict is not an option.
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
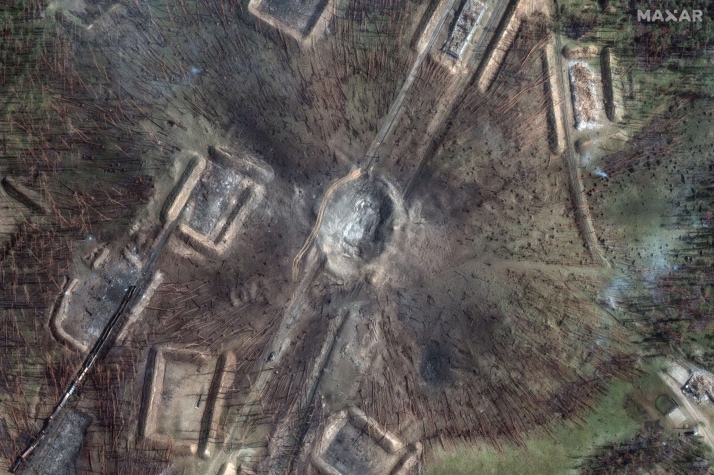
Recent Ukrainian strikes on Russian ammunition depots in Tver Oblast and Krasnodar Krai have caused significant damage, as shown by satellite imagery. The strikes destroyed numerous storage buildings, rail cars, and exposed ammunition stockpiles. This reveals a lack of security in Russia’s rear supply areas, highlighting how Western restrictions on Ukraine using Western-provided weapons against targets in Russia have allowed Russian forces to operate these facilities with less concern for protection. This situation has enabled Russia to efficiently stockpile and transport large amounts of military supplies to Ukraine.
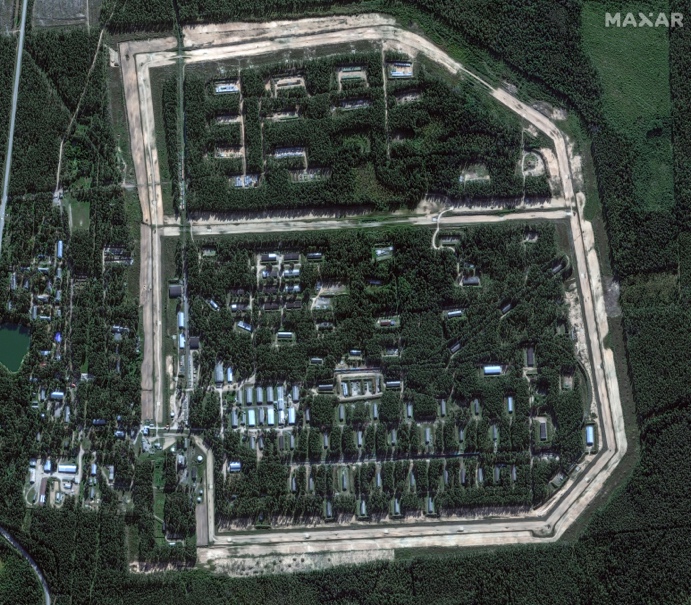
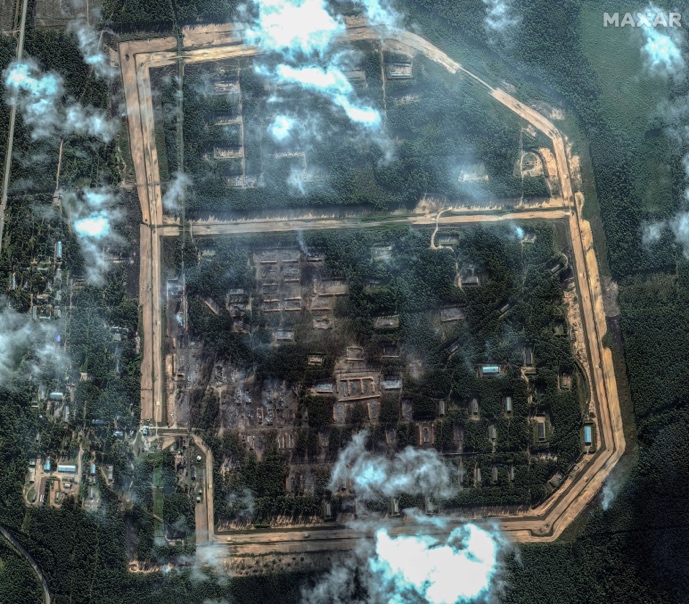


Oktyabrsky Ammunition Depot Before and After Strike.
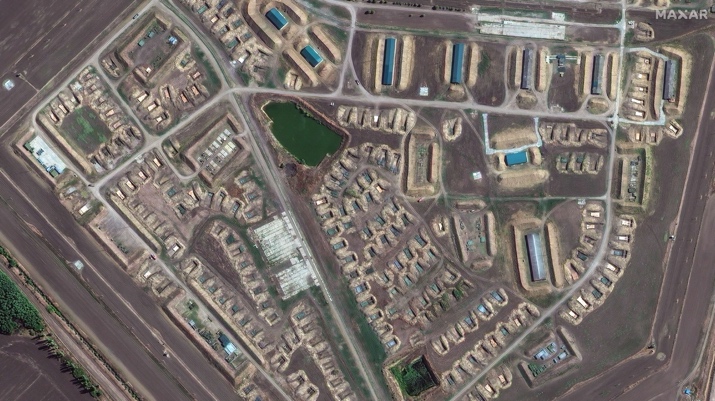
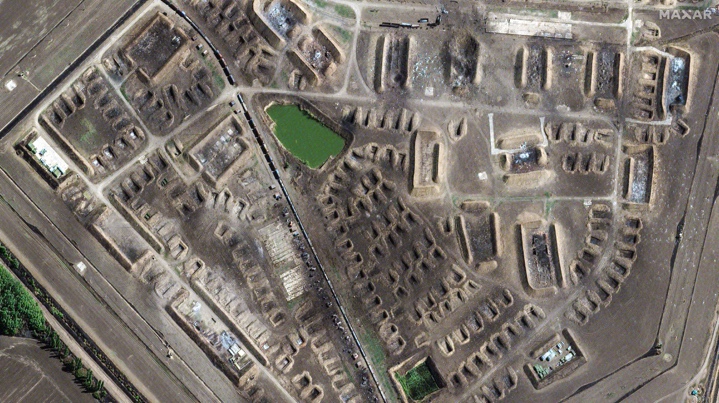


Tikhoretsk Ammunition Depot Before and After Strike
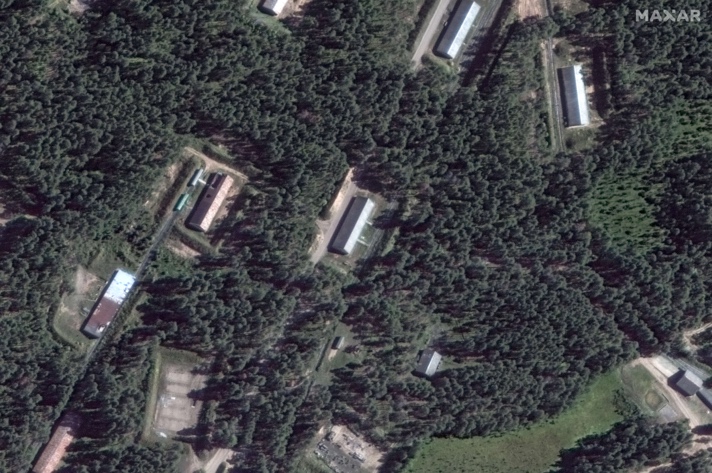


Toropets Ammunition Depot Before and After Strike
A Russian military blogger has highlighted a significant vulnerability in Russia’s logistics: the lack of concealment for large-scale facilities like warehouses and airfields. These are easily visible on open-source maps and satellite imagery. The blogger also noted that Russia hasn’t implemented a system to distribute ammunition supplies, making them vulnerable to large-scale destruction from Ukrainian strikes. Western countries could potentially exploit this weakness by allowing Ukraine to use precision weapons against targets in Russia, forcing Russia to use smaller, less efficient, and more distant storage facilities.
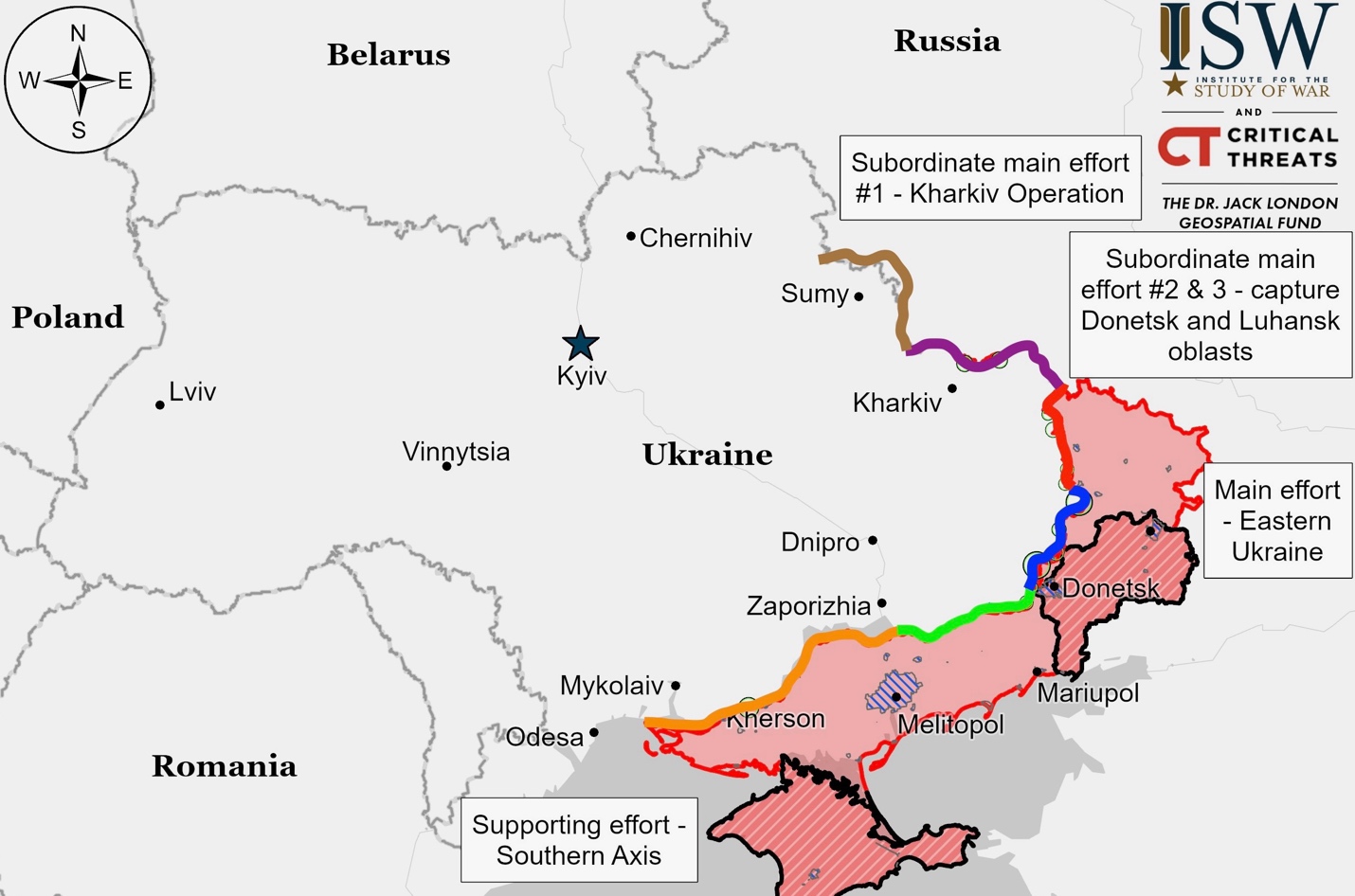
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Ukrainian forces have made recent advances in Russia’s Kursk Oblast, according to multiple reports and video evidence. On September 23, Ukrainian mechanized units were seen pushing southeast of Veseloye, with additional footage from September 20 confirming progress east of the same location. Russian sources claim to have repelled Ukrainian attacks towards Novy Put and Medvezhye on September 23-24, but these claims remain unverified.
The offensive continued on September 24, with a Russian blogger reporting that Ukrainian forces had captured forest areas near Martynovka and possibly Malaya Loknya, though this information is yet to be confirmed. Russian sources also reported ongoing Ukrainian attacks near Olgovka, Lyubimovka, Tolstyy Lug, and Obukhovka, but no confirmed changes to the frontline have been reported.
In a significant development, Ukrainian forces successfully struck a Russian Buk-M3 air defense system near Rylsk in Russia’s Kursk Oblast on September 23. Video evidence confirms the attack, which occurred approximately 20 kilometers northwest of the Ukrainian-held salient in Kursk Oblast.
Russian forces have continued their counterattacks on the Ukrainian salient in Kursk Oblast. A Chechen commander claimed that Russia had recaptured 12 settlements in the area, although independent assessments confirm only 11. Various Russian airborne and naval infantry units are reportedly engaged in the fighting.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Ukrainian forces have made significant advances in central Vovchansk, located northeast of Kharkiv City, as confirmed by video evidence and Ukrainian intelligence reports on September 24. The most notable gain was the capture of the Vovchansk Aggregate Plant, a strategic location that had been under Russian control for months.
The operation to recapture the aggregate plant was carried out by Ukrainian military intelligence (HUR) special forces in what has been described as a difficult and intense engagement. The mission involved clearing 30 buildings and included close-quarters combat, with reports of hand-to-hand fighting. Russian forces defending the plant were said to be professional units, reportedly including elements of the 45th Guards Spetsnaz Brigade, as stated by Ukrainian intelligence.
During the defense of the plant, Russian forces employed a variety of weapons, including drones and guided bombs, highlighting the complexity and intensity of the battle. The capture of this facility marks a significant development in the ongoing conflict in the Kharkiv region.
In the broader context of the conflict, Russian forces have continued their attacks near several locations in the area, including Lyptsi, Hlyboke, Tykhe, and Vovchansk itself. However, it’s noted that the intensity of fighting in this particular sector has decreased compared to other eastern fronts such as Pokrovsk, Vuhledar, and Toretsk.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces continued attacks along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line on September 24-25, without confirmed advances. Russian sources claimed progress near Kruhlyakivka and Berestove. Ukrainian reports indicate Russian attacks in numerous settlements around Kupyansk, Svatove, and Kreminna.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces attacked near Fedorivka, south of Siversk, on September 24 without making confirmed advances.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces launched limited attacks near Chasiv Yar on September 24, without confirmed advances. They targeted areas north of Chasiv Yar (near Kalynivka and Minkivka), southeast (near Klishchiivka), and south (near Bila Hora, Predtechyne, and Stupochky).
Toretsk
Ukrainian forces regained some positions in eastern Toretsk along Tsentralna Street, as shown in recent footage. Meanwhile, Russian forces reportedly advanced in eastern Toretsk and south into Nelipivka and Leonidivka. Russian attacks were reported near Toretsk, Dachne, Nelipivka, and towards Shcherbynivka. The claim of Russians fully controlling Nelipivka remains unconfirmed.
Pokrovsk
Russian forces reportedly advanced east and southeast of Pokrovsk, though frontline changes were unconfirmed on September 24. They attacked multiple areas including Zelene Pole, Vozdvyzhenka, Myrolyubivka, Novotoretske, Krasnyi Yar, Novohrodivka, Mykolaivka, Marynivka, Zhuravka, Tsukuryne, Zhelanne Druhe, and Ukrainsk. Russian troops also reportedly advanced near Hrodivka, Selydove, and Ukrainsk.
West of Donetsk City
On September 24, Russian forces continued offensive operations west of Donetsk City, focusing on areas near Heorhiivka and towards Dalnye. However, no confirmed advances were reported in these areas.
Southwest of Donetsk City
In recent developments on the eastern front of the Ukraine conflict, Russian forces have intensified their offensive around the town of Vuhledar in Donetsk Oblast. Reports indicate that Russian troops have advanced to the outskirts of the town, which has been a key Ukrainian defensive stronghold for nearly two years.
According to military sources, Russian forces have reached eastern Vuhledar and are attempting to encircle Ukrainian positions by advancing through nearby settlements of Vodyane and Prechystivka. The capture of the Pivdennodonbaska Mine No. 3 in western Vodyane by Russian troops has been confirmed. Some sources suggest that Russian forces now control the main supply route to Vuhledar, although this claim remains unverified.
The Ukrainian 72nd Mechanized Brigade, which has been defending the area since the beginning of the full-scale invasion in 2022, is reportedly facing significant pressure. Ukrainian military officials describe the situation as tense, with daily assaults by Russian forces using a variety of weapons including guided bombs, artillery, and drones.
Russian troops have reportedly made progress near Bohoiavlenka and crossed the Kashlahach River, further threatening to encircle Vuhledar. While Ukrainian forces continue to resist, some officials predict that Vuhledar may fall to Russian forces within days.
The potential capture of Vuhledar by Russian forces could have strategic implications for the region. Located 50 kilometers south of Pokrovsk, the town’s fall could threaten Ukrainian positions in southwestern Donetsk Oblast and compromise the southern flank of Pokrovsk. However, military analysts note that Vuhledar’s capture may not significantly impact Russian offensive operations in the broader region, as it is not a crucial logistics hub and Russian forces already control most main roads in the area.
The outcome of the battle for Vuhledar remains uncertain. If Ukrainian forces choose to withdraw to avoid encirclement or costly urban combat, Russian forces could potentially take the town quickly. However, if Ukraine opts to defend its positions, Russia may face challenges overcoming fortifications built over the past two years.
It is worth noting that previous Russian offensives on Vuhledar in late 2022 and early 2023 resulted in significant losses, allowing Ukraine to further fortify the area and study Russian tactics. The approaching autumn rains could also hinder Russian advances in the surrounding rural areas.
As the situation continues to evolve, the battle for Vuhledar represents a critical juncture in the ongoing conflict in eastern Ukraine.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
On September 24, there were no reports of combat in the border region between Donetsk and Zaporizhia Oblasts, according to both Russian and Ukrainian sources.
Zaporizhia Line
On September 23-24, positional fighting continued near Novoandriivka in western Zaporizhzhia Oblast, without confirmed changes to the front line.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
On September 23-24, Russian forces made unsuccessful attacks in eastern Kherson Oblast. Ukrainian officials reported that Russia is consolidating forces, including Wagner Group and airborne units, in southern Ukraine, possibly preparing for a future offensive. Russian airborne forces continue to strike Ukrainian positions on the western bank of the Dnipro River.
Ukraine News
In a series of events unfolding in Ukraine, Russian forces launched a large-scale attack on the night of September 23-24, utilizing both missiles and drones. Ukrainian defense systems intercepted 66 Shahed drones across several oblasts, while an additional 13 were disabled. The city of Zaporizhzhia suffered damage to its infrastructure from a missile strike. These attacks reportedly originated from various Russian regions, including Rostov, Bryansk, Kursk, and Krasnodar Krai.
The Ukrainian Air Force detected a “low-speed” air target entering Ukrainian airspace from Belarus near the Kyiv-Zhytomyr border. This incident triggered an air alert in northern Ukraine. The Belarusian Hajun Project identified the aircraft as a Belarusian Yak-130 fighter jet, which reportedly crossed the border near Dyatlik in Gomel Oblast, Belarus.
In diplomatic news, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky met with Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi in New York during the United Nations General Assembly. The leaders discussed strengthening cooperation between Ukraine and India in various sectors, including trade, defense, and post-war reconstruction. They also conversed about Ukraine’s peace formula and an upcoming peace summit.
This marks the third meeting between Zelensky and Modi in a year, following Modi’s recent visit to Kyiv where four cooperation agreements were signed. India, which has historically maintained strong ties with Russia, has continued its relationship with Moscow since the invasion of Ukraine began. However, Prime Minister Modi has expressed support for resolving the conflict in Ukraine.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 7+ INJURIES: 73
A series of Russian attacks across multiple regions of Ukraine on September 24 has resulted in numerous casualties and significant damage to civilian infrastructure. In Kharkiv, Ukraine’s second-largest city, Russian forces launched five glide bombs, killing at least three people and injuring 34 in residential areas. The strikes targeted densely populated areas, damaging residential buildings in the Kyivskyi and Saltivskyi districts. A bakery plant was also hit, contributing to the casualties.
FAB-250 and FAB-500 bombs were used in the attack. Rescue operations are ongoing, with some individuals still trapped under rubble. President Volodymyr Zelensky condemned the attack and called for international action to stop Russian aggression.
In Zaporizhzhia City, Russian forces targeted residential areas for the second consecutive night using guided aerial bombs, according to local officials. An overnight strike on September 23 killed one man and injured seven civilians, including two teenagers. The attack also hit a critical infrastructure facility, causing a fire that was later extinguished. At least two houses were destroyed, and some of the injured were hospitalized.
The attacks extended to other regions as well. In Kharkiv Oblast, strikes on Kupiansk and Osynove resulted in one death and one injury. Donetsk Oblast saw two fatalities in Kramatorsk and Udachne, with 18 people injured across the region. In Kherson Oblast, 23 settlements were targeted, leaving 13 people wounded.
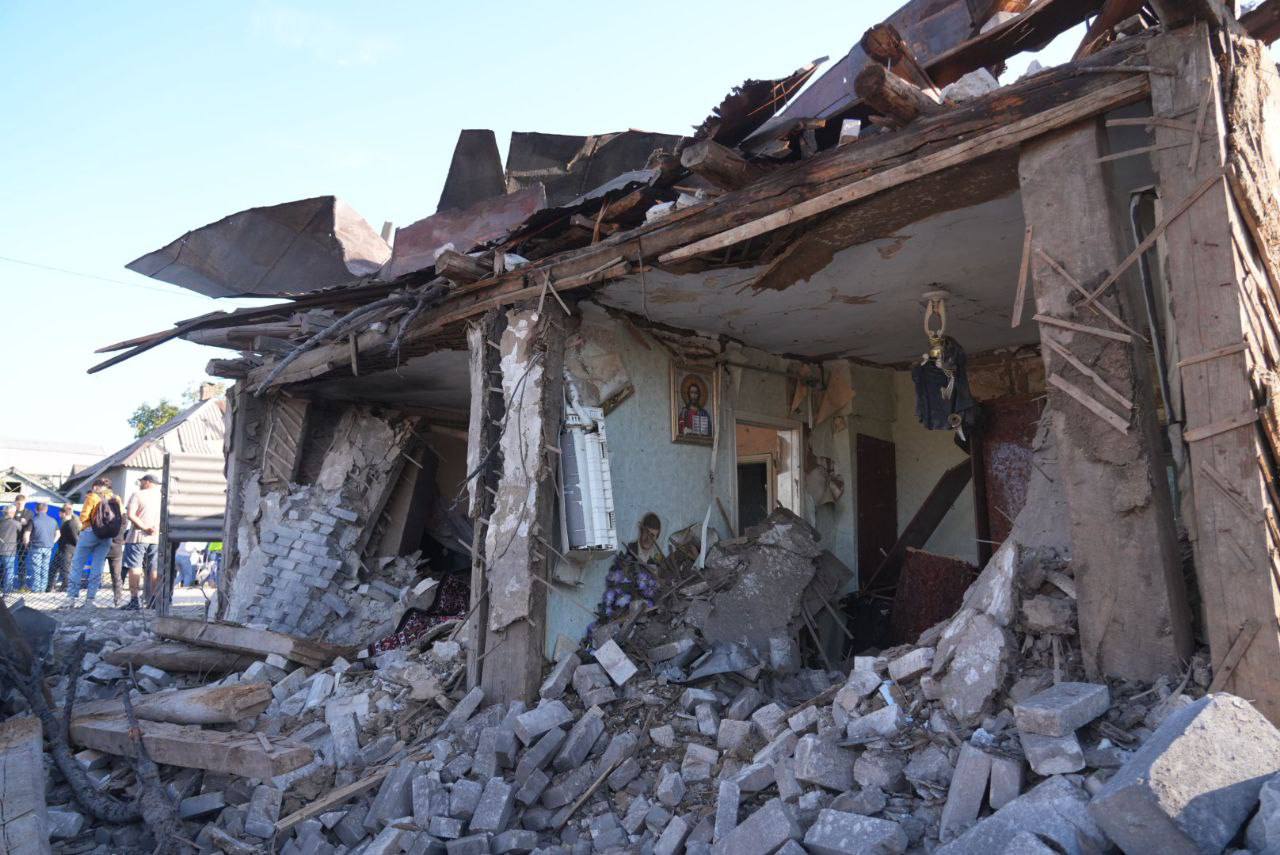 The aftermath of a Russian attack on the city of Zaporizhzhia on Sept. 24, 2024. (Ivan Fedorov/Telegram)
The aftermath of a Russian attack on the city of Zaporizhzhia on Sept. 24, 2024. (Ivan Fedorov/Telegram)
Ukraine’s Allies
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky is set to present a detailed “victory plan” to U.S. President Joe Biden during his visit to the White House on September 26. The plan, which includes both diplomatic and military components, focuses on five key points: security guarantees, continued military aid, economic support, a NATO invitation, and a clear path to EU membership.
While the exact contents of the plan remain undisclosed, sources speculate it may include requests for modern weapons, long-term financial aid, and permission to conduct operations in Russia’s Kursk region. A significant aspect of the proposal is Ukraine’s request to use long-range missiles against Russian targets. Although the Biden administration has not officially changed its policy on this matter, reports suggest ongoing discussions between the U.S. and UK about potentially allowing such strikes deep within Russia.
The timing of Zelensky’s visit is crucial, as it may coincide with the announcement of a new $375 million U.S. military aid package for Ukraine. However, Western diplomats stress that the outcome of the upcoming U.S. presidential election could significantly impact Russia’s approach to peace talks. Some suggest this visit could be Zelensky’s last chance to secure critical commitments from Biden, particularly regarding long-range strikes against Russia.
In addition to meeting with President Biden, Zelensky plans to discuss his victory plan with presidential candidates Donald Trump and Kamala Harris. The Ukrainian leader is also presenting the plan to world leaders at the UN General Assembly in New York. Despite allies’ commitment to Ukraine, they are seeking clarity on what peace might look like.
Andriy Yermak, head of Ukraine’s Presidential Office, announced that an invitation to join NATO is part of the victory plan. While NATO allies have affirmed Ukraine’s path toward membership, no definitive timeline has been set. President Biden has previously stated that peace in Ukraine doesn’t necessarily require NATO membership, but rather a guarantee against future Russian occupation.
Meanwhile, Ukraine’s international support faces some challenges. Czechia’s initiative to supply Ukraine with artillery shells has encountered minor issues, with about 0.05% of delivered shells exploding prematurely during combat. Despite these problems, President Zelensky has expressed gratitude for Czech support, which includes tanks, helicopters, and other military equipment.
In the United Kingdom, Foreign Secretary David Lammy is working to strengthen Ukraine’s position as winter approaches. While not confirming the use of British long-range weapons inside Russia, Lammy acknowledged Iran’s supply of ballistic missiles to Moscow as a major escalation. The UK has pledged a total of £12.8 billion in military and non-military assistance to Ukraine.
Polish President Andrzej Duda has criticized recent remarks suggesting Ukraine’s EU accession should be blocked until the Volyn massacre issue is resolved. Duda argued that such threats align with Kremlin policy and emphasized the importance of resolving historical issues without hindering Ukraine’s EU membership prospects.
The ongoing conflict and U.S. support for Ukraine continue to be debated in the context of the 2024 U.S. presidential race. At a recent rally in Atlanta, former President Donald Trump criticized U.S. involvement in Ukraine, promising to settle the conflict if elected. Trump’s potential return to the White House has raised concerns in Ukraine, particularly after pro-Trump Republicans blocked U.S. aid to Ukraine in Congress earlier this year.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Reports from Moscow indicate growing divisions within the Kremlin over potential new military mobilization efforts for the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. According to Meduza, security officials are advocating for additional mobilization, while civilian officials oppose such measures. The debate comes as Russia grapples with manpower shortages in its Ukraine campaign, despite increased incentives for soldiers and claims of sufficient voluntary recruitment.
President Vladimir Putin has thus far avoided involuntary mobilization, likely due to concerns over negative public reaction. In an effort to bolster recruitment without resorting to further mobilization, Russian lawmakers have approved a bill allowing prosecutors to drop criminal charges against individuals who agree to military service in Ukraine. This legislation, applicable during times of mobilization, martial law, and wartime, offers accused criminals an alternative to prosecution if they join the Russian military.
Meanwhile, Russian authorities have concluded an investigation into the deaths of two drone operators from the 87th Separate Rifle Regiment. The operators were killed in a frontal assault after criticizing their command. The investigation found no wrongdoing by the regiment’s commander in reassigning the drone unit to combat operations and dismissed allegations of drug trafficking on the frontline. While some military commanders faced disciplinary action, the regiment’s commander retained his position.
In response to the incident, Defense Minister Belousov ordered an inspection of drone units’ manning and equipment and requested proposals for establishing regular drone units within military formations. However, this response has failed to satisfy Russian ultranationalist military bloggers, who criticized the misuse of technical specialists in infantry assaults.
The military bloggers expressed skepticism towards a Kremlin-affiliated blogger’s report on the investigation, which downplayed command responsibility and suggested the operators might have been at fault for using mobile devices. Critics argue that this aligns with recent efforts to ban personal devices on the frontlines and centralize control over information. They also point to a pattern of misusing specialized personnel, including Spetsnaz officers, aerospace engineers, and even disabled servicemen, in infantry-led assaults.
As Russia faces these internal challenges, plans for a significant increase in defense spending have emerged. According to Bloomberg, the proposed budget for 2025 would allocate 13.2 trillion rubles ($142.2 billion) to defense, up from 10.4 trillion rubles ($112 billion) in 2024. This represents about 6.2 percent of Russia’s annual GDP, far exceeding NATO’s 2% target and indicating a substantial commitment to military expenditure.
In contrast, social spending for 2024 is set at 7.7 trillion rubles ($87 billion). Despite the increased military spending, Russia faces economic challenges including labor shortages and competition between military and business sectors for recruits. Economists predict a slowdown in GDP growth, potentially dropping to 0.5% – 1.5% in 2025, as the effects of high interest rates and reduced state subsidies impact key economic sectors.
Russia’s Allies
In a significant development, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky has alleged that Russia is utilizing Chinese satellites to photograph Ukrainian nuclear plants, potentially in preparation for future attacks. This claim underscores growing concerns about China’s role in supporting Russia’s war efforts in Ukraine, despite Beijing’s assertions of neutrality in the conflict.
According to Ukrainian officials, China is supplying approximately 60% of foreign components found in Russian weapons used against Ukraine. Vladyslav Vlasiuk, an adviser to Ukraine’s President’s Office, highlighted that crucial parts for surveillance systems, drones, and missiles also originate from countries including the United States, Netherlands, Japan, and Switzerland. President Zelensky noted that a single Russian missile attack on Kyiv contained an estimated 1,500 foreign components per missile.
Further evidence of Chinese involvement has emerged with the sighting of Russian troops in Ukraine posing with Chinese-made ZFB-05 Xinxing “Tiger” armored personnel carriers. These vehicles, which have been modified for battlefield use with anti-drone protection and camouflage, are also reportedly being used by Chechen “Akhmat” units and Moscow’s metro security. While China widely exports these vehicles to various countries, their presence in the conflict zone contradicts Beijing’s claims of not providing military assistance to Russia for the war in Ukraine.
The United States had previously warned about China providing geospatial intelligence to Russia. President Zelensky’s recent statement adds weight to these concerns, as he specified that Russian forces are using Chinese satellites to photograph open distribution devices at nuclear power plants and transmission substations crucial for the safe operation of Ukraine’s nuclear energy system.
Ukraine currently operates three nuclear plants on its territory: Rivne, Khmelnytskyi, and Pivdennoukrainsk. The Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant, Europe’s largest, has been under Russian occupation since March 2022, with reports suggesting that Russian forces are using the facility to deploy military personnel and store ammunition. Ukrainian authorities have informed international partners and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) about these threats to nuclear safety.
Meanwhile, Russia and China are conducting joint naval exercises in the Sea of Okhotsk, further demonstrating the strengthening ties between the two nations. Despite Western sanctions aimed at curbing Russia’s military capabilities, reports indicate that Russia continues to acquire banned items such as microchips through third countries.
These developments collectively point to China’s ongoing support for Russia’s war effort, raising questions about the extent of Beijing’s involvement and its implications for the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
