Summary of the day: Ukrainian forces sank a Russian Black Sea Fleet landing ship off Crimea, while both Ukraine and Russia seek battlefield advantages through technological innovation amidst ongoing conflicts. Russia continues to build forces capable of sustaining operations through 2025 and advances near Bakhmut, Marinka, and Krynky, signaling intensified military efforts against NATO and potential escalation in Moldova. Amid these developments, NATO warns of the constant risk of hybrid attacks, and concerns rise over Russia’s development of a space-based anti-satellite weapon, reflecting the broader strategic tensions in the region.
Situation On The Ground And Air
Commander-in-Chief Oleksandr Syrskyi and Defense Minister Rustem Umerov visited front-line command posts near Avdiivka and Kupyansk, where Ukrainian troops are being reinforced against intensified Russian attacks. Umerov highlighted the resolute resistance of the 3rd Separate Assault Brigade and the 110th Separate Mechanized Brigade, defending Avdiivka since 2022. Syrskyi noted the complexity of the operational environment, with Russia increasing offensive efforts and employing tactics like “human wave” attacks alongside aerial bombings and artillery fire.
Luhansk Front – Initiative Russia
Donetsk Front – Initiative Russia
Zaporizhia Front – Initiative None
Kherson (Dnipro River) Front – Initiative None
Positional battles persisted along the Kupyansk-Svatove-Kreminna line, with engagements reported in several areas including northeast and southeast of Kupyansk, as well as west, southwest, and south of Kreminna. Ukrainian forces noted an intensification of Russian assaults in the Kupyansk and Lyman directions, although Russian operations are reportedly hindered by equipment and weapons shortages.
Russian forces achieved a confirmed advance near Bakhmut, with geolocated footage showing progress near Ivanivske along the Kostyantynivka-Bakhmut highway. Although Russian claims of an advance south of Bohdanivka lack visual confirmation, continued positional fighting around Bakhmut has been reported in multiple locations, including northwest, west, southwest, and south of the city. Additionally, Russian military bloggers reported glide bomb strikes on Ukrainian positions in Chasiv Yar, with various Russian military units, including airborne and special forces, actively engaging in areas surrounding Bakhmut.
Russian forces have achieved a confirmed advance west of Donetsk City, with geolocated footage showing progress west of Marinka. While Russian claims of advances near Novomykhailivka and Heorhiivka lack visual confirmation, ongoing positional engagements are reported near Krasnohorivka and southwest of Donetsk City.
Ongoing positional fighting was reported in the Donetsk-Zaporizhia Oblast border area, specifically south of Zolota Nyva and near Prechystivka, both southeast of Velyka Novosilka.
Positional fighting persisted in western Zaporizhia Oblast, with engagements reported near Robotyne and its surrounding areas, including Novopokrovka, Mala Tokmachka, Verbove, and Novoprokopivka. Russian military bloggers claimed that the Russian forces downed a Ukrainian helicopter near Robotyne on February 13.
Russian forces made recent advances in Krynky, as evidenced by geolocated footage, amidst ongoing engagements on the east bank of Kherson Oblast. Although a Ukrainian military observer claimed recapture of positions within Krynky, this has not been confirmed by ISW. Meanwhile, the Ukrainian General Staff reported repelling seven Russian assaults in the area, with significant Russian military presence, including various regiments and brigades, noted near Krynky.
Human Cost Of War
The death toll from Russia’s attack on Kyiv on Feb. 7 rose to five as a woman injured in the assault succumbed to her injuries.
9 Ukrainian were killed and another 23 were injured in Russian attacks on civilian targets over the last 24 hours:
- Overnight Russian attacks on Selydove in Donetsk Oblast resulted in three fatalities, including a child, and injured 12 others, including four children. The assaults damaged several apartments and a hospital building in the town.
- One civilian sustained injuries in Zaporizhia and an infrastructure facility was also targeted in the attack.
- Lviv was targeted resulting in an explosive wave that shattered windows in several buildings on Naukova Street. Fortunately, no casualties were reported.
- A 19-year-old victim of a Russian attack in Kherson died in the hospital. The strike also injured a 14-year-old girl, an 84-year-old man, and two women, with the girl in critical condition. Additionally, the attack caused structural damage and fires in the city.
- Russia attacked Mykolaivka in Donetsk Oblast, resulting in the deaths of two women aged 62 and 74, with at least one person injured.
- Two men died in a Russian missile strike on the village of Velykyi Burluk in Kharkiv Oblast, with three men and two women injured and four people rescued from the rubble. The attack occurred around 4 p.m., likely employing S-300 missiles, damaging a two-story building with eight of its 16 apartments affected, along with a house and two police cars.
- At least one person died in a Russian missile strike on Chuhuiv, Kharkiv Oblast, with a woman found dead in a destroyed home in a targeted residential area.
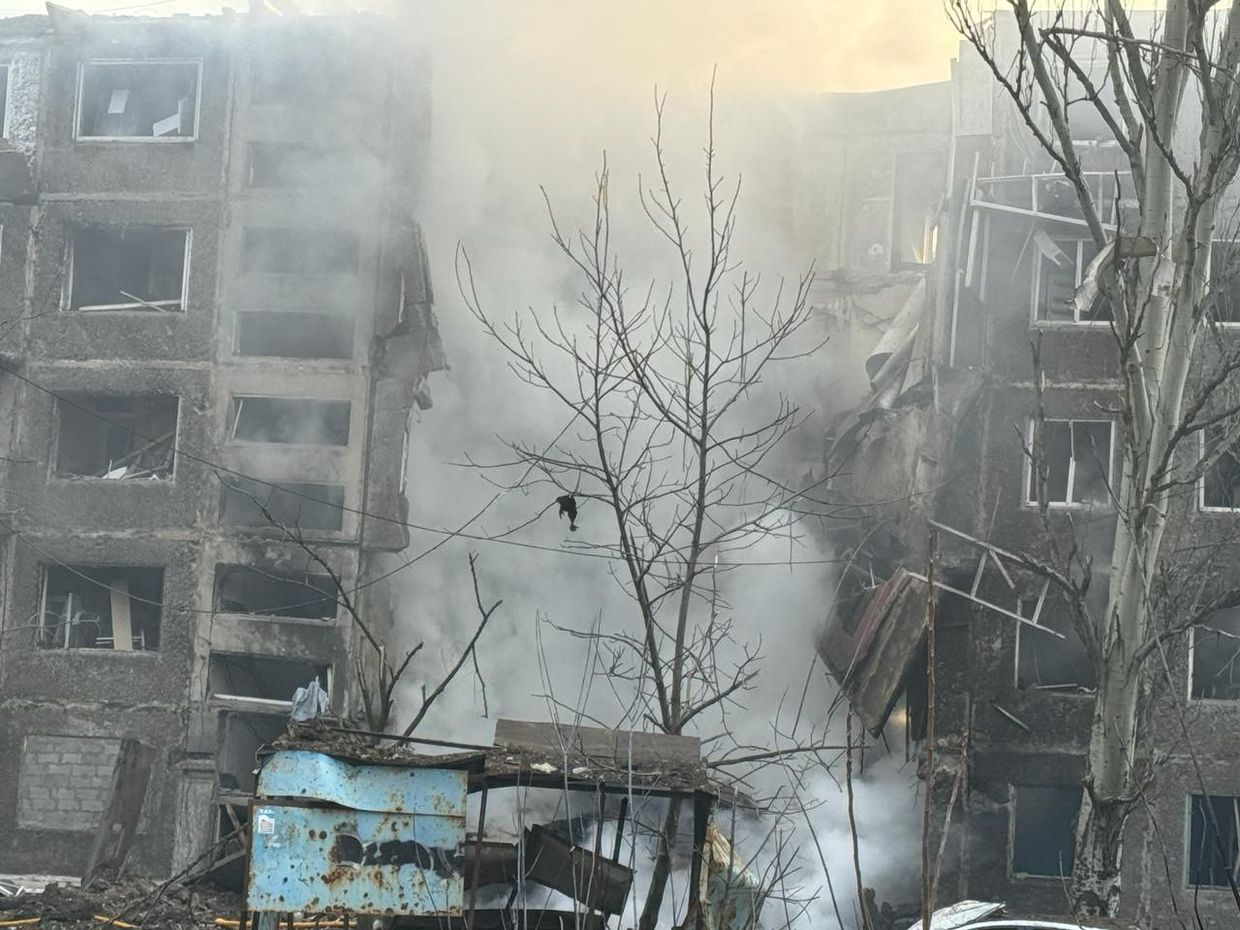 Aftermath of Russian attack on civilians in Selydove
Aftermath of Russian attack on civilians in Selydove
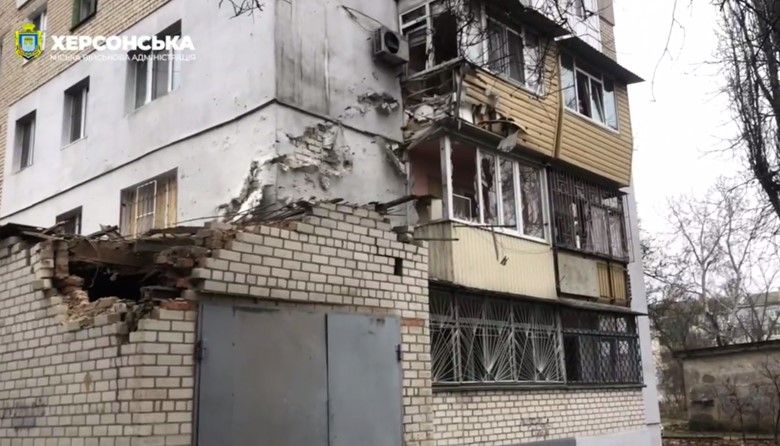 Aftermath of Russian attack on civilians in Kherson
Aftermath of Russian attack on civilians in Kherson
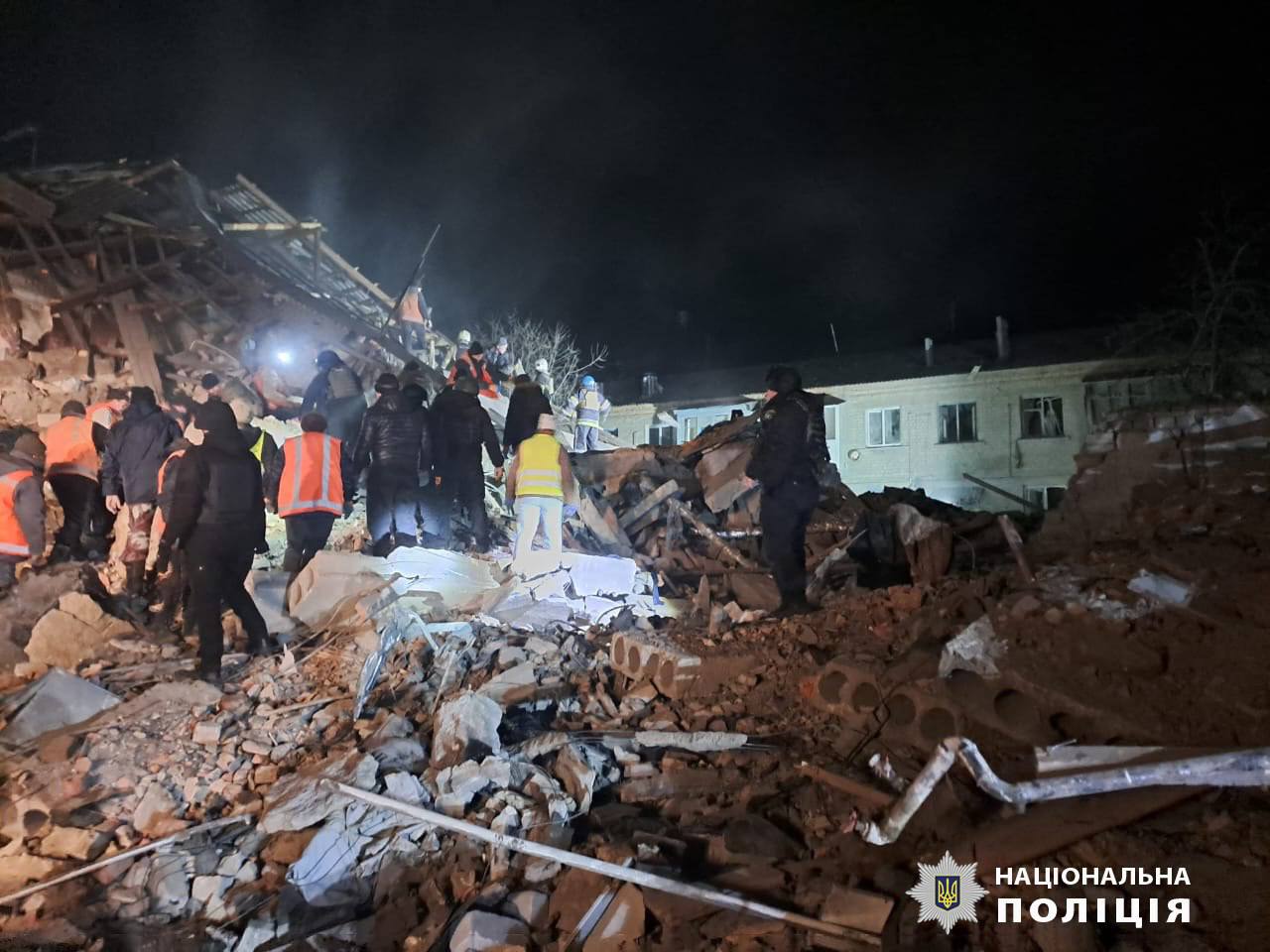 Aftermath of Russian attack on civilians in Velykyi Burluk
Aftermath of Russian attack on civilians in Velykyi Burluk
Ukraine News
Ukrainian forces destroyed the Russian Caesar Kunikov Ropucha-class landing ship with maritime drones off Crimea’s coast on February 13-14, marking the fifth such loss for Russia’s Black Sea Fleet since 2022. The incident, captured on video by Ukraine’s military intelligence, significantly reduces Russia’s amphibious operation capabilities in the area. The failure of subsequent search and rescue operations remains a stark detail in the ongoing conflict.
On the night of February 13 to 14, Russian forces launched a limited series of missile strikes on Ukraine, hitting residential areas in Velykyi Burluk, Kharkiv Oblast, with an S-300 missile and targeting Selydove and Novohrodivka in Donetsk Oblast with missiles.
Ukrainian carriers are set to protest at the Dorohusk-Yahodyn border crossing with Poland on Feb. 15 in response to a blockade by Polish farmers, who plan to extend the blockade across the entire Polish-Ukrainian border starting Feb. 20. The protest aims to last a month, with organizers requesting Ukrainian government support to safeguard truckers and cargo. The Polish farmers’ blockade, initiated over concerns of unfair competition from Ukrainian imports, has led to tensions and disruptions in cross-border trade.
Ukraine Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
President Volodymyr Zelensky mandated the establishment of a comprehensive system connecting the military and industry. The objective is to enhance coordination between manufacturers and the armed forces to address frontline needs effectively amid the ongoing conflict with Russia. Ukraine, nearing two years into the war, intensifies efforts to bolster its defense production capabilities, prioritizing self-reliance amidst delays in U.S. military support.
Ukraine is advancing its domestic production of weapons and military equipment, with efforts to modernize and increase the output of a wide range of items such as anti-tank guided missiles, grenade launcher ammunition, and air defense concealment systems. Deputy Defense Minister Lieutenant General Ivan Havrylyuk highlighted these developments, underscoring the country’s commitment to bolstering its defense capabilities.
Ukraine is leveraging advanced weaponry to counterbalance Russia’s numerical superiority in manpower and materiel, as stated by Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Lieutenant General Ivan Havrylyuk, emphasizing that high-tech arms give Ukraine an edge despite a disadvantage in artillery shells, tanks, and soldiers. Havrylyuk highlights the effectiveness of well-trained forces equipped with sophisticated weapons against a numerically superior enemy, underlining the importance of long-range high-precision munitions and Western artillery systems for maintaining this advantage. He points out the integration of strike drone capabilities across Ukrainian forces as part of a strategy to increase the ratio of machines to personnel on the battlefield. However, Havrylyuk admits that drones cannot fully substitute for the need for advanced artillery systems and other long-range capabilities, noting artillery’s critical role and the majority of Russian losses caused by Ukrainian MLRS and artillery units. He acknowledges the limitations of drones, including vulnerability to electronic warfare and weather, and advocates for combined drone and artillery operations to enhance fire accuracy and conserve ammunition. The success of such operations depends on continued Western support, with Havrylyuk noting that shortages in artillery shells are forcing adjustments in Ukraine’s operational plans.
Ukraine is enhancing its oversight of international military aid usage, with the Cabinet of Ministers establishing new procedures for the monitoring, receipt, transfer, and accounting of such assistance, as announced by the Ministry of Defense. Deputy Defense Minister Yuriy Dzhyhyr engaged with US embassy officials to discuss the reform of Ukraine’s audit system and the establishment of a Ministry of Defense auditing committee. These discussions also covered plans for joint inspections of weapons storage facilities.
Ukraine’s Allies
NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg announced on February 14 that 18 of the 31 NATO members are expected to meet the target of 2% GDP defense spending in 2024, up from the previous year, in response to the security climate since Russia’s annexation of Crimea and the invasion of Ukraine. This anticipated increase in defense investment, including a significant boost by Germany, aligns with the alliance’s objective to deter conflict and comes amid discussions of NATO’s collective resolve and readiness. Stoltenberg’s remarks follow controversial comments by former U.S. President Donald Trump regarding NATO members who fall short of the spending goal.
NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg acknowledged that while there is no immediate threat of military attacks on NATO members, the alliance faces a “constant risk” of hybrid attacks. To counter these threats, NATO is enhancing its intelligence capabilities, sharing, and cooperation with civil society. The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) has noted that Kremlin figures, including President Putin, are actively shaping narratives to justify potential Russian hybrid attacks on countries including Moldova, the Baltic states, Denmark, and Finland.
U.S. House Speaker Mike Johnson is seeking a personal meeting with President Joe Biden before deciding on the $95 billion foreign aid bill, which includes $60 billion for Ukraine, passed by the Senate. Facing internal party pressures and opposition from former President Donald Trump, Johnson’s stance on the bill has created tensions, particularly as it now confronts challenges in the Republican-controlled House. Republican senators who supported the legislation have warned of political repercussions if the aid is delayed and Russia gains an advantage in Ukraine.
During the 19th Ramstein-format meeting of the Ukraine Defense Contact Group, Defense Minister Rustem Umerov announced the launch of an allied coalition to bolster Ukraine’s air defense capabilities, with support from Germany, France, and the U.S. Umerov highlighted the involvement of 15 countries in the initiative, which aims to strengthen Ukraine’s military capacities, including air defense, artillery, and other areas crucial for the conflict’s future. The summit also addressed the delivery of F-16 fighter jets and focused on meeting urgent needs in artillery, ammunition, and air defenses, according to U.S. Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin.
The Estonian Foreign Intelligence Service reports that Russia’s military restructuring, including forming the Leningrad and Moscow Military Districts, aims to bolster its posture against Finland and NATO, and strengthen its units in the Baltic region amid the Ukraine conflict. Russian military assets, heavily engaged in Ukraine, are part of a broader strategy to prepare for potential conflict with NATO, with plans to double forces and increase armored vehicles, tanks, and artillery systems near the Estonian border as confidence in Ukraine war outcomes grows. This expansion serves Russia’s long-term objective of intensifying threats against NATO to weaken and contain the alliance.
Canada is contributing 60 million Canadian dollars ($44 million) to Ukraine for F-16 fighter jet support, as announced by Defense Minister Bill Blair. This support is part of a larger package announced in June 2023 and will fund equipment such as spare parts and ammunition. Additionally, Canada is providing training for Ukrainian Air Force personnel, with pilots expected to be combat-ready by the summer of 2024.
German Defense Minister Boris Pistorius announced plans to increase artillery ammunition deliveries to Ukraine in 2024 by three to four times compared to 2023, emphasizing the critical role of munitions in operational readiness.
The Netherlands announced its participation in a Latvia-led coalition to supply Ukraine with advanced military drone technology, joining approximately 20 other countries.
Ukraine could potentially receive $4 billion from frozen Russian assets this year, with projections reaching $15-$18 billion over the next four years, according to Deputy Justice Minister Iryna Mudra. The EU and G7 countries have immobilized around $300 billion of Russian Central Bank assets since the onset of the conflict, with discussions ongoing on how to redirect these funds to aid Ukraine’s reconstruction efforts. The EU recently took a step by deciding to concentrate the frozen assets in one institution, laying the groundwork for potential transfer to Ukraine under the Ukraine Facility mechanism.
Life in Russian Occupied Ukraine
Russian authorities are intensifying the militarization and cultural indoctrination of youth in occupied Ukrainian territories by promoting the Russian Young Army Cadets National Movement (Yunarmiya) to foster pro-Russian sentiments and military skills among the youth. In Mariupol, children are being taught to handle small arms as part of the program, while in Luhansk, a new “Voin” military sports training center has been launched, offering drone operator training among other military skills to local students. This effort is supported by high-ranking Russian officials, underscoring the strategic importance placed on indoctrinating occupied Ukrainian regions’ youth with Russian military and cultural values.
Russia News
Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitri Peskov refuted Western reports of Russia proposing to freeze the conflict in Ukraine, labeling such claims as false and asserting Russia’s intention to continue the war until its objectives are met. Reuters cited sources stating the US rejected a ceasefire proposal from Russia, with the US emphasizing it will not participate in negotiations without Ukraine’s involvement. The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) and Estonian intelligence suggest Russia’s purported interest in peace talks may be a strategy to weaken Western support for Ukraine and secure concessions without genuinely seeking a resolution.
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken confirmed speaking with former Marine Paul Whelan, imprisoned in Russia since 2018 on disputed espionage charges, during a phone call on Feb. 12. Whelan maintains innocence, stating he was in Russia for a wedding. Blinken reiterated ongoing efforts to secure Whelan’s release, as well as that of journalist Evan Gershkovich, detained on similar charges.
Russian Mobilization and Defense Industrial Base
The Chechen authorities are reportedly intensifying efforts to coerce residents into joining the Russian military, with opposition outlet Vazhnye Istorii citing that about 30% of Chechen personnel in Ukraine were forced into service. This includes targeting critics of the government, those avoiding mobilization, and individuals labeled as “extremists” or “Islamists.” Ramzan Kadyrov, the head of the Chechen Republic, stated that over 36,000 personnel, including around 16,000 volunteers trained at the Spetsnaz University in Gudermes, have been sent to Ukraine.
Russia, aiming to match Ukraine’s technological advancements, is expanding its defense industrial base (DIB), importing critical equipment, and utilizing a crypto-mobilization system to deploy more personnel and materiel in Ukraine, despite primarily focusing on amassing greater manpower and materiel. Although emphasizing quantity, Russia is also adapting technologically, notably in deploying electronic warfare (EW) systems and drones. However, Russia’s potential for further mobilization is constrained by economic and human capital limitations, without resorting to significant, possibly unpopular measures. The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) suggests that while Russia might focus more on technological innovation if it retains the initiative, there’s no indication of such a strategic shift yet. This contrasts with Ukraine’s deliberate use of technological innovation, underpinned by revitalizing its DIB and partnerships, to counter Russia’s numerical superiority, a strategy heavily reliant on sustained Western support to maintain and potentially increase battlefield advantages against Russian forces.
The Royal United Services Institute (RUSI) suggests that Russian military recruitment is effectively sustaining forces, meeting 85% of contract recruit quotas, which may allow Russia to maintain its offensive operations in Ukraine through 2025 despite significant casualties. The current rate of Russian frontline losses in Ukraine is nearly matched by its force-generation capabilities, but the quality of forces is not expected to improve if Ukraine continues to effectively attrit Russian manpower and materiel. The sustainability of Ukraine’s defense relies heavily on ongoing Western support, with warnings that the cessation of such aid could critically undermine Ukraine’s resistance. Russian military tactics involve pushing units in localized assaults until they sustain up to 30% losses before rotation and reconstitution, a strategy that often extends beyond the point of combat effectiveness. Ukrainian intelligence notes that Russian units are withdrawn for replenishment when reduced to 50% strength, a practice that maintains the operational pattern observed by ISW in the Kupyansk and Lyman areas since January 2024. This approach allows Russia to persist in its campaign but limits the potential for accelerated progress without committing more effective, well-equipped units to large-scale offensives.
Reports from Estonia’s Foreign Intelligence Service and the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) on Feb. 13 indicated Russia’s loss of over 8,000 armored fighting vehicles in its Ukraine invasion, with the General Staff of Ukraine’s Armed Forces estimating over 12,000 losses since February 2022. Estonia’s report detailed losses of 8,300 vehicles, while the IISS suggested a figure of 8,800, emphasizing Russia’s ability to sustain its assault on Ukraine despite significant losses through refurbishment and manufacturing efforts. Ukraine’s equipment levels have remained near pre-war levels, with increases in armored personnel vehicles and infantry fighting vehicles due to Western support, although supply challenges persist.
Reports indicate that Russia may be developing a nuclear anti-satellite weapon intended for space deployment, which has led US House Intelligence Committee Chair Michael Turner to call it a serious threat and advocate for declassification. Despite concerns, the capability is not considered an immediate threat as it remains undeveloped and not deployed, aligning with the Russian Ministry of Defense’s recent cosmodrome launch for undisclosed defense purposes.
Russia is actively working to enhance its defense industrial base (DIB), with Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu visiting the NPK KBM enterprise in Moscow Oblast to review the production of missile systems. During the visit, Shoigu examined various defense systems including the Khrizantema-S anti-tank missile system and the Gibka-S MANPADS combat vehicles. NPK KBM officials reported on the expansion of production capacities and the improvement of systems like Arena-M for better protection against loitering munitions, highlighting the significant increase in equipment production.
Russia Allies
The Belarusian Ministry of Defense reported that Belarusian troops have concluded combat training with Russian forces at the 333rd Training Center in Mulino, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, and have since returned to Belarus. Major General Alexander Bas, head of the Belarusian Armed Forces Combat Training Department, noted that Belarusian military instructors will persist in their training endeavors at the 333rd Training Center.
Russian Narratives for Propaganda
The Kremlin is mirroring its pre-invasion information tactics against Ukraine to potentially justify future actions against Moldova, with Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov making unfounded claims about US and EU influence over Moldova and alleging cessation of the 5+2 Transnistria negotiation process. Lavrov’s statements aim to position Russia as a protector of its citizens in Transnistria, drawing parallels to previous justifications for aggression in Ukraine. Additionally, Lavrov’s remarks on Moldova’s internal policies towards regions like Gagauzia echo Russia’s narrative of defending Russian-speaking populations abroad, a pretext used in its invasions of Ukraine. The Institute for the Study of War (ISW) observes these narratives as part of Russia’s broader strategy to destabilize Moldova and hinder its Western integration. Russian officials and affiliated milbloggers amplify these claims, accusing Moldova of economic and military aggression towards Transnistria, while Moldovan authorities report Russian peacekeeping violations. This information campaign suggests the Kremlin is laying the groundwork for possible hybrid operations in Moldova, with the timing remaining uncertain.
During his address to the Russia State Duma on February 14, Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov framed the US as a destabilizing force globally while positioning Russia as a dependable partner in international security. Lavrov emphasized Russia’s diplomatic engagements with China and Africa, reinforcing the Kremlin’s narrative of Russia being at the heart of a supposed “world majority” opposing Western influence. This rhetoric reflects the Kremlin’s concerns over potential diplomatic isolation, heightened by the international response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
The Kremlin is targeting Catholic audiences with claims that Pope Francis supports Russia’s stance on negotiations and opposes alleged religious discrimination in Ukraine, despite no public comments from the Pope confirming such positions. Russian Ambassador to the Vatican, Ivan Soltanovsky, has stated that Pope Francis is willing to mediate, and that Russia is open to discussions with a papal envoy, even as Russian leadership, including President Putin, shows no genuine interest in meaningful negotiations with Ukraine. Additionally, Soltanovsky’s assertions of the Pope’s concern over the treatment of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church Moscow Patriarchate contrast with the Kremlin’s own record of religious persecution in occupied Ukrainian territories.
Source Materials
Institute for the Study of War – understandingwar.org
The Kyiv Independent – kyivindependent.com
