Summary of the Day:
Russian forces secured minor territorial advances near Kreminna, Pokrovsk, and Kurakhove, while suffering staggering losses – approximately 80,000 casualties, 200 tanks, and 650 armored vehicles during September-October 2024. Ukrainian forces successfully counterattacked, regaining positions near Siversk and Pokrovsk, demonstrating their continued defensive capabilities despite Russian pressure.
Ukraine conducted a significant strike against Russian military infrastructure, targeting the Aleksin Chemical Plant in Tula Oblast with drone attacks. The US announced plans to strengthen Ukraine’s combat effectiveness by deploying defense contractors to maintain critical weapons systems, including F-16 fighters, Bradley vehicles, and air defense systems.
Ukraine’s Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha warned that Russia’s artillery shell production could exceed combined EU production by 30% in 2025 without additional sanctions. This development comes as Russia considers merging its three largest oil companies to secure better energy deals with non-Western states, potentially increasing its war funding capabilities. Russia’s military industrial challenges were further highlighted by the arrest of a former Defense Ministry construction official for fraud related to military contracts.
Picture of the Day:
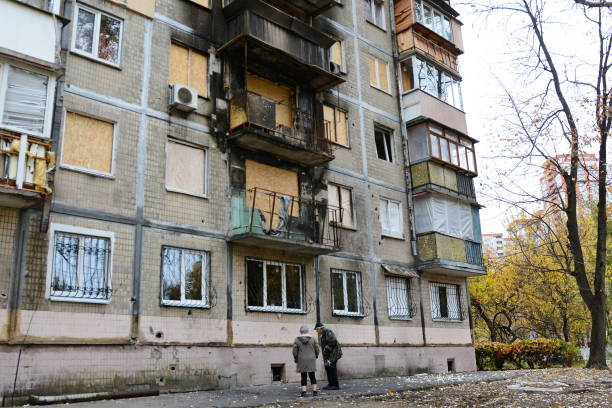 Local residents seen near a damaged residential building with traces of fire after a Russian drone attack on Kyiv. Russia continues to attack Ukrainian cities, particularly the capital Kyiv, with dozens of kamikaze drones every day. (Aleksandr Gusev/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images)
Local residents seen near a damaged residential building with traces of fire after a Russian drone attack on Kyiv. Russia continues to attack Ukrainian cities, particularly the capital Kyiv, with dozens of kamikaze drones every day. (Aleksandr Gusev/SOPA Images/LightRocket via Getty Images)
Beyond Ukraine – The March Towards World War
The unprecedented military alliance between Russia and North Korea marks a dangerous escalation that threatens global stability beyond Ukraine’s borders. North Korea’s deployment of combat troops and provision of ballistic missiles not only intensifies the Ukraine conflict but also undermines the international nuclear non-proliferation system, especially with Russia’s declaration that North Korean denuclearization is “off the table.” This collaboration between a UN Security Council permanent member and a sanctioned nuclear state violates multiple UN resolutions and creates a concerning precedent that destabilizes both European and Indo-Pacific regions. The partnership signals a significant shift in global power dynamics, potentially encouraging other nations to disregard international law and nuclear containment agreements, raising the risk of wider international conflicts and nuclear proliferation.
The Path to Peace
Following President-elect Trump’s victory and a 25-minute phone call with President Zelenskyy on November 6 (which reportedly included Elon Musk), Ukrainian Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha announced that teams from both countries will prepare a meeting between the leaders. Trump’s campaign promise to end the Ukraine war within 24 hours faces significant challenges, with political analysts warning that Russia would likely demand unacceptable concessions. The Telegraph reports Trump is considering a peace plan that would freeze the current front line, create a buffer zone monitored by British and European troops (specifically excluding U.S. forces), provide U.S. weapons to Ukraine, and require a 20-year delay in NATO membership considerations. This development follows Trump’s earlier statement to President Zelenskyy in New York about working out a solution “before January 20,” coming as Russian forces conduct a significant offensive on the front lines.
Trump’s potential strategy of pressuring both sides – by threatening to cut Ukraine’s military aid while simultaneously threatening Russia with economic sanctions – could lead to escalation rather than resolution. Ukrainian experts note that regardless of U.S. leadership, the basic strategy of controlled conflict and reduced foreign aid would continue, though Trump might pursue it more drastically. Bryan Lanza, Trump’s senior advisor, told the BBC that Ukraine needs to be “realistic” about its war aims, stating that “Crimea is gone,” though Trump’s transition team later distanced themselves from these comments, clarifying that Lanza was only a campaign contractor who doesn’t speak for Trump. While Russian Deputy Foreign Minister Sergei Ryabkov expressed willingness to “listen” to proposals while cautioning against expecting simple solutions, French President Macron has urged Trump that any diplomacy should include real concessions from Moscow. The proposed plan would have Poland, Germany, Britain, and France maintain the peace, with a Trump staffer stating, “We are not sending American men and women to uphold peace in Ukraine.”
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukraine’s Commander-in-Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi reported that the military situation is worsening, with Russia intensifying attacks particularly near Pokrovsk and Kurakhove. Russia maintains a numerical advantage and may be preparing to deploy North Korean soldiers alongside its forces. Ukraine has lost significant territory since August, including areas in southern Donetsk Oblast and near the settlements of Toretsk and Chasiv Yar. Russian forces have also made gains near Kupiansk and in Russia’s Kursk Oblast, with Syrskyi describing this as “one of the most powerful” Russian offensives since the war began.
Russia suffered heavy losses during its intensified offensive operations in September and October 2024, while gaining limited territory. According to UK defense intelligence, Russian forces lost approximately 80,000 troops, nearly 200 tanks, and over 650 armored vehicles while capturing about 1,500 square kilometers of territory – an area smaller than a third of Delaware – including the settlements of Vuhledar and Selydove in Donetsk Oblast, while increasing operations near Kupyansk in Kharkiv Oblast and Kurakhove in Donetsk Oblast. The Russian casualty rate reached record highs during this period, with about 1,345 troops lost per day in October alone, while US Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin reports Russian forces are suffering about 1,200 casualties daily. In the Pokrovsk area alone since October 2023, they’ve lost equipment equivalent to five divisions. Putin acknowledged Russia’s labor shortage during a November 7 address, highlighting the challenge of maintaining both military recruitment and the civilian workforce while trying to avoid another involuntary mobilization. Russian military bloggers, who hold significant influence with the Kremlin, have become increasingly critical of high casualty rates and poor tactical decisions, with one former Storm-Z instructor highlighting that while proper assault training takes six months, command is treating soldiers as expendable “meat,” particularly in repeated small-group assault waves. The criticism intensified after specialized drone operators were reportedly sent on punitive assault missions resulting in their deaths, with bloggers focusing on the disproportionate losses compared to minimal territorial gains.
UK Defense Secretary John Healey reported that Russian forces are quickly adapting to new Ukrainian drone technology, developing countermeasures within about two months of their battlefield introduction. He emphasized that Ukraine needs to maintain rapid innovation and production to stay ahead of these Russian adaptations.
A new video has emerged showing Russian forces executing an unarmed, wounded Ukrainian soldier, according to Ukraine’s Ombudsman Dmytro Lubinets. This incident adds to 124 documented cases of Ukrainian POWs being executed by Russian forces during the war, with most cases occurring in Donetsk Oblast. Ukrainian prosecutors are investigating 49 cases of POW executions, including a recent incident involving six captured soldiers near Pokrovsk. Officials note that 80% of these executions occurred in 2024, marking a significant deterioration in the treatment of Ukrainian POWs since November 2023. The Prosecutor General’s Office is investigating these actions as war crimes under the Geneva Conventions.
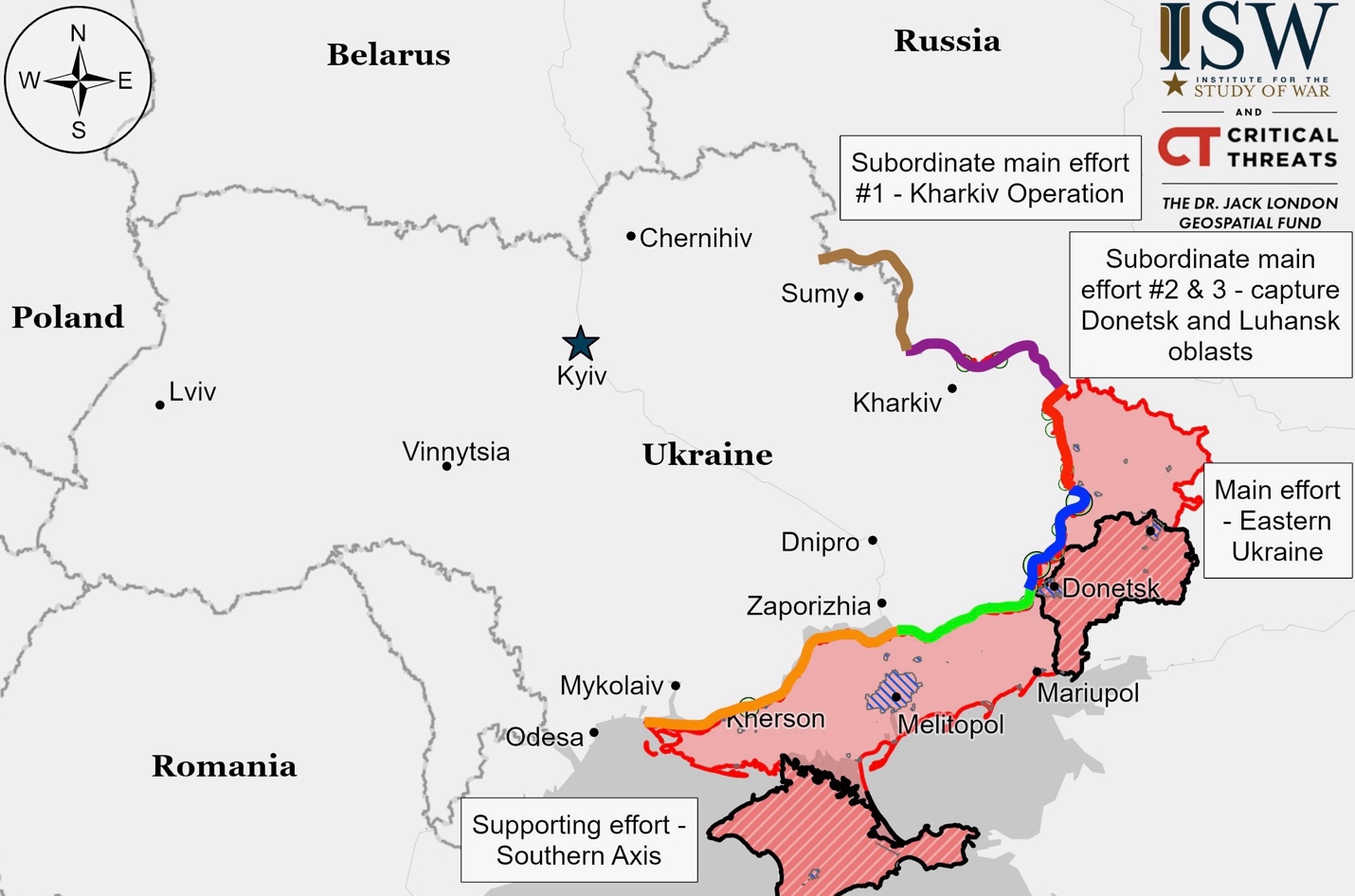
Ukrainian Operations in the Russian Federation – Initiative None
Fighting persisted in Ukraine’s salient in Kursk Oblast. Russian sources claim their forces advanced near Staraya Sorochina and retook Pogrebki and Orlovka, though these claims lack visual confirmation. Combat continued in several areas: near Darino, Nikolayevo-Darino, Leonidovo, Novoivanovka, Zeleny Shlyakh, Novaya Sorochina, Staraya Sorochina, Martynovka, and Plekhovo. Russian forces reportedly blocked a Ukrainian cross-border attack near Novy Put in Glushkovsky Raion.
Ukraine conducted drone strikes on Russia’s Aleksin Chemical Plant in Tula Oblast reportedly launching 13 drones. According to Ukraine’s Security Service, the successful strikes caused a fire and subsequent chemical explosion at the Rostec-owned facility, which produces ammunition and gunpowder for Russia’s military, resulting in orange smoke from burning gunpowder and forcing the plant’s evacuation. The attack also damaged a nearby power transmission line at the Aleksinskaya Thermal Power Plant. While Russian officials claim they intercepted all 50 drones launched across seven regions that day (with 28 reportedly shot down over Bryansk Oblast), they acknowledged drone debris damaged several houses in the area. In October, Ukrainian forces used drones to strike over 52,000 Russian targets, including artillery systems, radio equipment, and around 4,000 troops, according to Commander-in-Chief Syrskyi. This follows Ukraine’s strategy of using homemade drones to strike deep inside Russia, targeting military infrastructure, with recent successful drone operations including the destruction of major ammunition warehouses in Tver Oblast, which the UK Defense Ministry described as Russia’s largest ammunition loss of the war. Despite being outgunned, Ukraine is increasingly using drone technology to counter Russian forces.
Kharkiv Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces continued attacks north and northeast of Kharkiv City near Lyptsi and Vovchansk with no confirmed territorial changes. Ukrainian military spokesperson Lt. Col. Yevhenii Romanov reported that Russian forces are conducting small infantry assaults with air and artillery support near Vovchansk, notably without armored vehicles. Poor weather has significantly reduced both sides’ drone and artillery capabilities in the area.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Russian forces made slight advances near Kreminna, specifically in northeastern Terny, as confirmed by video footage. While Russian sources claimed additional advances southwest of Stelmakhivka and within northern Terny, these remain unconfirmed. Fighting continued across multiple locations: near Kucherivka, Kruhlyakivka, Kindrashivka, Kolisnykivka, Zahryzove, Lozove, Berestove, Hrekivka, Nevske, Terny, Torske, and Hryhorivka. A Ukrainian commander reported that Russian forces are conducting operations with excessive force while attempting to push Ukrainian forces from the east bank of the Oskil River, resulting in significant Russian losses.
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Siversk
Russian forces reportedly attacked near Siversk with fighting occurring around Bilohorivka, Ivano-Darivka, and Verkhnokamyanske. Ukrainian forces successfully reclaimed some previously lost positions in northern Bilohorivka. While a Russian military blogger claimed Russian advances near Ivano-Darivka, this has not been independently verified.
Chasiv Yar
Russian forces continued attacks near Chasiv Yar with fighting reported around Bondarne and Bila Hora. While Russian sources claimed advances near Hryhorivka, these claims remain unverified.
Toretsk
Russian forces continued attacks around Toretsk with fighting reported in multiple nearby locations including Dyliivka, Druzhba, Shcherbynivka, Petrivka, and Nelipivka. No frontline changes were confirmed.
Pokrovsk
Recent fighting near Pokrovsk saw both sides make advances. Ukrainian forces regained positions north of Novohrodivka, while Russian forces advanced along the E-50 highway near Selydove. Combat occurred in multiple locations including Promin, Myrolyubivka, Novotoretske, Lysivka, Krutyi Yar, Vyshneve, Petrivka, and Chumatske.
Kurakhove
Russian forces advanced to central Sontsivka near Kurakhove, with fighting continuing in multiple locations around the area including Illinka, Novoselydivka, Novodmytrivka, Berestky, Voznesenka, Maksymilyanivka, and Dalne. While Russian sources claimed additional advances near Voznesenka and other locations, these remain unverified. A Russian source noted slow progress toward Kurakhove, attributing this to the need for air or artillery support before attacking Ukrainian fortifications.
Southwest of Donetsk City
Russian forces claimed advances near Vuhledar, particularly near Maksymivka and Bohoyavlenka, though these claims remain unverified. Fighting occurred in multiple locations including Yelyzavetivka, Katerynivka, Antonivka, Shakhtarske, Yasna Polyana, and Trudove.
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia-Donetsk Border Area
No combat operations were reported along the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border.
Zaporizhia Line
Ongoing fighting continued near Novoandriivka and Robotyne in western Zaporizhia Oblast, with no confirmed frontline changes. Russian forces have intensified air strikes in the region, particularly targeting Mala Tokmachka with over 100 munitions since November 1.
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Fighting continued along the eastern bank of Kherson Oblast with no frontline changes. Ukrainian forces reportedly launched 20 rockets at occupied Radensk, according to local Russian-appointed official Vladimir Saldo.
Ukraine News
Russia launched a widespread drone attack against Ukraine, sending 51 drones primarily from regions in southern Russia. Ukrainian forces successfully intercepted 32 drones, while 18 others were disabled through electronic warfare. The strikes affected multiple regions, with Odesa City suffering damage to its City Council building and a warehouse fire. Additional attacks included a ballistic missile launch toward Mykolaiv Oblast and a guided missile strike on Kharkiv City, which damaged civilian infrastructure.
Vantiq’s $500,000 AI software donation marks a significant step toward Ukraine’s post-war rebuilding efforts, enabling the development of “hyper-modern” smart cities across the country. The system, which will be implemented in over 100 industrial parks serving 2.5 million citizens, will help Ukraine optimize resource allocation and attract foreign investment for reconstruction. Working with Ukrainian partners Economy of Trust and Mayor’s Club, this initiative could catalyze broader U.S. tech industry involvement in Ukraine’s recovery. The technology’s ability to monitor infrastructure, analyze data from multiple sources, and provide real-time management tools positions Ukraine to emerge from the war with modernized, efficient urban centers ready for sustainable development.
Innocent Victims Of War
The casualty count of civilians in the past 24 hours: (Russian War Crimes)
DEATHS: 1 INJURIES: 13
Russian forces launched a major drone attack on Odesa and surrounding areas in southern Ukraine killing one person and injuring 13, including two children aged 4 and 16. Ukraine’s Air Force reported that Russia deployed 51 drones in the assault, which damaged apartment buildings, homes, warehouses, and vehicles in the region. Local authorities are still assessing the full extent of the damage.
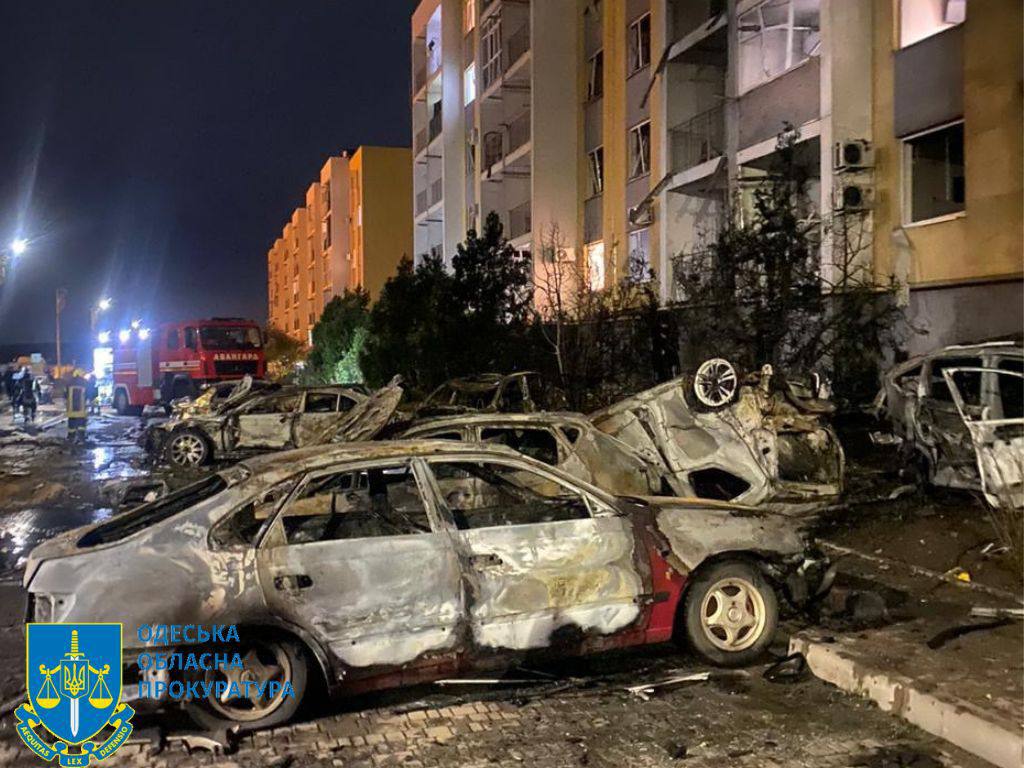 A photo capturing the aftermath of an overnight Russian drone attack on Odesa. (Odesa Oblast Prosecutor’s Office/Telegram)
A photo capturing the aftermath of an overnight Russian drone attack on Odesa. (Odesa Oblast Prosecutor’s Office/Telegram)
Ukrainian Mobilization and Industrial Defense Base
President Zelensky announced that Ukraine has produced its first 100 missiles as part of its domestic weapons program, which began after Russia’s 2022 invasion. While specific details weren’t revealed, this follows Ukraine’s successful test of a domestically-made ballistic missile in August, possibly the Hrim-2. This development is crucial for Ukraine’s defense strategy since Western allies restrict the use of their weapons for deep strikes into Russia. Ukraine is also expanding its domestic production of artillery, ammunition, and various types of drones for battlefield operations.
Ukraine’s Allies
Ukraine’s defense capabilities will receive a significant boost with the US decision to send technical experts to maintain critical weapons systems directly in Ukraine. This direct support will ensure Ukraine’s F-16 fighters, Bradley fighting vehicles, and air defense systems remain combat-ready with minimal downtime – addressing a crucial maintenance challenge that has previously limited their effectiveness and enabling Ukraine to more efficiently utilize the $60 billion worth of military aid it has received, including HIMARS rocket launchers and tanks. The addition of 500 new interceptors for Patriot and NASAMS systems, arriving within weeks, will substantially strengthen Ukraine’s ability to protect its cities and infrastructure from Russian missile and drone attacks through 2024. This comprehensive support package addresses both Ukraine’s offensive capabilities through functioning F-16s and Bradleys, while bolstering its defensive shield against Russian aerial threats. However, the timing of these deliveries is crucial, as delays could jeopardize Ukraine’s defense capabilities if a new U.S. administration changes policy on military support in 2025, with the $7 billion remaining in military aid representing vital resources for Ukraine’s continued ability to defend itself.
During his visit to Kyiv, EU diplomat Josep Borrell announced a significant boost to Ukraine’s defense efforts with a planned 15th sanctions package, aimed at cutting off Russia’s access to crucial weapon components. The new restrictions will help protect Ukrainian cities from Russian attacks by targeting the foreign-made parts essential for Russian weapons, particularly the Shahed drones that launched 2,000 strikes against Ukraine in October alone, as Moscow currently relies on 170,000 foreign components from shadow networks supported by China, Iran, and North Korea. Borrell pledged “unwavering” European support to counter Russia’s intensifying drone attacks and China’s increasing military assistance to Moscow, while advocating removing restrictions on Ukraine’s ability to strike deep inside Russia with Western-provided long-range weapons, which could help counter Russian aggression more effectively. This support gains added importance as Ukraine faces potential changes in U.S. aid under President-elect Trump, with Borrell announcing that EU defense ministers will meet next week specifically to discuss boosting both military and diplomatic assistance to Ukraine at this “critical hour,” demonstrating Europe’s commitment to strengthening Ukraine’s defense capabilities.
Russia News
Russia’s potential merger of its three major oil companies signals a critical effort to fund its war in Ukraine by boosting energy revenues. This consolidation, creating the world’s second-largest oil producer, aims to counter declining energy profits that have strained Russia’s military budget since its 2022 invasion. The merger would strengthen Russia’s bargaining power with India and China for better oil prices, potentially providing crucial funding for its increasing defense spending despite Western sanctions. The move reflects Russia’s urgent need to secure alternative revenue streams to sustain its military operations, especially after failing to reach key energy deals like the Power of Siberia-2 pipeline with China in early 2024.
The arrest of Alexander Molodchenko, former head of Russia’s Defense Ministry Construction Directorate, highlights ongoing issues in Russia’s military infrastructure development. This fraud case, involving misrepresented military construction contracts, suggests potential weaknesses in Russia’s military readiness and infrastructure support for its war effort. The timing of his dismissal in September 2024 and subsequent arrest points to possible broader problems in Russia’s military construction and development programs during a critical period of the war in Ukraine.
Russian War Losses (Today/Total)
| Troops +1350
708890 |
Tanks +11
9249 |
Artillery +31
20280 |
Arm. VEH +29
18726 |
Aircraft
369 |
Heli
329 |
Ships
28 |
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine’s Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha warned that Russia could outproduce the entire European Union in artillery shell manufacturing by 30% in 2025 without stronger sanctions, and its production will already exceed the EU’s combined output by 30% in 2024. This comes amid Ukraine’s ongoing ammunition shortage, as the EU failed to meet its goal of producing 1 million shells between March 2023-2024, and U.S. aid has been delayed. While several countries support a Czech initiative to procure 800,000 shells for Ukraine, and the EU has allocated 500 million euros to increase production, Ukraine still heavily depends on Western supplies. Although Ukraine has begun domestic production of some ammunition types, NATO-standard 155mm artillery rounds won’t be produced locally until late 2024. Sybiha noted that Russia is funding this production through profits from its “shadow fleet,” which sells oil illegally by evading international price caps and sanctions, and urged the EU to implement tougher sanctions to cut off this funding source and limit Russia’s industrial capacity.
Source Material
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
