Summary of the day: Ukrainian forces carried out a large-scale drone attack on multiple Russian airbases overnight between April 4th and 5th, signaling a bold offensive maneuver. As the conflict intensifies, Russia’s military actions in Ukraine are leading to increased losses, though efforts to mitigate these are reportedly in place. Meanwhile, Ukraine’s Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal emphasized the formation of new units and the critical need for Western military support, particularly as Russian strikes have heavily damaged Ukraine’s power infrastructure. On a strategic level, Russian advances near Avdiivka and the use of hybrid warfare tactics, including cyber-attacks and the controversial use of chemical weapons, underline the conflict’s evolving complexity and brutality.
What Can I Do To Help Ukraine? This is a question I receive all the time. We at Transform Ukraine are building longer-term housing for internally displaced Ukrainians. Visit Rebuild Ukraine for how you can assist in housing a Ukrainian family displaced by the war.
Beyond Ukraine – March Towards World War III
Amidst concerns of Kremlin-led destabilization efforts in Moldova, a drone struck a military unit in Transnistria, a pro-Russian region of Moldova, targeting a radar station in Ribnita. The attack caused minor damage but no casualties. Although Transnistrian officials hinted at Ukrainian involvement, Ukraine denied any connection. This incident adds to regional tensions, potentially exploited by Russia to blame Ukraine and undermine Moldova’s integration with the EU. Moldova’s Bureau of Reintegration condemned the attack as a provocation, highlighting restricted access for investigation. This event follows a similar drone attack on March 17. Transnistria, bordering Ukraine’s Odesa Oblast, remains internationally recognized as part of Moldova, with Russian troops stationed there since the 1990s.
Russia is accused of launching thousands of cyber-attacks on the rail transport systems of Czechia and other European countries, aiming to undermine NATO members’ logistics since the invasion of Ukraine began. Czech Transport Minister Martin Kupka highlighted a concerted effort to disrupt Czechia’s national railway and damage EU infrastructure, though he assured of Czechia’s defensive capabilities. The European Union Agency for Cyber Security (ENISA) confirmed an increase in cyberattacks against transport sectors across Europe, including railways, air, and maritime transport, attributing these to pro-Russian hacker groups.
Dmitry Medvedev, Russian Security Council Deputy Chair, has been vocal in bolstering Kremlin-led information campaigns aimed at deterring Western involvement in Ukraine. On April 4, he suggested rewarding Russian soldiers for targeting NATO personnel in Ukraine, a statement he reiterated in English on social media the following day, implying NATO forces in Ukraine would be legitimate targets. This strategy, particularly Medvedev’s use of English, targets Western audiences, intending to intimidate and influence Western policy decisions related to supporting Ukraine. The Kremlin is likely to persist with such escalatory rhetoric as part of its broader information warfare tactics.
Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko proposed legislation to suspend Belarus’s participation in the Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE) Treaty, not withdrawing but pausing adherence to its terms. The CFE Treaty, signed in 1990 by NATO and Warsaw Pact members and ratified in 1992, aimed to establish equal caps on key military equipment to prevent dominance by any one side post-Cold War. Belarus’s suspension could signal intentions for military expansion or facilitate the deployment of larger Russian forces within its territory.
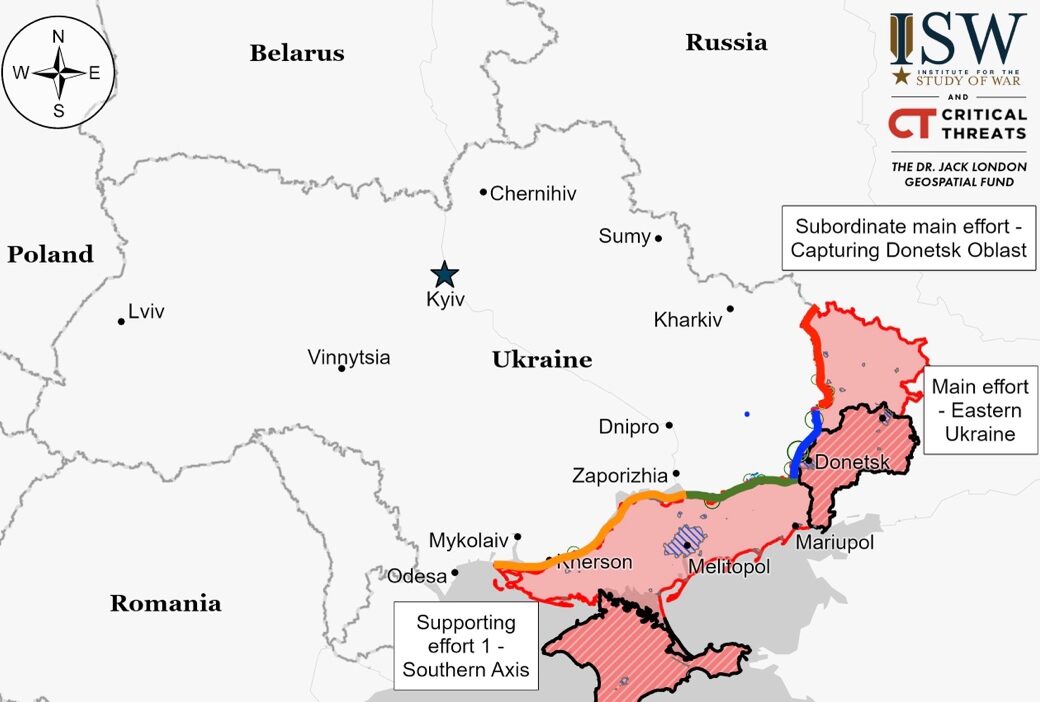
Situation On The Land, Sea, and Air in Ukraine
Ukrainian forces executed a major drone strike on four Russian airbases on the night of April 4th to 5th, targeting facilities including the Morozovsk airfield, resulting in substantial damage to Russian aircraft, notably three strategic bombers at Morozovsk where six Russian military aircraft were destroyed and another eight were heavily damaged, affecting about 20 Russian servicemen. These coordinated attacks, which also hit Russia’s Rostov region, and other strategic locations such as Belgorod, Kursk, Saratov, and Krasnodar, mark a significant enhancement in Ukraine’s ability to target and degrade Russian military infrastructure and aerospace capabilities. Such capabilities are critical in the broader conflict dynamics, given these airbases have been key in launching attacks against Ukraine. Despite Russian claims of downing 53 drones and mitigating damage, the operations underline Ukraine’s strategic approach to undermine the support for Russia’s military efforts and the proactive efforts to challenge Russian military operations, as evidenced by significant explosions in the cities of Yeysk and Engels.
Russia has increased its offensive operations in Ukraine, leading to higher manpower and equipment losses. However, the Russian Ministry of Defense is effectively managing these setbacks, shifting from infantry-led assaults to more mechanized attacks involving armored vehicles, indicating a strategic adjustment. Russia’s recruitment efforts, reportedly adding around 30,000 personnel per month, alongside its ability to sustain vehicle losses through reactivation from storage and production, suggest resilience in replenishing its forces. This change in tactics reflects confidence in maintaining the offensive with available resources, despite the continued consumption of manpower and materiel, as Russia prepares for continued operations into the summer of 2024.
Ukrainian officials report a significant increase in Russian forces using chemical weapons in Ukraine, with 371 instances noted last month and a total of 1,412 cases from February 2023 to March 2024. These attacks often involve munitions from K-51 and RG-VO grenade launchers containing banned chemical agents. This marks a concerning trend of Russia’s use of prohibited chemical substances in combat, despite being a signatory to the Chemical Weapons Convention.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative Russia
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative Russia
Fighting persisted along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line in Ukraine, with reports of Russian forces making advances towards Terny, west of Kreminna. The conflict involved positional battles near several locations, including Synkivka northeast of Kupyansk and Bilohorivka south of Kreminna. Russian forces are gearing up for intensified offensives near Kupyansk and Lyman
Russian forces were reported to make advances northeast of Bakhmut, particularly north of Vesele, with some milbloggers stating a two-kilometer advance by Russian forces supported by armored vehicles. However, these claims lack visual confirmation. The Ukrainian General Staff noted unsuccessful Russian attacks near Spirne, northeast of Bakhmut. Ukrainian observer Kostyantyn Mashovets highlighted advancements by Russian forces near Vyimka and Spirne.
Russian forces are intensifying their military efforts to capture Chasiv Yar, west of Bakhmut, with claims of advances near the town’s eastern outskirts and the Siversky-Donets Donbas Canal. Milbloggers reported a significant mechanized assault on Chasiv Yar, with Ukrainian forces reportedly destroying many of the attacking Russian armored vehicles. Despite these claims, there’s no visual confirmation of Russian control over the reported areas, and Ukrainian forces deny Russian breaches in Chasiv Yar. Fighting has become positional with both sides engaging in assaults and counterassaults. Russian efforts also include aviation support and attempts to bypass the Siversky-Donets Donbas Canal, aiming for strategic control over the area. The situation in nearby Ivanivske remains contested, with Russian control varying. Ukrainian eastern command spokesperson, Andrii Zadubinnyi, refuted Russian claims of their troops entering Chasiv Yar’s suburbs, emphasizing ongoing fighting and denying Russian presence. Despite Russian proxies’ assertions, Zadubinnyi emphasized ongoing fighting but denied Russian presence. The Institute for the Study of War noted a Russian assault towards Chasiv Yar’s outskirts on April 4, with Ukrainian forces halting further advances. President Zelensky mentioned stabilization of positions amid ammunition shortages, countering Moscow’s anticipated success. Zelensky earlier speculated a possible major Russian offensive by May’s end or June.
In the Bakhmut area, Ukrainian forces repelled Russian attacks near Ivanivske and in the southwest near Andriivka, Klishchiivka, and Zelenopillya. Russian forces were active near Klishchiivka, indicating ongoing clashes without significant changes in front line positions.
Russian troops achieved partial advances in Avdiivka through a mechanized infantry assault, particularly making progress in southern Semenivka. While claims of advances near Berdychi exist, there’s no confirmed visual evidence. Ukrainian forces managed to repel a Russian assault near Berdychi. Ongoing clashes continue around Avdiivka, including in areas west and southwest of the city. Russian forces reportedly face challenges in maintaining their positions in Semenivka and Berdychi, attributed to Ukrainian drone superiority.
Around Donetsk City, ongoing skirmishes took place without shifts in the frontline. The clashes occurred west of Donetsk near Krasnohorivka and Heorhiivka, and to the southwest near Novomykhailivka and Kostyantynivka.
In the Donetsk-Zaporizhia border region there were no shifts in the frontline despite ongoing conflicts. Russian attempts to attack near Velyka Novosilka and the surrounding southern areas were unsuccessful.
In western Zaporizhia Oblast, skirmishes took place without any changes to the frontline, particularly northwest of Verbove, east of Robotyne.
There was ongoing positional fighting in the eastern part of Kherson Oblast, specifically near Krynky, without any reported changes to the frontline.
Ukrainian Victims Of War
In the past 24 hours, Russian attacks on civilian targets resulted in the death of 10 people and the injuries to 39 others:
- Russian forces launched an attack on Kharkiv on April 6, resulting in seven fatalities and 11 injuries. The assault damaged or destroyed multiple residential buildings, dormitories, administrative structures, and vehicles. Russian troops employed a “double tap” tactic, targeting first responders. The second strike occurred within 30 minutes of the initial attack, utilizing Soviet-era S-300 missiles. Additionally, a missile hit a store, igniting nearby vehicles. Earlier explosions were reported near a residential building.
- Three people have died, and 19 others were injured in Russia’s missile strikes on Zaporizhzhia. Among the injured are two journalists and a nine-year-old boy. Four victims are in critical condition. The attack damaged three apartment buildings, around 10 houses, stores, and a dormitory.
- Three civilians were injured in Rivne Oblast when their tractor detonated a mine. The incident occurred near the Belarusian border after the driver disregarded warning signs.
- Russian forces launched attacks on Kherson and Beryslav in Kherson Oblast on April 5, injuring six people. In Kherson, a 60-year-old man and a 54-year-old woman were hospitalized with moderate injuries, while an 81-year-old woman received medical assistance on-site. In Beryslav, three individuals, including an 84-year-old woman and two men aged 59 and 56, sustained blast and shrapnel wounds to their limbs and were hospitalized.
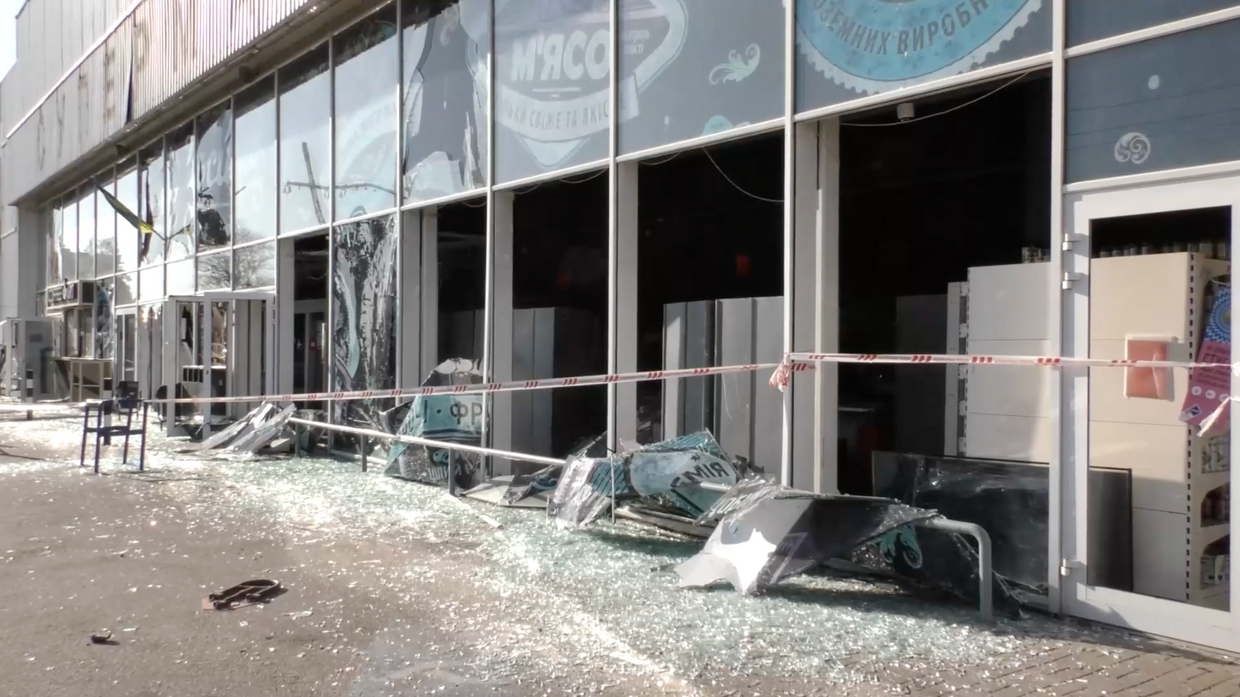 A store damaged by a Russian missile strike on Zaporizhzhia
A store damaged by a Russian missile strike on Zaporizhzhia
Ukraine News
During the overnight and daytime of April 4 to 5, Russian forces conducted missile and drone attacks on Ukraine, deploying air defense missiles, Iskander-M missiles from Belgorod Oblast, and Shahed drones from Crimea. Ukrainian forces successfully intercepted all 13 Shahed drones. Pokrovsk in Donetsk Oblast was hit by two S-300 missiles, causing damage, including to energy infrastructure in Odesa Oblast. Additionally, Zaporizhzhia City experienced two missile strikes, targeting a residential building initially and again when emergency services arrived, a tactic previously employed in Kharkiv and Odesa. These attacks damaged energy infrastructure in Odesa Oblast, as reported by Ukraine’s energy operator Ukrenergo, but no blackouts occurred. Russia’s intensified strikes on Ukraine’s critical infrastructure include large-scale attacks on energy facilities, with a recent drone attack in southern Ukraine damaging Ukrenergo’s high-voltage substation.
Russian missile and drone attacks have severely impacted Ukraine’s energy infrastructure, damaging or disrupting about 80% of the country’s thermal power plant output. These strikes, particularly intensified since March 22, have targeted critical energy facilities, including hydroelectric plants, crippling over six gigawatts of power generation. This concerted effort to undermine Ukraine’s energy grid aims to weaken Ukraine’s defense capabilities and long-term war effort. The situation is exacerbated by delays in US security assistance, further compromising Ukraine’s air defense and energy stability.
The Security Service of Ukraine (SBU) arrested two foreigners in Odesa accused of working for Russia’s Federal Security Service (FSB) and planning a missile strike on Ukraine’s Armed Forces regional headquarters. The suspects, from one of the Southern Caucasus countries, allegedly conducted reconnaissance, gathering information on Ukrainian troops and infrastructure. The SBU stated they intended targeted strikes on military positions. The suspects also allegedly tracked air defense locations and shared intelligence with the FSB. They face up to 12 years in prison if convicted. The suspects aimed for key roles in Odesa’s occupation administration if Russian forces seized the city.
Doctors Without Borders reported that their office in Pokrovsk, Donetsk Oblast, was bombed and destroyed amid ongoing Russian attacks in conflict zones. The attack caused injuries to nearby residents but no harm to the organization’s staff. This incident underscores the dangers faced by humanitarian organizations and civilians in war zones.
President Volodymyr Zelensky visited Chernihiv Oblast to inspect fortification progress and meet local officials amid concerns about potential Russian offensives. Criticized for slow progress, Ukraine aims to fortify 2,000 kilometers of defensive lines. In Chernihiv, Zelensky reviewed construction of three defense lines. Officials highlighted barriers and strongholds along the Russia-Belarus border. Zelensky also discussed security and socio-economic issues, particularly post-Russian occupation challenges. Despite liberation, ongoing Russian strikes cause civilian casualties and infrastructure damage. Zelensky pledged accelerated demining efforts and allocated $31 million for economic development. Soldiers and civilians involved in Chernihiv’s defense two years ago were honored.
Ukrainian authorities have mandated the evacuation of children from 52 settlements in Sumy Oblast due to escalated Russian shelling. The move aims to relocate 297 children and their families or guardians to safer regions amid ongoing attacks. Russian forces targeted six border areas and settlements in Sumy Oblast, resulting in at least 83 explosions, with Bilopillia experiencing the most attacks. President Zelensky recently visited the region to inspect fortifications, highlighting its vulnerability to potential offensives from Russia, as observed in 2022.
Polish farmers, protesting Ukrainian agricultural imports, temporarily lifted their blockade at the Hrebenne-Rava-Ruska crossing, Ukraine’s Border Guard Service said. The blockade, initiated in February, strained Kyiv-Warsaw relations, leading to grain spills and trade disruptions. Prime Minister Shmyhal and his Polish counterpart seek solutions, including trade verification systems.
Ukrainian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Ukraine’s Armed Forces will call up citizens aged 25 for military service following President Zelensky’s approval of a law lowering the minimum age. The new law allows those aged 25 to join the military register. Previously, the minimum age was 27. Men aged 18-25 with prior military experience can also be mobilized. The government aims to bolster troop numbers in 2024 by updating mobilization laws. A new draft law is being considered after the withdrawal of the initial version, with over 4,000 amendments submitted. The draft includes provisions for basic military training and allows recruits to choose their service year before turning 24.
Ukrainian Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal has announced the formation of new military brigades, emphasizing the urgent need for more Western military aid to fully equip these units. Despite staffing these brigades, Ukraine awaits delivery of essential military gear, weapons, and ammunition from Western allies. Shmyhal reassured that with regular mobilization efforts, including lowering the mobilization age and rotating frontline personnel, Ukraine can manage its defense needs. However, he stressed the importance of continued Western support to sustain Ukraine’s military capabilities in the face of ongoing conflict.
Ukraine’s Allies
Japan will ban the export of 164 goods to Russia, including automobile engine oil and optical equipment, starting April 17, as part of sanctions against Russia due to the Ukraine conflict, Jiji Press reported. The ban targets items that could strengthen Russia’s industrial base. Japanese Trade Minister Ken Saito stated efforts would be made to enforce the ban in cooperation with the international community. The list includes technical and industrial items, as well as yachts. Additionally, imports of Russian non-industrial diamonds used in jewelry will be banned from May 10. Japan, part of the G7, has supported Ukraine with non-military aid exceeding $12 billion since the conflict’s onset.
Lithuania will supply 3,000 drones to Ukraine and allocate 15 million euros ($16 million) for rehabilitating wounded soldiers, Ukraine’s Prime Minister Denys Shmyhal announced during his visit to Vilnius. Additionally, Lithuania will contribute 5 million euros to education and 12 million euros for veteran support and infrastructure rebuilding. Lithuania previously allocated 35 million euros for artillery shells for Ukraine. Vilnius remains a steadfast supporter against Russian aggression, with high defense contributions relative to GDP. Latvia also pledged drone support worth 1 million euros during Shmyhal’s visit to Riga on April 4.
Portugal’s new government, led by Prime Minister Luis Montenegro, expressed full support for Ukraine’s EU membership bid, marking a shift from the previous administration’s stance. Former Prime Minister Antonio Costa had backed EU accession talks with Kyiv but emphasized the need for extensive reforms within the EU and integration of Western Balkan countries. Foreign Minister Paulo Rangel highlighted Montenegro’s clear support for EU enlargement, addressing past hesitations. Ukraine applied for EU membership in 2022, and discussions on accession began in December 2023.
The U.S. Treasury’s OFAC imposed new sanctions on Oceanlink Maritime DMCC for shipping material to the Iranian military, aiming to disrupt Iran’s support for Russia’s aggression against Ukraine. Tehran and Moscow have strengthened military ties since Ukraine’s invasion. Iran provided drones and allegedly ballistic missiles to Russia. Oceanlink Maritime DMCC operates vessels shipping commodities for Iran, including military goods. Treasury official Brian Nelson emphasized the U.S. commitment to targeting illicit funding supporting Iran’s destabilizing activities.
French dairy company Danone dissolved its last subsidiary in Belarus, DanoneBel, as reported by independent Belarusian media outlet Plant B on April 4. Danone had been operating in Belarus since 2008 and previously divested its stakes in two Belarusian factories. The move follows a trend of Western companies leaving Belarus and scaling back operations in Russia in response to the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. Danone initially intended to remain in Russia but later pursued a sale of its Russian operations. The company’s Russian assets lost management control to the Russian government in July 2023. Danone announced on March 22 that it obtained regulatory approvals from Russia to dispose of its business to Vamin R company, with the closing expected soon. The company reported a total loss in its accounts of $1.3 billion.
Life in Russian-Occupied Ukraine
The Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine lost a critical power line due to Russian shelling, risking essential cooling and safety functions. Energoatom, the Ukrainian state company, reported that the disconnection of the 330-kilovolt line puts the plant close to a blackout, threatening safe operations. The International Atomic Energy Agency confirmed the disconnection and cited nearby military activities, including artillery fire. With the plant under Russian control and not generating power since September 2022, any further power disruptions could lead to an emergency. Currently, five power units are in a cold shutdown state, and one is in a hot shutdown mode for operational necessities.
Russian President Vladimir Putin revealed plans to open two youth centers in occupied Zaporizhia and Kherson oblasts to immerse Ukrainian youth in Russian culture and historical perspectives. Praising the efforts of the “Istoki” youth center in Sevastopol, Crimea, Putin highlighted the center’s role in educating Ukrainian children as part of Russia’s cultural legacy. Over 2,000 children have participated in the center’s programs, with an expected 3,000 more to attend this summer to explore their “Russian heritage.”
Russian opposition media report on the ongoing forced deportation of Ukrainian children to Russia, with efforts underway by Ukraine to bring them back. Investigations revealed that 285 Ukrainian minors have been forcibly integrated into Russia’s orphanage system, with Ukrainian children being placed across 15 Russian regions. More than 450 Ukrainian children are likely adopted by Russian families since the 2022 invasion. Some siblings have been separated, and older children placed in cadet schools to pledge loyalty to Russia. Ukraine prioritizes the repatriation of these children, with recent successes in returning seven children and their families from occupied territories back to areas under Ukrainian control.
Russia News
The General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces reported 860 casualties inflicted on Russian forces in the past day.
Turkey’s trade with Russia is declining due to expanding Western sanctions, Bloomberg reported. Turkish machinery exporters are expected to suffer a $1 billion revenue drop in 2024, a third of last year’s sales to Russia, according to the Machinery Exporters’ Association chairperson. Exports to Russia fell by 33.7% in the first quarter of 2024 compared to the previous year. India and China, key trade partners for Russia, are also reducing business ties due to sanctions pressure.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
Russian sources indicate that the country’s military recruitment and force generation efforts are causing societal strain and impacting military effectiveness. An insider highlighted the need for the Russian Ministry of Defense to solve several issues before the summer 2024 offensive, including building manpower reserves, motivating volunteers, providing rotations, and improving pay for those mobilized in fall 2022. A Russian milblogger pointed out the necessity to address disparities in treatment and compensation among military personnel types, noting the challenge in formulating plans due to the military command’s reliance on overly positive, likely inaccurate reports. Concerns were also raised about Russia’s capacity to train an increased number of recruits.
Russia’s defense industry is actively ramping up to supply its military operations in Ukraine. The United Aircraft Corporation, a Rostec subsidiary, announced the delivery of Su-34 bombers from its Novosibirsk plant, which is also looking to hire over 1,000 new workers to boost production. Similarly, Kurganmashzavod has supplied the military with BMP-3 infantry fighting vehicles. Additionally, the Simbirsk Design Bureau is producing 300 Piranha-10 drones daily at its facilities in Ulyanovsk, showcasing significant increases in military manufacturing to meet the demands of the conflict in Ukraine.
Russia is retrofitting its tanks and armored vehicles with electronic warfare (EW) systems to fend off Ukrainian drone attacks. Uralvagonzavod, the tank manufacturer, is implementing a new standard EW system for this purpose. Images have circulated of Russian T-72 and T-90 tanks equipped with these systems, including additional diesel generators for power. However, this adaptation reportedly compromises the tanks’ visibility and hampers their machine gun usage. This modification underscores Russia’s prioritization of countering the significant threat posed by drones, even at the expense of tank performance.
Russian forces are working to incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) into quadcopter drones to enable them to identify and hit targets independently, especially when facing electronic warfare (EW) disruptions.
Russian Narrative and Propaganda
Russian officials are attempting to implicate Ukraine in the Islamic State’s March 22 attack on Crocus City Hall by claiming evidence found on an assailant’s phone ties Ukrainian forces to the incident, despite a lack of verified proof. The Kremlin seems to be leveraging these unproven allegations to fuel domestic fear and rally support for its war efforts, depicting Ukraine and the West as terrorist threats. Independent sources, like ISW, however, link the attack to the Islamic State, noting Russian internal security measures focus on threats from the North Caucasus and Central Asian migrants rather than any external Ukrainian involvement. Despite the United States providing Russia with warnings of potential extremist threats to a Moscow venue, Russian authorities and President Putin dismissed the specificity and urgency of these warnings, labeling them as provocations and not acting upon them, before the Crocus City Hall was ultimately targeted, resulting in 140 casualties.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
Kyiv Post – kyivpost.com
